Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a chronic disease caused by compression, irritation or inflammation of one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve and manifested by sharp shooting pain in the areas of its innervation. Treatment of trigeminal neuritis is aimed at eliminating the symptoms and the cause of their occurrence.
What is it and the ICD-10 code
Trigeminal neuritis is a neurological disorder characterized by inflammation and pain in the area innervated by the branches of the fifth pair of cranial nerves.
The disease is typical for people between 30 and 40 years old . People with multiple sclerosis are at risk.
Unlike neuralgia, neuritis is always accompanied by swelling, while trigeminal neuralgia is an irritation of the nerve endings and can progress without symptoms of inflammation. In addition, neuralgia does not cause changes in the structure of neuron fibers.
With the development of neuritis, inflammation affects the inner part of the trigeminal nerve, which can lead to a violation of its integrity. Therefore, the patient has a disorder of sensitivity and motor skills.
The disease according to the ICD-10 classification received code G50 . The trigeminal nerve is paired, so when the pathology develops, the patient experiences shooting attacks of pain on one side of the face.
When the pain subsides, the patient feels numb. In some cases, paralysis or muscle spasm occurs.
Vitamins
For successful treatment, it is imperative to use vitamins, since without them it is impossible to restore the body, and the normal functioning of the nervous and muscular systems is impossible. If there is a deficiency of the vitamin, it is almost impossible to effectively eliminate inflammation and pain. The main vitamins that should be included in therapy are taken in the following daily dosages:
- Vitamin PP – 60 mg
- Vitamin H – 150 mcg
- Vitamin B1 – 4.5 mg
- Vitamin B2 – 5.4 mg
- Vitamin D – 45 mcg.
It is also recommended to take vitamin C in double dosage - 1000 mg per day. It promotes the active occurrence of redox reactions, normalizes metabolic processes, and eliminates free radicals. This has a positive effect on the activity of the nervous system: it increases tissue conductivity, normalizes excitability, relieves inflammation and pain.
Classification of neuritis
There are several classifications of neuritis of the V pair of cranial nerves:
- depending on location;
- by the nature of the flow;
- according to the etiology of the disease.
By localization
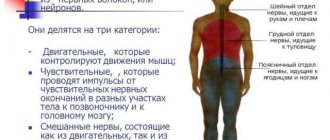
The right and left trigeminal nerves are located on both sides of the face. Each of them is divided into 3 branches, therefore it is considered a mixed fiber:
- Optic nerve .
The first branch is formed from sensitive neurons that are responsible for the perception of the surrounding world: pain, temperature, pressure and other factors. This part of the trigeminal nerve is responsible for the innervation of the visual organs, forehead, lacrimal gland and upper eyelid. - Maxillary nerve . The second branch, like the ophthalmic branch, is formed from sensory fibers. Neurons are responsible for the innervation of the nostrils, upper lip, gums and lower eyelids.
- Mandibular nerve .
Unlike the other two, the third branch of the trigeminal pair is mixed - it is formed from motor and sensory neurons. This means that this branch is responsible for external perception and muscle movements. The latter are responsible for the participation of the lower jaw in chewing food and facial expressions.
The inflammatory process can affect each of the 3 branches. The pain may be felt all over the face or localized only in a certain area.
Typically, pain appears on only one side of the face. Bilateral trigeminal nerve involvement is rare.
According to the nature of the flow
According to the pathological process, neuritis can be acute and chronic . The latter occurs in 50% of patients and is characterized by the development of periodic pain that is throbbing, burning, or aching in nature.
If the disease is associated with damage to the structure of nerve fibers, then the pain syndrome will be permanent.
Acute pathology develops suddenly. When it develops, a shooting pain is observed, similar to an electric shock.
For reasons of occurrence
There are 2 types of pathology:
- Primary. It occurs as a result of damage to the trigeminal nerve: compression by surrounding soft tissues, atrophy, trauma.
- Secondary. Neuritis develops as a complication of other neurological or infectious diseases.
Homeopathy
Homeopathic remedies are widely used in modern medicine. Despite the fact that they are safer than traditional medications, precautions should not be neglected. You should always consult your doctor before starting to use any medication.
To treat neuropathy, an ointment based on herbal components and propolis extract is used. To prepare, take propolis and a small amount of water, melt it in a water bath, add half a teaspoon of flax seed, as well as a quarter spoon of dried cloves, and boil for 3-4 minutes.
Also, in order to prevent the progression of the disease and restore the affected area, it is recommended to do warming with bone meal. Take a linen bag, pour a small amount of bone meal into it, and tie it tightly. Heat it in a hot frying pan or in the oven, apply it to the place where the pain is felt most strongly.
Oil also works well for rubbing and lubricating the sore area. To prepare it, take any base oil. It is better to take oil from the seeds of fruit trees, for example, apricot, peach seed, almond oil. Add 2-3 drops of spruce oil and the same amount of eucalyptus to it, mix thoroughly, and apply externally.
For warming and resolving inflammatory processes, it is recommended to use pepper oil. To prepare it, take any oil, for example, olive. Add a teaspoon of ground pepper (preferably red), stir thoroughly, let it brew for an hour, and rub the affected area.
Etiology in men, women and children
The main cause of the development of neuritis is a neurovascular conflict when the trigeminal nerve or its branches are compressed by a vessel.
Secondary neuritis (inflammation) of the trigeminal nerve develops due to the following factors:
- head injuries that damage the skull and lead to displacement of bone tissue, mechanical damage to the trigeminal nerve;
- neoplasms of a malignant and benign nature, compressing the nerve during its growth;
- vascular malformations;
- bite pathologies;
- bacterial viral diseases: herpes, syphilis;
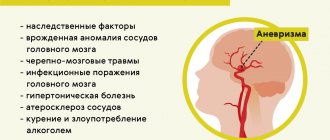
- vascular pathologies developing near the trigeminal pair and its branches: atherosclerosis, aneurysms;
- pathologies of bite, teeth and jaw;
- chronic inflammation of the nasal sinuses: frontal sinusitis, sinusitis, sinusitis;
- neuralgia that occurs after improper removal of a wisdom tooth;
- dental diseases: periodontal disease, stomatitis, gumboil, periodontitis.
What else causes inflammation of the trigeminal nerve? Neuritis from hypothermia develops in rare cases, occurring in only 2% of patients . At the same time, low temperature promotes the development of infection, weakens the immune system and slows down metabolism, which can result in neuritis.
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve in a child occurs due to hypothermia and childhood infectious diseases (mumps, adenovirus, otitis). In newborns due to birth trauma.
In rare cases, the cause of pathology is compression of the nerve roots by large vessels . Ischemia develops, which forms a nerve impulse - the child suffers from attacks of pain.
If children have not been vaccinated, then neuritis develops as a result of viral diseases against the background of hypothermia of the ENT organs.
In some cases, neuritis acts as a symptom of a growing tumor , congenital neurological disorders. In a child, the pathology progresses much faster, which leads to the accelerated appearance of complications.
In middle-aged women, trigeminal neuritis occurs 2 times more often than in men.
The highest risk of developing any diseases, including inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, occurs during pregnancy , when hormonal changes occur in the body.
At this time, the cause of inflammation of the V pair may be compression of the nerve roots by surrounding soft tissues, rupture of the myelin sheath of the nerve.
Such situations arise as a result of stress, infections, injuries to the ears and face, and hypothermia . The exact etiology of neuritis in pregnant women cannot be established without instrumental diagnostics.
Find out about the causes of other types of neuritis:
- vagus nerve and polyneuritis;
- facial nerve;
- cochlear, ophthalmic, glossopharyngeal nerves.
Psychosomatic problems
Psychological factors can provoke the disease. The risk of neuritis increases under conditions of constant stress or severe emotional upheaval:
- death of a loved one;
- childhood psychological trauma;
- consequence after an illness;
- phantom manifestation of pain after brain surgery: removal of a tumor, aneurysm, post-stroke condition.
Psychosomatics that arise from emotional stress cannot be treated with traditional methods. The patient needs the help of a psychotherapist. A specialist will help you share your experiences and eliminate negative feelings.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
The main method of physiotherapeutic treatment is electrophoresis. During this procedure, medications are administered to the patient through the skin or mucous membranes. To improve their penetration into tissues and target specifically those tissues that need therapeutic effects, microcurrents are used.
The medicine penetrates directly into the inflamed area of the nerve and has a therapeutic effect there. The advantage is that the drug acts precisely and purposefully; accordingly, its dosage can be reduced. This significantly reduces the likelihood of overdose and side effects. Salicylates and hydrocortisone are often administered using electrophoresis.
Physical therapy has a good effect. It is recommended to work with an instructor who will select the right exercises that will have the necessary effect and eliminate symptoms. The instructor will also control the intensity, load force, multiplicity and repetition rate. In most cases, the instructor develops an individual set of exercises to perform at home. Exercises should be performed in small dosages, but often. Some movements need to be excluded.
Clinic of the disease: symptoms and signs
The main sign of neuritis is high-intensity pain . The pain can last from 3 minutes to several hours.
Depending on the cause and form of the disease, the nature of the pain can be:
- piercing;
- aching;
- pulsating;
- cutting;
- burning.
Pain syndrome occurs due to inflammation of the nervous tissue . Irritation of neural fibers leads to increased secretion of saliva, and lacrimation is observed. Patients often experience facial redness on the side of the affected nerve.
The location of pain may differ depending on which branch of the trigeminal nerve was damaged:
- Neuritis of the first branch (optic nerve) characterized by the appearance of pain in the bridge of the nose, forehead and upper eyelid. The patient feels a loss of sensation in this area.
Violation of innervation is accompanied by a decrease or absence of the superciliary and corneal reflex.With inflammation of 1 branch of the trigeminal nerve, the patient feels numbness of the conjunctiva. Inflammation of the cornea is often observed.
- Neuritis of the maxillary branch is accompanied by pain and loss of perception from the outer corner of the eye, palate, and upper lip. There is numbness in the upper gums and teeth.
- Neuritis of the mandibular nerve manifests itself in the form of pain, sensitivity disorders in the lower part of the cheek, temple, lip and chin. Numbness is felt on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, on the body and tip of the tongue, on the sublingual tissues, gums and teeth. In addition, the chewing process is disrupted and facial expressions are distorted. Attacks of pain are accompanied by a nervous tic of the facial muscles.
The pain intensifies when touching the skin of the face, while brushing teeth, eating or when there are temperature changes.
Neuritis is characterized by decreased hearing and visual acuity . When inflammation of the trigeminal nerve occurs, the temperature often rises to 37°C.
In case of innervation disorders, swelling of the mucous membranes of the mouth and eyelids is observed. In some cases, trophic disorders appear: the skin on the face peels off, and muscle wasting on the temples and cheeks is observed.
Are the manifestations different on the right and left sides of the head and face?
In most cases, only one half of the face suffers from neuritis . Bilateral pathology is rarely observed and does not differ in the development of its specific symptoms.
Symptoms that occur on the left and right side will depend on the area of the lesion. Rarely, the pathology spreads to 2 identical branches.
In clinical practice, the pathologies on both sides differ due to damage to different branches of the trigeminal nerve . For example, if there is numbness in the upper half of the face on the right side, then nervous tics will appear on the other side.
Pain in teeth
The II and III branches of the trigeminal nerve innervate the gums and teeth on both sides . Therefore, when they become inflamed, pain can radiate along the nerve fibers to the alveoli. Often the pain syndrome is accompanied by swelling of the mucous membranes of the mouth.
Irritation of the nerves leads to increased salivation. When the trigeminal nerve is inflamed, teeth hurt; the pain prevents you from chewing food normally, opening your jaw and speaking.
From the eyes
The optic nerve in the orbital cavity is divided into 3 branches:
- Frontal. In addition to the skin of the crown and forehead, this nerve is responsible for the sensitivity of the upper eyelid. When it becomes inflamed, the patient develops a nervous tic and the skin of the eyelid begins to pinch. The presence of a foreign body is felt.
- Tearful. Innervates the lacrimal gland, so when the nerve is irritated, tear production increases. The patient feels a burning sensation and sharp tingling in the area under the eyebrows.
- Nosociliary. This branch is responsible for the innervation of the eyeball and the inner corner of the eye, so when it is damaged, the patient has vision problems. Acute pain appears and visibility deteriorates.
Earache
Sensory neurons of the mandibular nerve are responsible for perception:
- skin of the auricle;
- parotid gland;
- skin in the external auditory canal;
- eardrum.
With inflammation of the third branch of the trigeminal nerve, the patient experiences acute pain in the ear, which is accompanied by profuse salivation. In some cases, hearing acuity deteriorates.
Surgical treatment of trigeminal neuropathy
Various products of animal, plant, as well as organic and inorganic origin have found wide use among the people. The ointment has proven itself well. To prepare, take 50 grams of badger fat, melt it over low heat, add pre-prepared garden tree ash, and boil for several minutes.
Used in the form of applications or ointment bandages, which are applied to the affected area. For application, take a bandage folded in several layers, apply a thin layer of ointment on it and place it on the affected area. After this, stand for 10-15 minutes. After removing the application, the skin is wiped with a dry cloth, and dry heat is also applied on top.
In order to make an ointment bandage, it is necessary to apply the application in the manner described above, after which dry heat is applied on top. It is recommended to apply insulated fabric, preferably made of natural wool. You can apply a layer of cotton wool over the application, and then wrap it with a warm scarf. It is necessary to stand for at least 40 minutes.
An alcohol tincture of buckthorn leaves with sea buckthorn berries is well suited for wiping affected areas. It relieves pain, eliminates inflammation and swelling, improves tissue conductivity, and has a calming effect on the nervous system. To prepare the tincture, you need to take grass and berries in a 1:2 ratio and add vodka or alcohol. Then we give it the opportunity to brew for a day.
Can be used for rubbing and wiping the surface of the skin. To wipe, soak a bandage or cotton wool in the infusion, squeeze it out, and wipe the affected area. Allow it to dry, then wipe it again, and so on 3-5 times.
For rubbing, it is recommended to perform a preliminary massage. First, use light stroking movements to warm up the skin at the affected area. After this, perform squeezing movements: apply stronger pressure in the area of pain, and moderate pressure in other areas. Squeezing is done by grasping the massaged area with both hands, moving it across the entire part of the body, to the nearest lymph node. Stroking and squeezing are done on dry skin, without tincture.
After this, they proceed directly to rubbing. Take a small amount of tincture into your hands and apply it to the skin. It is better to use a warmed tincture. With sharp movements, the skin is shifted so that a fold is formed under the arms, which needs to be moved. You need to do intense movements. An indicator of high-quality rubbing is redness of the skin and a slight burning sensation.
For oral administration, you can use a stimulant that restores the protective potential, endurance of the body, its ability to resist infectious and inflammatory processes, and stimulates the activity of the nervous and muscular systems. To prepare, you will need to squeeze the juice of one lemon.
[1], [2], [3], [4], [5]
Surgical methods are used only after conservative treatment has demonstrated ineffectiveness. Indications for this procedure include progressive muscle weakness and severe pain along the nerve. Often the cause is a narrowing of the canal through which the nerve passes.
During the operation, all areas that put pressure on the damaged nerve are cut and removed, or the nerve is moved to another area where nothing will put pressure on it.
Patient complaints
The main complaint among patients who come to see a neurologist is attacks of severe pain that appear along the innervation of the branches of the trigeminal nerve.
When taking a medical history, people describe pain in different ways, citing manifestations:
- acute;
- burning;
- stupid;
- aching;
- shooting pain syndrome.
Patients complain of the sudden onset of pain, accompanied by various vegetative phenomena . The latter includes copious secretion of saliva, sweat, tears, and redness of the skin. The pain may radiate to different parts of the head and neck.
Step-by-step diagnostic procedure
There are no special diagnostic methods for identifying neuritis, so a clinical diagnosis is made based on complaints and physical examination of the patient .
In this case, the doctor excludes the presence of other diseases with similar symptoms. First, the specialist collects a complete medical history of the patient, after which he conducts a physical examination.
How to diagnose inflammation of the trigeminal nerve? With trigeminal neuritis, specific pain appears, accompanied by a number of unusual symptoms:
- numbness of the facial skin;
- deterioration of vision and hearing;
- dysfunction of facial muscles, including nervous tics;
- dizziness.
How to determine the causes of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve of the face? To determine the cause of neuritis, laboratory tests and instrumental examinations are performed as part of additional diagnostics.
What does the doctor pay attention to?
When collecting anamnesis, suspicion of neuritis appears when:
- the patient had previously suffered traumatic brain injuries;
- the patient was exposed to a neurotropic infection;
- the person has caries;
- the patient complains of attacks of pain localized along the innervation of the trigeminal nerve.
During a physical examination for neuritis, the doctor pays attention to the duration and nature of the pain syndrome.
With inflammation of the nervous tissue, attacks last up to 2 minutes and intensify with palpation, conversation, and muscle movement. At the same time, the patient does not have a neurological deficit, and little time passes between attacks.
Additional Research
To establish the reason why the trigeminal nerve is inflamed, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- Laboratory tests: general analysis of urine and blood . If the nerve fibers become inflamed as a result of infection, the level of leukocytes in the blood rises. Thanks to this technique, sinusitis and dental diseases are detected.
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography of the head . The pictures show the condition of the nerves and blood vessels. The latter can put pressure on the trigeminal nerve, causing inflammation and pain. In addition, MRI and CT scans detect the presence of tumors.
- X-ray of the head, mouth, and sinuses. Allows you to identify the source of infection.
- Angiography using contrast . Allows you to identify vascular abnormalities and the state of blood flow if there is a risk of compression of the trigeminal nerve by large arteries.
What diseases should be differentiated from?
Differential diagnosis is carried out by comparing the clinical picture of trigeminal neuritis and diseases with similar symptoms.
The latter include:
- Pulpitis. There is caries on the teeth, which causes a gradual increase in pain over 3-6 months.
During this period, pain does not appear in the form of attacks. Pain develops only when diseased teeth come into contact with cold or hot.In addition, the pain syndrome is localized at a certain point, covering 3-4 adjacent teeth. With neuritis, all the gums and teeth on the side of the affected nerve hurt.
- Temporomandibular pain. It has a dull and aching character. Distributes to the temple and neck. When opening the mouth, a characteristic click is heard.
- Paroxysmal hemicrania . The pain is localized only in the temple area and lasts from 5 minutes to half an hour. Accompanied by migraine and headache.
- Various infectious and inflammatory diseases: sinusitis, conjunctivitis, otitis media, sinusitis . In such a situation, the neurologist consults and refers the patient for examination to another specialist: an ENT doctor, a dentist, an ophthalmologist.
Herbal treatment
High mullein is used to relieve inflammation and pain. Flowers and leaves are used. Due to the high content of essential oils and saponins, they have an anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effect. Used as a tincture for rubbing into the affected area. You can apply a compress. To do this, apply a layer of gauze soaked in tincture, cover the top with cellophane, and then apply a layer of cotton wool.
Burdock is used to relieve pain and inflammation from affected areas. It is often used in puree form. To prepare, you need to take a large burdock leaf, cut it into small pieces, mix with honey. Add half a glass of water or milk and simmer for a few minutes. Then strain. The decoction can be used separately for rubbing and compresses. The thick mass is applied to the affected areas for 10-15 minutes.
A decoction or infusion of prickly tartar is used to tone nerve and muscle fibers, normalize excitability processes, and transmit impulses. They can also be used to wipe the affected areas to relieve pain and eliminate the inflammatory process. To prepare decoctions or infusions, take approximately 30 grams of herb per glass of water.
What can be dangerous: consequences and complications
If left untreated, the disease leads to the development of complications:
- paresis, paralysis of facial and masticatory muscles;
- decreased visual and hearing acuity;
- ataxia;
- loss of facial skin sensitivity;
- nervous tics.
Attacks of acute pain disrupt the patient's psycho-emotional state.
The patient becomes irritable, develops depression, and decreases appetite. Stress weakens the immune system and leads to metabolic disorders. Unlike neuralgia, neuritis is a more dangerous disease that, if left untreated, leads to the destruction of nervous tissue. Inflammation often provokes motor disorders of the facial muscles, numbness and nervous tics . The pathology is accompanied by attacks of acute pain.
The trigeminal nerve is divided into 3 branches that innervate the area of the face, eyes and ears. Therefore, if left untreated, the pathology can lead to hearing, facial expression and vision disorders. Symptoms of trigeminal neuritis are similar to other inflammatory diseases, which requires differential diagnosis.
Medicines
When using medications, you must strictly observe precautions: consult a doctor about each step taken, follow all instructions, without changing the dosage or duration of taking the drug yourself. Treatment of neuropathies is very dangerous due to its side effects.
If you make even a minor mistake in therapy, the treatment will, at best, be useless, and at worst, it will cause a deterioration in the condition and progression of the disease. The most dangerous complication is brain damage and paralysis. It should be borne in mind that many drugs have a long-term effect.
Quite often, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed: acetylsalicylic acid 2-3 grams per day, indomethacin 100-150 mg per day, voltaren 100-150 mg per day, brufen 1-2 grams per day. These drugs are used for a long time, for many years. At the same time, corticosteroid drugs, for example, hydrocartisone, kenalog, can be injected directly into the site of inflammation.