Ear neuritis is associated with malfunctions of the nervous system. The nerve that supplies our hearing can become inflamed, causing these problems. The medical name for this disease is cochlear neuritis. Auricular neuritis occurs especially often after 50, men are more susceptible to it than women. Recently, this disease has become younger, and residents of large cities are increasingly suffering from it.
Acute neuritis of the auditory nerve (code – ICD-10) is a dangerous disease, in the presence of which patients do not immediately seek the help of a doctor, losing their hearing and the possibility of effective therapy.
Remember that hearing loss is not always associated with aging of the body, therefore this condition requires qualified treatment from an ENT specialist and other specialists.
The essence of the disease
The location of the auditory nerve is the inner ear. It is charged with performing two important functions:
- Transmission of signals from the vestibular apparatus to the brain area.
- Conversion of sound vibrations into electrical vibrations, their transmission to the brain.
With neuritis, the inflammatory process affects both the nerve itself and the tiny hair cells located on the inner surface of the ear. Next, the pathological process moves to the nerve centers of the brain stem, where sound recognition occurs.
Please note that hair cells can quickly die and then they will not recover. Because of this, hearing acuity suffers greatly and hearing loss appears.
Neuritis affects one ear or both. It all depends on its cause and characteristics. With a benign tumor, only one side is affected.
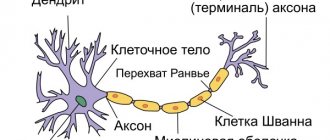
Anatomy of the auditory nerve
The auditory nerve is made up of hair cells that run in the inner ear. Sound entering it causes vibrations of the liquid in this zone. As a result, impulses arise that are perceived by hair cells. That is, the functions of the auditory nerve are to receive and transmit sound to the brain.
The human ear consists of three parts:
- outer ear;
- middle ear;
- inner ear.
The first is responsible for capturing sound, the second is for reproducing vibrations that enter the conductive section (inner ear). The latter also contains receptors responsible for balance. And the conduction section is represented by the auditory nerve.
In a simplified way, the perception of sound information occurs as follows: impulses enter the brain stem. Further along the auditory nerve they penetrate into the temporal lobes. In this zone, the processing and perception of sound information occurs.
The inflammatory process develops in any part of the inner ear. But they talk about neuritis if hair cells are damaged. Inflammation of the tissues of the semicircular canals, also located in the inner ear and responsible for coordination, is called cochleitis.
The hair cells are distributed unevenly, which determines the nature of the clinical picture. At the initial stage of development of the inflammatory process, the fibers located on the periphery and responsible for conducting low tones are affected. Therefore, the inability to perceive such sounds indicates the presence of neuritis.
Some of the fibers of the auditory nerve are intertwined with the areas responsible for the coordination of movement. If this part of the inner ear is affected, the patient experiences attacks of dizziness and nausea.
Symptoms
Acoustic neuritis, the symptoms of which do not appear immediately, and in the chronic form may not bother you for a long time, has become a very common illness. As medical statistics show, residents of megacities more often suffer from this pathology. This is due to a complex of reasons: high pace of life, poor ecology, constant stress, acoustic pollution, etc. One of the main reasons is constant background noise, which gradually reduces hearing function.
The main symptoms are:
- weakness;
- dizziness, discomfort in the occipital region;
- pain, ringing in the ears;
- elevated temperature;
- cough;
- nausea;
- a sore throat;
- spots before the eyes;
- increased blood pressure;
- hearing loss.
The development of acute and chronic neuritis differ in their symptoms. In the acute form, the pathological process occurs suddenly and develops rapidly. Before this, the person did not feel any symptoms at all and was completely healthy. Subsequent symptoms are mild, there is no redness or pain in the affected area.
As soon as you feel that your hearing is decreasing, immediately go to the doctor. Treatment should begin at this stage so as not to start the pathological process. If ignored completely, it can lead to a number of complications (tinnitus, ringing and even complete deafness). With proper treatment, the prognosis is most often favorable. If left untreated, vestibular system disorders and irreversible pathologies of the auditory organs will begin.
In the chronic form, remission alternates with exacerbation. The main symptoms of chronic course:
- Neuralgia. It can be left-sided, right-sided or mixed.
- Dizziness.
- Intoxication. She makes herself known with attacks of nausea and weakness.
- There may be noise, buzzing and buzzing in the ears, and congestion.
Causes
Elderly people primarily suffer from neuritis. This situation is due to the fact that with age, blood circulation in the head area is impaired. Elderly people often face the problem of increased blood pressure, they develop strokes, thrombosis, atherosclerosis of the arteries and other vessels of the brain.
The hearing aid reacts extremely negatively to constant background noise. Workers of plants, factories and other facilities associated with high noise levels often suffer from neuritis. Pathology can also be triggered by acoustic or barotrauma, constant vibration.
It is extremely important to treat infectious processes in a timely manner, since viruses often lead to complications. Influenza is very dangerous in this regard, since the virus quickly penetrates all mucous membranes and, once in the blood, quickly spreads throughout the body. For infants and the elderly, parainfluenza and adenovirus are especially dangerous.
Malaise may appear after meningitis, when inflammation from the membranes of the brain spreads to the auditory nerve. Children often encounter it after suffering from mumps or rubella. The pathological process begins with the salivary glands, which are located near the ears, being affected. With rubella, the virus quickly penetrates the blood, causing toxic poisoning of the entire body, having a negative effect on the nervous system.
Pathology can be caused by long-term use of certain medications and antibiotics. They have a toxic effect on the hearing organs and can damage the auditory nerve and vestibular apparatus. Drugs used to treat cancer and products containing acetylsalicylic acid also have a negative effect on the hearing organs.
The disease can cause contact with dangerous substances such as lead, mercury, arsenic, phosphorus, gasoline, petroleum products, alcohol, and nicotine. Neuritis in adults is often a consequence of TBI. It can even start the process of tumor formation. This is due to the fact that when injured, blood vessels are damaged, blood circulation is disrupted, and inflammation develops. The nerve can be damaged by bone fragments or an infection that occurs during injury.
How to deal with the problem
Treatment of acoustic neuritis depends on the cause of the disease. So, if the inflammation is caused by the activity of the virus in the body, the patient is prescribed antiviral drugs. When the abnormal process is caused by a bacterial infection - antibiotics . Additional therapeutic measures:
· Taking vitamins, including ascorbic acid (this is a powerful antioxidant that helps prevent cell damage).
· Drink plenty of fluids (to remove toxins and waste from the body).
· If necessary, bed rest.
· Correction of diet (lots of protein, fiber, fresh juices, “light” soups).
How to treat neuritis - a consequence of intoxication of the body:
· take adsorbent medications – medications that accumulate, bind and remove harmful substances from the blood, lymph, and gastrointestinal tract;
· use symptomatic medications (for example, diuretics, painkillers) and neuroprotectors (drugs that protect nerve cells from damage);
· if severe intoxication of the body provokes fainting or even coma, resuscitation measures are carried out.
Acoustic neuritis due to TBI is treated only in a hospital. “ Drug therapy involves the use of painkillers, drugs to improve coronary circulation, and diuretics (to eliminate swelling).”
Hearing restoration after TBI is gradual; patients must periodically take angioprotectors, medications to regulate coronary circulation, and multivitamins.
How to restore normal functions of the auditory nerve if its inflammation has been caused by occupational hazards:
· take biostimulants (dietary supplements) - such drugs protect the lesions “affected” by inflammation from the negative effects of physical, chemical, mechanical environmental factors;
· attend physiotherapeutic procedures. Basically, patients who have suffered neuritis are prescribed electrophoresis on the skull area - electrical impulses contribute to better penetration of drugs to the auditory nerve.
· Take mud baths, undergo sanatorium-resort treatment - such measures are aimed at the overall health of the body, have a positive effect on the nervous system, and contribute to a faster recovery of “damaged” fibers.
· Resort to play-reflexo- and magnetic therapy - modern techniques that cope with pain, help stop the inflammatory process, and speed up the healing of affected areas.
For acoustic neuritis in elderly patients, treatment is rather symptomatic. The main components of the therapeutic regimen are:
· antihypertensive drugs (lower blood pressure);
· medications to control blood cholesterol levels (prevention of atherosclerosis);
· thrombolytics (thin the blood);
· vitamins, dietary supplements;
· physiotherapy;
· mud, sanatorium and resort treatment.
Kinds
Based on the duration of the course, the following forms are distinguished:
- acute;
- subacute;
- chronic.
The main symptom is decreased hearing. Patients believe that the culprit is the formation of sulfur plugs.
Chronic cochlear neuritis occurs hidden. The patient may not even be aware of his illness, because he does not feel any symptoms. Only with the appearance of periodic exacerbations can he suspect the development of the disease.
Etiology
Acoustic neuritis most often develops against the background of other diseases. This disease can be caused by:
- otitis;
- osteochondrosis;
- otosclerosis;
- flu;
- auditory nerve atrophy;
- cardiovascular diseases.
One of the common causes of neuritis is oxygen starvation of tissues. In most cases, cochlear neuritis becomes a complication of infections. In addition to the reasons listed above, pathology can be provoked by smoking, alcoholism, and noise at work.
Another disease is neuroma. This is a benign tumor, which in its symptoms is very similar to neuritis. These symptoms include tingling and numbness in a certain part of the face.
Very rarely, genetic diseases in which the patient’s genetic code is disrupted can lead to neuritis.
Causes of the disease
Most often, exacerbations of this neuralgia occur in the cold season, with colds, and have a clearly defined “autumn - spring” orientation.
The following reasons can influence attacks of pain:
- Space-occupying formations in the cranial cavity, such as tumors of bone and nervous tissue (craniopharyngiomas, neurofibromas, neuromas). As a rule, glossopharyngeal neuralgia occurs when the structures of the glossopharyngeal nerve enter a space-occupying formation with the development of edema and compression. In addition to the cranial cavity, such formations can also be located outside the skull - in the area of the stylohyoid ligament, as well as in the area of the larynx and pharynx.
- Viral infections with an affinity for the nervous system. Such diseases include influenza and herpes virus infection, which causes blistering rashes on the skin, in the projection of the nerve trunks, as well as in the external auditory canal;
Herpes infection is necessarily the usual herpes on the lips, it is a serious infection, the consequence of which can be glossopharyngeal neuralgia
- Such neuralgia may not be primary, but secondary - that is, it can be a consequence of inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system - meningitis, encephalitis, both serous and purulent. A rare cause of the development of glossopharyngeal neuralgia may be cerebral arachnoiditis, which in Soviet times was a very common diagnosis, but its existence is currently questioned by many leading neurologists;
- Ossification (calcification) of the structures of the stylohyoid ligament. Most often occurs in old and senile age, in women - in the postmenopausal period;
- An increase in the size of the styloid process, a change in its configuration;
- Enlargements of the carotid arteries, which are called aneurysms. This is a rather rare reason; internal lumen stenoses without expansion of the outer diameter occur much more often;
More rare causes of this unpleasant pathology include chronic infections of the oropharynx (sore throat, tonsillitis), the occurrence of acute surgical emergencies (abscesses), and severe atherosclerosis of arterial vessels.
Inflammation of the tonsils (tonsillitis) - is a rare case of inflammation of the glossopharyngeal nerve
Particular mention should be made of the role of industrial intoxication of thermal power plants - tetraethyl lead in the development of this neuralgia in particular, and damage to the nervous system in general. Most often, tetraethyl lead injury occurred during work where inhalation of leaded gasoline vapors is possible. In the 21st century, due to the ban on the use of this type of fuel, the number of cases of chronic poisoning from thermal power plants began to decrease.
Diagnostics
If auditory neuritis is accurately diagnosed, treatment will be influenced by the form of the disease and its cause. Accurate and timely diagnosis is important. As soon as the first manifestations of the disease begin to bother you, you need to go to the doctor. It is necessary to perform a comprehensive diagnosis as early as possible. You absolutely cannot ignore the symptoms and hope that they will go away on their own. Damage to the auditory nerve is observed even in the absence of visible symptoms. Remember that relief can only be temporary, and then the disease will return, but in a chronic form.
First, the doctor collects anamnesis, examines the patient, and inquires about his well-being and manifestations of pathology. He can ask clarifying questions about the type of professional activity, chronic diseases, etc.
There are a number of examination methods that will help establish an accurate diagnosis and form of the disease, as well as the causes of its occurrence:
- Tympanometry.
- Audiometry.
- Weber test.
- Rene's test.
It is very important to establish the pathogenesis, that is, the cause of the development of neuritis. To install it, specialists with a narrow focus can connect. Sometimes a CT scan, an X-ray of the skull, and a blood test for biochemistry are prescribed.
There are pathologies whose symptoms are very similar to neuritis (neurinoma or other diseases of the hearing aid). When diagnosing, they need to be excluded.
Peripheral nerve fibers are destroyed very quickly, so it is important to start therapy as early as possible. Those patients who seek medical help when the first symptoms appear are completely cured. The lack of adequate treatment leads to an increased risk of complications, including deafness.
The final conclusion is written by the ENT specialist. He necessarily takes into account the results of all studies, the patient’s complaints, the current state of the hearing aid and the whole body.
Research methods
The functional state of the vestibular-cochlear nerve is determined by a comprehensive study of the auditory and vestibular analyzers (see Audiometry, Vestibulometry). Vestibulometric, audiological and otoneurological research methods make it possible to differentiate P.'s lesions. n. within the inner ear or its root in the internal auditory canal and the cerebellopontine angle. When tonic diagnostics takes into account the possibility of involvement in the process of the V, VI, VII, IX, X cranial (cranial, T.) nerves, topographically combined with the vestibulocochlear nerve.
Treatment methods
To develop a treatment plan, the doctor must find out what caused the disease. The effectiveness of medicines directly depends on this. For an experienced ENT specialist this will not be difficult to do.
This should be followed by comprehensive treatment. Its goal is to eliminate the causes of the disease and its symptoms, and restore the lost functions of the hearing aid. It is important to ensure adequate nutrition of the nerve and remove substances from the body that have become a factor in the development of the disease. Laxatives will help cleanse the body, anti-inflammatory drugs will help eliminate the source of infection. Agents that can constrict blood vessels and biostimulants are also indicated.
In the acute form, treatment is carried out in a hospital. It is strictly not recommended to treat the acute form at home, since the doctor must constantly monitor the dynamics of the process, the condition of the tissues, the auditory canal and the behind-the-ear area.
Please note that the acute form of neuritis can be fatal due to damage to brain tissue.
In acute cases, you need to limit fluid intake and follow a special diet. Traditionally, the following groups of drugs are used in treatment:
- Diuretics.
- Drugs that stabilize metabolism.
- Medicines that normalize blood circulation in brain tissue.
- Detoxification products.
The therapeutic effect from them does not occur immediately, so drug treatment can be quite lengthy. It is important to start it before irreversible changes occur. To prevent diseases and improve hearing, Akustin may be prescribed in combination with the listed medications.
To cure the chronic form of the disease, it is important to identify the etiological factor. For infectious neuritis, antiviral and anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics are indicated. To speed up metabolism in cells, antioxidants and vitamins are prescribed.
In the case of a toxic form, special antidotes are used that quickly remove toxins from the body. Intoxication takes a long time to treat, since it is impossible to remove all toxins at once. Along with drug treatment and relieving symptoms of poisoning, it is recommended to take mineral and mud baths and undergo physiotherapy.
If the tumor is benign on the right or left side, it may require radiation or surgical removal. If it is definitely benign and has stopped growing, the doctor can only observe such a patient.
This disease can be completely cured only at its first stage of development. In advanced cases, it is impossible to completely restore hearing; you can only try to stop its decline. If the hearing is very damaged, the patient is recommended to install a hearing aid. If left untreated, neuritis leads to deafness, and with extremely unfavorable development it can be fatal.
The doctor also develops symptomatic treatment, carries out rehabilitation and recovery measures.
Please note that it is strictly contraindicated to treat this disease using traditional methods and remedies. People offer such a common remedy as propolis. It is even recommended to put it in the ear canal. With this diagnosis, it is not enough to simply drink herbal infusions or apply ear drops. The most miraculous herb will not help if neuritis has already been diagnosed. This requires a thorough diagnosis, on the basis of which a treatment plan is built.
It is important not only to take a range of medications, but also to improve your diet. The diet must include dairy and meat products, egg yolk, cheese, and legumes. Among the physiotherapy procedures, acupuncture is interesting, and electrophoresis has long proven its effectiveness.
Folk remedies not only will not help, but can even harm if you approach the matter irresponsibly. They can temporarily stop the pathological process, but extremely rarely eliminate its cause completely. The person may feel relief, but their hearing aid will continue to deteriorate. Even a specialist begins treatment for neuritis only after the patient has been examined by a neurologist. One of the complications of this pathology is neurosis, neurasthenia, neuropathy, which develop due to constant discomfort and pain. An X-ray of the skull is often prescribed to rule out the development of a tumor.
The standard treatment regimen includes:
- diuretics;
- anticonvulsants;
- analgesics;
- vitamins;
- nootropic drugs.
If the drugs are correctly selected according to the cause of the disease, they can improve the overall condition quite quickly, but it is important not to give up treatment halfway. Pain sensations go away first, but pathological changes can still continue. Only a doctor should stop prescribed medications. He must constantly monitor the dynamics of treatment, because an untreated disease can quickly return and become chronic.
Elderly people have to take prescribed medications almost until the end of their lives.
Drug treatment is often supplemented with physiotherapy; electrophoresis and acupuncture are effective. During treatment, complete rest, proper nutrition are recommended, you need to drink a lot of water, take vitamin C (it prevents cell destruction).
Conclusion
Acoustic neuritis is a common and extremely dangerous phenomenon. Remember that the consequences of neuritis can be extremely serious, including death. Contact your doctor promptly if you begin to worry about the slightest symptoms of this insidious disease. With timely treatment, the outcome is quite favorable.
Interestingly, there is an unconventional method for restoring hearing, vision and other functions. It was developed by Norbekov M.S., a well-known representative of alternative medicine. This technique is based on intuitive perception. Official medicine does not recognize this method of recovery and questions its results, but they are positive.
Diagnostic measures
Before starting treatment for neuritis of the auditory nerve, the ENT doctor identifies the degree of sensorineural hearing loss (there are 5 in total) using audiometry:
· I. The patient hears sounds whose volume exceeds 26-40 dB. The patient can hear whispers from a distance of 1-3 m, and spoken speech no further than 4-6 m.
· II. The ears do not perceive sounds quieter than 41-55 dB. Whispering is accessible to the patient at a distance of up to 1 meter, conversation – 1-4 m.
· III. Whispering is not available, the patient is able to hear spoken speech at a distance of no more than 1 meter, and hearing loss is determined to be up to 56-70 dB.
· IV. This degree of hearing loss is determined when the patient can, in principle, distinguish at least some sounds.
· V. Hearing in both ears is completely absent.
Comprehensive diagnostics of NSD includes:
MRI of the brain;
· Ultrasound of head and neck vessels;
· laboratory tests of blood, urine;
· ECG.