For an explanation - to the animal pose
Although a person is not a caterpillar, his body also has a segmental structure, from which comes the genesis of such pathology as muscular neuralgia (burning pain in the back, chest, etc.).
To better understand the technology of its development, the human body should be placed on all fours, in an animal pose. Then the location of the spinal (spinal) nerves will become parallel to each other at all levels. In the area of the chest and abdomen, semicircular arcs are naturally formed from them, parallel to the ribs, and from the zones where the arms and legs originate, the nerves will continue in them - here the arcs do not encircle the body, but, as if “hanging” down, go into the limbs.
In accordance with the described structure of the spine and the spinal nerves emanating from it, the muscle groups of the chest and abdomen also form muscular arc-rings, while in the limbs they create a multi-link, multi-level chain that continues in the direction away from the body.
Unlike the animal ancestor, man is an upright walking creature. But this does not make the segmentation of his body go away: the thoracic spinal nerves serve the thoracic skeletal muscles, the lumbar nerves serve the group of the same name, and the same thing happens in the cervical and sacral segments.
But in addition to the innervation of skeletal muscles, spinal nerves also provide motor function and sensitivity of internal organs at each “level” of service.
Therefore, muscular neuralgia is accompanied not only by purely muscular manifestations, but almost always has the character of a dysfunction of one or more organs (individual zones of which are located at a given level), which can be either true or only apparent. Therefore, intercostal neuralgia so successfully imitates myocardial infarction, the back in the lumbar region - renal colic, and so on.
It is worth noting that damage to only one spinal neuromuscular segment never leads to a complete disruption of the vital functions of any organ. Because the functions of each formation inside the body are provided by cross innervation - it is carried out not strictly from one, but from several adjacent levels at once.
In turn, sensations during organ dysfunction are also transmitted to several segments at once, which is why myocardial infarction manifests itself as paravertebral pain at several levels at once.
What is neuralgia
Neuralgia is a disease that occurs equally often in both adults and children. In most cases, patients come to doctors with an advanced form of the disease, when there are risks of complications. To avoid this condition, it is necessary to contact a specialist at the first manifestations of the pathology.
Neuralgia is an acute pain syndrome associated with nerve damage of various etiologies and resulting muscle spasms.
The most common are intercostal, sciatic, and trigeminal neuralgia.
Diagnosis is carried out on the basis of X-ray methods and electroneuromyography. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of the nerve damage and relieving pain.
Neuralgia is accompanied by acute pain and muscle spasms. The disease affects peripheral nerves. For this reason, a sign of pathology can appear in any part of the body.
Symptoms of neuralgia
Neuralgia is a pathological process that can occur suddenly.
The disease has many varieties, since there are many nerve trunks in the human body. Often the problem extends to the face and back of the head.
Neuralgia also includes damage to the trigeminal nerve, despite the fact that the cause of the pathological condition may be the gasserian node located in the cranial cavity.
Necessary examinations
When I encounter such phenomena, I immediately refer the patient for an ECG. This is especially true for people over 45 years of age, even if the signs are not typical for myocardial ischemia. It is better to make sure that the person is not in danger, and only then calmly carry out treatment for neurological or other abnormalities. If you have angina, you should do an ECG with stress, since it may not show any changes when pain is eliminated.
In some cases, it is necessary to use other instrumental methods:
- Coronary angiography. It is carried out using contrast injection and helps determine the presence of narrowing in the vessels of the heart.
- EchoCG. Ultrasound is used for this. It allows you to see the structure of the chambers of the heart muscle, the condition of the valves, the thickness of the walls, and the presence of inflammatory processes.
- Tomography of the spinal column (or MRI). Performed after ruling out cardiac pathology. During the manipulation, the size of the intervertebral spaces and the condition of the bone tissue, the presence of disc protrusions and pinched neurovascular roots are assessed.
The laboratory evaluates biochemical markers (ALT and AST), their increase indicates the development of a heart attack or myocarditis. More modern ways to determine acute necrosis are to increase the concentration of troponins in the blood.
Prevalence of the disease
The World Health Organization notes that neuralgia is quite rare in the world - 3-5 patients per 100,000 people. On average there are 4.3 cases in the world and about 5 in Russia. The ratio between women and men is 65/35.
Neuralgia can have a recurrent course.
Repeated exacerbations occur as a result of unfavorable factors: overwork, hypovitaminosis, hypothermia, etc. A patient who has suffered from neuralgia should undergo an examination to determine its causes and exclude exposure to cold on the affected area (including outside of an exacerbation).
Neurologist, reflexologist, hirudotherapist
Kislitsyna Ekaterina Nikolaevna
10 years of experience
Neuralgia can occur in children, but this is rare. Most often, people over 40 years of age become victims of the disease (80 to 90% of cases). Moreover, the older you are, the stronger the consequences for the body.
Kinds
The problem can affect any nerve in the human body, especially if the nerve fiber passes through narrow channels and openings. The most common neuralgia are:
- intercostal space;
- sciatic nerve;
- nerve of the thigh;
- trigeminal nerve;
- occipital nerve;
- glossopharyngeal nerves.
According to the form of manifestation, pathology is divided into essential and secondary. The first type of problem is characterized by symptoms in the affected area and does not affect other areas of the body. In the secondary form, in addition to acute pain, another clinical picture is observed - inflammation and swelling of the damaged area.
| Peculiarities | Peripheral type | Central type |
| Feelings of pain | Painful, aching | Shooting, burning, like an electric shock |
| Duration of pain | Constant (hours and days), can alternately intensify and subside | A few seconds - a few minutes |
| Pronounced areas of pain | Not expressed | One or more |
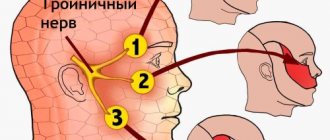
Types of trigeminal neuralgia
Each type of neuralgia has its own characteristic signs, so treatment is selected individually for each case.
How to distinguish
To distinguish heart pain from neuralgia and other pathologies that are successfully masked by cardialgia, it is necessary to take into account the following factors:
- duration;
- localization and depth;
- provocative factors;
- drugs to relieve symptoms.
When trying to determine the cause, I always pay attention to the accompanying signs. This allows you to fairly accurately diagnose the disease, even at the stage of a preliminary survey, before using additional research methods.
Angina pectoris lasts 3-20 minutes, and a heart attack is characterized by a long-lasting attack (the same pain is observed with myocardial inflammation, pericarditis and aneurysm). Suffering of varying intensity and duration is observed with pinched nerves and myositis.
It is necessary to determine the depth and localization of pain. In case of cardiac pathology or vascular problems, it is internal, as if going outward. Superficial sensations are characteristic of neuralgia and muscle inflammation. In this case, it is possible to distinguish pinching from pain in the heart using palpation.
Provoking factors for the development of IHD are psycho-emotional stress or physical overload. The latter factor can also provoke an exacerbation of osteochondrosis and hernia. Myositis occurs against the background of general inflammation, hypothermia or intoxication.
If the attack is relieved by sublingual nitroglycerin, then angina pectoris should be suspected. For a heart attack, acute aneurysm or thromboembolism, this action will not have a significant effect; in this case, only narcotic analgesics, which are administered to the patient immediately after admission to the department, will help. To distinguish intercostal neuralgia from cardiac pain, you should know that the first pathology can be easily eliminated with the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the use of muscle relaxants, but cardiac problems cannot be solved in this way.
Causes
There are many factors that trigger the problem. The main cause of the pathology is tissue pressure on the nerve endings. The most common causes of the anomalous process should be noted:
- injuries ;
- external pressure on the nerve;
- poisoning;
- inflammation of the nerve sheath;
- diabetes mellitus in later stages of development.
Facial neuralgia
The trigeminal nerve is the fifth of 12 pairs of human cranial nerves.
Spinal diseases such as spondylosis or osteochondrosis, as well as neoplasms in this area, lead to compression of the nerves. Provoking factors also include infectious diseases:
- tuberculosis;
- herpes zoster.
Infections affect tissues located near the nerve trunk and negatively affect its fibers.
Poisoning is a less common cause of neuralgia, but it poses a serious threat to the entire human body. Intoxication can occur as a result of:
- eating poisonous mushrooms;
- inhalation vapors ;
- long-term and severe infections;
- drinking alcohol.
Nerve fibers can be damaged due to a lack of B vitamins in the body when there are problems in the gastrointestinal tract.
The secondary form of pathology manifests itself against the background of chronic diseases of the cardiac and endocrine systems. Among them are:
- atherosclerosis;
- lack of hemoglobin in the blood;
- disease ;
- increased blood pressure.
Identifying the exact cause of the problem is an important condition for proper treatment. The fight against the disease should be aimed at reducing the intensity of pain and eliminating unfavorable factors.
Symptoms
Signs of a problem can change the intensity of manifestation as a person moves and turns his body. Often patients have to take unnatural positions in which the discomfort subsides. The nature of the attacks is varied - from burning, shooting to dull aching. Sometimes the problem is accompanied by constant pain.
| Indicators | Intercostal neuralgia | Non-coronary heart pain | Coronarogenic heart pain |
| What usually causes | Uncomfortable position, sudden movements | Emotional or physical stress | Emotional or physical stress |
| Where is it felt | In the area of the intercostal nerve | Chest on the left, between the ribs | To the left of the sternum or behind it |
| Type of pain | Short-term, strong and burning | Long, aching and dull | Pressing and strong |
| Additional symptoms | Increased blood pressure, sweating, stiffness of movement | Not identified | Cold sweat, pale skin, shortness of breath |
Differences between neuralgia and heart pain
The clinical picture of the pathology largely depends on the location of the affected nerve. Therefore, you should consider in detail the signs of each type of neuralgia.
Intercostal neuralgia
Spasms during intercostal neuralgia spread from the thoracic spine along the surfaces of the chest. The problem is characterized by girdle pain. When coughing, moving, turning the body, a person feels acute unbearable attacks. When you press your fingers into the intercostal space, pain is also felt.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Symptoms of pathology may disappear and appear with even greater intensity. Sometimes a slight tingling sensation is felt in the area of the affected nerve.
When the nerves of the lower ribs are damaged, signs characteristic of renal colic are observed. In such a situation, you should immediately consult a doctor for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Sciatic nerve damage
The sciatic nerve runs in the buttock and back of the thigh. A common cause of damage to these areas is pathology of the spinal column. The disease occurs due to increased physical activity, hypothermia, and less often due to damage to the pelvis and malignant tumors.
Pain in the shoulder blades
Pain under the shoulder blades can be a consequence of cardiac, neurological, gastrointestinal diseases, including pathologies of the lungs, bronchi, spine, intervertebral hernia or others.
With neuralgia of the sciatic nerve, the following clinical picture is observed:
- Spasms that occur unilaterally.
- Numbness of the legs.
- Pain localized in the lower back, buttocks, and back of the thigh.
The discomfort with this type of disease is constant, pulling and burning. They are periodically replaced by “lumbago”. Spasms occur when a person changes body position.
Neuralgia of the cutaneous nerve of the thigh
Unpleasant signs with this type of pathology spread along the outer sides of the limbs. The attacks intensify when walking and are accompanied by a “lumbago” sensation and a sensation of goosebumps.
Trigeminal nerve damage
Signs of the disease are especially acute during the daytime. The onset of discomfort may be gradual or acute. The trigeminal nerve has three branches, most often the lesion involves one of the branches. Symptoms develop in the forehead, upper or lower jaw. The pathology has several characteristic features:
- Only one half of the face is affected, and only in rare cases is bilateral neuralgia noted.
- The pain is of high intensity.
- The onset of attacks is noted after talking or eating food.
- Symptoms of the disease are accompanied by twitching of the muscles on the face, loss of sensitivity in the innervation of the nerve.
- The duration of attacks does not exceed 2 minutes.
Neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve
The symptoms of the disease are similar to trigeminal neuralgia. Spasms extend to the ears, pharynx and root of the tongue. The cause of the attack is irritation of trigger points, as with neuralgia of the facial nerve. Pain can occur both during the day and at night.
Occipital nerve damage
The occipital nerves control sensation in the neck, scalp, and back of the head. Neuralgia occurs due to hypothermia, brain tumors. Pathology can manifest itself in healthy people as a result of a sudden movement of the head.
| Neuralgia | GB | |
| Frequency, once a day | More than 50 | Up to 8 |
| Duration | Few seconds | 10 minutes - 3 hours |
| Patient's reaction | Tries not to touch his face, freezes | Grabs his head, feels anxious |
| Main risk group | Women from 45 to 59 years old | Men from 20 to 29 years old |
Differences between trigeminal neuralgia and cluster headache (CH)
The following signs of occipital neuralgia are distinguished:
- One-sided defeat.
- Increased pain when turning the head and touching the skin of the back of the head.
- Spasms localized in the neck, behind the ears and in the back of the head.
Heart diseases with similar symptoms
I want to say that there are many cardiac and vascular pathologies that are accompanied by similar symptoms. I propose to consider the most common abnormalities, this will help to understand whether the heart or neuralgia is the cause of the pain.
Pain in this case occurs in the area of the heart muscle (but do not forget that there are atypical attacks). It has a diffuse nature, a person is not able to indicate the exact location. Its strength and description are variable: it can be pressing, piercing, cutting, baking. It radiates to the left arm, under the shoulder blade, neck, lower jaw. It does not depend on the position of the body, but can be provoked by physical overload, nervous stress, as well as sudden hypothermia or overheating.
At this moment, there is a fear of death, shortness of breath with difficulty in inhaling. The attack can be one-time, occurring 1-2 times a day or more often. Its duration ranges from 3-5 to 20 minutes. Almost the same signs are characteristic of myocardial infarction. But unlike angina, the attack usually lasts a long time. The patient takes a certain position in bed - sitting with his legs down or lying on several pillows. You can read more about angina pectoris and how to deal with it in the article at the link.
Inflammatory diseases are accompanied by moderate pain, which is monotonous. Occurs in 90% of all patients. They describe it as aching or pressing. In the acute period, signs of inflammation are observed (fever, body aches), shortness of breath with impaired inhalation or exhalation. The history often reveals a recent infectious disease. There is no clear dependence on physical activity.
Often myocarditis simulates angina pectoris, especially in older people, when pain and lack of air come to the fore, and the rest of the symptoms are smoothed out or do not appear.
The pain of pericarditis gradually increases, but when effusion appears, it can significantly decrease or go away completely. It stings, cuts, radiates to the neck, back, shoulder, to the right side, and lasts for a long time. Some relief occurs in a sitting position with anterior tilt.
In acute dry inflammation, an attempt to make a deep entrance increases the pain, so with this disease a person breathes quickly and shallowly. During auscultation, in this case, I clearly heard the pleural friction noise. The heart most often hurts with this type of pericarditis in the apex area.
A complete collection of information about pericarditis and its treatment methods is here.
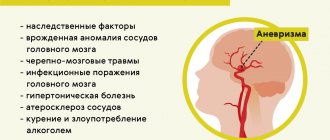
The symptoms of this acute condition are largely reminiscent of myocardial infarction. A sharp increase in blood pressure, stress or physical activity can be a provocation. The pain is tearing, bursting, localized in the retrosternal region, radiating to the neck, lower jaw, right side of the chest, and sometimes runs along the spine. Has a wavy character. In some cases, it spreads to the projection area of the abdominal aorta and even to the legs.
At the same time, sharp pressure surges appear; when the pressure drops, a collapsible state may occur. There is an asymmetry of the pulse on the left and right arms. As blood begins to accumulate under the inner lining of the aorta, symptoms of anemia (pallor and blueness of the skin, dizziness) quickly develop.
Pulmonary embolism is accompanied by sharp and severe pain, which is localized in the center of the sternum, as well as to the left or right of it. It can last from a few minutes to 3-5 hours and is associated with respiratory movements of the chest. At the same time, a lack of air comes to the fore, a sharp decrease in pressure, up to collapse. Clinical manifestations depend on the location of the thrombus and its size. When the lumen of a large vessel is blocked, cyanosis appears in the upper part of the body, arrhythmia with an increase in pulsation frequency. When small arteries are blocked, the skin develops blue, shortness of breath, the pain is most often moderate, cough and sputum streaked with blood are observed.
Diagnostics
When the first signs of neuralgia occur, a person needs to visit a neurologist. In severe cases, you may need to consult other specialists - a cardiologist, vascular surgeon or endocrinologist.
During the appointment, the specialist:
- Asks the patient about the symptoms of the disease, the intensity and time of their manifestation.
- Feels the affected areas of the body.
He also prescribes studies:
- electroneuromyography if there is suspicion of damage to the nerve trunk;
- CT or MRI of the spine to detect abnormal formations - hernia, soft tissue tumors;
- X-ray of the chest and spine;
- ECG if the patient complains of heart pain;
- OAM, UAC, when unpleasant symptoms appear in the lumbar region;
In most cases, the diagnosis is made based on an initial examination. Laboratory tests are prescribed only for severe forms of the disease.
Case from practice
A 56-year-old woman came to see me with complaints of chest pain that radiated to her arm. She noticed her first attacks 1.5 years ago, with a history of large-focal infarction of the anterior wall. Palpation reveals increased sensations in the area of the 6-7 thoracic vertebrae. Some relief is noted after lying on a flat, hard surface.
After taking an ECG and conducting additional drug tests, cardiac pathology was excluded. The patient was referred for consultation to a neurologist. An MRI reveals an intervertebral hernia. Treatment is rest during an exacerbation, NSAIDs, massage, electrophoresis with novocaine, traction. After completing the full course, my condition is satisfactory.
The following sources of information were used to prepare the material.
Treatment
Treatment of neuralgia is most often carried out at home. The patient must observe a gentle regimen for several days and use an orthopedic mattress and pillow for sleep and rest. Sleeping on a bed with a metal mesh is prohibited: this may cause the problem to progress.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
Drug therapy
The doctor prescribes the following groups of medications to a patient with neuralgia:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. The drugs have an effect not only on the damaged nerve, but also on the cause of the problem - the site of inflammation.
- Muscle relaxants to reduce muscle tension.
- Sedatives .
- Vitamins to improve the conduction of nerve impulses.
Drug treatment lasts from 5-7 days. After the patient’s condition improves, the doctor may recommend additional methods of therapy - physical therapy, massage or acupuncture.
Local therapy
The local effect on damaged tissue is due to the thermal effect. You can use a down scarf or knitted scarf to keep the area of pain warm. Applying a hot object to a sore spot may worsen the patient's condition.
Doctors recommend using ointments and creams with an anti-inflammatory effect in the acute period. For aching, mild pain, the use of gels with a warming effect is indicated.
Relatively recently, drugs in the form of a patch have appeared for the treatment of muscular neuralgia. The products are impregnated with a mixture of anesthetic substances. The patches are glued to the affected area in order to provide a long-term analgesic effect on the affected area.
Neuralgia of the ear
Auricular neuralgia is a lesion of the autonomic ganglion, manifested by periodic intensification of the pain symptom, which spreads to the lower jaw, back of the head or upper areas of the chest.
Products made from natural ingredients can be purchased at the pharmacy, for example, pepper patch. Before use, the area to be applied is treated with an antiseptic solution and dried.
After some time, the drug will begin to warm the skin. The main thing is not to overexpose the patch, as this can cause skin burns.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
The method is used only after the acute symptoms of the pathology disappear. Physiotherapeutic procedures help restore the functionality of damaged tissues. Among them are:
- physical therapy to help strengthen the muscle corset;
- massage to improve blood supply around the spinal muscles;
- manual therapy;
- acupuncture;
- UHF.
When performing therapeutic exercises, it is not recommended to make sudden movements and turns of the body. It is also important to avoid heavy lifting and prolonged sitting.
Improvement should occur within 2-4 weeks from the start of the procedures. If the above measures do not help, the doctor may prescribe surgery to treat certain types of neuralgia. This method helps to get rid of pain in 80-90% of cases.
Consequences and complications
The consequences of muscular neuralgia appear depending on the severity of the disease. Pathology manifesting itself in any form should be treated under the supervision of an experienced physician. Otherwise, you can miss serious diseases:
- chest pain
- pneumonia;
- postherpetic neuralgia;
- oncological diseases.
Without timely treatment, the pathology passes into the chronic stage, in which the nerve endings lose sensitivity.
Due to constant pain, patients experience depression, loss of appetite and decreased immunity.
Intercostal neuropathy in its chronic course is accompanied by attacks of frequent pain, which prevents the patient from breathing normally and supplying the body with oxygen. Damage to the sciatic nerve can cause circulatory problems in the pelvic organs.