Medical information is reliable Checked by Eremin Alexey Valentinovich
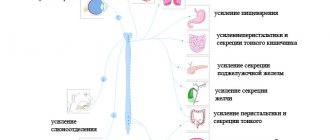
Acute psychotic disorder belongs to the group of transient psychoses. They are characterized by manifestations in the form of delusions, affective deviations, disorganization of thinking, hallucinations, mood disorders and other symptoms. It begins suddenly, there is no prodromal period. Recovery occurs after a few days or months. This pathological condition is most often observed in women, which distinguishes it from schizophrenia, in which the likelihood of its occurrence does not depend on gender.
Causes of acute psychotic disorder
The main reason for the development of acute psychotic disorder is severe psychotrauma, that is, a situation that is perceived by a person as severe stress:
- death of a loved one;
- divorce;
- job loss;
- car accident;
- stay in a war zone;
- physical or mental violence;
- long stay in a mentally aggressive environment;
- loss of money;
- economic difficulties.
Provoking factors contributing to the appearance of an acute psychotic reaction may be:
- hereditary predisposition;
- severe fatigue;
- lack of sleep;
- alcohol abuse;
- taking drugs.
Most often, acute psychotic disorder occurs in a certain type of person. Usually these are impressionable people who tend to take difficulties to heart, or people with a high level of fear and anxiety. In some cases, strong positive emotions can also cause the development of the disease.
Diagnostics and varieties
According to the international classification, acute psychotic disorder is diagnosed based on the following signs:
- sudden onset with hallucinations, delusions, incoherent speech;
- not meeting criteria for a depressive episode or mania;
- confusion not associated with organic disorders;
- exclusion of possible brain diseases, severe metabolic disorders;
- lack of connection between the attack and the use of a psychoactive substance;
- the presence of a connection between a stressful situation that occurred no earlier than two weeks before the development of clinical symptoms of acute psychosis.
Depending on the characteristics of the manifestation, the following types of acute psychotic disorder are distinguished:
- polymorphic with signs of schizophrenia;
- polymorphic without signs of schizophrenia;
- schizophrenia-like (with a schizophrenic reaction, acute form of schizophrenia, schizophrenomorphic);
- other types of delusional nature (including paranoid psychogenic deviations);
- other forms;
- unspecified disorder or reactive psychosis.
The symptoms of acute psychotic disorder are quite diverse, and often they can simulate other mental disorders - manic-depressive syndrome, schizoaffective disorders, depressive episode. But these diseases are preceded by a prodromal period and require long-term treatment. And in an acute process, symptoms increase quickly and are quickly relieved with the help of medications.
Acute polymorphic psychotic disorder
Acute polymorphic psychotic disorder without signs of schizophrenia most often manifests itself in the form of delusions, where the main theme is one’s own greatness, or guilt, the presence of a serious illness, or persecution. Hallucinations and delusions replace each other every day and hour.
There is also a constant change of affects, the mood can be elevated, and after a while it is replaced by severe depression. The symptoms of this disorder are very variable and changeable over time. Thinking and physical activity may slow down or speed up. Anxiety, confusion, and lack of attention are often observed. Distinctive features of polymorphic disorder are:
- constant change in the intensity of manifestation and nature of hallucinations, delusional ideas, mood;
- suddenness of symptoms;
- absence of criteria characteristic of other mental disorders.
Acute polymorphic mental disorder with symptoms of schizophrenia is considered a more severe form of the disorder, it can develop into schizophrenia, and is usually accompanied by the following symptoms:
- delirium of influence of external forces on the patient;
- confidence in your superpowers;
- conviction in reading his thoughts, imposing them from the outside;
- hallucinations with voices that evaluate his actions, talk to each other, laugh at him (Kandinsky-Clerambault syndrome);
- other psychotic manifestations and affective disorders.
These symptoms do not always indicate that a person has developed schizophrenia. If assistance is started in a timely manner, severe mental deviation can be avoided. Otherwise, the patient’s condition worsens, and a schizophrenic personality defect gradually forms. Thus, an acute disorder of this type is diagnosed based on the following signs:
- rapid development of the clinic and abrupt start;
- typical changes characteristic of schizophrenia that last less than a month;
- constantly alternating psychotic and affective disorders (anger, euphoria, anxiety).
Symptoms of schizophrenia-type psychosis
With schizophrenia-like mental disorder, the symptoms are not as variable as in the variant described above. These include:
- delusions of various types;
- delusional ideas;
- “echo thoughts” and their supposed openness;
- hallucinations (auditory, visual);
- intermittency of speech, strange neologisms;
- catatonia (freezing, agitation, stupor, “waxy flexibility” of the limbs and body);
- apathy, lack of expression of emotions.
The main difference between such psychosis and schizophrenia will be its duration of up to one month. If the delusional picture, hallucinations and other above-mentioned symptoms persist for more than a month, then a diagnosis of “schizophrenia” is made, while organic damage to brain cells and the use of psychoactive substances are excluded.
Schizophrenia-like acute psychotic disorder
Schizophrenomorphic acute disorder is accompanied by Kandinsky-Clerambault syndrome, delusions and hallucinations. Usually the patient experiences confusion or is in a state of passion. In the first case, a person does not understand who he is, where he is and at what time. The second option is accompanied by anger, severe fear, anxiety, and some experience a state of ecstasy and euphoria.
Acute schizophrenia-like psychotic disorder develops very quickly. In some cases, a person exhibits disorganization of speech; it is fragmented and devoid of meaning. Sometimes he experiences catatonia - freezing for a long time in one position, or motor agitation.
With this deviation, typical symptoms characteristic of schizophrenia are noted. But the main difference between this disorder and other acute psychoses is that affective and psychotic symptoms do not change, but are stable. Thus, during a schizophrenia-like attack there are a number of manifestations that make it possible to determine this deviation:
- rapid onset and development of the clinical picture of the disease;
- symptoms typical for schizophrenia;
- stability of affective and psychotic disorders.
Other acute psychotic disorders
Another type of acute psychotic disorder is diagnosed when a person has delusions and hallucinations but does not have other signs of schizophrenia. Paranoid psychosis is a severe disorder and is accompanied by unsystematized delusional ideas. Most often, a person is convinced that he is being persecuted and wants to harm or kill him. Affective disorders include anxiety, fear, and severe agitation.
In the reactive form of acute psychotic disorder, a state of shock and complete loss of the patient in time and space are observed. The cause is severe psychological trauma. This type of psychosis can be of two varieties - hypokinetic and hyperkinetic type. In the first case, stupor prevails, complete numbness, accompanied by severe anxiety and fear. In the second, chaotic movements and strong excitement are observed.
Kinds
Impaired sound pronunciation is a common ailment, divided into several separate forms. The table below describes them all.
| Burr classification | Peculiarities |
| Organic | It is characterized by a congenital and acquired structure of a defect in the articulation apparatus with adequate regulation by the highest activity of the nervous system. |
| Functional | This is an acquired disease that occurs in cases where morphological pathology of the nervous system and organs of the speech apparatus is excluded. There are two types of it: motor and sensory. The first is characterized by a neuromolecular shift in the center of pronunciation, when the lips, tongue and cheeks move with some difficulty. Sensory is manifested due to shock in the parietal region, which is responsible for the reproduction of sounds. |
| Physiological | This form is also called transient, and it manifests itself in most of humanity; it easily goes away on its own in children under 5 years of age. |
| Monomorphic | This is one of the simplest violations of the pronunciation of individual sounds, for example, only whistling sounds. |
| Polymorphic | This is one of the complex forms of the disease, when a person cannot pronounce more than 4 sounds correctly and all of them can be from separate sound groups. |
Dyslalia is a disease of the passive and active oral speech apparatus, which includes the lips, tongue, teeth, cheeks, and palate. But disturbances in the pronunciation of sounds can also occur due to structural and functional diseases.
This is why dyslalia occurs:
- articular-phonetic;
- acoustic-phonemic;
- articular-phonemic.
Also, this disease in speech therapy is classified according to phonetic type and depends on problematic sound pronunciation:
- Sigmatism is a more common form when a person has problems pronouncing whistling and hissing sounds.
- Impaired pronunciation of sonorous sounds. There are 4 separate forms: lambdaism, pralambdaism, rhotacism, pararotacism. The first form is characterized by difficulty pronouncing the sounds “l” and “l”, and rhotacism – by the sound “r”.
- Disturbances in the pronunciation of back-lingual sounds, such as “k”, “k”, “g” and “g” and others.
- Yottacism is characterized by disturbances in the pronunciation of letters containing the sounds “th”, “ya”, “yu”.
- Voicedness defect, when a person replaces voiced consonant sounds with voiceless ones and vice versa.
- A defect of softness, when there is an unconscious replacement of soft consonants with hard ones and vice versa.
In addition to types and forms, experts divide sound pronunciation disorders into several levels:
- This is when a child is completely unable to pronounce sounds. The child is unable to independently pronounce sounds in phrasal speech, in individual words, in isolation.
- A child can pronounce a sound correctly in isolation in words and even when repeating phrases, but can distort or miss in words and phrases.
- The child pronounces the sound in isolation, but mixes it with another similar in articulation or sound.
It is very important to accurately establish the level of the disease, because the nature of the specialist’s further work depends on this: setting sound - the first level, automating - the second level, differentiating with another sound - the third level.
Acute psychotic disorder treatment in Moscow with drugs
The most favorable prognosis is considered to be polymorphic psychotic arousal, in which signs of schizophrenia are not observed. In some cases, it may go away on its own. But any form of acute psychosis requires hospitalization, since the symptoms of the disorders are very similar to other deviations, and long-term monitoring of the patient’s condition during treatment, at least a month, is necessary to establish the correct diagnosis. Dr. Isaev’s psychiatric clinic allows for round-the-clock monitoring and provides comfortable conditions for the patient’s stay in the hospital. If the symptoms only intensify while taking antipsychotics, then in this case schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder is diagnosed.
Treatment of acute psychotic disorder in Moscow should be comprehensive. For this purpose, drug therapy and rehabilitation are used. A psychiatrist deals with this pathology. If the deviations are mild, assistance begins with the use of neurometabolites, usually prescribed:
- nootropics to restore brain cell function;
- B vitamins;
- amino acids.
A mild degree of dysfunction can be relieved with the help of these drugs in combination with psychotherapy. But most often it is necessary to resort to eliminating the symptoms of acute psychosis with the prescription of antipsychotics; they successfully help cope with delusional ideas and hallucinations of any type. After leaving the hospital, the person is transferred to long-acting medications. When choosing a product, the specialist is guided by the following principles:
- duration of the violation;
- features of manifestation;
- types of antipsychotics previously used;
- intolerance and resistance to drugs.
As additional therapy for acute psychotic disorders, depending on the characteristics of their manifestation, the following groups of drugs are used:
- mood stabilizers - improve mood;
- tranquilizers – calm and reduce anxiety;
- antidepressants - help treat depression and prevent suicide attempts;
- minor antipsychotics - used in elderly people and people with impaired renal and liver function, help normalize behavior.
Treatment of acute psychotic disorder in Moscow at Dr. Isaev’s clinic continues until positive dynamics appear. It is determined by the following criteria:
- absence of psychotic abnormalities;
- readiness to transfer to outpatient treatment;
- the patient’s understanding of his problem and the desire for a complete recovery;
- lack of resistance to treatment;
- the mental state assessment on the BPRS scale is no more than 35-40 points.
Without the use of competent therapy, many forms of acute psychosis develop into more severe mental disorders. In order not to undergo treatment for schizophrenia, schizoaffective and manic-depressive psychosis, you must strictly follow the recommendations of your doctor. Then the attack, as a rule, is observed as a one-time episode, and the person returns to normal life.
Treatment of acute psychotic disorder: psychotherapy
In addition to medication methods, psychotherapy and social rehabilitation methods are used in treatment. Such assistance to the patient is structured according to the following scheme:
- determination of the patient’s personal problem;
- finding out his attitude towards his illness;
- finding the optimally effective method of therapy;
- planning work strategy;
- elimination of a person’s reaction to illness (feelings of guilt, shame, hopelessness, etc.);
- developing the right attitude towards the problem and treatment;
- training in self-identification of exacerbations;
- restoration of all possible personal resources, including skills, knowledge, interaction with other people, and the ability to solve problems.
Thanks to properly selected psychotherapy techniques, the patient will be able to:
- respond correctly to stress;
- learn productive ways to overcome it;
- develop communication skills;
- master methods of self-control;
- regulate your behavior within generally accepted limits;
- overcome difficulties without loss;
- stabilize emotional balance.
The difficulty of treating such patients is that many do not recognize their pathology, do not trust specialists, and do not want to establish contact. Often the reason for this behavior is a person’s fear of a psychiatrist. And this fact has an extremely negative impact on the course of the disease and prognosis. Therefore, at the first stage, every effort is made to achieve complete trust and interaction with the patient.
Many people do not understand why a patient needs rehabilitation if he was prescribed medications and his condition has stabilized. In fact, psychotherapy plays a huge role, since while a patient is in psychosis, his self-esteem is significantly reduced and social connections are disrupted, which affects his future life and can cause a second attack. To restore communications and normalize relationships in the family, individual work, group classes and family psychotherapy are used.
Groups bring together patients with similar problems. Some of them do not admit that they have a disease, but after classes they begin to see abnormalities in themselves. For example, one of the patients shares his delusional ideas, while others evaluate them as pathology. Such therapy also helps to establish connections with people, learn to communicate in microsociety, and respond to the behavior and statements of others. This allows you to successfully restore a person’s ability to communicate after leaving the clinic.
For complete recovery after an acute psychotic disorder, the following is also used:
- psychoeducation;
- auxiliary psychotherapy;
- communication trainings;
- art therapy;
- occupational therapy;
- cognitive behavioral therapy;
- Gestalt therapy;
- psychodynamic approach.
Hypnotic suggestion, bodywork practices, and holotropic breathing should not be used in people with psychotic disorders. These methods can significantly worsen a person’s condition and even transform psychosis into a severe form of schizophrenia.
Full recovery in a person with this disorder occurs within 3 months, in some cases it is possible to stop the condition in a few days. After this, the person must regularly visit the doctor for another year, or contact him if precursors of psychosis are detected.
Diagnostics
Polymorphic dyslalia or sound pronunciation disorder is a disease that should be correctly distinguished from other speech defects. More often than not, parents are concerned about the fact that their child, who cannot pronounce certain sounds well, will be laughed at by his peers. That is why they come to see a speech therapist.
The cause may not necessarily be dyslalia; other speech problems are often observed:
- dysarthria;
- phonetic-phonemic underdevelopment;
- general speech underdevelopment.
Only a speech therapist can make an accurate diagnosis and determine the cause of incorrect pronunciation.
He will carry out several diagnostic stages:
- Initially, phonemic hearing is checked and functional tests are carried out. To do this, the child must repeat all the words spoken by the speech therapist or tell what is shown in the picture. Words and pictures are specially selected so that all sounds localized at the beginning, middle and end of words are covered.
- Additional clarifying tests must be carried out, thanks to which it is possible to exclude any other speech defects.
- If the case is advanced, the speech therapist may require a child’s card, which describes the entire history of the disease. Additionally, opinions from specialized specialists may be required: psychologist, otolaryngologist, neurologist.
After all the tests have been completed, the speech therapist draws up a plan for further activities with the child. The plan is individually selected for each child, because the stages of the disease and the type may be different. It is necessary to determine in what sequence the pronunciation of sounds will be corrected.
Often, disturbances in the pronunciation of sounds can be part of other more complex speech disorders, such as dysarthria, alalia and others, so it is important to undergo a comprehensive examination and make a diagnosis in time to prevent complications.
Questions and answers
What should you do if a loved one has signs of a disorder, but does not want to undergo treatment?
You need to talk to him about this, try to understand and support him. The main thing is to identify how much the violation affects his work, personal relationships and life in society. If these parties suffer greatly as a result of the disease, then consultation with a psychiatrist and subsequent implementation of his recommendations are required.
Can the disorder be cured with medications alone?
Treatment must be prescribed by a doctor, and he takes into account many aspects and characteristics of each patient’s body. In some cases, for mild forms of disorders, only psychotherapy can be used. For moderate disorders, combined treatment with the use of medications. Severe types of illness require the use of drugs to normalize the condition, and psychotherapy acts as an additional method for the rehabilitation and resocialization of the patient.
Therapeutic measures and correction of speech disorders
Therapeutic measures include therapy for the disease that caused the speech pathology, as well as correctional classes to correct the speech defect. In the presence of brain pathology (hypoxia, trauma, cerebral palsy), medications are prescribed that improve cerebral blood flow. Nootropic drugs are actively used: Pantogam, Cortexin and others. If a child’s speech function is inhibited by a severe chronic disease, then doctors try to reduce the severity of the disease and reduce the frequency of relapses.
In addition to treatment of the underlying disease, the child is prescribed regular speech therapy sessions. They can be group or individual. Group classes allow the patient to learn to listen and recognize errors in the words of other children. Classes are held both at home and in schools and kindergartens.
The main direction in the treatment of sound pronunciation disorders is an individual approach to each patient. Another aspect of correction is the use of the child’s compensatory capabilities. The correct selection of teaching materials is also of great importance during classes. The correction is aimed not only at correcting speech defects, but also at developing the intellectual abilities of children.
Corrective work methods
| Specific | Didactic |
| · Motor-kinesthetic. · Auditory-kinesthetic. | · Visibility. · Literature (with and without clarity). · Practice (games). |
The motor-kinesthetic form of training helps to establish a connection between the work of the articulatory apparatus and the sensation of it. The visual-kinesthetic technique allows you to visually remember how the functional articulatory apparatus works when pronouncing a particular sound, while helping with hand movements. Visualization involves the use of pictures, books, toys during learning so that the child can see what a sound or word looks like. The verbal method is characterized by the use of riddles, tongue twisters, words, sentences, and songs. Hands-on techniques combine learning and games. The game method of correction involves staging skits, fairy tales, and using intentional errors in words.
Classes include exercises for the articulatory apparatus, development of linguistic skills, breathing training and voice volume. Speech therapists also try to stimulate speech function with fine motor skills and coordination training. Massage movements of the fingers and facial muscles are actively carried out.
During training, the speech therapist tries to automate the sounds in the child’s speech by repeating syllables, words, sentences, and phrases. During the classes, the patient learns to speak correctly, retell and present what he has read or heard. For children who can write, a speech therapist teaches them how to spell words correctly. With severe dyslalia, the duration of correction is longer than with a normal sound pronunciation disorder. First, the patient is taught to distinguish incorrect sounds by ear, and then the defects are corrected. After the sounds are set, they are used in words, phrases, poems, and tongue twisters.
Timely diagnosis and speech correction helps restore speech function and prepare the child for school.