A lump on a child’s head is a postpartum, post-traumatic or pathological neoplasm with different pathogenetic mechanisms. Its appearance is based not only on soft tissue swelling and hematoma formation in the usual sense, but also on pathological tissue transformations.
…
A lump on a child’s head requires constant monitoring and sometimes urgent medical intervention. The peculiarity of localization requires careful attention to any neoplasms. If a bump appears on your head, it is important to consult a doctor for consultation, examination and to rule out life-threatening complications.
Why does a child have a bump on his head?
Parents who find a lump on the back of their child’s head are advised to know that this is not always a consequence of a blow. There are many reasons for the occurrence of neoplasms.
Insect bites
During insect activity in spring and summer, bumps often appear as a result of bites. Most often they do not pose a danger, but they cause discomfort. The site of inflammation may hurt, redness appears, and the child is bothered by itching. The seal goes away on its own after a few days.
As a result of the impact
A bump on the top of a child's head is often formed as a result of a fall or blow from something hard on top. While playing, the baby may hurt his head. Due to mechanical damage, a hematoma forms. It may vary in color. When pressed, a sharp pain occurs. The formation takes place on its own; to speed up the process, the doctor may recommend anointing it with special ointments or creams.
If a soft tissue bruise occurs, then most often the tubercle subsides within a few hours. The appearance of a hematoma indicates that the vascular area is damaged.
Important! Be sure to consult a doctor if a lump occurs after a bruise. A neoplasm can be very dangerous. If there is a crack in the skull, severe bleeding may occur.
Parents can provide first aid before the damage is examined by a specialist. To do this, apply ice to the area of impact and make a cold compress from any cloth moistened with cold water. If there is nothing cold, you can apply a cotton swab treated with vegetable oil to the bruised area. The doctor may prescribe medications to resolve the hematoma, prevent thrombosis, and relieve swelling. It is important to rule out a concussion.
If you fall, you need to ensure rest before being examined by a doctor, and it is important not to let the child fall asleep. This is necessary to control his condition.
Often, hematomas in the head area occur due to blows
The lymph nodes
Large lumps on a child's throat that extend into part of the head may appear as a result of inflammation of the lymph nodes. The seals are easily palpable and visible visually. They can form not only near the head and neck, but also in the armpits.
The disease can occur either independently or as a result of an infectious pathology, for example, chickenpox. The child may develop additional symptoms such as fever, loss of appetite, and lethargy. When you touch the lump, pain is felt. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, the inflammation may turn purulent.
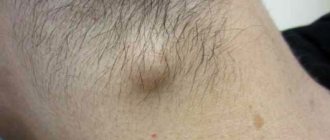
Lipoma (wen)
This is a type of benign tumor that forms from adipose tissue. It does not cause inconvenience because it does not hurt. When pressed, the tubercle is mobile and soft. The causes of lipoma may be hormonal imbalance, stroke, or problems with fat metabolism. It is necessary to treat a lipoma only if it grows strongly, as it can begin to compress adjacent skin tissues.
Other reasons
Often, mothers of newborns discover a soft lump on a child’s head. This is a hematoma that occurs as a result of mechanical trauma during the birth process. Damage can be caused by instruments used by medical personnel. It is most pronounced in the first month of the baby’s life. Most often, the neoplasm disappears completely within a year.
A lump in a child may occur as an allergic reaction. For example, after vaccination with DPT, lumps form on the legs of babies. Therefore, after any injection, vaccination or taking a new drug, it is important to look at the baby’s reaction.
Neoplasms can often be seen in newborns as a result of injury during childbirth
Patient management tactics
For the most part, a bump on the head does not pose a serious danger, especially if it does not hurt. But even in this case, it is worth undergoing an examination to clarify the cause and nature of the formation and to be aware of the possible risks.
- Surgical diseases and injuries. Sukovatykh B.S., Sumin S.A., Gorshunova N.K. – 2015.
- Atlas of pathology of human tumors. Paltsev M.A., Anichkov N.M. – 2005.
- Acute purulent surgical diseases. B. M. Khromov - “Medicine”, 1965.
Ankylosing spondylitis and other autoimmune diseases
Back pain (dorsalgia)
Other pathologies of the spinal cord and brain
Other musculoskeletal injuries
Muscle and ligament diseases
Diseases of the joints and periarticular tissues
Curvatures (deformations) of the spine
Treatment in Israel
Neurological symptoms and syndromes
Tumors of the spine, brain and spinal cord
Answers to visitors' questions
Soft tissue pathologies
X-ray and other instrumental diagnostic methods
Symptoms and syndromes of diseases of the musculoskeletal system
Vascular diseases of the central nervous system
Spinal and central nervous system injuries
©, medical portal about back health SpinaZdorov.ru
All information on the site is presented for informational purposes. Before using any recommendations, be sure to consult your doctor.
Full or partial copying of information from the site without providing an active link to it is prohibited.
Associated symptoms
Rash on the face and head of a newborn - what is it?
If an occipital neoplasm does not go away on its own over a long period of time, it is necessary to show the child to a doctor. Often at such moments additional symptoms appear:
- rapid heartbeat, parents can control it themselves by placing a finger on their wrist;
- pale skin;
- long-term pain in the area of inflammation;
- the size of the pupils changes;
- there is a violation of coordination of movements, orientation in space;
- general weakness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting;
- heaviness when turning the head.
The child may be bothered by severe headaches that occur with increasing intensity, and loss of appetite. If at least one of the listed signs appears, you must immediately call an ambulance. Their presence indicates the development of severe pathology. Often, the success of treatment depends on how long after the tumor occurred the parents sought qualified help.
Types of pathologies with symptoms
The main types of bumps on a child’s head:
- Hemangioma is a small red lump, consists of clots of blood vessels, grows with the child, and can affect neighboring tissues. Occurs in newborns or appears in the first months of life and requires constant monitoring. More often girls are born with hemangiomas, but boys also have them. On the head they are usually localized in the eye area or behind the ears. If the hemangioma continues to grow, it requires treatment. If in the first year of life it does not increase in size, then it goes away without treatment by 10-12 years.
- Lipoma or wen. In itself, it is harmless, easily mobile, and grows slowly. If it causes discomfort, you can remove it.
- Atheroma is a blockage of the sebaceous gland (sebaceous gland cyst). It often grows and reaches impressive sizes. It is removed surgically. Usually located at the back of the head under the hairline. It is usually not painful, but when infected, it becomes inflamed, causing discomfort and pain.
- Fibroma is a hard, benign tumor. To determine the nature, it is necessary to consult an oncologist and undergo tests.
- A wart is a small flesh-colored or brown lump, usually under the hair. The cause of the appearance is unknown, perhaps due to decreased immunity or heredity.
- Enlarged lymph nodes. Often this happens on both sides simultaneously - symmetrical bumps form behind the ears.
The baby may have a birth injury or cephalohematoma. This is a small tumor on the occipital region. On palpation, liquid is felt inside. It requires only observation and by the age of two weeks it completely goes away on its own. Concerns arise when the swelling grows, turns red, or produces fluid. You should immediately consult a doctor and take action, as an increase in formation can be life-threatening.
Cephalohematoma on the head of a newborn (more details in the article: cephalohematoma on the head in newborns)
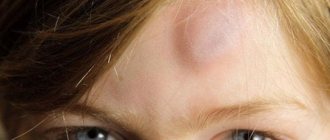
Bumps on a child’s forehead are simply an individual anatomical feature of the structure of the skull (more details in the article: what to do if a bump appears on a child’s forehead?). They are not a pathology and do not require special treatment. Don’t worry if a child is born with such a lump - by the age of two months, with proper care, everything disappears without consequences.
Diagnosis of pathology
During the initial examination, based on appearance and size, the doctor can guess the factors that caused the formation of a bulge on the baby’s head. The main criteria that the specialist focuses on during the examination are:
- number of neoplasms;
- size;
- location;
- color;
- general condition of the child.
Wen on the face of a newborn, on the nose, on the head - what is it?
To make an accurate diagnosis, the baby is prescribed:
- general blood and urine tests that will show whether there is an inflammatory process in the body;
- MRI, CT.
Based on the results of the examination, a diagnosis is made and, if necessary, treatment is prescribed.
Important! You cannot try to self-medicate or apply folk remedies to emerging formations. All appointments should be made only by a specialist.
Laboratory tests are ordered to determine the cause.
Features of the development of osteoma and its treatment
Some patients suddenly face a diagnosis such as osteoma; what it is must be studied in detail before starting treatment. This is the name for a benign tumor that begins to develop from bone tissue. The neoplasm does not degenerate into oncology and is characterized by slow development.
Osteoma does not form metastases and does not penetrate the tissues of other organs. The disease occurs mainly in children or young people under 20 years of age. Despite the fact that the tumor is benign, it is necessary to diagnose osteoma as early as possible; what it is and what methods will be effective is determined by the doctor in an individual case.
general characteristics
Because osteoma is a tumor growing from the bone, the growths feel hard to the touch. The following localization zones are distinguished:
- scull;
- facial skeleton;
- big toes;
- femur and humerus.
Osteoma of the frontal bone is a rare disease; growths appear in the skull area, on the frontal bone. A dense neoplasm appears, which can be detected by palpation. Osteoma does not cause pain.
Unlike other growths, this one cannot be removed quickly with skin particles. If such a problem occurs, you should contact an oncologist for a diagnosis.
The frontal sinus is the space in the frontal bone. All people, without exception, have such a cavity. It is necessary for better perception of sounds, to reduce the overall heaviness of the skull, and also for the separation of mucus.
Osteoma of the frontal sinus is a growth that forms in this cavity, most often rushing into the inner part of the bone. When such a neoplasm forms in the sinus of the forehead, the processes of air movement and mucus secretion slow down. The patient has breathing problems and develops a chronic inflammatory process.
Osteoma of the femur - grows in the hip area, reaching impressive sizes, thereby making life difficult for the patient. The growth can be located above the bone or inside.
According to ICD 10, osteoma has a code of D16. Benign bone formation is divided into types:
- Consists of a solid substance, grows parallel to the neoplasm - solid. Localized: skull bones, sinuses, pelvic bones.
- A porous neoplasm in the form of a sponge, most often occurring on the jaw bone - spongy. Osteomas of this type can appear as part of mixed neoplasms.
- The cavity containing the bone marrow is the medulla.
Bone osteoma appears in most cases as a single lesion. Multiple growths occur in people with a genetic predisposition to the disease.
Causes
The exact reason why tumors develop from bone tissue has not been identified. However, there is an assumption that such a disease is formed due to traumatic damage to the bone, as well as if close relatives have encountered the deviation.
Some sources indicate a connection between osteoma and diseases such as gout, rheumatism and syphilis. Such pathologies cause changes in the structure of bone tissue, but do not lead to the development of tumors.
Osteoma of the frontal sinus often occurs as a result of chronic diseases of the maxillary sinuses. Especially if a puncture was performed in an advanced form of the disease.
Some doctors do not exclude the possibility of osteoma forming in a child in the womb. Such processes can occur due to poor environmental conditions, nervous stress in a pregnant woman, as well as under the influence of infections in the body.
Osteoid osteoma is a neoplasm inside which contains not only hard bone fragments, but also blood vessels. Therefore, some researchers do not at all classify such an inflammatory process as a tumor.
In addition to the above reasons, osteoma of the frontal bone and osteoma of the jaw may appear in the presence of the following factors:
- persistent colds;
- lack of nutrients in the body, especially if there is a deficiency of calcium and vitamin D;
- irradiation with x-rays.
Osteoma has the international classification code: D16. This type includes benign formations of the skeletal system and cartilage.
Osteoma of the femur is much less common. The cause of this disease can also be various injuries to the hip joint, poor nutrition, and lack of calcium.
Danger of disease
Osteoid osteoma is a neoplasm that causes an inflammatory process, thereby causing pain in the localized area. Typically, this type of tumor is small in size. This pathology can significantly worsen the quality of life, because in its advanced form unbearable pain occurs.
The danger is that if the neoplasm is localized in a child near the growth zone in the leg, then this phenomenon provokes rapid growth of the bone itself. As a result of this pathology, the bones are deformed, one limb becomes longer than the other.
Osteoma of the spine often causes scoliosis. And also with such a diagnosis, pinching of the sciatic nerve can occur at any time. After which the person risks completely losing the ability to move.
Over time, the skin over the location of the growth begins to turn red, this is especially often provoked by spongy osteoma and other mixed forms of the disease. If a neoplasm occurs near a joint, then fluid accumulates in the cavity, and gradually the patient stops bending the joints.
Compact osteoma is a growth formed from mature bone tissue. The tumor is most often localized in the frontal area or on the jaw. Such osteomas can be multiple. The growths are dangerous when they begin to actively increase in size, especially if they are located in the frontal sinus.
Symptoms
Usually, when a tumor occurs, no symptoms appear, especially if the growth is located outside and is small in size. The neoplasm is easily detected by palpation and has a clear shape.
The greatest danger is damage to the bones of the skull from the inside. With such a tumor the following symptoms appear:
- aching pain in the head area;
- seizures;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- endocrine disorders;
- deterioration of memory functions.
The consequences of a tumor in the jaw area can cause deformation. After which some patients have difficulty chewing food, and this pathology also negatively affects speech.
After the appearance of osteoid osteoma, the following signs can be noticed:
- pain that periodically progresses;
- Osteoma of the tibia suggests chromatosis;
- rachiocampsis.
If the tumor begins to grow into the eye orbit, the following symptoms occur:
- protrusion of the eyeball outward, partial or complete loss of its mobility;
- eyelid deformation;
- pupils of different sizes;
- a sharp drop in visual acuity.
When diagnosing a disease, it is important to recognize the causes in time and carry out treatment. If there are radiological signs, the doctor will determine the treatment method.
When to see a doctor immediately
Peeling skin on a baby's head - what to do
You should immediately consult a doctor if a bump on your child’s head appears as a result of injury or mechanical damage. If the baby’s condition worsens sharply, the following symptoms will occur:
- the appearance of drowsiness;
- severe dizziness;
- pale skin;
- the occurrence of seizures.
Important! In such a situation, parents should call an ambulance. Before the doctors arrive, provide the child with complete rest by placing him on his side.
If a child is bothered by a severe headache, nausea, vomiting and weakness, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance
Painful lump
A large or small bump on the head can be painful or tender, especially when it is infected. Symptoms will often depend on what the underlying cause is.
The lump can be very painful, especially if it drains, is damaged, or is cracked. This also opens the door for a possible viral or bacterial infection, which can lead to a buildup of pus and dead skin cells. In such cases, the cyst becomes painful, itchy and will most likely emit a foul odor from the semi-solid contents.
A painful lump under the skin is a clear sign of infection. Other symptoms may include itching and irritation. The lump may also become red, tender, and hot. To relieve the pain, you can apply a cold compress. All you have to do is wrap a few ice cubes in a clean towel and place them on the pine cone.
If the lump continues to hurt, it is recommended to seek advice from a specialist as soon as possible. Painkillers can help relieve pain, and oral or topical antibiotics can help eliminate infection.
Some people may notice one or more hard bumps under the skin on the head that do not hurt, but do not go away for a long time. This could be osteoma, a form of benign, slow-growing tumor consisting of bone tissue. Most often, osteomas are asymptomatic and are discovered by chance, but sometimes when large in size and in certain places they cause serious complications.
Osteomas are benign and require removal only for cosmetic purposes or if they cause related complications (eg, impact on the paranasal sinuses).
Possible consequences and complications
If a child has a tubercle on his head, this requires increased attention. If the tumor appears as a result of a blow or fall, it is very important to exclude a concussion, which requires long-term treatment and bed rest. The condition of blood vessels is also examined - as a result of injury, the risk of their rupture increases.
Important! The danger of bumps on the head is that without the manifestation of additional symptoms, they can quickly turn from benign tumors into malignant ones and metastasize to other organs.
Severe complications can occur if a purulent process develops in the lump. This can lead to an abscess and pathological conditions.
Any actions with neoplasms in the head area in children should be performed only after consultation with a doctor. If we are talking about seals that appeared as a result of a bruise, special ointments and compresses can be prescribed.
There are many types of neoplasms that, for various reasons, appear on a child’s head. They can be both benign and malignant, so you should not neglect visiting a doctor.
Tumors: what they are, their types and symptoms
Hemangioma
- What is this and why do red bumps appear on the skin?
Formed when the function of the circulatory system is impaired.- A red neoplasm occurs due to the non-stop enlargement of veins.
- Hemangioma affects not only the growth zone, but also the surrounding tissues of the scalp. At first, hemangioma is a benign formation, but over time it can become malignant, so it is necessary to promptly contact specialists and remove it surgically.
Fibroma and sarcofibroma
- Fibroma is a benign tumor formed from connective tissue that feels and looks like a wart.
- The reason for the appearance of such formations has not been determined by experts; hereditary predisposition or hormonal imbalance are possible.
- It does not cause pain, discomfort, itching, and is more of a cosmetic defect.
Warts
- A benign tumor caused by papillomavirus infection.
- It has a round or elongated shape, brown, black, gray, pink color.
- It occurs due to hormonal imbalance, stress, physical damage, and the presence of a long-term inflammatory process.
- To remove warts, the laser method, cryodestruction, electrocoagulation and surgical excision are used.
Atheroma
- Growth on the scalp at any age.
- It occurs due to blockage of the sebaceous glands under the skin.
- It has a convex surface, smooth to the touch, yellow in color.
- It is painful and brings discomfort.
- Similar to a lipoma (wen), only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
Wen
- A solid, round tumor.
- Wen forms over the human skin.
- They arise due to hormonal imbalances and frequent stressful situations. They usually have a non-infectious etiology.
- Usually the tumor is small, rarely large, and it does not hurt when pressed.
- If the wen interferes with a comfortable life (clings to clothing), it is removed. Removal takes place in a hospital under the supervision of a doctor.