Alzheimer's disease is one of the most common forms of dementia today. It can appear at different ages, but in most cases the first symptoms are diagnosed at around 60-65 years of age. Life expectancy with Alzheimer's disease can also vary.
How long do sick people live?
It is quite difficult to definitively answer the question of how long people with Alzheimer’s disease live. It depends on the age at which the disorder was discovered, gender, and measures taken to eliminate symptoms. But Alzheimer's disease and life expectancy are certainly linked:
- As the disease progresses, more and more areas of the brain are affected, causing it to stop functioning.
- Persons with severe forms of the disorder often create dangerous conditions for themselves and those around them: they injure themselves, leave home and find themselves unable to return.
- To treat symptoms, medications are used that have a large number of side effects, which means they are harmful to the body to some extent.
The age at which it is detected has a decisive influence on life expectancy in Alzheimer's disease. If the disorder appeared at the age of 60-65 years and the patient immediately began to receive good medical care, he can live for about another 20 years. Most of the time will be spent in the first stages of the disease, so life will be relatively normal.
If the disease manifests itself by age 70-75, the transition to severe disease will be faster, so death from Alzheimer's will most likely occur within 10 years. Half the duration of the disorder may occur in the final stages, so that the patient will require constant supervision quite soon.
If the disorder appears at the age of 80-90 years, life expectancy will be no more than 5 years. At this age, the brain already has senile changes, so the disorder will immediately manifest itself as severe. Such patients quickly become bedridden and require intensive care.
Important! Sometimes Alzheimer's is detected at the age of 50, but this does not mean that a person will be able to live normally for another 30 years. Most likely, the development of the disease will be rapid and death will occur within 10-15 years.
Prevalence
Alzheimer's disease is most often found in people over 65 years of age, but in rare cases, earlier onset occurs. According to statistics, the number of patients is increasing from year to year, which is associated not only with improved diagnosis, but also with a general increase in people’s life expectancy. If in 2006 almost 27 million people worldwide suffered from Alzheimer's disease, by 2050 this figure could quadruple. Women are slightly more likely to be diagnosed with senile dementia of the Alzheimer's type, but this may be due to their longer average life expectancy.
What does life expectancy depend on?
As stated earlier, the key factor determining how many years an Alzheimer's patient will live before death is drug therapy, but other incentives can also help extend lifespan:
- Proper care. Very often, the true cause of death in patients with Alzheimer's is concomitant diseases, such as pneumonia, bedsores, leading to sepsis. With proper care, they can be avoided, which means the likelihood of death is reduced.
- Comfortable social conditions. The more stressful situations that arise in a person's life, the more nerve cells die daily. As a result, depression of brain activity occurs much faster, which means that a severe degree of the disease occurs earlier.
- Proper nutrition. For normal nutrition of brain tissue, it is extremely important to receive large amounts of vitamins and beneficial nutrients. It can be difficult for an elderly person to independently provide himself with a complete five-a-day diet.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures. They are important for ensuring normal blood supply. In hospitals and boarding houses, acupuncture, aromatherapy, music therapy and other procedures are often prescribed.
In other words, the life expectancy of Alzheimer's patients is influenced by the environment around the patient. A calm, measured life and regular communication with other people have a positive effect on brain activity, which means they reduce the rate of development of the disease from the first stages to the last.
Important! If relatives and friends objectively cannot provide proper care, it is better to seek help from specialists.
Effective treatment regimens
The drug regimen is prescribed after all necessary diagnostic tests have been performed.
The most effective protocols are those containing targeted antiviral medications:
- Sovaldi;
- Daklinza;
- Sunvepra;
- Epclusa;
- Viqueira Park et al.
Treatment with original medications is very expensive, so many people choose therapy with Indian generics. In terms of effectiveness, such drugs are not inferior to original drugs; they also cure pathology for 12 weeks (or 24 in the presence of cirrhosis and other risk factors).
In case of relapse of hepatitis C, cirrhosis (including decompensated), ribavirin is additionally prescribed. Interferon regimens are practically not used, with the exception of HCV therapy in pediatric practice.
Is it possible to recover completely?
With the right prescriptions, hepatitis C is completely curable, especially if the pathology is diagnosed in the early stages, before severe liver damage. But when choosing a treatment regimen, you should not rely on reviews on forums. Treatment should only be carried out by a doctor. The key to complete recovery is a combination of modern targeted antiviral drugs, hepatoprotectors, diet and a healthy lifestyle.
How to extend lifespan
The doctor determines the treatment tactics, but much depends on the patient himself. To reduce the risk of complications and prolong life, you need to:
- completely give up alcohol;
- follow the doctor's recommendations;
- perform feasible physical activity, especially if you are overweight;
- draw up a diet in accordance with the menu recommended for diet No. 5, and in severe cases – No. 5a;
- do not give up your diet after finishing therapy; expanding your diet is possible only after consulting a doctor.
It is possible to use healing folk remedies. But it is worth considering that St. John's wort is contraindicated. Decoctions based on milk thistle, chamomile and some other herbs are useful.
If you suspect hepatitis C, you should consult a physician. The doctor will give directions for basic tests: ELISA, PCR, blood biochemistry, liver tests. If positive results are obtained, the patient is referred to a hepatologist or infectious disease specialist. Subsequently, the patient undergoes treatment from a specialized specialist.
How does the disease affect life expectancy?
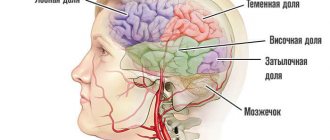
The speed of development of the disease is always individual, but on average, people with Alzheimer's disease live for about 8 years from the moment the first subtle symptoms appear. Experts identify 4 main stages of Alzheimer's, each of which has its own impact on the patient's general condition and life expectancy. More detailed relationships are presented in the table below.
Relationship between Alzheimer's stage and life expectancy
| Disease stage | Main symptoms | Impact on life expectancy |
| Predementia |
| The disorder at this stage does not have a serious impact on a person’s life, so not everyone seeks medical help. But if the neurologist still prescribes treatment, life expectancy before moving to the next stage is approximately 8 years. |
| Early dementia |
| The duration of this stage usually does not exceed 4 years, even with correctly prescribed treatment. |
| Moderate dementia |
| The life expectancy of an Alzheimer's patient with adequately prescribed treatment and constant supervision at this stage does not exceed 3 years. If there is no proper care, the duration is reduced to one year, while the death of Alzheimer's patients occurs from secondary causes (they leave home and get lost, do not notice the symptoms of other dangerous diseases, and so on). |
| Severe dementia |
| From the moment of transition to this stage, the patient lives on average six months. At the same time, it does not matter whether he receives help from specialists in a boarding house or from relatives at home. The brain is so destroyed that medications are unable to provide any activity. |
Important! The sooner a diagnosis is made, the longer an Alzheimer's patient will live a normal, active life. Without properly selected drug therapy, the transition from stage to stage occurs catastrophically quickly.
Signs
The course of Alzheimer's disease varies from person to person, but as a rule, it develops unnoticed and gradually progresses. The first symptoms are often ignored, considering a person’s strange behavior to be age-related or an atypical reaction to stress.
At the very beginning of Alzheimer's disease, patients experience short-term memory disorders - they forget what happened recently, but remember well events that happened 20-40 years ago. Gradually, long-term memory begins to suffer, and patients lose self-care skills. Ideas about safe behavior also suffer, which can cause premature death.
Common symptoms of Alzheimer's disease include:
- unreasonable anxiety;
- depression;
- delusional ideas;
- inability to recognize familiar objects and faces;
- forgetting individual words;
- violation of orientation in space and time;
- indifference to events happening around;
- problems with gait;
- inability to make decisions.
Behavior change is something that relatives of an elderly person should pay attention to first. The sudden transformation of a calm and balanced uncle into a “daredevil,” as well as the grandmother’s refusal of long-loved hobbies and activities, are a cause for concern and a visit to a neurologist.
What do Alzheimer's patients die from?
Alzheimer's disease and death are not always directly related. In the first 3 stages, the patient more often dies from concomitant diseases resulting from poor care. The most popular among them are: pneumonia, sepsis, necrotic lesions due to bedsores, and various infections. You can avoid them if you constantly look after the patient and show him to the doctor.
Things are different for those patients who are already at the last stage of the disease. In this case, the cause of death in Alzheimer's disease is that a large number of senile plaques have accumulated in the brain, and the tissue itself has become like a sponge. Neural activity simply could not continue, which is why the death of the organism occurred.
It is impossible to stop the process today. Drugs are effective in slowing the progression of the disease only in the first three stages. When the fourth occurs, the remaining time counts down to weeks. Without the help of a doctor, patients die from Alzheimer's in just a couple of months.
Features of the disease
Hepatitis C occurs only in humans, and infection also occurs through contact with contaminated blood or body fluids. The widespread spread of the disease is facilitated by the resistance of the pathogen in the external environment.
Until recently, it was believed that the pathogen remained contagious for no more than 5 days at room temperature. But it has now been established that the virus is contagious for one and a half months and slightly less if the temperature rises above 20°C. The causative agent of hepatitis C is not harmed by freezing. Moreover, the risk of infection remains after defrosting.
Dried biological fluids (including semen, menstrual fluid) also serve as a source of infection.
However, the virus is quickly destroyed by standard disinfection and sterilization methods. In this regard, treatment with ultraviolet light, ethanol (a solution with a 70% concentration), miramistin and other antiseptic liquids is effective.
Even experienced hepatologists find it difficult to list the symptoms that distinguish hepatitis C from other, much more common and harmless diseases. In adults, signs of pathology increase gradually.
Men and women note:
- general malaise resembling intoxication;
- disorders caused by disturbances in the production of liver enzymes, bile secretion (diarrhea, loss of appetite, flatulence, nausea, unpleasant taste in the mouth);
- skin rashes (papules, vesicles, manifestations of urticaria);
- extremely rarely - jaundice;
- feeling of discomfort and distension in the liver area;
- low-grade fever.
In severe cases of viral infection, extrahepatic manifestations of the disease may develop.
Diagnose the presence of:
- endocrine disorders, usually associated with a disorder of the secretory activity of the thyroid gland;
- dysuric disorders associated with kidney damage;
- cardiovascular and rheumatoid pathologies caused by cryoglobulinemia.
In children, signs of hepatitis C are often more pronounced. Often the disease manifests itself in the form of jaundice, and digestive disorders are more pronounced. At an early age, a deterioration in appetite is accompanied by a lag in physical development, symptoms of vitamin deficiency, and a deficiency of basic macro- and microelements.
How to extend your lifespan
As mentioned earlier, according to statistics, Alzheimer's disease lasts about 8 years. This happens due to late diagnosis. That is why the best prevention of the disease and the most effective way to prolong life today remains timely seeking medical help. Annual examinations and timely prescribed medications can increase life expectancy by up to 15 years.
Other preventive measures include:
- Regular brain training. Intellectual games (chess, crosswords, puzzles) are best suited. They stimulate brain activity by improving conduction between neurons.
- Moderate physical activity. Frequent walks in the fresh air improve blood circulation, stimulating brain nutrition.
- Proper diet. It is extremely important to get a large amount of vitamins, preferably of natural rather than synthetic origin.
- Comfort, relaxation, good sleep. Stress and excessive psycho-emotional stress significantly worsen the condition of a patient with Alzheimer's.
Other things will help to avoid the rapid development of the disease or its complications. Try to spend more time with the patient in familiar surroundings. New places usually have a negative impact on the condition of a sick person. Do not leave it completely alone, it contributes to the development of panic attacks. Monitor your relative’s immunity and help him treat even the simplest colds.
These simple recommendations will help create comfortable conditions for a patient with Alzheimer's and thereby increase his life expectancy. If there is no opportunity to be with a loved one around the clock, and the disorder is already at a moderate stage, the best solution would be to place the patient in a boarding house, where specialists will take care of both compliance with preventive recommendations and drug treatment.
Quality of life after stroke
Quality of life after a stroke is determined by several factors:
- The degree of loss of function;
- Possibility of self-service;
- Possibility of movement;
- Depression;
- Pain or discomfort;
- Daily activity.
People after a stroke require constant support, both physical and psychological. With prompt diagnosis, proper treatment and rehabilitation, patients recover successfully and return to their normal lifestyle. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital will answer all your questions and create an individual treatment plan.