Causes
The main reason for the formation of hematomas is traumatic effects on soft tissues: bruise, compression, blow, pinching, stretching. The mechanism for the appearance of bruises lies in the rupture of blood vessels. The size and severity depend on their size, location and number of damaged areas. Certain medications can also cause vascular rupture, for example, anticoagulants and acetylsalicylic acid. Non-mechanical causes also include some diseases, such as:
- Mallory-Weiss syndrome - cracks in the upper part of the stomach or lower esophagus, caused by vomiting due to excessive overeating or drinking alcohol.
- Leukemia is a malignant neoplastic disease of the hematopoietic system.
- Atherosclerosis is the formation of cholesterol plaques in the lumen of blood vessels.
- Hemorrhagic vasculitis is a lesion of the smallest vessels in the body: capillaries, arterioles and venules.
Intramuscular hematoma can be associated with injections given into the buttock. Cephalohematomas are sometimes observed in newborns. Their cause is the discrepancy between the baby's head and the woman's narrow birth canal. Intracerebral trauma in newborns is also associated with difficult births. A separate group consists of postoperative hematomas. In pregnant women, they can occur after cesarean section . The list of causes of postoperative hematomas also includes the following:
- decreased blood clotting;
- vascular pathologies;
- increased fragility of vascular walls;
- worsening blood clotting;
- high blood pressure after surgery;
- increased permeability of blood vessels, which causes their rupture.
Causes of hemorrhages
A hematoma on the head occurs for several reasons:
- After being hit with a heavy object during a fight. The damage affects the skin, muscles and bones. Damage to blood vessels occurs. The space between the skin and the periosteum is divided by bridges. Blood from injured vessels enters one of the areas on the head. This leads to severe hemorrhage.
- A person can injure his head when falling from a height.
- A hematoma is formed due to prolonged compression of the soft tissues of the head.
What does a hematoma look like?
When blood leaks into the subcutaneous tissue, a dense and painful swelling forms at the site of injury. Externally, a bruise looks like a spot on the skin, the color of which can determine the age of the injury. At the initial stage, the skin turns red, and then gradually becomes purple-bluish. After 2-3 days the bruise becomes yellowish, and after 4-5 days it becomes greenish. During this time, hemoglobin decomposes. In 4-5 days, the spot may slide down a little.
Subungual hematoma
Injury to fingers or toes is not considered critical for a person’s life, but such hematomas bring quite a lot of concern. As a result of such injuries, the nail plates are often damaged. To reduce the pressure of a blood clot on the nail, you need to open the hematoma by pinpoint burning a hole in the nail, after treating the area with an antiseptic.
The nail does not contain nerve endings, so the procedure is not very painful. After it, you need to apply a damp bandage soaked in an antiseptic, such as Chlorhexidine, or a bandage, on which a little antibiotic ointment is applied.
Symptoms
The main symptom is a change in skin color in the wound area to crimson-red, burgundy, blue-violet. The general clinical picture of the development of hematoma depends on the degree of its severity. In total, according to the main classification, there are three of them: light, medium and severe. They are determined by the size and depth of the damage. The characteristic differences of each stage are as follows:
- Easy. Develops within 24 hours after injury. The damage is accompanied by moderate pain. Edema and swelling are not observed, motor activity is maintained at a normal level. With timely assistance, the formation quickly regenerates.
- Average. Forms 3-5 hours after injury. The tissue damage is deeper, which causes pain. Against this background, swelling of the skin and sometimes limitation of motor activity are noted.
- Heavy. It is noted in the first couple of hours after injury. The patient experiences a general and local increase in temperature, impaired movement of the injured limb, and severe pain.
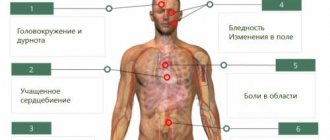
When a brain injury occurs, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and headache occur. Intracranial hematomas are accompanied by a number of other symptoms, such as:
- psychomotor agitation, turning into epileptic seizures;
- bradycardia;
- hemiparesis on the side of injury;
- visual impairment;
- pyramidal signs;
- loss of consciousness up to coma;
- anisocoria – different pupil sizes in the right and left eyes.
In case of hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity, peritonitis develops, which is indicated by sharp abdominal pain and a rise in temperature. Additionally, the victim experiences nausea and vomiting, cough, and shortness of breath. The retrochorial type of hematoma, which can occur in the first trimester of pregnancy, is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- brownish or bloody vaginal discharge;
- pain in the lower abdomen and lower back;
- red vaginal discharge.
First aid
The first thing to do when a superficial hematoma forms is to apply cold and apply pressure or a pressure bandage. If the patient experiences severe pain, the doctor may prescribe painkillers.
With mild hematomas, a blue spot on the surface of the skin appears after 24 hours. For moderate hemorrhages - after 5-6 hours. In case of severe consequences of injury, a hematoma appears on the surface of the skin a couple of hours after the blow. Here, the help of a professional traumatologist is urgently needed. For hematomas that are large, deep, or have complications, surgical intervention is necessary.
Kinds
A bruise and a hematoma need to be distinguished from each other. The latter is a more serious injury that often requires urgent treatment. A bruise is a mild form when only small capillaries are damaged . It is characterized by slight swelling and moderate pain. No increase in temperature is observed.
There are many classifications. One of the criteria for distinguishing their types is the degree of severity: mild, moderate or severe - their symptoms were described above. Depending on the clinical signs, hematoma can be of the following types:
- Limited to the periphery. In the center they have a softened structure, and at the edges they have a dense contour.
- Ensembled. They dissolve on their own only in small sizes. An encysted hematoma is characterized by the accumulation of a large amount of fluid inside.
- Diffuse. They increase very quickly, so they require immediate opening to detect a bleeding vessel.
If there is a bruise in the eyeball, a paraorbital hematoma is diagnosed. Because of it, a person can lose his sight. A periorbital hematoma is a bruise around the eyes associated with head trauma. These are two different disorders that need to be distinguished. Taking into account the state of the spilled blood, hematomas are divided into coagulated and non-coagulated (fresh), uninfected and suppurating. The criterion for another classification is the appearance of the hemorrhage. It depends on the type of blood shed. Taking this factor into account, the following are distinguished:
- Arterial. When arterial blood spills into the cavity, the color of the injury site is bright red, and its area is often more extensive compared to other types.
- Venous. If the integrity of the vein is broken or the vein is compressed, venous blood leaks into the cavity, causing a bluish-violet spot to appear on the skin.
- Mixed. A more common case in which both arterial and venous blood enters the cavity. The color of the bruise is mixed.
Article on the topic: Cogitum for children - instructions for use, composition, indications, mechanism of action and price
Taking into account the relationship to the vessel, pulsating and non-pulsating hematomas are distinguished. Ripple occurs when all layers of the vascular wall are damaged, causing blood pressure to be transferred to the liquid contents at the site of hemorrhage. The most extensive classification divides hematomas by location into the following types:
- Subcutaneous. The most common ones are formed in different areas of the skin after injury or as a result of vascular pathologies.
- Submucosal. They are localized not in the subcutaneous tissue, but in the mucous membrane.
- Intramuscular. They are formed as a result of more serious injuries and are localized in muscle tissue.
- Subserous. Affects internal organs, most often the abdominal cavity or lungs.
- Subfascial. The fascia, the connective tissue membrane covering the vessels, nerves and organs, is injured.
- Retrochorial. Hematomas that occur during pregnancy due to detachment of the fertilized egg from the chorion.
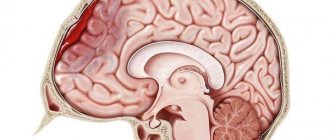
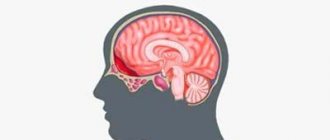
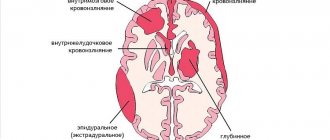
The most dangerous are hematomas in the brain area. They differ from other types in the complexity of treatment and more dangerous consequences for the patient. They are also classified into several types:
- Intracerebral. They are rare and are accompanied by the accumulation of blood inside the brain tissue.
- Subarachnoid. Blood accumulates between the arachnoid and inner layers of the dura mater.
- Intraventricular. Blood enters the cerebral ventricles.
- Epidural. An accumulation of blood between the inner surface of the skull and the outer layer of the dura mater, which often accompanies fractures or injuries in the temporal and parietal bones.
- Subdural. Blood contents accumulate under the dura mater of the brain. They are divided into acute, subacute and chronic.
Formation of encysted hematoma
There are cases when blood does not pass through the tissue, but accumulates in one place, forming a cavity. This results in an encysted hematoma. It doesn't go away on its own. Over time, fibrin and calcium salts accumulate, and suppuration can form. Treatment is carried out by opening the hematoma.
Small encysted hematomas can be drained in the clinic by a local surgeon. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. The surgeon makes an incision in the central part of the cavity and removes blood clots. The cavity formed after opening the encysted hematoma must be washed with Chlorhexidine or hydrogen peroxide to prevent purulent infection.
If the wound is clean, then during suturing, a drainage tube is placed and a tight pressure bandage is applied. In case of purulent formations, no sutures are placed on the hole after surgery, and treatment continues with the use of antibiotics.
If the hemorrhages are deep and large in area, then surgical treatment is performed in a hospital.
Why is a hematoma dangerous?
Only mild soft tissue hematomas occur without serious consequences. Complications develop after severe and extensive hemorrhages. Without opening by a surgeon, they can lead to the formation of scar tissue. This is at best, but at worst the cavity into which the blood has spilled becomes infected and suppurates. When it accumulates in the joint, the following diseases may develop:
- Chronic synovitis is an inflammation of the synovium of the joint, in which effusion accumulates in the cavity lining it.
- Hemarthrosis is hemorrhage inside the joint that occurs due to bruises and intra-articular injuries.
- Bursitis is an inflammation of the synovium of a joint due to injury.
With extensive hemorrhages in the cavities of internal organs, irritation of nerve receptors occurs. This condition is called paresis. It affects the motor pathways of the nervous system, causing incomplete paralysis. When this condition resolves, the spilled blood begins to decompose, i.e. hemoglobin breaks down. This process causes endotoxicosis - the accumulation of toxins in the tissues of the body that poison it.
Intracranial hemorrhages do not go away without consequences. After a head injury, amnesia, disturbances in reaction and attention, and increased anxiety may develop. Serious consequences include epileptic seizures. They appear not only immediately after brain damage, but also after a long period of time. After recovery from intracranial injury, many patients complain of the following symptoms:
- headache;
- attacks of dizziness;
- fatigue;
- increased weakness;
- severe anxiety;
- mental disabilities;
- frequent mood changes;
- headaches.
Treatment at home
An intramuscular hematoma may go away on its own if it is not too extensive. This is quite difficult to determine. The cavity may be deep in the soft tissue. Therefore, only a doctor can determine her condition.
If pain is absent or mild, and muscle mobility is not impaired, you can treat the hematoma at home. However, you need to constantly monitor your well-being. If fatigue or fever appears, you should immediately call an ambulance.
At home, you can use various ointments and compresses. Similar products can be purchased at the pharmacy. Traditional medicine also offers many recipes for hematomas. Complex treatment allows you to quickly get rid of the problem.
Diagnostics
A doctor can diagnose superficial injuries visually by examining the site of the injury. To clarify the nature of the disease, the specialist performs palpation, which helps determine the degree of pain, possible local hyperemia and swelling . More serious hemorrhages require detailed diagnosis, which includes the following measures:
- X-ray. Necessary for identifying subserous forms of hemorrhages. An X-ray of the head is taken in two projections to clarify the location of the spilled blood and the extent of damage.
- Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Mandatory for any intracranial injuries. These procedures pinpoint the location of the damage and help study its nature.
- Ultrasound. Helps evaluate the location and structure of any internal bleeding.
- Echoencephalogram. Evaluates intracranial pressure, which is necessary to identify brain pathologies.
- Lumbar puncture. Prescribed in doubtful cases for the purpose of studying cerebrospinal fluid. This procedure helps identify subarachnoid bleeding in brain injuries.
Hematoma on the leg
There are several joints on the leg, and in case of extensive leg bruises, you need to check for hematomas located near the knee joint or foot. First, the swelling is removed by applying cold, then the doctor examines the leg to identify internal cavities.
There are cases when, after puncture, the cavity is filled with blood again, since the vessel is not docked or thrombosed. Then the hematoma on the leg is opened surgically. Blood is removed from the cavity, the blood vessel is ligated and sutured.
In order to prevent hemarthrosis, if necessary, the doctor performs a puncture from the joint cavities. If there is an accumulation of blood there, it is removed, and the pain is significantly reduced. It also helps prevent the formation of intra-articular adhesions.
Treatment of hematoma
Superficial subcutaneous hematoma tends to resolve on its own. Immediately after receiving an injury, it is recommended to apply cold to the injury site. This will help prevent blood from entering the tissue and causing swelling. Then the limb can be tightly bandaged, leaving the bandage on for 1-2 hours. In the future, ointments based on bodyaga, heparin or hirudin are used to speed up the resorption of blood . 6-8 hours after injury, the following drugs can be used:
- Voltaren gel;
- Dexpanthenol ointment;
- Lyoton gel;
- Finalgon ointment;
- Troxevasin gel;
- Gepatrombin gel.
Article on the topic: Treatment of VSD with folk remedies - recipes and reviews
For bruises on the face, it is recommended to use Bruise-OFF ointment. It is based on hirudin, a leech extract. In addition to resorption, this drug helps to tone the injury site. The ointment smells pleasant, so using it on the face does not cause discomfort. Since a bruise is a local problem, topical medications are more effective at treating it. In some cases, the use of systemic means is allowed. They are indicated for those who bruise very often. The following drugs help cope with this:
- Ascorutin – contains vitamin P and ascorbic acid. Prescribed for vascular pathologies and some types of hemophilia. The dosage is 1 tablet up to 2-3 times per day. The course of treatment lasts 3-5 weeks.
- Capilar is a plant-based drug. Its action is to strengthen the walls of capillaries. Capilar is especially often prescribed to elderly people suffering from the initial form of hypertension.
More extensive intermuscular hematoma requires surgical opening. During this procedure, the doctor opens the site of injury, removes blood from there and treats it with antiseptics. If there is pulsation, hyperemia and swelling in the area of injury, you should definitely consult a doctor, as bleeding may continue. In this case, the doctor also performs an autopsy, but additionally finds the source of the hemorrhage and eliminates it.
For intracranial hemorrhages, conservative treatment is indicated only if their volume is up to 40 ml, there are no symptoms of brain dislocation and slight depression of consciousness. Otherwise, the patient is hospitalized for craniotomy. The procedure for this operation is as follows:
- Under general anesthesia, the neurosurgeon bleeds the scalp using a cutting suture.
- Next, the specialist cuts out a flap of soft tissue and opens the skull.
- The neurosurgeon then removes the blood using an aspirator, after which the cavity is washed and the source of bleeding is eliminated.
- The bone flap is returned to its place and fixed with thick threads. The tissues are sutured in reverse order, sometimes leaving drainage.
Opening
The procedure for opening and cleansing the cavity into which blood has leaked is indicated for extensive hematomas. This is especially true for injuries to internal organs. For small formations, the autopsy is performed on an outpatient basis, otherwise the patient is hospitalized. The course of the operation includes several stages:
- The patient is provided with local anesthesia.
- The area of spilled blood is cut and cleared of contents.
- Next, it is washed with antiseptics and sutured. If the patient has a festering hematoma, then the area of damage is infected. For this reason, full suturing is not carried out, but the cavity is drained to ensure that the pus escapes out.
- A tight bandage is applied on top.
- After 10 days, the stitches are removed. During this time, the patient takes antibiotics prescribed by the doctor.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine methods can be used for minor injuries that are not accompanied by severe pain, hyperemia and swelling, i.e. for superficial injuries. Most remedies only help relieve mild pain and speed up the resorption of accumulated blood. The following recipes receive positive reviews:
- Collect a couple of fresh cabbage leaves, not from the surface of the head, but from 2-3 layers of greens. Crush one of them a little and then apply it to the sore spot. Wrap the sheet with a bandage and leave the compress for the whole day.
- Peel raw potatoes, rinse, cut in half. Apply one half to the bruise and hold for 15-20 minutes. Repeat several times throughout the day.
- Wash a couple of plantain leaves and grind them to a paste. Apply it to the sore spot and wrap it with a bandage. Keep the compress all day.
- Dissolve 2 tbsp in 100 ml of water. l. salt. Moisten a clean natural cloth in the resulting solution. Place it on the sore spot and wrap it with a bandage. Leave for the whole day.
Treatment
To get rid of a tumor, surgeons use the following methods: opening, craniotomy (in the case of an intracranial type), using special ointments to relieve swelling, resolve blood clots, applying a cold bandage; physiotherapeutic techniques (sollux, infrared lamp, Minin reflector).
Treatment for minor deviations is conservative. Immediately after a bruise, apply local cold and a pressure bandage (to prevent further formation) and use analgesics (to reduce unpleasant pain), and a few days after the injury, physiotherapeutic procedures are recommended (to speed up resorption). For large formations, liquid blood must be evacuated by puncture followed by the use of a bandage.
If bleeding resumes, an incision, ligation of the bleeding vessel, or a vascular suture is indicated. If it suppurates, it will need to be opened and drained. In uncomplicated forms, the prognosis is favorable.
Physiology of the brain is also conservative. It consists of supporting vital functions and correcting intracranial pressure to maintain it below 25 mmHg. (ventricular drainage, barbiturates, hyperventilation). If the condition worsens, surgical intervention will be necessary.
In acute subdural form, craniotomy and removal of the bruise are required. The absolute indication for surgery is a tumor more than 1 cm thick according to computed tomography.
In the postoperative period, intensive therapy is needed to support vital functions and control the level of intracranial pressure. If you have an epidural, urgent surgery is needed.
Forecast
A favorable prognosis is typical for soft tissue hematomas. The correct treatment regimen ensures the patient’s full recovery without any serious consequences. The same applies to retrochorial hematomas that develop in the first trimester of pregnancy. With timely diagnosis and adequate therapy, childbirth is carried out naturally. The cesarean section method is used only when a hematoma forms late in pregnancy - at 38 weeks of pregnancy. This does not have any dangerous consequences for the mother and child.
An unfavorable prognosis is observed only with brain injuries. This is especially true for subdural and epidural hematomas. Only mild and moderate injuries are completely cured, but the process can take several years. Among the consequences of such injuries, the following are especially common:
- problems with urination, bowel movements, or swallowing;
- post-traumatic convulsions;
- speech disorders;
- behavioral disorders;
- perception disorders (inability to reproduce what you see);
- disturbances of mental activity and memory.
Types of hematomas
There are several types of hematomas:
- Epidural hemorrhage is the mildest type of injury. Mechanical impact leads to destruction of the walls of blood vessels. The patient is fully conscious.
- A subdural hematoma on the head is characterized by damage to the vessels supplying the brain.
- An intracerebral hematoma requires the help of specialists. Blood begins to accumulate in the brain tissue. The victim's neurons die.
What are the features of epidural hemorrhage?
The cause of this injury is a rupture of the artery that is located between the skull and the brain. The formation of blood clots leads to compression of soft tissues. Signs of epidural hemorrhage include:
- The patient's pupils dilate and the eyelids droop.
- There are malfunctions in the functioning of the brain.
- The patient feels weak.
- A severe headache indicates increased intracranial pressure.
- Coordination of movements worsens.
An epidural hematoma can complicate breathing and cause arrhythmia.
Types of subdural hematoma
- A progressive type of hematoma on the head appears immediately after the blow.
- The first symptoms of the subacute type of subdural hemorrhage can be noticed 2-3 hours after the injury.
- A hematoma with a protracted course is characterized by slight bleeding. There may be no external signs of injury. The victim may not even know that there are injuries on his body. The chronic course of the disease is dangerous because the symptoms of injury can appear suddenly. Damage can lead to speech impairment, headaches, confusion and seizures. A final diagnosis can only be made after undergoing a tomography.
What is the danger of internal hemorrhage?
Hemorrhage inside the head most often affects the frontal area. Blood gradually accumulates in the brain tissue. An internal hematoma can be recognized by the following signs:
- the patient does not understand what his interlocutor is talking about;
- the sensitivity of some parts of the body decreases;
- doctors note asymmetry of the facial muscles;
- a person loses the ability to move limbs.
Prevention measures
The main preventative measure is to minimize injuries. Young children often hit furniture or doors. You can reduce the risk of childhood injuries and generally reduce the likelihood of developing hematomas as follows:
- arrange furniture, observing minimal passages between objects;
- in a house with small children there should be a minimum of sharp corners;
- teenagers when cycling or roller skating, skating, etc. are recommended to use protective equipment such as knee pads, elbow covers and a helmet;
- take anticoagulants and Aspirin with caution;
- Athletes should warm up before each workout.
Causes of pathology
The cause of intracerebral hemorrhage is a head injury, which can be sustained, for example, in a car accident, although it must be said that in some cases this pathology can develop due to blows to the head, which at first glance seem insignificant. This pattern is especially clear in older people - they often develop brain hematomas even with minor blows to the head. Among the provoking factors are:
- vascular damage that leads to arteriovenous malformation and aneurysms;
- constant increase in blood pressure;
- neurological pathologies;
- liver diseases;
- taking anticoagulants;
- autoimmune disorders in the body;
- blood diseases in which normal blood clotting is disrupted - hemophilia, leukemia, a specific type of anemia - sickle cell form;
- Brain hematoma in newborns most often becomes a consequence of complicated childbirth and injuries during the woman’s birth canal.
This disease comes in three types: subdural, epidural and intracerebral, which is the accumulation of blood directly in the brain tissue. A subdural hematoma, which occurs when blood vessels (in most cases veins) rupture, is localized between the membranes of the brain and is considered a serious lesion, potentially life-threatening. Between the two layers of the meninges, most often between the hard and soft, a localized accumulation of blood is formed - this is manifested by a pronounced and progressive loss of consciousness.
Among the population, there are several risk groups that most often develop this type of disease - these are people who abuse aspirin, take anticoagulants for a long time, or drink alcohol in excess. It must be said that subdural hematoma of the brain is in most cases registered in very young patients and people who have already reached old age.
Epidural hematoma is often recorded in children and adolescents and is characterized by a high mortality rate if medical care is not provided in a timely manner. Often patients, although they remain conscious, are drowsy or in a comatose state. With this type of disease, the blood that accumulates between the skull and the dura mater of the brain strongly compresses the brain tissue, and therefore requires immediate treatment.
Intracerebral hematoma (intraparenchymal form) occurs when blood penetrates into the brain tissue and gradually soaks it. With this hematoma, the white matter is damaged, nerve connections are broken, namely, the neurites responsible for transmitting nerve impulses from the brain to the executive organs are affected, so nerve cells in different parts of the body are not able to interact - the integrity of the nervous regulation of all processes in the body is disrupted.