Irina Baranova
Cardiologist
Higher education:
Cardiologist
Kuban State Medical University (KubSMU, KubSMA, KubSMI) Level of education - Specialist 1993-1999
Additional education:
“Cardiology”, “Course on magnetic resonance imaging of the cardiovascular system”,
Research Institute of Cardiology named after. A.L. Myasnikova
"Course on functional diagnostics"
NTsSSKh them. A. N. Bakuleva
"Course in Clinical Pharmacology"
Russian Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education
"Emergency Cardiology"
Cantonal Hospital of Geneva, Geneva (Switzerland)
"Therapy course"
Russian State Medical Institute of Roszdrav
Contacts
Stroke is considered to be the most dangerous and severe damage to blood vessels and brain tissue for human life. Various parts of the central nervous system suffer, and disruptions in physical activity begin. All this occurs due to the lack of normal blood circulation in the brain, which in turn can be caused by hemorrhages or blockage of blood vessels. The patient’s relatives must be patient in order to help the person get through the critical days after a stroke as easily as possible.
Critical moments after a stroke
Any type of stroke is most often heterogeneous in terms of the nature of its course. At the same time, periods of slight relief may be replaced by a crisis state. It is these periods after a stroke that experts call critical. In the first 3-6 hours of an attack, a critical moment occurs when negative changes in the brain can still be reversible. This is when it is important to promptly recognize an attack and promptly consult a doctor.
It is worth noting that in any of the periods, a hemorrhagic stroke (caused by hemorrhage) will pose a serious danger to the patient’s life, while the ischemic form is slightly less dangerous. Hemorrhagic stroke is characterized by a sudden acute period characterized by high criticality. Occurs primarily during the daytime and is associated with hemorrhage.
The symptoms that appear in this case increase very sharply and there may be no precursors before this, unlike an ischemic stroke. A major stroke can cause an initial critical period. May be accompanied by loss of consciousness. Convulsions, vomiting, and uncontrollable urination may occur.
Transfer to the general ward
When transferred to a general ward of a hospital after a stroke, the patient must meet the following requirements:
- he does not need a ventilator;
- the person is conscious, he not only lies, but can move if there is no paralysis;
- the pulse is normal, and pressure drops do not occur;
- the risk of recurrent stroke is reduced.
Only if all indicators are normal does the person continue to lie in the general ward of the hospital, in the neurology department. This is where the rehabilitation period begins, which includes drug therapy and a set of therapeutic exercises.
After 3 weeks in the general ward, the patient is sent home for further outpatient treatment. If a person was working at the time of the attack, he is issued a certificate of incapacity for work. In this case, the length of sick leave depends on the type of pathology and disorders that arose against the background of a stroke.
After a minor stroke, the patient does not stay in the hospital for more than 21 days, and he can begin work only 3 months after discharge. If the hemorrhage was average, then the period increases to 4 months.
In severe forms of stroke, a disability is often assigned, and the person is released from his usual work. A medical and social examination must establish and assign a disability group. It should be noted that patients after a rupture of an aneurysm leading to a hemorrhagic stroke remain in intensive care for at least 60 days . After this, they receive sick leave for at least 4 months.
What happens at the initial critical moment?
When a cerebral artery ruptures, an extensive hematoma most often occurs. It begins to gradually increase and puts pressure on the brain. It can even cause sudden death. Only modern surgical treatment in the case of hemorrhagic stroke can significantly reduce the risk of death.
Accordingly, in the case of a hemorrhagic type of stroke, it is impossible to single out any individual days that can be considered the most critical. The most risky period may be the first few weeks from the moment cerebral symptoms appear. It is in the first 2 weeks that about 85% of deaths occur in patients who have suffered a cerebral hemorrhage.
Acute period
After the first 24 hours, when the patient must be admitted to the hospital, an acute period of stroke begins. In time, it lasts until the end of 3-4 weeks from the moment of cerebrovascular accident.
During this period, the patient must be under constant medical supervision. They monitor the dynamics of changes in the condition, normalize blood circulation and pressure, and conduct therapy that is aimed at relieving swelling of brain tissue. During the acute stage, the extent to which the body’s functions have been affected and the prospects for their recovery are assessed, and symptomatic treatment of the disorders is carried out.
It should be noted that during the acute period of a stroke, the likelihood of death decreases, but does not disappear completely. If on the first day it is almost 50%, then by 21 days it drops to 12%, which is still a fairly high figure.
Doctors also note that deterioration of the condition can occur at any time, often late in the evening or at night. This is the reason why the patient must be in the hospital.
Selected most critical time periods
Doctors have developed some statistics that have made it possible to determine certain periods of time that are most dangerous to the life of a patient who has suffered a stroke. The most dangerous period is the first two days after the onset of a cerebral catastrophe.
Also, the risk increases significantly on days 7-10 and 14-21 after the pathology has occurred. The percentage statistics for deaths are as follows:
- 1st day – 45.9%;
- 7th day – 24.5%
- 14th day – 17.3%
- 21st day – 12.2%.
That is why back in the 60-70s. The World Health Organization has identified a 21-day period as the most critical period for the life of a person who has suffered a stroke. After active recovery and properly prescribed therapy, the situation begins to improve and the person gets better.
Early recovery period
This stage of stroke lasts up to six months. Doctors continue drug treatment, but physiotherapy, physical therapy, and other rehabilitation measures are becoming increasingly important. If there is such a possibility, the patient undergoes rehabilitation in a specialized rehabilitation center or sanatorium.
At this time, the patient undergoes a course of physical therapy, works with a speech therapist, can undergo a course of physical therapy and exercise on rehabilitation simulators. The main thing you need to pay attention to at this time is the planned and systematic nature of your classes.
In recent years, biofeedback therapy, or biofeedback, has been actively used for the rehabilitation of patients after a stroke. It consists in the fact that the patient sees (on a monitor, on a computer screen, etc.) how the activity of parts of his brain changes. While doing the exercises, he can monitor the progress of his condition himself. For many stroke survivors, biofeedback therapy helps them quickly learn to regulate various functions and believe in the possibility of restoring the affected areas of the brain.
The development of ischemic pathology and critical days in this case
In a situation with ischemic stroke, critical moments often begin to occur less abruptly than with hemorrhages. The onset of the acute period can be characterized by the fact that symptoms increase gradually:
- Harbingers appear;
- Precursors turn into general disruptions in brain function;
- Disorders begin in the musculoskeletal system.
Such ailments can last quite a long time - from a couple of days to several weeks. With a stroke of this type, the critical periods of time will also differ, although the first day for the victim is still always the most dangerous.
Doctors consider the 3rd day, as well as the 7th and 10th days after the primary manifestations of the pathology to appear critical for ischemic stroke. According to statistics, ischemic stroke most affects older people and occurs most often at night or in the early morning.
Duration of sick leave
So, sick leave is issued only when the threat to life has passed, the person has left intensive care after a stroke and has undergone a course of treatment. There is no single standard for setting deadlines. It all depends on the disorder, the amount of skills lost and the recovery process:
- in case of micro-stroke and minor violations, sick leave is issued for 3 months;
- moderate stroke is treated for at least 3 months, it can be increased without commission to 4 months;
- with a severe stroke, rehabilitation is often required for 6-8 months, and the person is given temporary disability.
If during rehabilitation, while on sick leave, a repeated relapse occurs, then treatment is extended for 2.5 months.
The length of time a patient spends in the hospital after a stroke depends on many factors. It should be remembered that doctors do not have the right to discharge a patient earlier than 21 days after transfer to the intensive care unit from intensive care. If the hemorrhage is followed by a coma, things are more complicated, and the days are counted individually after the person leaves this state. Sick leave after a hemorrhage is issued for an average of 3 months with the possibility of extension.
The danger of a recurrent attack and how to behave
After primary ischemia has occurred, the risk of a second brain stroke increases significantly. In almost 70% of cases, relapses lead to death. And no matter how much time passes from the moment of the attack, it will not be possible to definitely get rid of the risk of relapse. The most dangerous in terms of the risk of relapse is the 1st year after the attack.
To reduce the risks during critical days and reduce the likelihood of relapse, it is necessary to develop the right behavior strategy. A brain stroke in any form always requires immediate hospitalization in a medical institution that has the necessary diagnostic and treatment equipment. Often, after an attack, it may be necessary to carry out competent resuscitation measures.
How to recognize a stroke?
A characteristic sign of a stroke is a complaint of weakness in the limbs. You need to ask the person to raise both hands up. If he really has a stroke, then one arm can rise well, but the other may either not rise, or the movement will be difficult.
With a stroke, facial asymmetry is observed. Ask a person to smile, and you will immediately notice an asymmetrical smile: one corner of the mouth will be lower than the other, and the smoothness of the nasolabial fold on one side will be noticeable.
Stroke is characterized by speech impairment. Sometimes it is obvious enough that there is no doubt about the presence of a stroke. To recognize less obvious speech disorders, ask the person to say, “Thirty-Thirty-third Artillery Brigade.” If he has a stroke, impaired articulation will become noticeable.
Even if all these signs appear in a mild form, do not expect that they will go away on their own. You need to call an ambulance using the universal number (both from a landline and a mobile phone) – 103.
Diagnostics
An in-depth diagnosis of ischemic stroke is carried out after the doctor has examined the patient and recorded general cerebral symptoms and neurological disorders characteristic of the disease: paralysis of one half of the body, loss of vision, loss of sensitivity.
Their presence already indicates a diagnosis, but a full diagnosis is needed to confirm it and determine the nature of the pathology. The following are used in the diagnosis of ischemic stroke:
| Type of diagnosis | Description |
| Blood analysis | Look for signs of blood thickening. |
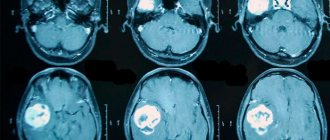
| Magnetic resonance imaging | Detection of damage in the brain, as well as determination of the size and location of the affected area. |
| Ultrasound diagnostics of extracranial arteries | Examination of the arteries outside the skull that supply blood to the brain for patency. |
| Transcranial Dopplerography | Examination of the arteries in the skull that provide blood supply to the brain for patency. |
| Magnetic resonance angiography | Another method for studying the patency of arteries in the cranium. |
| Electrocardiogram | Search for heart rhythm disturbances. |
| Ultrasound diagnostics of the heart | Search for blood clots in the cavities of the heart. |
If an ischemic stroke is suspected, not all diagnostic methods are used, but some of them. The necessary ones are selected by a doctor who, after a preliminary examination of the patient, determines a diagnosis that will reveal all the nuances of the disease.
Features of female stroke
There are two main types of stroke:
- Ischemic. Leads to contraction of blood vessels in the head, which clogs their walls, causing hypoxia.
- Hemorrhagic. The process of bleeding into the brain, often fatal.
According to statistics, the ratio between the two species is 80% to 20% (Consilium Medicum No. 02 2000).
Ischemic stroke can develop at any age - in children, adolescents, middle-aged people and the elderly. The severity of the consequences is also individual, depending on the speed of decision-making after the attack, the correct diagnosis, and the prescribed treatment.
Hemorrhagic stroke can happen to a person of any age. It occurs suddenly and is accompanied by a serious condition of the patient, constant gag reflexes and severe headache. At the first signs, a person often loses consciousness.
Causes:
- sudden movements, change of position;
- food with a lot of fat and other harmful ingredients;
- bad habits - smoking, alcohol addiction, drug addiction;
- high water temperature during water procedures or outdoors;
- excessive physical or psychological load on the human body;
- cardiac arrhythmia;
- blood pressure problems.
Information about stroke - clickable
When the first symptoms of a stroke appear, you should be careful and prompt; minutes count. On average, 3-4 hours after the first signs appear, the condition of the blood vessels in the brain deteriorates, and the consequences may become irreversible. The first 3-4 hours are the most important in the fight against the disease.
If the signs and pain go away within 24 hours, the person most likely had a mini-stroke.
Symptoms of left-sided and right-sided strokes differ
Algorithm of actions when symptoms appear:
- Place the patient on a horizontal surface, holding his head at an angle of 30 degrees.
- If the victim feels sharp gag reflexes, you need to turn his head to the side.
- You should carefully monitor changes in blood pressure and pulse. It is recommended to measure them and monitor fluctuations.
- When emergency doctors appear, you should fully describe the picture of what happened. Tell what actions were taken before the doctors arrived.
Women are more susceptible to stroke, take longer to recover and are more likely to die from its consequences.
- smoking;
- use of hormonal contraceptives (especially over the age of 30);
— hormone replacement therapy for menopausal disorders.
Atypical signs of female stroke:
- an attack of severe pain in one of the limbs;
- sudden attack of hiccups;
- an attack of severe nausea or abdominal pain;
- sudden fatigue;
- short-term loss of consciousness;
- sharp chest pain;
- attack of suffocation;
- suddenly increased heart rate;
- insomnia (insomnia).
Causes of ischemic stroke
Most cases of ischemic stroke develop due to arterial problems. There are statistics according to which nine out of ten cases of the disease are provoked by atherosclerosis - a chronic disease of the arteries, due to which cholesterol is deposited in the lumen of blood vessels, causing them to block. The causes that contribute to the development of the disease are divided into uncontrollable and controllable.
The first group of them is given or not given to a person from birth. He cannot influence their presence. This also includes reasons that are caused by a random factor. Uncontrolled causes of ischemic stroke include:
- floor. It is reliably known that men aged 30-80 years have a higher risk of developing the disease than women. Outside this age range (before thirty and after eighty years), the ratio changes. The risk is higher in women;
- age. The older a person is, the higher the risk of developing ischemic stroke. According to statistics, at the age of 20 the risk level is 1 in 3000, and at the age of 84 years – 1 in 45;
- hereditary factor. The presence of ischemic stroke in parents increases the risk of its development in children;
- stressful situations. This point, in theory, can be attributed to controllable causes, but more often it is completely impossible to exclude them from life.
Controllable causes of ischemic stroke are those causes whose occurrence directly or indirectly depends on the person. These include diseases and bad habits:
- atherosclerosis,
- arterial hypertension,
- diabetes,
- osteochondrosis of the cervical skeleton,
- smoking,
- alcohol abuse,
- problems with excess weight,
- insufficient mobility (hypodynamia).
All of the controllable causes affect the circulatory system in one way or another:
- impair the elasticity of blood vessels;
- provoke blockage;
- impair blood circulation.
Symptoms
The manifestations of an ischemic stroke depend on which blood flow problems develop in which vessel and, accordingly, which part of the brain experiences problems with blood supply.
| Vessels with impaired blood supply | Symptoms |
| Internal carotid artery | Paralysis of one limb or one half of the body, absence or impairment of speech. |
| Anterior villous artery | Decreased strength in one side of the body, loss of sensation on one side of the body, problems with speech, bilateral blindness in one side of the body. |
| Anterior cerebral artery | Paralysis of the leg on the side opposite to the lesion, loss of the ability to walk, lack of will, urinary incontinence. |
| Middle cerebral artery | Problems with speech, disturbance of purposeful actions and movements, disturbance of perception. |
| Posterior cerebral artery | Memory loss, speech problems, decreased strength in one side of the body, lack of coordination in muscle function. |
| Basilar and vertebral arteries | Lack of coordination in muscle function, paralysis of one limb, loss of sensation in one half of the body, paralysis of the eye muscles, damage to the facial nerve. |
Principles of treatment
Future prospects depend on the early start of stroke treatment. With regard to stroke (as with most diseases), there is a so-called “therapeutic window” when the treatment measures are most effective. It lasts 2-4 hours, then the part of the brain dies, unfortunately, completely.
The treatment system for patients with cerebral stroke includes three stages: prehospital, inpatient and recovery.
At the prehospital stage, a stroke is diagnosed and the patient is urgently transported by an ambulance to a specialized facility for inpatient treatment. At the stage of inpatient treatment, stroke therapy can begin in the intensive care unit, where emergency measures are carried out aimed at maintaining the vital functions of the body (cardiac and respiratory activity) and at preventing possible complications.
Consideration of the recovery period deserves special attention, because its provision and implementation often falls on the shoulders of the patient’s relatives. Since strokes occupy the first place in the structure of disability among neurological patients, and there is a tendency towards “rejuvenation” of this disease, each person should be familiar with the rehabilitation program after a cerebral stroke in order to help his relative adapt to his new life and restore self-care.
Dependence on the location of the lesion
- A favorable prognosis awaits patients who have unilateral lesions from the primary lesion. They can recover faster and have all the prerequisites for returning to work.
- If there is bilateral localization, then favorable and unfavorable prognoses correlate 50 to 50. This may be due to a combination of locations of the affected areas of the brain.
- When the primary focus is on the pons of the brain, then, unfortunately, negative dynamics are observed here during recovery and treatment.
We can conclude that the smaller the volume of brain damage, the more favorable the prognosis for recovery will be.