Organic damage to the central nervous system is a pathology that consists of the death of neurons in the brain or spinal cord, necrosis of tissues of the central nervous system or their progressive degradation, due to which the human central nervous system becomes defective and cannot adequately perform its functions in ensuring the functioning of the body , motor activity of the body, as well as mental activity.
Organic damage to the central nervous system has another name - encephalopathy. This may be a congenital or acquired disease due to a negative effect on the nervous system.
Acquired can develop in people of any age due to various injuries, poisoning, alcohol or drug addiction, past infectious diseases, radiation and similar factors.
Congenital or residual - damage to the organs of the central nervous system of the child, inherited due to genetic failures, disturbances in fetal development during the perinatal period (the period of time between the one hundred and fifty-fourth day of pregnancy and the seventh day of extrauterine existence), as well as due to birth injuries.
Classification
The classification of lesions depends on the cause of the development of the pathology:
- Discirculatory – caused by a violation of the blood supply.
- Ischemic – discirculatory organic lesion, supplemented by destructive processes in specific foci.
- Toxic – cell death due to toxins (poisons).
- Radiation – radiation damage.
- Perinatal-hypoxic – due to fetal hypoxia.
- Mixed type.
- Residual – resulting from a violation of intrauterine development or birth injuries.
Causes of acquired organic brain damage
It is not at all difficult to acquire damage to cells of the spinal cord or brain, since they are very sensitive to any negative impact, but most often it develops for the following reasons:
- Spinal injuries or traumatic brain injuries.
- Toxic damage, including alcohol, medications, drugs and psychotropic drugs.
- Vascular diseases that cause circulatory disorders, and with it hypoxia or lack of nutrients or tissue injury, for example, stroke.
- Infectious diseases.
You can understand the reason for the development of one or another type of organic lesion based on the name of its variety; as mentioned above, the classification of this disease is based on the reasons.
How and why residual damage to the central nervous system occurs in children
Residual organic damage to the central nervous system in a child occurs due to a negative impact on the development of his nervous system, or due to hereditary genetic abnormalities or birth injuries.
The mechanisms for the development of hereditary residual organic damage are exactly the same as for any hereditary diseases, when distortion of hereditary information due to DNA damage leads to improper development of the child’s nervous system or the structures that ensure its vital functions.
An intermediate process to a non-hereditary pathology looks like a failure in the formation of cells or even entire organs of the spinal cord and brain due to negative environmental influences:
- Serious illnesses suffered by the mother during pregnancy, as well as viral infections. Even the flu or a simple cold can provoke the development of residual organic damage to the fetal central nervous system.
- Lack of nutrients, minerals and vitamins.
- Toxic effects, including medicinal ones.
- Bad habits of the mother, especially smoking, alcoholism and drugs.
- Bad ecology.
- Irradiation.
- Fetal hypoxia.
- Physical immaturity of the mother, or, conversely, the advanced age of the parents.
- Consumption of special sports nutrition or certain dietary supplements.
- Severe stress.
The mechanism of the influence of stress on premature birth or miscarriage through convulsive contraction of its walls is clear; not many understand how maternal stress leads to the death of the fetus or disruption of its development.
With severe or systematic stress, the mother’s nervous system suffers, which is responsible for all processes in her body, including the life support of the fetus. With the disruption of its activity, a variety of malfunctions and the development of vegetative syndromes can occur - dysfunctions of internal organs, which destroys the balance in the body that ensures the development and survival of the fetus.
Traumatic injuries of various types during childbirth, which can cause organic damage to the child’s central nervous system, are also very different:
- Asphyxia.
- Injury to the spine or base of the skull due to improper removal and twisting of the child from the uterus.
- Child falling.
- Premature birth.
- Uterine atony (the uterus is unable to contract normally and push out the baby).
- Compression of the head.
- Entry of amniotic fluid into the respiratory tract.
Even during the perinatal period, a child can become infected with various infections, both from the mother during childbirth and from hospital strains.
Overview of the pathological process
Organic damage to the central nervous system does not have a code according to ICD -10. Practitioners use a generalized concept using the G96.9 label. In the case of diagnosing certain psychiatric disorders (with damage to the central nervous system), a type of code for psychiatric diseases is used.
Organic damage to the nervous system in the medical literature is otherwise called encephalopathy or residual organic damage (ROD) of the central nervous system. It can occur both in childhood and in adults (most often after 65 years).
In a child, the disease often manifests itself in the form of cerebral palsy. Organic damage to the central nervous system can cause speech, mental and epilepsy disorders in adults.
The diagnosis of CNS ROP in childhood is especially dangerous, since it means irreversible death of the cellular structures of the brain or spinal cord.
Symptoms
Any damage to the central nervous system has symptoms in the form of disturbances in mental activity, reflexes, motor activity and disruption of the functioning of internal organs and sensory organs.
It is quite difficult even for a professional to immediately see the symptoms of residual organic damage to the central nervous system in an infant, since the movements of infants are specific, mental activity is not immediately determined, and disturbances in the functioning of internal organs with the naked eye can only be noticed with severe pathologies. But sometimes clinical manifestations can be noticed from the first days of life:
- Violation of muscle tone.
- Tremor of the limbs and head (most often tremor in newborns is benign, but can also be a symptom of neurological diseases).
- Paralysis.
- Impaired reflexes.
- Chaotic rapid eye movements back and forth or frozen gaze.
- Impaired functions of the sense organs.
- Epileptic seizures.
At an older age, from about three months, you can notice the following symptoms:
- Impaired mental activity: the child does not follow the toys, shows hyperactivity or, on the contrary, apathy, suffers from attention deficit, does not recognize acquaintances, etc.
- Delayed physical development, both direct growth and acquisition of skills: does not hold his head up, does not crawl, does not coordinate movements, does not try to stand up.
- Rapid physical and mental fatigue.
- Emotional instability, moodiness.
- Psychopathy (tendency to affect, aggression, disinhibition, inappropriate reactions).
- Organic-psychic infantilism, expressed in the suppression of personality, the formation of dependencies and increased reporting.
- Loss of coordination.
- Memory impairment.
Complications, consequences and prognosis
According to the experience of doctors, organic damage to the central nervous system in children can cause the following consequences:
- mental development disorders;
- speech defects;
- delayed speech development;
- lack of self-control;
- hysterical attacks;
- disruption of the normal development of the brain;
- post-traumatic stress disorder;
- epilepsy attacks;
- vegetative-visceral syndrome;
- neurotic disorders;
- neurasthenia.
In children, quite often such disorders affect adaptation to environmental conditions, manifestations of hyperactivity or, on the contrary, chronic fatigue syndrome.
Today, the diagnosis of “residual organic damage to the central nervous system” is made quite often. For this reason, doctors are trying to improve their diagnostic and treatment abilities.
The exact characteristics and features of a certain type of lesion make it possible to calculate the further development of the disease and prevent it. In the best case, suspicion of the disease can be completely removed.
If a child is suspected of having a central nervous system lesion
If any symptoms of a disorder of the central nervous system appear in a child, it is necessary to immediately contact a neurologist and undergo a comprehensive examination, which may include the following procedures:
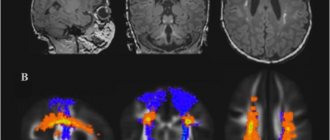
- General tests, various types of tomography (each type of tomography examines from its own side and therefore gives different results).
- Ultrasound of the fontanel.
- EEG is an electroencephalogram that allows you to identify foci of pathological brain activity.
- X-ray.
- CSF analysis.
- Neurosonography is an analysis of neuron conductivity that helps identify minor hemorrhages or disturbances in the functioning of peripheral nerves.
If you suspect any abnormalities in your child’s health, you should consult a doctor as early as possible, since timely treatment will help avoid a huge number of problems, and will also significantly shorten the recovery time. You should not be afraid of false suspicions and unnecessary examinations, since, unlike probable pathologies, they will not harm the baby.
Sometimes this pathology is diagnosed during fetal development during a routine ultrasound examination.
Perinatal brain damage: treatment in Saratov, treatment in Russia
Sarclinic treats perinatal brain damage in children on an outpatient basis. Treatment is carried out in courses. The number of courses depends on the severity of perinatal damage to the nervous system. Sarklinik knows how to treat perinatal damage, how to cure perinatal damage, how to get rid of it and what to do if a child has perinatal damage to the central nervous system and brain. Do not expect the development of such serious complications as cerebral palsy (cerebral palsy), MMD (minimal cerebral dysfunction), tone disorder syndrome, general speech underdevelopment, movement disorder syndrome, mental retardation, imbecility, debility, alalia, dyslalia, intracranial hypertension syndrome, mental retardation, PVRD, PVMR, delayed motor development, delayed mental development, delayed speech development, delayed psychomotor, psychospeech development, asthenic syndrome, hydrocephalus, psychopathic syndrome, encephalopathy, convulsive syndrome, epilepsy, hypertension syndrome. At the first consultation, the doctor will tell you what the symptoms of perinatal damage to the central nervous system (CNS) are in newborns , children, boys, girls at 2, 3, 4 months, at 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 months, at 1 year, 2 years, 3 years of life, 4 years, at 5, 6, 7, 8 years, what medical services are provided. Perinatal damage to the brain and central nervous system must be treated as early as possible! The child’s nervous system is flexible, and with timely comprehensive treatment, excellent positive results are observed.
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications, consultation with a specialist is required.
Text: ® SARCLINIC | Sarclinic.com \ Sarlinic.ru Photo: (©) Genika | Dreamstime.com \ Dreamstock.ru The child depicted in the photo is a model, does not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Why does a child twitch strongly: legs, arms, eyes, body
The child stutters, began to stutter, began to stutter, what to do
Early childhood autism, treatment of children, signs, symptoms, causes and development
Apgar scale, assessment of the newborn on the Apgar scale, points
Fecal incontinence: treatment in Saratov, how to cure fecal incontinence in children in Russia
Comments ()
Methods of treatment and rehabilitation
Treatment of the disease is quite labor-intensive and lengthy, however, with minor damage and proper therapy, congenital residual organic damage to the central nervous system in newborns can be completely eliminated, since the nerve cells of infants are able to divide for some time, and the entire nervous system of young children is very flexible.
- First of all, this pathology requires constant monitoring by a neurologist and the attentive attitude of the parents themselves.
- If necessary, drug therapy is carried out both to eliminate the root cause of the disease, and in the form of symptomatic treatment: relieving convulsive symptoms, nervous excitability, etc.
- At the same time, as a method of treatment or recovery, physiotherapeutic treatment is carried out, which includes massage, acupuncture, zootherapy, swimming, gymnastics, reflexology or other methods designed to stimulate the nervous system, encourage it to begin recovery by forming new neural connections and teach the child himself to use his body in case of impaired motor activity in order to minimize its inability to live independently.
- At a later age, psychotherapeutic influences are used both on the child himself and on his immediate environment in order to improve the moral environment around the child and prevent the development of mental disorders in him.
- Speech correction.
- Specialized training tailored to the individual characteristics of the child.
Conservative treatment is carried out in a hospital and consists of taking medications in the form of injections.
These medications reduce brain swelling, reduce seizure activity, and improve blood circulation. Almost everyone is prescribed piracetam or drugs with a similar effect: pantogam, caviton or phenotropil. In addition to the main medications, symptomatic relief of the condition is provided with the help of sedatives, painkillers, improve digestion, stabilize the heart and reduce any other negative manifestations of the disease.
After eliminating the cause of the disease, therapy for its consequences is carried out, designed to restore brain function, and with them the work of internal organs and motor activity. If it is impossible to completely eliminate residual manifestations, the goal of restorative therapy is to teach the patient to live with his body, use his limbs and self-care as independently as possible.
Many parents underestimate the benefits of physiotherapeutic methods in the treatment of neurological ailments, but they are the fundamental methods for restoring lost or impaired functions.
The recovery period is extremely long, and ideally lasts a lifetime, since when the nervous system is damaged, the patient has to overcome himself every day. With due diligence and patience, by a certain age a child with encephalopathy can become completely independent and even lead an active lifestyle, the maximum possible at the level of his damage.
It is impossible to cure the pathology on your own, and mistakes made due to a lack of medical education can not only aggravate the situation, but even lead to death. Cooperation with a neurologist for people with encephalopathy becomes lifelong, but no one prohibits the use of traditional methods of therapy.
Traditional methods of treating organic damage to the central nervous system are the most effective methods of recovery, which do not replace conservative treatment with physiotherapy, but complement it very well. Only when choosing one method or another is it necessary to consult a doctor, since it is extremely difficult to distinguish useful and effective methods from useless and harmful ones without deep specialized medical knowledge, as well as minimal chemical literacy.
If it is impossible to visit specialized institutions to undergo a course of exercise therapy, massage and aquatherapy, they can be easily carried out at home, having mastered simple techniques with the help of a consultation with a neurologist.
An equally important aspect of treatment is social rehabilitation with psychological adaptation of the patient. You should not overprotect a sick child, helping him in everything, because otherwise he will not be able to fully develop, and as a result, will not be able to fight pathology. Help is needed only for vital things or special cases. In everyday life, independently performing everyday duties will work as additional physiotherapy or exercise therapy, and will also teach the child to overcome difficulties and that patience and perseverance always lead to excellent results.
Perinatal pathology of the central nervous system
Home → Information about diseases → Perinatal pathology of the central nervous system
Perinatal damage to the nervous system is precisely this diagnosis that is increasingly being made to newborn babies. Behind these words lies a fairly large group of various lesions of the brain and spinal cord that occur during pregnancy and birth of a baby, as well as in the first days of his life. What it is? Children under 1 year of age are often diagnosed with PEP (perinatal encephalopathy), which is “incomprehensible” to parents. An abbreviation such as PPP CNS is also possible ( consequences of perinatal pathology of the central nervous system - most often established after 1 year).
This does not change the essence: the child’s brain was damaged in the perinatal period (in utero, during childbirth, or immediately after birth). The damaging factors are different: from intrauterine hypoxia (lack of oxygen to the fetal brain), prematurity, toxicosis in the mother, birth injuries during rapid and prolonged labor, ending with prolonged jaundice of newborns, etc.
All possible manifestations of the central nervous system can be divided into 2 groups:
- HHS (hypertension-hydrocephalic syndrome) Manifestations of hydrocephalus that parents may notice: dilated veins on the forehead and temples, tense or pulsating fontanel, throwing the head back in sleep, profuse regurgitation, causeless crying, head hot and wet, holding hands in fists, leaning on socks when trying to put them on their feet. Unfortunately, hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome is often asymptomatic, so even if there are 1 or 2 symptoms, it is necessary to consult a specialist. To avoid complications of hydrocephalus in the future.
- Muscular dystonia syndrome: muscle tone is increased in the upper and lower extremities, the child holds his hands in fists, does not reach for objects, does not take them, when trying to put him on his feet, he leans on his toes, takes steps with a cross
Having noticed these manifestations, you should not engage in self-diagnosis. Only a neurologist can confirm the diagnosis of central nervous system and hydrocephalus after examining the child. If necessary, the doctor prescribes additional examination methods (NSG, electropuncture diagnostics).
The situation is much more serious when, in addition to the indicated manifestations and the conclusion of examinations about detected hydrocephalus, the child lags behind his peers in motor development, because later, without treatment, the diagnosis may turn out to be much worse - cerebral palsy.
NORMAL development of a child up to one year: 2 months - begins to hold his head in an upright position, opens his fists. 3 months - leans on his hands, lying on his stomach, sometimes reaches for a toy, begins to roll over, holds the toy placed in his hand and pulls it into his mouth. 4 months - reaches for a toy and grabs it, when trying to put it down, it rests well on its legs, turns over on its side. 5 months - makes attempts to sit down, sits with support. 6 months - sits independently, tries to stand up in the playpen, pulling himself up with his arms. 7 months - sits up on his side independently, begins to crawl, actively manipulates objects. 8 months - gets on all fours, sits from any position, knocks toy against toy. 9 months - moves independently on all fours, tries to place cube on cube. 10 months – stands up independently and stands against a support, picks up small objects with his fingers. 11 months - walks with support, stands independently, tries to string rings onto a pyramid. 12 months - walks independently, can turn pages of a cardboard book.
That is why it is necessary to identify and treat hydrocephalus as early as possible. But what combination of treatment methods is necessary to restore the baby’s health (drug therapy, massage, MICROCURRENT REFLEXOTHERAPY, etc.) should be decided by parents together with a neurologist-reflexotherapist. Seek expert advice without delay.
Parents remember that only healthy children can be vaccinated! That is why it is necessary to promptly identify and treat hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome and delayed motor development in order to avoid its exacerbation after routine vaccinations. The most terrible complications of hydrocephalus: cerebral palsy, convulsions, debility. At the time of vaccination, the diagnosis should not only be “removed”, the child should not have signs of hydrocephalus and the baby’s motor development should also be normal.
IT IS IMPORTANT TO START TREATMENT OF HHS (hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome, CNS) IN A TIMELY manner
You can get more detailed information by calling 8-800-22-22-602 (calls within RUSSIA are free) Microcurrent reflexology for the treatment of the central nervous system and hysterical system is carried out only in the divisions of the Reatsentr in the cities: Samara, Kazan, Volgograd, Orenburg, Tolyatti, Saratov, Naberezhnye Chelny, Izhevsk, Ufa, Astrakhan, St. Petersburg, Kemerovo, Kaliningrad, Barnaul, Chelyabinsk, Voronezh, Krasnodar, Almaty, Nursultan, Shimkent, Tashkent, Fergana.
OUR DIVISIONS
Select city:
- Samara - Ward No. 1
- Samara - Ward No. 2
- Samara-Pensionat
- Kazan
- Volgograd
- Naberezhnye Chelny
- Kemerovo
- Boarding house in Astrakhan
- Kaliningrad
- Barnaul
- Chelyabinsk
- Tashkent
Consequences
Organic damage to parts of the central nervous system in the perinatal period or at an older age leads to the development of a large number of various neurological syndromes:
- Hypertension-hydrocephalic – hydrocephalus, accompanied by increased intracranial pressure. It is determined in infants by the enlargement of the fontanel, its swelling or pulsation.
- Hyperexcitability syndrome - increased muscle tone, sleep disturbance, increased activity, frequent crying, high convulsive readiness or epilepsy.
- Epilepsy is a convulsive syndrome.
- Comatose syndrome with opposite symptoms of hyperexcitability, when the child is lethargic, apathetic, moves little, lacks sucking, swallowing or other reflexes.
- Autonomic-visceral dysfunction of internal organs, which can be expressed as frequent regurgitation, digestive disorders, skin manifestations and many other abnormalities.
- Motor disorders.
- Cerebral palsy is a movement disorder complicated by other defects, including mental retardation and weakness of the sensory organs.
- Hyperactivity is an inability to concentrate and lack of attention.
- Retardation in mental or physical development, or complex.
- Mental illness due to brain disorders.
- Psychological illnesses due to the patient’s discomfort among society or physical disability.
- Endocrine disorders, and as a result, decreased immunity.