If you take a medical reference book and try to find information in it about what organic brain damage is, it is unlikely that you will be able to do this. This is due to the fact that such a diagnosis is a group of diseases accompanied by impairments of intelligence, thinking and intelligence; in some cases, there is a change in physical activity.
In other words, we can say that organic brain damage is a pathological condition of the central nervous system in which the brain does not function fully. Symptoms in adults and children depend on the degree of damage.
Causes of the disorder
Unfortunately, today organic brain damage is often diagnosed in newborns. Such disorders are a sign of hypoxia, intrauterine infection, head and neck injuries received during labor.
The disease can also develop in older children and adults due to previous infectious diseases, vascular pathology and other various reasons.
Infectious lesions
Organic brain disease is largely caused by infectious lesions. The earlier it was diagnosed and treatment started, the greater the chances of returning to a full life. Late detection of infection is fraught with irreversible consequences.
The main types of infections that can provoke organic disease include:
- Coxsackie viruses;
- Herpes that affects the central nervous system;
- Staphylococcus;
- Echoviruses.
Also, the cause of the anomaly is HIV infection in advanced stages. In all of the above cases, intoxication of the body occurs rapidly. Therefore, at the first symptoms of an infectious lesion, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor and conduct a quality diagnosis.
Vascular pathologies
Changes in the structure of the brain can occur due to vasoconstriction. Against this background, the brain is poorly supplied with blood, which causes the development of coronary artery disease, hemorrhagic stroke or DEP.
The main signs by which a headache can be identified include:
- Severe pain in the head, which is difficult to reduce or does not go away at all after taking a painkiller;
- General weakness and dizziness;
- Nausea;
- The appearance of sleep disorders - difficulty falling asleep and waking up, insomnia, which is accompanied for a long time;
- General nervousness, irritability and depression;
- Numbness of the limbs;
- Speech impairment – it becomes slurred and inhibited, problems may also arise when swallowing and chewing food;
- Blood pressure surges.
In severe stages of the disease, fainting and short-term memory loss may occur. If the above symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance.
Demyelinating diseases
Another type of organic brain disorder, which is a consequence of the following types of disease:
- Strokes within cerebral hemorrhages;
- Multiple sclerosis;
- Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.
The consequences of the above diseases are severe fatigue, weakness, decreased performance, impaired memory and intelligence.
Poisoning
Brain pathology sometimes results from severe poisoning of the body with the following substances:
- Alcoholic drinks;
- Narcotic substances;
- Potent drugs;
- Heavy metals or combustion products of polyvinyl chloride.
The first signs of poisoning of the body may be dizziness, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, pain in the head, low blood pressure or chills.
Some signs of psychiatry may also appear, for example, nervousness or clouding of consciousness; the person begins to seem lost in space and has poor control over his actions.
Brain injuries
Brain damage can result from severe trauma. As a rule, it can occur in the perinatal period or during childbirth, in which case the baby is born with a congenital pathology.
Organic damage can also cause:
- Concussion;
- Severe head injury;
- Fractures of the bones that make up the skull;
- Compression of the brain;
- Intracranial hemorrhage.
It is worth considering that pathology is formed not only in the place where the blow occurred. After physical exposure, the overall functioning of the brain may be disrupted.
Place of pathology in the ICD
Each disease, regardless of which organ is malfunctioning, has a specific code in medicine. Otherwise, it is called the stake of the International Classification of Diseases. Damage to the brain or central nervous system is indicated by ICD 10 code.
However, disorders of an organic nature do not exist in this classification; there are only concomitant or previous diseases. It is for this reason that many doctors classify this type of pathology as mysterious or unspecified.
Definition of OPCNS
Organic damage to the central nervous system, abbreviated as OPCNS, is a dysfunction of the brain of a permanent, persistent nature. It can appear in absolutely anyone at different stages of life - during pregnancy, during childbirth, in childhood, adulthood or old age.
It is always based on morphological changes in the central nervous system. This disease is divided into two large groups, each of which has its own characteristic features:
Functional disorders
The peculiarity of this pathology is that when a person undergoes an ultrasound (for children under one year old), an MRI of the brain or an ultrasound of the vessels and neck, no pathological changes are detected during diagnosis. But, at the same time, a person feels ailments and some disruptions in the functioning of the body.
The main manifestations of functional disorders include;
- Veto-vascular dystonia;
- Panic attacks;
- The emergence of communication problems;
- Constant headaches and migraines;
- Nausea and vomiting.
In most cases, the cause of this pathological process is a sharp change in vascular tone. However, brain functions are not impaired.
Organic pathology
This type of disease is the most serious and its consequences can be irreversible. Such permanent changes can result from:
- Perinatal damage;
- Birth injury;
- An inflammatory process on the membranes of brain structures or in the brain itself.
Changes are always visible on MRI, even if quite a lot of time has passed since the lesion.
The consequences of this type of OPCNS include decreased intelligence, impaired physical activity, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, obesity and other types of diseases.
Types of organic lesions
Today, many types of organic brain damage are known, these include the following types of pathologies and diseases:
- Ischemia and intracerebral hemorrhage;
- Spinal stroke;
- Parkinsonism syndrome;
- Meningitis;
- Polio;
- Herpetic lesion of the nervous system;
- Tumors;
- Injuries and bruises;
- Toxic damage to the body.
At the same time, it is worth noting that all true diseases of the nervous system of an unspecified nature have nothing to do with organic damage, even if they have fairly severe symptoms and an aggressive onset.
What cannot cause OPCNSL
The cause of organic damage can never be those types of diseases that are characteristic of the peripheral nervous system. These today include osteochondrosis with radicular symptoms or compression-ischemic neuropathies.
The most common form of dementia
Among the causes leading to the development of dementia, Alzheimer's disease ranks first. The first mention of it dates back to 1906, and its discoverer is considered to be the German psychiatrist Alois Alzheimer.
The disease begins to manifest itself at the age of 55–70 years. This is one of the forms of senile insanity and refers to the atrophic type of dementia, when the destruction of brain neurons occurs. There may be several reasons contributing to this disease: internal diseases, obesity, low intellectual and physical activity, diabetes. A special place is given to the hereditary factor.
The disease begins to manifest itself with a violation of short-term memory. First, the patient forgets events that happened to him recently, and then those that happened a long time ago. A person does not recognize his children, mistaking them for deceased loved ones. He has difficulty remembering what he did a few hours ago, but talks in detail about what happened to him as a child. At this stage of the disease, the patient develops egocentrism and delusional ideas. Speech, perception, and motor disorders are observed.
The next stage is characterized by emotional disruptions. The person becomes irritable, grumpy, and shows dissatisfaction for any reason. He claims that his relatives want to get rid of him in order to take possession of his property, and his neighbors and friends want to slander him in order to spoil his reputation.
Intelligence decreases sharply: analytical functions suffer, reasoning becomes poor. Interests are narrowed, the opportunity to perform professional skills is lost.
Such people need care and supervision. Behavior disorder is manifested by vagrancy, uncontrollability in eating and sexual intercourse. Aimless actions appear, speech contains constant repetition of one word or phrase, and replacement of words with new ones. But, despite extensive degenerative changes, self-criticism remains.
At the final stage, the patient loses cognitive functions, the ability to care for himself, does not understand what they want from him, self-control and criticality are lost. Motor restrictions, paralysis, pathological reflexes, and convulsive seizures occur. The patient assumes the fetal position, refuses to eat, and cachexia progresses.
The disease lasts on average 10 years. But the earlier it manifests itself, the faster and more severe it progresses.
Unfortunately, at the moment there is no treatment that could stop the progression of the disease and return the patient to his former life. But early signs in menopausal women can be stopped with hormonal therapy.
Scientists have found that Alzheimer's in the early stages can be recognized by the nature of laughter. The fact is that in this case a person gradually loses control and does not understand what to laugh at and where it is inappropriate. He increasingly turns to black humor, laughs at absolutely unfunny, offensive, and sometimes tragic events, and at the failures of other people. Thus, one patient laughed at his wife when she was scalded by boiling water.
It is believed that a change in the sense of humor is an important criterion in establishing a diagnosis, since its diagnosis is, in principle, difficult.
Alzheimer's disease is a very common disorder. For example, Peter Falk, better known as Lieutenant Colombo, was also smitten by him. After he found out about this, he immediately stopped all his filming. Lately, the actor has completely forgotten about the existence of Columbo and wonders why people on the street call him by that name.
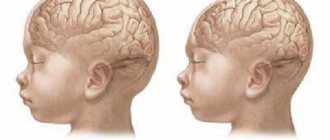
Organic brain damage in children
Organic brain damage in children most often occurs during fetal development or during birth. It is believed that premature babies are mainly susceptible to this pathology. However, as statistics show, it also appears in those children who were born on time.
The main reasons that could lead to such consequences include:
- Fetal hypoxia, popularly called oxygen starvation, begins when blood begins to circulate poorly in the baby’s brain;
- Bad habits of the mother during pregnancy, such as smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages or taking drugs;
- Poor diet that is not enriched with microelements and nutrients;
- Identified chronic or acute diseases, this can also include intrauterine infection;
- Injuries during childbirth.
It is worth noting that very premature babies suffer more often. By the time they are born, the brain is underdeveloped, so any external influence causes a negative reaction in it.
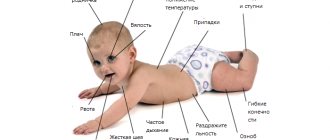
It is possible to detect that an organic lesion has occurred in a child almost immediately, even in infancy. The following characteristic signs will indicate this:
- Lack of crying after childbirth;
- A very sluggish sucking reflex, often the baby is not able to feed on his own, so a special probe is used for this purpose;
- Sleep disturbance - the baby may constantly wake up or, conversely, sleep for a very long time and almost continuously;
- Throwing back the head or arching the whole body;
- Very frequent regurgitation;
- Tremor of the chin and limbs can appear at any time, both during wakefulness and sleep;
- Muscle hypotonicity or hypertonicity, and, unlike healthy children, it is difficult to remove it with the help of several courses of massage;
- Decreased activity.
Only diagnostic measures, such as ultrasound of the brain and MRI, will help determine exactly whether there is an organic lesion or not. An EEG is often performed as an additional diagnosis in children; this examination allows one to determine epileptic activity and check how neural communication works.
It is important to start treatment of the pathology in a timely manner. If this is not done on time, there is a great risk that this disorder will progress more and more, affecting brain cells. As for the consequences, in the future organic damage may manifest itself in the form of:
- Distracted attention and impaired concentration;
- Retardation;
- Delayed physical and psycho-speech development;
- Tearfulness and restlessness;
- Obsessive fears;
- Decreased memory and mental intelligence.
More complicated consequences of the pathology are also possible - cerebral palsy, epilepsy and neuropathy. Fortunately, there are cases when a child lives a full life, is physically well developed and thinks adequately.
It is worth highlighting separately that this is an organic lesion of a residual nature. This pathology can develop in young children who were initially healthy. The cause may be head trauma at an early age.
Clinical signs
The main signs that indicate that a child or adult has had organic brain damage include:
- Very weak distracted attention, he has difficulty concentrating on one thing;
- Apathy - as a rule, there is no interest in anything;
- Problems with speech, it becomes slurred and inhibited, and some problems also appear with its understanding.
The table shows which clinical signs may differ depending on which area of the brain is affected:
| Region | Symptoms of the lesion |
| Frontal lobes | Mental abnormalities accompanied by irritability, aggression or, conversely, depression and apathy. Speech becomes difficult, and some phrases or sentences are misunderstood. Loss of sense of smell is common |
| Parietal region | The most obvious sign is a decrease in attention and concentration; in a child this is accompanied by poor learning at school, and in an adult, problems at work. Along with this, convulsions may appear at any time of the day. |
| Temporal lobe | The disorder is presented in the form of logoneurosis and absent-mindedness. A common symptom is partial or complete hearing loss, as well as epileptic activity. |
| Occipital region | A person has hallucinations - actions appear in his subconscious that, in fact, do not happen to him. This pathology is often accompanied by impaired vision frequency and psychiatric instability. |
More severe symptoms of the disease appear in older people. He develops memory lapses, he begins to forget important dates and the names of his loved ones. Problems of an emotional nature are also observed, presented in the form of inappropriate behavior or expression of one’s emotions.
Establishing diagnosis
Diagnosis of organic focal diseases of the brain is important both at the earliest stages and at later stages with already prescribed treatment.
Early detection of the disease will allow you to take action and prescribe medications that can stop its progression or even reverse it. The most important diagnostic stages:
- taking anamnesis;
- neurological examination;
- computed tomography of the brain.
Foci of organic brain damage are shown by arrows
Anamnesis allows you to determine the duration of the disease, its course, and its connection with heredity. A neurological examination is mandatory to identify the causes. Tomography identifies atrophic lesions that cause symptoms.
Diagnostics
Detection of organic brain damage is a complex and difficult process. This means that in order to make a correct diagnosis, the doctor will need to carry out a set of diagnostic measures, which include the following types of research:
- Ultrasound of the brain. It is possible to do this only if the fontanelle has not yet closed. That is, such a diagnosis can only be performed on a child under one year old.
- MRI and CT. Allows you to determine whether there is a change in the brain and which lobes are damaged. A complex procedure that requires complete silence and stillness. For young children, it is usually performed under anesthesia.
- EEG. The study is carried out using special sensors that make it possible to determine how correctly the neural connection is working and whether epileptic activity is present. The study can be carried out from 15 minutes to 2 hours, however, in order to get a more detailed picture of brain function, it is recommended to monitor during sleep. Many clinics currently offer paid services - installing the device overnight.
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck. The procedure allows you to determine how correctly the blood supply to the brain is.
On the recommendation of a neurologist or neurosurgeon, a number of additional types of research may be required, such as neurosonography, EchoEg, laboratory tests of blood and urine, as well as ultrasound of internal organs to identify the threshold.
In rare cases, the patient needs to undergo a cerebrospinal fluid puncture. If the diagnosis was carried out correctly, then the doctor will have the opportunity to correctly diagnose and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Organic brain diseases: their types
Organic brain damage (OMD) is characterized by the presence of pathological changes that can be seen using neuroimaging methods.
Any pathological processes are visualized and correlated: tumors, abscesses, benign cysts, hemorrhages, atherosclerosis, amyloid accumulation.
A feature of organic lesions is that there is a substrate in the brain. For example, epilepsy also has neurological pathological symptoms, but it is impossible to “see” anything. Organic disorders can be either local or diffuse. Symptoms are also different. With local damage, one type of activity (memory, intelligence) is impaired. And with generalized symptoms, general cerebral symptoms appear.
Types of organic brain lesions:
- Brain disorder associated with diseases of the heart, blood vessels and nerves . Most often this is observed in atherosclerotic lesions of cerebral vessels, Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. In the first case, a sufficient amount of energy, oxygen, and nutrients do not enter through the narrowed lumen of the vessels. This leads to insufficient trophism of the nervous tissue of the brain and its gradual death. In Alzheimer's disease, plaques form in the brain tissue, the basis of which is the protein amyloid. It is this that leads to degeneration of both the neuron bodies themselves and their processes.
- Brain damage, with diseases of internal organs . Pathological processes occurring in the brain cause functional failure of the liver or kidneys. This is due to the accumulation of a large number of toxins, which negatively affect all body systems, including destroying neural connections. If the organs do not begin to function normally (after transplantation or treatment), then dementia will only progress. Removing toxins is not enough.
- Brain damage associated with intoxication . Excessive amounts of alcohol or its substitutes can cause severe intoxication of the body and lead to damage to neural connections, and subsequently to dementia. The same effect will be observed in case of poisoning with arsenic or nitrogenous products. After the disappearance of the etiological factor and cleansing of the body, the condition may improve. This depends on the duration of exposure and the depth of possible damage. In older people, intoxication can occur due to taking large doses of medications. Additionally, to quickly improve the condition, sedatives and sleeping pills are prescribed to improve the condition of the cardiovascular system.
Treatment
It is known that neurocells do not recover in any way. Throughout the world, it has not yet been possible to develop a type of treatment that could contribute to the restoration of the affected area of the brain.
However, as a result of research, it was possible to prove that if healthy cells are stimulated, they will take over the work for the inactive area. There are several ways to treat this pathology:
Medications
Medicines that a doctor can prescribe are divided into 3 main groups:
- Neuroleptics and neuroprotectors. Helps improve blood supply to the brain and thin it.
- Anticonvulsants. They are prescribed only if the person has had seizures or epileptic activity has appeared on the EEG.
- Antibiotics and antiseptics. If the cause of organic brain damage is an infectious disease, then for further rehabilitation it is necessary to first eliminate it.
Unfortunately, there are no harmless pills to restore brain activity. They all have certain side effects. In most cases, aggression, restless sleep and irritability appear.
Important!
Before prescribing medications, an EEG procedure must be performed first. If epileptic activity has been detected, then drugs to stimulate brain activity cannot be prescribed. This can trigger severe cramps.
Additional procedures
In addition to medications, it is possible to carry out a number of other modern techniques to eliminate organic damage. These include:
- General body massage, exercise therapy and physiotherapy. The procedures are aimed at improving overall blood flow. They also allow you to relieve spasms, get rid of hypotonicity and hypertonicity.
- BAK, Tomatis and microcurrents. The procedures are aimed at external stimulation of the brain.
Procedures are also carried out only in the absence of epileptic activity. Basically, they are carried out in private clinics on a paid basis. Additional types of rehabilitation such as a swimming pool, classes with a speech pathologist and speech therapist, and visits to a psychiatrist may also be available.
Activities for fine motor skills and sensory integration are very important for children, which also helps improve brain function. In rare cases, surgery is required.
Symptoms
Not all individuals know what an organic lesion is. Organic brain damage does not have specific symptoms due to its complex genesis; they manifest themselves individually.
General changes: decreased activity, inability to concentrate for a long time, apathy, sloppiness.
Elderly people may forget the names of relatives, the day of the week, the date, and speech is impaired. If the disorder progresses, the patient forgets words and cannot maintain a dialogue. The emotional state has 2 types: the absence of any emotions or inadequate, aggressive behavior. There are hallucinatory attacks.
to contents ^