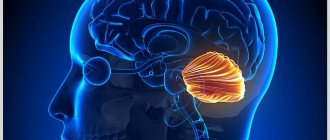
What is the cerebellum?
This section is located under the occipital zones of the cerebral cortex. In front of it is the medulla oblongata and the pons. The cerebellum is called the cerebellum or small brain. In fact, its structure resembles the cerebral cortex.
Its development is directly related to the complexity of the movements that the body performs. This organ is most developed in predators. Snails, slugs and parasitic organisms have a simple and primitive structure.
The job of the cerebellum is to coordinate complex movements, maintain balance and maintain muscle tone. Cerebellar functions resemble the extrapyramidal system. This is one of the zones that is closely connected with it.
Of course, the work of the body is impossible without clear coordination of connections. The cerebellum “communicates” with other parts of the brain. For this purpose it has three legs. They connect it with the following departments:
- Bark;
- Extrapyramidal system;
- Brain stem;
- And its dorsal section.
Structure
The cerebellum is similar to the cerebrum not only in name. The structure of the organ includes two hemispheres. In addition, the structure of the cerebellum is graded into gray and white matter.
So, the organ is located under the occipital lobes. It is separated from them by one of the outgrowths of the dura mater - the tentorium of the cerebellum. The two hemispheres are united by a “worm”. This unpaired structure is responsible for posture and tone. Forms balance and supporting movements. When the “worm” is damaged, the patient develops symptoms of locomotor ataxia. He cannot walk or stand on his own.
Gray matter is located on the outside of the lobes. And in the depths lies a white layer that forms the nuclei. These are paired structures. They have their own special functions. By name, some of them are similar to the nuclei of the extrapyramidal system. In addition, they are closely related to them.
For example, the dentate nucleus is similar to the olive nucleus. They share common nerve fibers. If their work is disrupted, the muscles of the limbs suffer. The spherical nucleus is responsible for the function of the muscles of the neck and torso. And the tent core performs the function of controlling the balance of the body. It is the oldest in phylogeny.
Fact! The tent nucleus is called the ancient cerebellum. It is connected with the vestibular apparatus.
Dynamic cerebellar ataxia
In this case, we are talking about problems with the smoothness and dimension of human movements. This type of ataxia can be unilateral or bilateral, depending on which hemispheres are affected. If we talk about what symptoms are observed with damage to the cerebellum and the manifestation of dynamic ataxia, they are similar to those described above. However, if we are talking about unilateral ataxia, then in this case the person will have problems moving or performing test tasks only in the right or left side of the body.
To identify the dynamic form of pathology, it is worth paying attention to some features of human behavior. First of all, he will experience severe trembling in his limbs. As a rule, it intensifies by the time the patient completes the movement. When in a calm state, a person looks absolutely normal. However, if you ask him to take a pencil from the table, at first he will stretch out his hand without any problems, but as soon as he begins to take the object, his fingers will begin to tremble violently.
When determining the symptoms of cerebellar damage, diagnosis includes additional tests. With the development of this pathology, patients experience so-called overshooting and overshooting. This is explained by the fact that a person’s muscles begin to contract disproportionately. The flexors and extensors work much harder. As a result, a person cannot fully perform the simplest actions, for example, putting a spoon in his mouth, buttoning a shirt, or tying a knot in his shoelaces.
In addition, changes in handwriting are a clear sign of this disorder. Most often, patients begin to write large and unevenly, and the letters become zigzag.
Also, when determining symptoms of damage to the cerebellum and pathways, it is worth paying attention to how a person speaks. With the dynamic form of the disease, a sign appears, which in medical practice is called scanned speech. In this case, the person speaks as if in jerks. It divides phrases into several small fragments. In this case, outwardly the patient looks as if he is broadcasting something to a large number of people from the podium.
Other phenomena characteristic of this disease are also observed. They also concern patient coordination. Therefore, the doctor conducts a number of additional tests. For example, in a standing position, the patient should straighten and raise his arm to a horizontal position, move it to the side, close his eyes and try to touch his nose with his finger. In normal conditions, it will not be difficult for a person to perform this procedure. If he has ataxia, he will always miss.
You can also try asking the patient to close his eyes and touch the tips of his two index fingers to each other. If there are problems in the cerebellum, the patient will not be able to match the limbs in the desired way.
Cerebellar diseases
Violations in the functioning of the organ are manifested by a diverse clinic. But problems associated with impaired coordination, gait, and muscle tone predominate.
The reasons that cause organ damage can be divided into three groups. These are congenital malformations, hereditary ataxias and acquired diseases.
Congenital pathologies appear from the first minutes of life. They are associated with underdevelopment of the cerebellum or one of its parts. The lesion becomes noticeable as motor skills develop. Ataxia almost always appears.
Hereditary problems are associated with a gene defect. They are transmitted from parents in an autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive manner. Among these pathologies are:
- Friedreich's ataxia;
- Ataxia-telangiectasia;
- Ataxia with vitamin E deficiency;
- Abetalipoproteinemia.
One type of ataxia is spinocerebellar disorders. They include a whole range of diseases with a hereditary transmission mechanism. In addition to the main symptoms, disturbances in walking, tone, and coordination dominate.
Acquired diseases of the cerebellum arise as a result of circulatory disorders in the organ, viral and bacterial infections. The toxic effects of alcohol, heavy metal salts, lithium, and anticonvulsants also lead to cerebellum problems. Atrophic phenomena in the organ appear from a lack of vitamin E and B12, with hypothyroidism.
Tumors develop in the cerebellum. They manifest themselves as symptoms of compression and loss of coordination. The most common types of tumors that develop are astrocytomas and meduloblastomas.
Cerebellar syndrome
Cerebellar syndrome is a neurological disease that causes a complex of symptoms. These include:
- "Drunk" gait;
- Tremor;
- Nystagmus;
- Violation of coordination tests;
- Decreased or increased tone.
What is cerebellar syndrome? This is a set of symptoms for any organ damage. Deficiency of this brain structure is manifested by abrupt onset, falls, unsteadiness and coordination problems.
Cerebellopontine syndrome
With this lesion, the nerves of the bridge and cerebellar tissue are involved in the pathological process. The causes of the syndrome are tumors or adhesions after inflammatory diseases.
The clinical picture is accompanied by intracranial hypertension: periodic paroxysmal headaches, vomiting, loss of consciousness. Added to this are walking disorders, difficulties with coordination of movements, and problems maintaining a posture.
In the later stages, swallowing and cardiac activity are impaired. The breathing reflex is difficult.
Vestibulocerebellar syndrome
The causes of this pathology are vascular lesions of various types. They range from vasospasm to severe atherosclerotic stenosis or ischemia from infarction.
Typical clinical picture:
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- Loss of coordination;
- Unsteadiness of gait;
- Flashing of flies before the eyes;
- Inability to hold a pose.
Vestibulocerebellar syndrome is the second most common pathology that is diagnosed by neurologists when the small brain is damaged.
Cerebellar-atactic syndrome
Cerebellar ataxia most often occurs in elderly people against the background of vascular lesions of the vertebrobasilar region. In people over 75-80 years of age, such disorders manifest themselves as falls. This can cause injury to patients and require additional care.
Cerebellar ataxia is manifested by a disorder in maintaining balance, unsteadiness when walking, and uncoordinated movements.
Cerebellopyramidal syndrome
This type of disorder occurs in spinocerebellar ataxia. Cerebellar-pyramidal syndrome has the following clinical picture:
- Violation of the innervation of skeletal muscles;
- Problems with conscious voluntary movements;
- The emergence of pathological nerve reflexes;
- Loss of coordinated concerted action;
- Unsteadiness of gait;
- Loss of stability;
- Problems maintaining posture.
Cerebellar descent
This is the descent of the cerebellar tonsils into the foramen magnum. In this case, compression of the medulla oblongata occurs. This raises the following problems:
- Occipital pain;
- Swallowing problems;
- Ataxia.
The causes of the problem are congenital diseases. In addition, Arnold-Chiari malformation occurs when the brain grows rapidly and the skull bones develop slowly.
Cerebellar herniation
The syndrome appears when the brain is dislocated and is accompanied by herniation of the tonsils into the foramen magnum. The cause of dislocation is local hypertension in one of the departments. In this case, structures move from one place to another.
Symptoms of circulatory disorders occur, breathing stops, and the swallowing reflex disappears. As symptoms progress, death occurs.
Fact! Disequilibrium is a complication of the hemodialysis procedure. When the osmotic properties of the blood are lost, cerebral edema occurs. In this case, the cerebellar tonsils wedge into the foramen magnum. The decompensated condition leads to death. Respiratory and cardiac arrest occurs.
Inflammation of the cerebellum
Acute cerebellitis most often occurs in children. The cause is viral infections or bacterial infections. As a result of the disease, ataxia occurs, gait and coordination are impaired. The patient is not stable in the Romberg position.
Sometimes cerebellitis occurs after an illness. Symptoms are similar to the acute period. Cerebellar inflammation is rare in adult patients.
Atrophy and dystrophy of the cerebellum
Cerebellar atrophy occurs in many degenerative brain diseases. There is a decrease in the volume of the tonsils, and the volume of functioning neurons decreases. With atrophy, problems with walking, instability in the Romberg position, unsteadiness in gait and instability in a standing position appear.
Cerebellar atrophy is rare in young people and is more often a consequence of senile diseases. At a young age, symptoms of atrophy occur against the background of schizophrenic disorders (cerebellar vermis atrophy) and with various hereditary or congenital pathologies. The onset of dystrophy is also caused by tumors that compress the tissues of the small brain and lead to the death of its cells.
Diagnostics
Considering the symptoms of cerebellar damage and research methods, it is worth noting that in case of any disturbances in the functioning of the brain, you must immediately contact a neurologist. He conducts a series of tests in order to clarify how a person’s superficial and deep reflexes work.
If we talk about hardware studies, it may be necessary to perform electronystagmography and vestibulometry. A general blood test is required. If a specialist suspects an infection in the cerebrospinal fluid, a lumbar puncture is performed. Markers of stroke or inflammation need to be checked. Additionally, an MRI of the brain may be required.
Symptoms of cerebellar damage
We list the characteristic cerebellar signs below.
- Ataxia is static;
- Locomotor ataxia;
- Nystagmus;
- Chanted speech;
- Intentional trembling;
- Adiadochokinesis;
- Dysmetria;
- Muscle hypotension;
- Dysmetria;
- Missing;
- Megalography;
- Asynergy;
- Unsteady gait.
These symptoms do not always appear when the cerebellum is affected. The clinic also resembles disorders of the extrapyramidal system. Therefore, each sign should be described in detail.
Gait changes
When the structure is damaged, gait becomes unsteady. Patients with symptoms of the disease are similar to drunk people. They move vaguely and spread their legs wide. In this case, the patient sways when walking. The rolling intensifies towards the affected hemisphere. Similar problems arise with cerebellar ataxia.
Fact! The patient cannot quickly change direction of movement. Turning is difficult.
Nystagmus
Nystagmus is the twitching of the eyeballs. It manifests itself clearly when the patient looks in one direction. Nystagmus can be horizontal, vertical and circular. Moreover, with cerebellar problems, horizontal nystagmus is more common. It is expressed when the patient looks towards the lesion.
Muscle tone in cerebellar lesions
The tone in such diseases is reduced until complete muscle atony. Disorders are especially pronounced when the “worm” is affected. With hypotension, the patient quickly gets tired and exhausted. Excessive passive movements appear in the joints. Superficial and deep tendon reflexes disappear.
Megalography
This is a characteristic change in handwriting due to problems with the cerebellum. The letters increase in size. At the same time, their outline is unclear and uneven. This is due to the difficulty of precise movements. Including when writing. Patients with a clinical picture of such diseases are recommended to use a computer to print text.
Tremor
Trembling occurs only when moving. There is no tremor at rest. This is a differential sign to exclude extrapyramidal symptoms. Trembling occurs only in the upper extremities. The head, trunk and legs are rarely involved. Intention tremor is characteristic when the patient reaches for an object. At this time, the hands begin to shake violently.
Loss of coordination
These lesions are noticeable when walking and at rest. In patients with damaged cerebellum, static ataxia occurs. This is a swaying of the body in a standing position. Locomotor ataxia appears - a lack of coordination when performing actions.
There are misses and misses when there is a need for precise small movements. Dysmetric syndrome is expressed in the disproportion of strength when performing actions or when asking to take an object.
Signs of pathology
If we talk about the main symptoms of damage to the cerebellum of the brain, then among them is ataxia, which can manifest itself in different ways. However, most often a person’s head and whole body begin to tremble, even with a calm body position. Muscle weakness and poor coordination of movements appear. If one of the hemispheres of the brain is damaged, then the person’s movements will be asymmetrical.
Patients also suffer from tremors. In addition, there are severe problems in the process of flexion and extension of the limbs. Many experience hypothermia. If symptoms characteristic of cerebellar damage occur, the patient may experience motor disturbances. In this case, when moving towards a certain goal, a person begins to perform pendulum actions. In addition, a problem with the cerebellum can cause hyperreflexia, gait disturbances, and severe changes in handwriting. It is also worth considering the types of ataxia of this organ.
Cerebellar lesions in children
Cerebellar insufficiency in children is a normal condition that develops in the first year of a newborn’s life. It is characterized by a shaky, unstable gait, frequent falls, and poor coordination. As you grow older, your movements become clearer and more precise. And the number of falls decreases by 2 years.
If the symptoms of ataxia do not go away by 2-3 years, this is a reason to consult a neurologist. At the same time, the baby lags behind in mental and motor development. He lacks the skills typical of his peers. Cerebellar insufficiency is formed as a result of hereditary or congenital diseases, with ischemia during childbirth and with a previous neuroinfection.
An enlarged cerebellum in a child appears as a result of active tumor growth. At the same time, other symptoms of ataxia are observed. Normally, the size of the small brain should not exceed the norms specified for imaging.
Consequences
Tissue changes as a result of injury, tumor or infection lead to serious consequences for the young body. For example, children may never master motor skills (walking, complex coordinated movements). With minimal consequences, the patient continues to have an unsteady gait, which leads to frequent falls.
When the small brain is damaged, there is a slight retardation of intellectual activity. But it can be compensated for by an adapted training program for such children. After all, their cognitive abilities are not reduced. They are simply limited in their capabilities.
Alcoholic cerebellar degeneration
A similar pathology appears against the background of chronic intoxication with alcoholic beverages. In this case, the cerebellar vermis is affected. First of all, when diagnosing the disease, patients experience problems with limb coordination. Sight and speech are impaired. Patients suffer from severe memory loss and other problems with brain activity.
Based on this, it becomes obvious that problems with the cerebellum appear against the background of other pathologies. Although neurological problems most often lead to ataxia, this is not the only factor that affects a person’s health. Therefore, it is important to promptly pay attention to the symptoms, contact a qualified specialist and conduct a diagnosis. Simple tests can be performed at home. However, after this you need to consult a doctor, identify the main cause of the unpleasant disease and begin immediate treatment with drugs and physiotherapy.
Methods for diagnosing cerebellar disorders
Neuroimaging methods (CT, MRI) are used to diagnose cerebellar disorders. In case of inflammatory changes, it is important to study blood and cerebrospinal fluid (search for antibodies to viruses).
But objective neurological research techniques make it possible to identify abnormalities characteristic of this particular part of the brain. The neurologist conducts tests during an objective examination. A neurological hammer is required as a special device.
The following samples are used:
- Finger;
- Index finger;
- Romberg test;
- Babinsky;
- Knee-heel;
- For dysmetria;
- For diadochokinesis;
- For nystagmus;
- For gait disorders.
Finger test
The patient is in a sitting or standing position. The doctor asks him to straighten his arm and move it to the side. Then the patient should touch the tip of his nose with his index finger. In this case, you need to perform the test with your eyes open and closed.
A patient with organ damage misses his finger on the affected side. At the same time, he has intention tremor of the hand and index finger. For problems with the cerebellum (ataxia), open or closed eyes do not affect the quality of diagnosis.
Finger pointing test
There are several modifications of the test. Most often, the patient is asked to spread his arms to the sides and bring them together, touching each other with his index fingers. A test is possible when the doctor puts his finger or a rubber band of a hammer.
On the affected side, the patient misses the target. In this case, a tremor appears in the hand. The finger deviates outward from its normal position. Performing with eyes open or closed does not affect the outcome.
Romberg test
Static ataxia is examined in this position. The patient stands straight, arms are lowered along the body, feet are brought together. The doctor stands behind, if necessary, insures the patient. If there is no wobble, then the test becomes more complicated.
The patient stretches his arms forward and tries to stand. If no problems are found, but the patient places his feet in one line. When performing the test, the patient falls in the direction of the lesion. However, open or closed eyes do not affect stability.
Babinski test
In the supine position, the patient crosses his arms. Then he needs to sit down without changing their position. When standing up, the patient's legs also rise. In this case, the leg on the affected side will rise higher.
The second asynergy test is also performed while lying down. The doctor bends the patient's arm at the elbow and places it on his chest. Now he must straighten his arm and suddenly let go. A patient without brain damage will restrain his hand and prevent the blow. After all, his antagonist muscles work. The patient will hit himself with his fist.
Knee-heel test
The patient is sitting. The doctor says to touch the opposite knee joint with your heel. Then go down the lower leg to the ankle. On the affected side, the patient with problems misses the knee. The heel jumps off the shin due to its greater amplitude. Opening or closing your eyes does not affect the sensitivity of the test.
Dysmetria test
Dysmetria is impaired proportionality of movements. In this case, the patient is asked to extend his hands, palms up. Next, he closes his eyes and turns them palms down. Excessive pronation is observed on the affected side. The palms rotate differently.
For diadochokinesis
Adiadochokinesis is the inability to quickly perform opposite movements. The patient is asked to perform supination and pronation in the wrist joint. In this case, on the affected side, the hand lags behind and makes excessive inaccurate movements. In this case, rapid depletion is observed.
For nystagmus
The doctor asks the patient to look at the hammer. He moves it up, down, to the sides. The patient watches him without turning his head. At the same time, rapid repeated movements of the eyeballs begin on the affected side.
Gait disorders
The patient is asked to walk forward and backward in one line. In this case, the test is first performed with open and then with closed eyes.
A patient with organ damage deviates to the side. In addition, his gait is characterized by long steps. He walks like he's drunk. Spreads legs wide apart. The body tilts in the direction where the cerebellar lobe is affected.
Static-locomotor
In this case, disturbances in a person’s walking are most pronounced. Any movement brings severe stress, which causes the body to become weaker. In this case, it is difficult for a person to be in a position where the heels and toes of the feet are in contact. Difficulty falling forward, backward, or swaying to the sides. In order to take a stable position, a person needs to spread his legs wide apart. There is a very unsteady gait and outwardly the patient who exhibits symptoms of cerebellar damage resembles a drunk. When turning, it can skid to the side, even falling.
To diagnose this pathology, several tests must be performed. First of all, you need to ask the patient to walk in a straight line. If he shows the first signs of static-locomotor ataxia, he will not be able to perform this simple procedure. In this case, he will begin to deviate too much in different directions or spread his legs too wide.
Also, in order to identify the main symptoms of cerebellar damage, additional tests are performed at this stage. For example, you can ask the patient to stand up sharply and turn 90° to the side. A person whose cerebellum is damaged will not be able to perform this procedure and will fall. With such a pathology, the patient also cannot move with an extended step. In this case, he will dance, and the body will begin to lag slightly behind the limbs.
In addition to obvious problems with gait, there is a strong contraction of muscles when performing even the simplest movements. Therefore, in order to determine this pathology, you need to ask the patient to stand up sharply from a lying position. At the same time, his arms should be crossed on his chest. If a person is healthy, then his muscles will contract synchronously, and he will be able to sit down quickly. When ataxia occurs and the first symptoms of cerebellar damage occur, it becomes impossible to simultaneously strain the hips, torso and lower back. A person will not be able to get into a sitting position without the help of his hands. Most likely the patient will simply fall backwards.
You can also ask the person to try bending backwards while standing. At the same time, he must throw back his head. If a person is in a normal state, then in this case he will involuntarily bend his knees and straighten in the hip area. With ataxia, such flexion does not occur. Instead, the person falls.
Treatment and prognosis
For any type of lesion, therapy is divided into symptomatic and etiological. The chances of restoring dead cells are very small. Therefore, doctors only treat the symptoms of the disease. Medicines and surgical techniques are used. The prognosis for the disease is unfavorable.
How to develop the cerebellum?
Children with cerebellar insufficiency may lag behind their peers in development. And in older people, frequent falls are a source of dangerous complications. How to develop a “small” brain?
- The most ancient method is rocking a baby in a cradle. It’s not for nothing that our ancestors made cradles for the birth of their first child. This is not only caring for the mother, but also the development of the child’s vestibular apparatus;
- Next, a swing is suitable for training a two-year-old. They must be modern and safe. Just play with your baby and develop not only vestibular skills, but also conversational speech;
- After 5-7 years of age, children are taught on Dr. Bilgow’s balancing board. You can make it yourself or buy it in a store. It’s better to attend courses with an experienced exercise therapy instructor;
- There's more to the board than just balancing. Exercises are used with throwing and catching bags of sand, a ball and other devices.
It is important to exercise regularly (3-4 times a week). The duration of classes is at least 30 minutes. If you feel well, such training is also available for older people.
Treatment
The success of therapy directly depends on the causes of this pathology. Therefore, speaking about the symptoms and treatment of cerebellar lesions, it is worth considering the most common cases.
If the disease is accompanied by an ischemic stroke, then lysis of blood clots is required. The specialist also prescribes fibrinolytics. To prevent the formation of new blood clots, antiplatelet agents are prescribed. These include Aspirin and Clopidogrel. Additionally, you may need to take metabolic medications. These include Mexidol, Cytoflavin and others. These funds help improve metabolic processes in brain tissue.
In addition, in order to prevent another stroke, it is necessary to take a course of medications that reduce the amount of cholesterol in the blood.
If, when studying the symptoms and causes of damage to the cerebellum, the doctor determines that the patient is suffering from neuroinfections (for example, encephalitis or meningitis), then treatment with antibiotics is required.
Problems caused by intoxication in the body can be solved with the help of detoxification therapy. However, for this it is necessary to clarify the type and characteristics of the poison. In difficult situations, immediate measures must be taken, so the doctor performs forced diuresis. In case of food poisoning, it is enough to perform gastric lavage and take sorbents.
If a patient is diagnosed with cancer, then everything depends on its stage and type of pathology. As a rule, radiation and chemotherapy are prescribed for treatment. In some situations, surgery may be required.
Experts also prescribe drugs that can improve blood flow (for example, “Caviton”), vitamin complexes, anticonvulsants and drugs that strengthen muscle tone.
Physical therapy and massage sessions have a beneficial effect. Thanks to a special set of exercises, it is possible to restore muscle tone. This helps the patient return to normal faster. Physiotherapeutic measures are also carried out (therapeutic baths, electrical stimulation, etc.).
Also, when considering the symptoms, causes and treatment of cerebellar damage, it is worth paying attention to several more brain pathologies encountered in medical practice.
Cerebellar diseases
Below we list all the lesions that are characteristic of this area of the brain.
- Tumors;
- Abscesses (bacterial and parasitic);
- Hereditary diseases (for example, Pierre Marie's ataxia);
- Alcoholic degeneration;
- Multiple sclerosis;
- Circulatory disorders;
- Traumatic brain injury;
- Developmental disorder (Arnold-Chiari malformation).
Cerebellar disorders are detected in children and adult patients. Symptoms of ataxia are accompanied by vestibular disorders and loss of coordination. Unfortunately, therapy for the pathology is impossible. However, rational rehabilitation allows you to maintain and develop motor skills.
Other reasons for the development of the disorder
In some cases, cerebellar damage is not a consequence, but a symptom. This applies to oncological diseases of the following organs and systems:
- lungs;
- brain;
- ovaries;
- lymph nodes.
With prolonged alcohol dependence, substance abuse and drug addiction, irreversible damage to the cerebellum occurs. Ataxia can also become a hereditary disease. In this case, therapy must be selected in a special way.
What is the cerebellum, its functions and structure:
Causes of the disease
It should be said that the cerebellum is not always to blame for the development of ataxia, and the doctor’s task is to figure out at what level the damage occurred. Here are the most characteristic causes of the development of both the cerebellar form and ataxia outside the cerebellum:
- Damage to the posterior cords of the spinal cord. This causes sensory ataxia. Sensitive ataxia is so named because the patient has impaired joint-muscular sensation in the legs and is unable to walk normally in the dark until he can see his own legs. This condition is characteristic of funicular myelosis, which develops in a disease associated with a lack of vitamin B12.
- Extracerebellar ataxia can develop in diseases of the labyrinth. Thus, vestibular disorders and Meniere's disease can cause dizziness and falling, although the cerebellum is not involved in the pathological process;
- The appearance of neuroma of the vestibulocochlear nerve. This benign tumor may present with unilateral cerebellar symptoms.
The actual cerebellar causes of ataxia in adults and children can occur due to brain injuries, vascular diseases, and also due to a cerebellar tumor. But these isolated lesions are rare. More often, ataxia is accompanied by other symptoms, for example, hemiparesis, dysfunction of the pelvic organs. This happens with multiple sclerosis. If the process of demyelination is successfully treated, then the symptoms of cerebellar damage will regress.
However, there is a whole group of hereditary diseases in which the motor coordination system is predominantly affected. Such diseases include:
- Friedreich's spinal ataxia;
- hereditary cerebellar ataxia of Pierre Marie.
Cerebellar ataxia of Pierre Marie was previously considered a single disease, but now there are several variants of its course. What are the signs of this disease? This ataxia begins late, at the age of 3 or 4, and not at all in a child, as many people think. Despite the late onset, the symptoms of cerebellar ataxia are accompanied by speech impairment such as dysarthria and increased tendon reflexes. Symptoms are accompanied by spasticity of skeletal muscles.
Typically, the disease begins with a disturbance in gait, and then nystagmus begins, coordination in the hands is impaired, deep reflexes revive, and an increase in muscle tone develops. A poor prognosis occurs with optic nerve atrophy.
This disease is characterized by a decrease in memory, intelligence, as well as impaired control of emotions and volition. The course is steadily progressive, the prognosis is unfavorable.