Share:
Beginners often complain of symptoms of overtraining - nausea, weakness or dizziness. But since the first workouts are not excessively intense, the body quickly adapts to the stress and easily copes with such symptoms. But it also happens that you get a headache after training, even if you did not receive any serious exercise. What does this indicate, how to relieve such pain and how to prevent such symptoms? You will find detailed answers to these and other questions in our article.
What are headaches
The most common complaint with which people go to doctors is headaches. Epidemiological studies in recent years show that more than 80% of the world's population suffer from this symptom, which causes a decrease in quality of life and performance. Pain in the head complicates the course of many ailments, provokes depression, and the development of autonomic disorders.
The most common forms of pathology are tension headaches and migraines. The first is caused by sinusitis, otitis and other diseases. Tension pain often occurs during physical activity. Risk factors include overwork, allergens, injuries and others. To cope with an attack, you just need to eliminate the cause of the pain. Migraine is a consequence of the expansion or sharp narrowing of the blood vessels surrounding the brain, and therefore requires careful diagnosis and comprehensive treatment.
The main causes of regular headaches:
- Organic diseases of the brain. They arise due to injuries, tumors, and inflammatory processes.
- Vascular disorders. Arterial hypertension, migraine and others.
- Psychogenic factors. Caused by mental stress due to acute or chronic stress.
- Extracerebral causes. Exposure to drugs or chemicals, bacterial or viral infections, pathologies of various facial structures (teeth, nose, ears, eyes), metabolic disorders, cervical osteochondrosis, weather changes.
How to treat depending on the reasons
If pain appears constantly, and not from time to time - that is, after almost every workout - you should consult a doctor, telling him what kind of pain appears, after what workouts and when it goes away.
There are quite a lot of reasons why after training you get worse and have a headache, and the treatment, accordingly, should also be different. Some have already been mentioned above, now for further consideration.
High blood pressure - this happens most often. It increases with physical activity. loads, but if you return to normal, the vessels should adapt fairly quickly. But if after training you experience a headache and nausea, there is nothing good about it - most likely, a hypertensive crisis begins. In this case, you need to check your blood pressure, and then decide on the necessary medications for treatment. If you are not sure that you understand this well, we again remind you of the opportunity to visit a doctor.
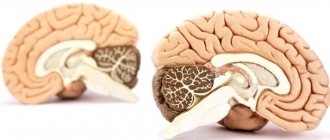
Pain due to physical tension - if you overload the muscles of your head and neck when exercising, you may not be doing the exercises correctly. Here it is worth considering consulting not only a doctor, but also a professional trainer. Now a little about the increase in ICP (pressure inside the skull). What it is? The fact is that in the tissues of the brain there is a special fluid, the so-called. liquor, which protects them from damage. When there is a lot of cerebrospinal fluid, it circulates worse and ICP increases. If there is swelling in the forehead and crown of the head, then there may be stagnation of cerebrospinal fluid.
If the ICP is very low, then there is pain in the temples. Sometimes with ICP we are talking about harmful formations inside the brain, in particular, hematomas. In any case, this variant of the disease is one of the most dangerous, so again you should go to the clinic. First, the volumetric intracerebral formations will be removed, and then the pressure inside the skull will be adjusted to the desired level.
Why do you get a headache after exercise?
During muscle activity, the body's metabolism accelerates, therefore the need for oxygen, glucose, and energy increases. Some diseases in which metabolism is reduced or gas exchange and blood circulation are disrupted lead to oxygen starvation, causing headaches. During periods of heavy work, intense exercise or heavy lifting, brain tissue especially needs oxygen. If something interferes with this process, then headaches occur during physical activity.
Diseases that cause pain
The main reason a person develops nagging pain in the temples and back of the head after intense exercise is the presence of chronic diseases. Among them:
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system. After training, you get a headache if the heart does not provide timely delivery of a biological oxidizer (oxygen) to the blood. Resistance to physical stress decreases with coronary artery disease, symptomatic hypertension, hypertension, and vascular atherosclerosis.
- Diseases of the respiratory system. Pain in the back of the head occurs during physical activity if the mobility of the lungs and their absorption of oxygen from the atmospheric air decrease. Vasospasm, which is provoked by chronic, acute or inflammatory diseases of the respiratory tract (frontal sinusitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis and others), leads to pain.
- Endocrine diseases. Diseases that are associated with hormonal activity provoke pain in the head due to increased production of the hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine. As a result, the pulse quickens, intracranial pressure increases, which provokes pain in the head.
- Anemia. The disease is characterized by a decrease in hemoglobin or a decrease in the number of red blood cells. This provokes a lack of oxygen, to which the brain immediately reacts.
- Traumatic brain injuries. When the brain is bruised or concussed, pain occurs in the head, worsening when bending or making sharp turns.
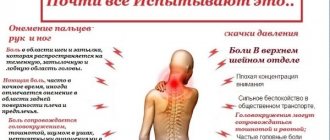
- Osteochondrosis. Damage to the cervical spine often causes dizziness and pain, which increases during heavy physical work or stress in the gym.
- Neuralgia. The disease is accompanied by pain in the back, front or back of the head.
Mistakes when playing sports
If you have a headache after the gym, several factors could be to blame: emotional state, fatigue, prolonged exposure to a hot or cold place. In order for the training to take place without unpleasant symptoms, the following mistakes should be avoided before training:
- do not perform exercises in a poorly ventilated, stuffy room;
- do not engage in strenuous sports after a long break;
- do not exercise immediately after eating or quickly climbing stairs;
- Do not play sports if you are stressed, psychologically upset, severely overexerted, or feel unwell.
- Vapor barrier for the walls of a wooden house
- How to tan quickly in a solarium
- Inflammation of the parotid, submandibular and sublingual salivary glands
Possible reasons
To find out the causes of post-workout headaches, it’s worth delving a little deeper into physiology. During physical activity, our body is subjected to serious stress. This leads to optimization and adaptive reactions on the part of the body, which are determined by our evolutionary survival mechanisms.
So, during training and other stress, the body redirects all resources to current tasks, which leads to a decrease in brain nutrition, vasoconstriction and other similar processes. If the load is not excessive, the body copes with it and restores internal balance.
But if a person trains constantly, increasing the intensity, sooner or later he hits the natural limit of recovery and there comes a time when overtraining leads to negative consequences - overloading various systems.
Symptoms such as:
- nausea;
- insomnia;
- dizziness;
- bad feeling;
- muscle pain;
- headache.
Symptoms that should alert you
When you have a headache after physical activity, this can lead to serious complications if you do not seek help in time. Since this symptom is not a separate disease, but occurs against the background of another pathology, it can cause death caused by other manifestations of the disease, for example, blockage of a vessel. Do not delay visiting your doctor if you experience:
- systematic headaches during physical activity;
- the appearance of psycho-emotional deviations in the form of personality changes or disturbances of consciousness;
- pain in the neck and shoulders;
- increased body temperature, vomiting, nausea;
- severe weakness, dots before the eyes, double vision, blurred vision;
- numbness of half the face.
Preventive actions
To prevent headaches after every intense workout, follow these tips:
- Don't come to training with a full stomach. At least 2 hours must pass after the last meal;
- Before purchasing a subscription, undergo a medical examination to be sure that training is not contraindicated for you;
- Never come to the gym if you feel unwell or are sick;
- Improve your sleep and get enough rest;
- Always start your training with a warm-up, and after the main part do a cool-down;
- Increase the load on any muscle groups gradually;
- Follow the correct technique for doing the exercises;
- Don't forget to drink water;
- Make sure you follow the correct breathing technique;
- Monitor your heart rate.
These simple rules will minimize the risk of developing a headache, but only if the cause is one-time and not associated with a serious problem.
Treatment
If you eliminate the causes of sudden pain that compresses the skull in time, then you can get rid of it forever or for a long period of time. Headaches during physical activity can be treated with medication and using traditional methods. In case of stress, osteochondrosis and spondylosis, throbbing pain is removed by massage techniques and physiotherapeutic procedures:
- Ultrasound. Mechanical vibrations of ultrasonic frequency help improve blood supply to the muscles located around the cervical spine, which relieves headaches.
- Laser. A low-frequency laser beam relieves tension in the muscles of the neck and head and restores the damaged nervous system.
- Electrophoresis. Medicines that are directed to the damaged area under the influence of direct electric current relieve painful symptoms quickly and for a long time.
If pain occurs due to overwork during training, then non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs will help relieve them: Citramon, Aspirin, Ibuprofen. In this case, you need to stop overexerting yourself in the gym and the problem will go away on its own. If a headache occurs for the first time during hard work or training, experts recommend:
- Stop your activity (work) and relax. You need to rest to regain your strength.
- Drink herbal tea with coltsfoot, St. John's wort, mint. It will have a calming effect and help cope with painful symptoms.
- After training, you need to sleep for 3-4 hours in a well-ventilated room. If the headache persists, take a warm bath with a solution of sea salt or medicinal herbs (chamomile, mint, lemon balm).
Traditional recipes also help cope with headaches. Among the most effective:
- grate half a lemon with the zest and apply to your forehead for 20-30 minutes;
- Before bed, take a 10-minute foot bath with mustard (2 tbsp.);
- twice within 1 hour, tap the bridge of your nose with the phalanx of your thumb continuously for 5 to 20 minutes;
- make a salt compress (1 tablespoon of salt per 0.5 liter of water) and place on the forehead for half an hour;
- Soak rye bread in vinegar and apply to the area of the head where the pain is worse for 20-30 minutes.
Alarming symptoms
When you get a headache after exercise, the reasons why this happens can be very dangerous.
As a rule, this is the result of previous injuries. In some cases, the problem may be hidden in sinusitis, then the headache begins during inclined movements when playing sports.
Sinusitis occurs more often in children than in adults. Additionally, it is necessary to carry out treatment and diagnosis if the following symptoms appear after playing sports:
- Headache and impaired consciousness appear, as well as other mental abnormalities.
- The person begins to feel a sharp pain, and it is very strong and appears in a matter of seconds.
- After training, you feel nauseous and may lead to vomiting, and the temperature also increases due to a headache.
- Headache appears after infectious diseases.
- Attacks from stress radiate to the cervical or shoulder area.
These symptoms after exercise and sports must be diagnosed and why this happens is determined.
Such symptoms often refer to serious illnesses.
Children present with symptoms differently than adults. Namely:
- attacks of pain are more short-lived;
- localization predominantly on both temporal sides.
The causes of pain can be completely different. And even an experienced specialist in his field will not be able to determine the character right away. This will require diagnosis, studying all the symptoms, taking tests, etc.
It happens that such ailments are the consequences of injuries or various diseases. For example, a headache during exercise when bending down is a sign of a disease such as sinusitis.
Prevention
If you do not want to take medications for headaches during physical activity, then you need to follow simple recommendations for its prevention:
- In order for the body to get used to strength training and not react with pain, the load should be increased gradually;
- When playing sports, watch your posture and the level of tension in your neck muscles;
- do not allow the body to dehydrate during physical activity; to do this, drink a glass of still water 1 hour before training;
- do not eat dairy yoghurts, nuts, citrus fruits, bananas before hard work;
- to avoid headaches during intense workouts, you do not need to hold your breath - you should breathe evenly while doing the exercises;
- Before any sport, a warm-up will help the body adjust to the load, for which moderate movements are suitable: running in place, swinging your arms, tilting your head.
Holding your breath
While playing sports, many people do not monitor their breathing. As practice shows, when performing difficult exercises or lifting a large load, the vast majority of people hold their breath. And because of this, intracranial pressure increases, resulting in migraine. To avoid this, you should inhale during the heavy phase and exhale during the mild phase.
NASA: 2021 repeated the temperature record of four years ago
Electric cars planned for release in the next five years
I definitely put chicken sauce on the table. Cook quickly, eat even faster
Main reasons
Exercise headaches have various causes. The most common causes of the phenomenon include:
- An increase in intracranial pressure due to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (a specific fluid produced by the cerebral ventricles) - it puts pressure on the brain centers, thereby causing pain;
- Atherosclerosis (pathology associated with the formation of “cholesterol plaques” on the vascular walls). In this case, the headache is a consequence of circulatory disorders as a result of narrowing of blood vessels.
- Arterial hypertension (the disease develops against the background of vegetative-vascular dystonia) - the course of the disease is accompanied by impaired blood supply to all internal organs, and therefore blood pressure increases.
- Cervical osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernias - such pathological phenomena are the main cause of impaired cerebral blood outflow. As a result, during physical activity there may be pain in the head and eyes (especially when moving), tinnitus is detected, the back of the head becomes “heavier,” and a person experiences a “pressing sensation” in the temples.
- Sharp pain in the frontal part of the skull is a sign of sinusitis and sinusitis.
- Infectious diseases can also cause headaches during exercise.
- Drinking strong coffee , alcoholic or energy drinks before intense physical activity can also trigger the problem under study.
- Inflammation of the middle ear , otitis.
- There is also such a thing as a “ tension headache ” - it “signals” about banal overwork.
Additional reasons
The reasons are more general.
- regular stress;
- insomnia;
- overstrain of the neck muscles;
- taking painkillers and antispasmodics.
Headaches during intense physical activity may be accompanied by other symptoms:
- loss of consciousness;
- sudden jumps in blood pressure;
- painful sensations in the spine.
Treatment of headaches in the occipital region
Do not forget that any treatment should be prescribed by a doctor, especially if it concerns headaches in the back of the head, because there are many serious causes of such pain. Therefore, it is not worth diagnosing yourself and prescribing treatment. First of all, you need to contact a specialist who will determine the cause, prescribe a full examination, and based on its results, a course of treatment. Specialists who treat headaches: - neurologist - physiotherapist - traumatologist - massage therapist - chiropractor - doctor who conducts physical therapy.
Each doctor can offer his own treatment method, but do not forget that each individual disease requires an individual approach and careful selection of a course of treatment. For example, if pain in the back of the head occurs after physical strain, stress, or occipital neuralgia, then an excellent way to relieve discomfort is massage or special manual therapy.
But, if pain in the back of the head is caused by high arterial or intracranial pressure, then intense massage is strictly contraindicated. In this case, light self-massage locally will help relieve discomfort, that is, you need to massage the back of your head yourself.
But a method such as physical therapy is universal and can have a beneficial effect on all types of diseases. Physiotherapy treatment has proven itself to be effective in relieving headaches. Ultrasound or laser treatment in just a few sessions can remove the cause of headaches and eliminate such an unpleasant phenomenon forever. This method is very effective if the cause of pain in the back of the head is pressure or vascular disease.
Also, do not forget about drug treatment. This type of headache treatment is the most effective; it very quickly relieves the main symptom - pain in the back of the head and effectively fights the very cause of the pain. After taking a course of specially prescribed medications, the likelihood of pain reoccurring is very low. If you combine massage, physiotherapy and medication, the fight against pain in the back of the head will be even more effective and will sooner lead the body to a complete recovery. Each type of treatment must be prescribed by a qualified doctor, based on tests, examinations and examination.
Prevention and home remedies for getting rid of pain in the back of the head
If a headache localized to the occipital part after physical overexertion takes you by surprise, then its symptoms can be relieved in several simple ways: - Put aside all your work and lie down to rest. — Apply a warm compress to the back of your head and drink as many warm drinks as possible. Tea made from chamomile, mint or sage will have a calming effect and help relieve spasms. — Apply a cabbage leaf compress. It perfectly relieves pain and gives a cooling effect. - Do a self-massage of the occipital region. Massage the back of your head with light circular movements for three minutes. - Go out into the fresh air or ventilate the room. - Apply lemon peel to the back of your head. It relieves pain well, and its smell gives vigor. — You can rub peppermint oil into the back of your head or temples. It has a cooling effect. — In ancient times, people fought against headaches by drinking a glass of potato or currant juice.
To prevent headaches from occurring, you need to beware of factors that can cause them and carry out regular prevention: - Complete active and passive rest. It will give the body additional energy and strength. — Physical education will help saturate the brain with oxygen and add vigor. — Healthy sleep allows the nervous system and this body to rest. - Correct diet. Overeating or starvation should not be tolerated. They can cause headache attacks. - It is worth giving up alcohol, tobacco and coffee - all of this contributes to increased pain and can worsen your overall health. — An apartment or house should always be ventilated; the air should not stagnate. — It is worth taking care of humidifying the air in the room. As we can see, headache is a very common phenomenon and there are many reasons for its occurrence. If you experience regular headaches in the back of your head, you should definitely consult a doctor to find out the causes and prescribe a course of treatment.