Despite its external strength and security, the human brain is extremely vulnerable. The fact is that almost any sudden movement can cause injury. Since the brain is not rigidly fixed in the cranium, but seems to float in it, during sudden acceleration or deceleration it tries to shift, which quite often leads to rather painful contact with the bones of the skull.
In its mechanical essence, a brain injury is nothing more than a bruise against the wall of the skull. Thus, even a fall on the buttocks may well lead to brain injury.
The characteristic symptoms of a concussion are considered to be headache in combination with nausea and dizziness, short-term and possibly long-term loss of consciousness, after which retrograde amnesia is possible.
It is clear that in the absence of proper treatment, all this can lead to irreversible consequences.
Causes of head injuries in children
A healthy child is active, purposeful and curious. Children constantly try new things and persistently study the world around them. This is why they often find themselves in dangerous situations. Unattended children are at risk. Some of the most common causes of head injuries in children include:
- falling from a bicycle, skateboard, scooter;
- falling from a swing;
- children's fight;
- sport;
- falling from a height (tree, roof of a house);
- falling under the wheels of a car;
- in older children, a fall may be caused by drinking alcohol;
- hitting your head during a car accident.
Also, schoolchildren are injured as a result of experiments with loss of consciousness. Waves of children fainting, caused by deliberate rapid breathing and subsequent falling without memory, periodically pass through schools. Usually at this moment the experimenters are held by their peers, but it happens that they are not held. Try to find out if your son or daughter practices this. Explain why this is harmful.
A baby who has just begun to walk is also not immune from a concussion. Even an unsuccessful fall on your butt can cause damage to a fragile head. Infants also suffer traumatic brain injuries from falls from beds, changing tables, and strollers. In some cases, mothers are to blame, because... during swaddling, especially when using a washing machine as a table, they don’t think that they can’t be distracted for even a second: children twitch and fall at the same time.
Dr. Komarovsky : “A fundamental feature of children in the first year of life is the fact that the amount of fluid in the cranial cavity is much higher than that in older children and adults. The baby's brain is not rigidly closed in the cranium, since there are fontanelles, as well as pliable and movable sutures between the bones of the skull. This creates cushioning and reduces the risk from impacts to the head and head to some extent.”
On the one hand, the brain of a small child is well protected. It is placed in cerebral fluid, which absorbs shock. But the shock-absorbing capabilities are not enough if the blow is too strong or the fall was from a great height. In addition, in children, the back of the head protrudes more than in adults, the head is proportionally larger in relation to the body, the neck muscles are weak, and the skull bones are thinner. Therefore, children are more susceptible to head injuries and serious consequences as a result. So, for example, the force of an impact, at which an adult will only have an intracranial hematoma, can cause cerebral edema in a child.
Signs of a concussion in a child
A concussion is a mild form of traumatic brain injury (TBI) that occurs with impaired neurological function without tissue damage. A concussion can be combined with other types of TBI, most often with brain contusion.
Damage is divided into primary (concussion and/or bruise) and secondary (consequences that develop due to primary injury, for example, damage to brain tissue due to hypoxia, i.e. lack of oxygen). The task of doctors during treatment is to prevent the development of secondary injuries. It is they, and not the concussion itself, that is life-threatening.
You need to be careful with kids, because... they may not always be able to tell you about the fall. The situation is complicated by the fact that the symptoms of a concussion in a child have slightly different symptoms than in adults. Children rarely experience deep and prolonged fainting. Parents should be alarmed by the following indirect signs of a concussion or bruise:
- screaming and crying;
- defocus of the pupils, involuntary movements of the eyeballs;
- sudden vomiting and convulsions;
- pale skin and cold sweat;
- sleep disturbance;
- bleeding from the nose and ears;
- increase in body temperature for no apparent reason.
In infants under one year old, the following signs are added to the listed signs:
- the baby literally starts crying and cannot calm down (this is caused by pain in the head);
- there is pulsation in the area of the fontanel;
- vomiting (often confused with regurgitation);
- The baby suddenly begins to fall asleep and has a restless sleep.
Such signs may not be observed, but the child’s lethargy and lethargy will make you wary. This sign alone is enough to suspect a concussion or brain injury.
School-aged children are also not always willing or able to talk about the injury because short-term memory loss occurs after a fall. You can suspect a traumatic brain injury by incoherent and confused speech, unfocused gaze, complaints of nausea and headache.
Only a doctor can diagnose concussion (closed brain injury). Temperature is only an indirect sign, especially since it may not exist. Only a combination of symptoms will indicate injury. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion, you should not delay your visit to the clinic.
It is more difficult to differentiate between a concussion and a mild bruise in children: their symptoms are not as severe as in adults. Children are looked at dynamically, because otherwise it is almost impossible to make a correct diagnosis. The older the child, the brighter the symptoms, and therefore the differential diagnosis is easier.
Can a concussion be cured?
Regardless of the complexity of the injury, after receiving it, it is necessary to take the child to the hospital for a detailed examination. Moreover, it is recommended to take the small patient to the hospital as soon as possible after receiving the injury, since after some time the symptomatic picture will be blurred. In addition to this, it is also worth noting that injury can lead to serious types of consequences.
It is impossible to treat brain injury at home unless there are signs of external damage to the integrity of the skin. This sign indicates the seriousness of the injury, so parents should stop external bleeding (if any) and then take the baby to the hospital.
Does a child have a fever during a concussion?
With an uncomplicated concussion, cerebrospinal fluid, blood pressure and body temperature usually remain unchanged. As we said, this is a mild form of traumatic brain injury.
An increase in temperature after a head blow may be a sign of a brain contusion (a local blow that causes tissue damage). Fever is explained by a temporary malfunction of the brain's thermoregulation center, an inflammatory process and/or hematoma. Temperature during a “concussion” in children can also be a sign of cerebral edema.
Doctors conventionally distinguish three degrees of severity of closed head injury. Temperature in this case will be an indirect indicator.
- With a mild traumatic brain injury (concussion), the body temperature, as a rule, does not rise.
- An injury of moderate severity (it is advisable to talk not about a concussion, but about a bruise or a combination) causes a low-grade fever of 37 to 38 degrees for 3-5 days.
- Severe brain injury causes swelling, inflammation and other complications, driving the mercury into a dangerous range of 40-42 degrees. However, sometimes the condition is characterized by a low-grade fever of 37 to 38 degrees.
Treatment of concussion with fever in children
Regardless of the presence of fever, treatment for head trauma of any severity involves bed rest. To alleviate the child’s condition, the following conditions must be created:
- place it in a dark, cool room;
- regularly ventilate the room;
- remove irritating factors - TV, computer, etc.;
- do not play music or give books;
- ensure there is no stress.
If after a concussion the child’s temperature rises slightly, there is no need to bring it down. Higher temperatures are reduced gradually and only as prescribed by a doctor.
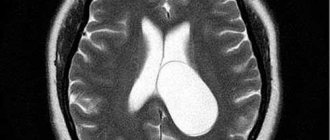
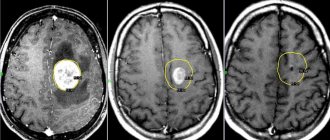
Before treatment, a number of examinations are carried out in a hospital setting: blood tests, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), X-rays, etc. The brain of infants is examined using neurosonography. The purpose of the study is to exclude the presence of hematomas at the site of the injury.
Lumbar puncture is a last resort and painful measure. Its task is to analyze cerebrospinal fluid. If blood is found in the fluid, even in small quantities, this indicates more severe brain damage caused by a contusion or subarachnoid hemorrhage. The puncture should be done only if indicated, because this is a traumatic and dangerous procedure.
The injured person is prescribed a number of drugs to stabilize the condition:
- tablets to relieve the gag reflex and nausea;
- diuretics to eliminate edema (prescribing such drugs without measuring spinal pressure is considered a mistake);
- sedatives to reduce anxiety and restlessness;
- nootropic drugs to improve blood circulation in the brain.
If pain is present, painkillers are prescribed. After 3-5 days, the child should begin taking medications to support heart function and B vitamins.
After an injury, it is advisable to monitor the patient in a hospital setting. The fact is that sometimes the first symptoms indicate a mild concussion, but later damage to brain tissue may appear. Therefore, it is advisable that recovery proceed under the supervision of doctors. They monitor the patient’s condition and promptly make decisions to change therapeutic tactics.
Treatment tactics
Regardless of whether the child has a fever during a concussion or not, bed rest is indicated for patients who have suffered a head injury. If the injury is mild, the patient may be sent home. It should be placed in a dark, cool room, and the room should be regularly ventilated. In case of a concussion, the patient is given a special regimen for at least three days:
- You can only get out of bed to go to the toilet.
- Anything spicy, pickled, as well as foods that can cause a gag reflex are excluded from the diet.
- It is forbidden to watch TV.
- You cannot play computer games or video games on your phone or tablet.
- Can't read.
- You can listen to music without headphones, in quiet mode.
The child should be protected from any emotional shocks: severe grief or joy can lead to his condition worsening.
With a concussion, there may be a temperature caused by the inflammatory process occurring in the body. But it must be reduced under the supervision of a doctor. After a head injury, the following medications are recommended:
- Diuretics - to eliminate tissue swelling and normalize cerebrospinal fluid circulation.
- Potassium-containing medications to support heart function.
- Nootropics - to strengthen brain vessels, restore neural connections.
- Sedatives - to eliminate feelings of anxiety, relieve nervous tension.
- Non-steroidal painkillers - to relieve headaches.
- Antiemetics – to eliminate the feeling of nausea.
During the recovery period, the child needs to take B vitamins, they help speed up regeneration.
p, blockquote 38,0,0,0,0 –> p, blockquote 39,0,0,0,1 –>
A slightly elevated temperature due to a concussion can last up to two weeks. There is no need to reduce it with medications. If the temperature rises higher than 37.5, you must consult a doctor again.
Neurologist, reflexologist, functional diagnostician
33 years of experience, highest category
Professional skills: Diagnosis and treatment of the peripheral nervous system, vascular and degenerative diseases of the central nervous system, treatment of headaches, relief of pain syndromes.
Consequences of temperature disturbances in children after head injury
Brain injury can last for a long time. The victim will become irritable, get tired quickly and often be capricious. Disturbances in sleep and short-term memory are often observed. Schoolchildren report decreased academic performance and headaches. Over time, these symptoms disappear with proper care and attention to the child. With a concussion we are talking about 1-2 months, and after a brain injury, unpleasant symptoms can be felt for another 2 years.
A high temperature after a concussion in a child can lead to a number of serious problems. One of the most dangerous diseases is epilepsy. Over time, psychosis may develop. Other consequences are:
- problems with the vestibular system;
- vegetative-vascular disorders;
- motion sickness in transport;
- irritability, anxiety, tearfulness;
- difficulty sleeping.
Children's brains are delicate and unpredictable. To eliminate the undesirable consequences of a concussion and brain injury, it is better to consult a doctor immediately. Strict adherence to bed rest and all accompanying recommendations contributes to a speedy full recovery. Serious consequences usually develop either as a result of severe traumatic brain injury or as a result of non-compliance with doctor's instructions.
Also read in a separate article on the website temperaturka.com what temperature indicates in case of head injury in adults.
Complications and consequences
After a concussion, the following disorders
:
If these signs persist for a long time, you need to take the child to the hospital and undergo examinations.
Speech and hearing impairments may also be present.
. Symptoms vary in each individual case and depend on how severe the damage is and which parts of the brain are affected.