A blow to the head or back of both an adult and a child can lead to damage to the skull and concussion. The main signs of the pathology are nausea, headache, dizziness. Some patients even develop a fever with a concussion. The reasons are the development of the inflammatory process or the displacement of brain structures responsible for thermoregulation.
What is a concussion?
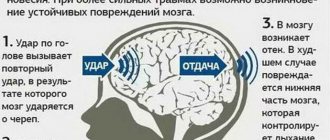
The brain of every person is in a “suspended state” in the cranium. Brain tissue does not come into contact with bones thanks to cerebral fluid, which keeps the hemispheres “afloat”. If the head hits something, the brain begins to rapidly move towards the bone tissue and hits the skull. In this case, a shift in brain structures occurs. Not only brain tissue is displaced, microcracks can occur in large vessels, capillaries rupture, and neuronal communication is disrupted.
In case of injury, a person may receive a concussion or bruise of the brain. Depending on the damage sustained, the patient may have a mild, moderate, or severe concussion of brain tissue.
The degrees are determined by the neurological signs exhibited, as well as by how quickly the symptoms of damage to brain tissue increase. Fever during a concussion can occur in moderate to severe stages of brain tissue damage.
Temperature in traumatic brain injury
With a traumatic brain injury, body temperature can rise and to what temperature?
A lot depends on the type and degree of TBI. With brain contusions or compression of the brain by hematomas, temperature rises to high levels are inevitable. Even with a decent concussion, low-grade fever is possible.
It's not so much about hematomas, but about small pinpoint hemorrhages in various structures of the brain. In addition, disruptions in the functioning of the thermoregulation center of the brain are possible.
After a head injury, the temperature is as unpredictable as the brain itself.
Traumatic brain injuryICD-10ICD-9DiseasesDBMedlinePluseMedicineMeSH
| S 06 06. |
| 800.0 800.0 — 801.9 801.9 , 803.0 803.0 — 804.9 804.9 , 850.0 850.0 — 854.1 854.1 |
| 5671 |
| 000028 |
| med/2820 neuro/153 neuro/153 ped/929 ped/929 |
| D001930 |
Traumatic brain injury
(TBI) is a complex of contact injuries (soft tissues of the face and head, skull bones and facial skeleton) and intracranial injuries (damage to the substance of the brain and its membranes), having a single mechanism and age of formation.
Classification [edit | edit code ]
Based on the severity of the injury, a distinction is made between mild, moderate and severe TBI [1]. The Glasgow Coma Scale is used to determine severity.
In this case, the patient receives from 3 to 15 points depending on the level of impairment of consciousness, which is assessed by eye opening, speech and motor reactions to stimuli [2].
Mild TBI is estimated at 13-15 points, moderate - at 9-12, severe - at 3-8 [3] [4] [5].
TBI is divided into closed and open. With an open craniocerebral injury, the skin and aponeurosis are damaged and the bottom of the wound is bone or deeper tissue.
Moreover, if the dura mater is damaged, then the open wound is considered penetrating. A special case of penetrating trauma is the leakage of cerebrospinal fluid from the nose or ear as a result of a fracture of the bones of the base of the skull.
In a closed head injury, the aponeurosis is not damaged, although the skin may be damaged.
Clinical forms of TBI:
- Fracture of the skull bones - Fractures are most often osseous-linear.
- A concussion is a trauma-induced impairment of neurological function. All symptoms that occur after a concussion usually disappear over time (within a few days - 7-10 days). Persistent symptoms are a sign of more serious brain damage. A concussion may or may not be accompanied by loss of consciousness. The main criteria for the severity of a concussion are the duration (from a few seconds to 5 (in some sources up to 20) minutes [6]) and the subsequent depth of loss of consciousness and amnesia. Nonspecific symptoms - nausea, vomiting, pale skin, cardiac dysfunction. Neurological examination is usually normal, but somatic symptoms (headache), physical signs (loss of consciousness, amnesia), behavioral changes, cognitive impairment, or sleep disturbance may be present. Some of these effects may last for months after the injury.
- Brain contusion: mild, moderate and severe (clinically). A brain contusion manifests itself as a bruised wound to the brain tissue. A blow-counter-impact contusion is caused when the brain hits the wall of the skull at the site of direct impact of an external object on the head, receives one contusion wound and then the contused wound is inflicted on the opposite side of the brain with a sharp slowdown in the movement of brain tissue. Clinical manifestations depend on the location of the injury and include changes in mental status, increased drowsiness, confusion, and anxious agitation. Small intraparenchymal hemorrhages and swelling of the surrounding tissue can often be detected on computed tomography.
- Diffuse axonal injury - severe damage to the axonal white matter of the brain as a result of shearing forces caused by strong acceleration or deceleration of the brain
- Brain compression
- Intracranial hemorrhage (bleeding in the cranial cavity: Subarachnoid hemorrhage, Subdural hematoma, Epidural hematoma, Intracerebral hemorrhage, Ventricular hemorrhage)
Combination [edit | edit code ]
At the same time, various combinations of types of traumatic brain injury can be observed: bruise and compression by a hematoma, bruise and subarachnoid hemorrhage, diffuse axonal damage and bruise, brain contusion with compression by a hematoma and subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Symptoms[edit | edit code ]
- damage to the cranial nerves indicates compression and contusion of the brain.
- focal brain lesions indicate damage to a certain area of the brain; they occur due to a bruise or compression of the brain.
- stem symptoms are a sign of compression and contusion of the brain.
- meningeal symptoms - their presence indicates the presence of a brain contusion or subarachnoid hemorrhage. A few days after the injury may be a sign of developed meningitis.
Clinical picture [7] [edit | edit code ]
- external hematomas, tissue ruptures
- pallor;
- vomiting, nausea;
- irritability;
- lethargy, drowsiness;
- weakness;
- paresthesia;
- headache;
- disturbance of consciousness - loss of consciousness, somnolence, stupor, coma, amnesia, confusion;
- neurological signs - convulsions, ataxia;
- the main indicators of the body's condition may change - deep or arrhythmic breathing, hypertension, bradycardia - which may indicate increased intracranial pressure
Pathophysiology in pediatrics [7] [edit | edit code ]
A protruding nape, increased head-to-body proportion, weak neck muscles, and a higher center of gravity predispose children to head injuries.
Thinner skull bones and a less myelinated brain make head injuries more severe and predisposed to intraparenchymal injury.
Therefore, when focal intracranial hematoma is more often observed in an adult, the likelihood of diffuse cerebral edema increases in a child.
In a normal state, blood circulation is maintained at a constant level through autoregulation (See Hemodynamics#Brain).
In severe traumatic brain injury, autoregulation is disrupted and blood flow to the brain begins to be determined by cerebral perfusion pressure, which is equal to mean arterial pressure minus intracranial pressure.
Thus, cerebral blood flow is impaired if the mean arterial pressure is too low (with hypotension) or if the intracranial pressure is too high (with cerebral edema).
Some approaches to the care of children with traumatic brain injury emphasize maintaining mean arterial pressure and lowering intracranial pressure, but control of cerebral perfusion pressure in the setting of injury may be difficult. Children have greater recovery potential than adults, especially newborns and young children whose open cranial sutures and fontanel allow the skull to expand when swelling or bleeding occurs.
Source: https://ogomeopatii.ru/temperatura-pri-cherepno-mozgovoj-travme/
What can cause a concussion in an adult?
An adult is susceptible to domestic and work-related injuries. A concussion can occur after:
- Falls from great heights.
- Hitting the head, neck, back with any object (brick, stone, bat).
- A strong blow to the head against a pole or wall.
- Car accident due to sudden braking (whiplash).
Athletes in contact sports are susceptible to concussions: boxers, basketball players, rugby players.
How do children get injured?
In children, head injuries quite often lead to concussions. And even babies are not immune to such brain damage. Children under one year old fall from strollers, changing tables, and beds. The reason is not only the oversight or carelessness of parents. Sometimes mothers and fathers cannot objectively assess the baby’s activity level; they calmly leave him on an open surface, confident that the baby will not be able to turn around or crawl.
Typically, fever during a concussion in children under one year of age is not a consequence of injury. Often the reason for this phenomenon is that literally all babies of this age are teething. Violation of the integrity of the gums leads to inflammation of the mucous membrane and a rise in temperature.
Even more injuries occur in children who are just starting to walk. Even a very mother will not be able to protect her child from collisions with tables, doors and corners of cabinets. In addition, babies have a shifted center of gravity, so when they begin to learn to walk, they fall and usually hit their heads, since they do not yet know how to put their hands up or group themselves.
In preschool age, children receive head injuries when falling from slides, scooters, or bicycles. Among schoolchildren, the percentage of concussions is even higher. The reason is increased mobility, inability to assess one’s capabilities. In children who have suffered a concussion, the temperature does not always rise, and this may go unnoticed by parents, since not all children talk about the incidents at home. Schoolchildren suffer head injuries:
- In physical education lessons when performing somersaults and jumps.
- During recess: if you hit the wall of the person in front of you with all your might, the displacement of your brain structures is guaranteed.
- At home - when jumping out of bed, on stairwells.
- In street fights.
Childhood injuries are dangerous because the child may consider the injury not significant and hide the fight for fear of being punished. Gradually, the victim’s condition worsens, because the child does not know that he cannot move, watch TV, and must remain in bed. As a result, severe cerebral edema develops, the student loses consciousness, and may fall into a coma.
Treatment methods
If the temperature rises above 380, then it must be brought down. It is recommended to ensure complete rest for the patient and call an ambulance. Making independent decisions about the treatment of such a problem is strictly prohibited, as this can lead to the development of serious consequences.
Therapy for this category of patients consists of treating the main problem – the traumatic brain injury itself. For treatment you need:
- keep complete peace
- protect from bright light and noise,
- regularly ventilate the room,
- It is forbidden to read books, watch TV or sit in front of a computer screen,
- exclude fried, spicy and fatty foods from the diet,
- get rid of stress and nervous tension.
If a traumatic brain injury of the second or third degree of severity is diagnosed, then the patient requires hospitalization. If there is a strong increase in body temperature, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic drugs.
Other medications used in the complex treatment of concussions include:
- nootropics that help strengthen the walls of blood vessels and neutron bonds,
- diuretics remove excess fluid from the body and prevent swelling of the brain,
- antiemetics and non-steroidal drugs dull the gag reflex, relieve cramps in the head and dizziness.
If the temperature after an injury lasts more than 3 days, then you should definitely seek medical help from a doctor who will adjust the treatment regimen.
Signs of a concussion in an adult
In case of a severe concussion, it is necessary to provide first aid to the patient even before the arrival of doctors. Can there be a fever with a concussion? In the first minutes after injury, such a symptom does not appear. Characteristic signs of a concussion:
- Darkening in the eyes.
- Involuntary twitching of the eyeballs.
- Nausea.
- When moving, turning the head - dizziness.
- Noise in ears.
- Arrhythmia, tachycardia.
- Drowsiness.
- Numbness on one side of the face, loss of sensitivity in the fingers.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Fainting.
The victim may complain of short-term memory loss, for example, he may not remember under what circumstances the injury was received.
How does a concussion manifest in a child?
Infants and preschool children rarely experience loss of consciousness after injury. They cannot tell anything at all about a head injury, and parents who did not see that their child fell should be guided by warning signs. The temperature during a concussion in a child, as in an adult, immediately after the injury remains stable. Other symptoms of brain damage are noted. In a baby:
- Brain scream caused by severe pain in the head (incessant screaming, the baby starts crying).
- The baby's gaze does not focus on one point.
- A strong pulsation of the fontanel is noticeable.
- The baby breaks into a sweat, his skin turns pale.
- The baby spits up profusely like a fountain.
- Involuntary convulsions appear.
- The baby suddenly falls asleep, sleeps nervously, often jumps up, or, conversely, cannot be woken up.
Older children experience similar symptoms, but they may also complain of nausea, vomiting, severe headache, and a feeling of heaviness in the head. The injured child cannot tell where he was injured, and his speech may be incoherent.
Although the temperature during a concussion in children may rise only after some time, if the numbers exceed 37.2 and a combination of the above symptoms (even two of them) appears, you should immediately consult a doctor.
How to treat childhood head concussion?
In any case, the baby should be sent to the hospital immediately after receiving an injury for examination by a doctor. It is better to call a neurologist right away, because after a couple of days the symptomatic picture becomes blurred and improvement occurs. But this only seems, in fact, an untreated injury can lead to serious consequences.
But it is not so easy to identify a concussion in a child, because it is often confused with an ordinary bruise, which does not lead to serious consequences. So you should show it to a doctor, let a specialist deal with such injuries.
Is it possible to protect your child from a concussion?
You should devote your time to your child if you want to avoid harming the health of your children.
- You should not leave, especially a small child, unattended.
- If you have a baby at the age when he begins to explore his world, you should make his movement around the apartment safe, so that later you do not constantly take him to doctors and do not treat the consequences of the injury.
- Do not allow children to ride without a helmet, regardless of whether it is rollerblading, a bicycle, a skateboard or something else. After all, after a bruise, if the baby was not wearing a helmet, unpleasant symptoms may occur.
What is the connection between rising body temperature and brain damage?
After some time, the victim's body temperature may rise. Neurologists note that numbers on a thermometer in the range of 37.0-37.5 are normal. The reason is that with a concussion, a person’s thermoregulation may be disrupted due to a displacement of the brain structures responsible for these functions. It usually takes at least a week for neuron connections to return to normal and the functioning of thermoregulatory centers to improve.
Another reason for fever is the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the victim’s body. It can occur even earlier, before the injury. The temperature during a concussion in a child who has had a cold rises already on the day of injury and can reach 38.5.
Sometimes the victim's fever is accompanied by a runny nose, and he complains of a headache. Symptoms similar to a cold can be caused by swelling of the brain.
A rise in temperature should alert parents. Fever may be a sign that the brain has been significantly damaged, there are vascular ruptures, and an inflammatory process has begun in the medulla. A concussion can provoke the development of meningitis - inflammation of the meninges, accompanied by a rise in temperature to 40-42 degrees.
What is a head injury: decoding, temperature during injury, periods and treatment, consequences
Quite a common occurrence in our lives. CTBI occurs in 30-40% of cases of human injury.
There are several types of closed traumatic brain injury:
A concussion is a closed traumatic brain injury of a mechanical type, which is caused by stretching of the nerve limbs of the brain, without affecting vascular disorders and serious changes in the structure of the brain. In this case, the bone of the skull and soft tissues are not affected.
Also, with SGM, secondary signs of manifestation are sometimes revealed:
- Congestion in the veins;
- Large blood flow to the membranes of the brain;
- Tumor of the space between brain cells;
- The release of blood elements through the walls of capillaries;
From medical practice statistics it is known that concussion is found in 65% of people who have a head injury.
First aid for concussion
If at least one symptom appears, you must call a doctor.
But, before her arrival you must:
- Carefully examine the victim and if there are skin or bloody wounds, they should be treated and bandaged.
- It has long been known to everyone that a cold thing is applied to the site of bruises; it could be something from the freezer or a cold spoon.
- After this, it is strictly necessary to give the patient rest.
- And it is imperative to remember that the victim must not make sudden movements, consume food or water, rise abruptly from a lying position, move around or take any medications.
- If a person is unconscious, then he must be placed on his right side and his left limbs bent at an angle of 90 degrees.
- Then you need to provide access to fresh air (open a window) and place a pillow or any rolled material of medium hardness under your head.
- In case of vomiting, it is necessary to lower the patient's head down so that he does not choke.
- injured patient should never be hit on the cheeks or on the head at all. Also, under no circumstances should it be planted or lifted.
- During aid , special attention should be paid to the pulse and breathing of the injured person.
- It is undesirable to transport the patient to the hospital without examination by doctors.
Severity
GM concussion is divided into three degrees of severity:
- A mild degree is accompanied by a short-term loss of consciousness (about 5-7 minutes) and vomiting;
- The average degree of concussion is characterized by fainting lasting up to 15 minutes. In addition, partial memory loss, weakness, frequent vomiting, constant nausea, slow heart rate, and increased sweating may occur;
- A complex degree makes itself felt by prolonged loss of consciousness, pale skin, pressure surges, slow pulse and even seizures. With a complex degree, constant monitoring of the patient’s vital functionality is required;
Regardless of the degree, a secondary symptom complex may appear:
- acrocyanosis;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- weakening;
- painful eye movements.
Neurological symptoms include:
- sleep disorder;
- mood swings;
- constant irritability.
There is an understanding among doctors that a person with a mild concussion quickly comes to his senses and gets better. But, the victim with a moderate or complex degree requires long-term treatment and monitoring.
Signs
So, like any disease, concussion has its own symptoms:
- Double vision;
- Noise effects in the ears;
- Broken capillaries in the nose;
- Stun;
- Retrograde amnesia;
- Staggering when walking;
- Loss of spatial orientation;
- Dulling of some reflexes;
- Lethargy;
- Increased restlessness;
- Psychomotor agitation;
- disorders ;
- Manifestation of speech defects, unclearness;
- Drowsiness.
Sometimes severe traumatic brain injury At this moment, the patient even suspects the seriousness of the injury, since there are no identical organisms and therefore the disease manifests itself in each person in its own way.
If the slightest manifestation of symptoms is detected, it is recommended to immediately consult a specialist doctor. If you slow down, there is a risk of injury complications.
Periods of traumatic brain injury
During the practice of studying closed traumatic brain injuries, three main periods of its course have emerged:
- Period of acute manifestation. At this time, the process of the body’s reaction to brain damage and the process of defense reaction interact with each other. Simply put, it is the body’s natural process of protecting itself from damage and its side processes.
Among all types of traumatic brain injury, each one manifests itself differently:
- Concussion – about 2 weeks;
- Mild bruise – about 1 month;
- Average bruise – about 5 weeks;
- Severe bruise – about 6 weeks;
- Diffuse axonal damage – from 2 to 4 months;
- GM compression – within 3-10 weeks;
- During the interval period, the body tries to actively restore internal areas of damage, and adaptive processes develop in the central nervous system. This period lasts from 2 to 6 months, depending on the severity of the injury.
- The most recent period is called remote . During this period, active recovery ends. The body tries to balance the shifts that have occurred due to injury. Under unfavorable circumstances, antibodies against healthy tissue cells may appear.
In old age there is a risk of atrophic processes. This period, at best, can last about 2 years. In the worst case, it may not end at all. It depends on the severity and correctness of treatment.
Temperature during traumatic brain injury
Usually, in mild form , body temperature remains normal. But, during the moderate form of injury, subarachnoid hemorrhage occurs, which causes the body temperature to rise to 39-40 on the thermometer.
In a severe form of injury , it can rise to 41-42 degrees and remain at this level for a long time until the cerebrospinal fluid into which the blood has entered is restored.
But, since this is a very long wait, measures must be taken to eliminate the high temperature, which in this case is called hyperthermia.
The temperature is always reduced with medication, but only with the prescription of the attending physician.
High temperature can disrupt the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to the brain tissues, this is due to a violation of the water-salt balance.
There are also situations due to injury when damage is caused to the caudal part of the hypothalamus, which, in turn, causes a strong drop in temperature, and as a result, weakness.
Diagnosis
To diagnose a closed craniocerebral injury, doctors need to establish a clinical connection between the fact of a head injury and the clinical and morphological picture, which is confirmed by an X-ray of the head.
In addition, for complete confirmation, an additional computed tomography (MRI) is performed.
If, as a result of these actions, there is reason to think that this is SHM , then he needs to undergo echoencephaloscopy to exclude the appearance of a developing hematoma.
The following factors may indicate the ease of SGM:
- Absence of breathing and blood supply pathologies;
- well ;
- No neurological symptoms;
- Absence of meningeal symptom complex;
To make an accurate diagnosis, inpatient monitoring of the victim is necessary for a week after the injury. This condition is necessary due to the fact that the systematization of a sign can increase or be replenished with other symptoms. After a week, a final examination is performed and a verdict on treatment is made.
Treatment
Despite the severity of the case, patients with a closed craniocerebral injury must be strictly registered for inpatient treatment at an outpatient clinic.
This need arose due to the fact that the destructive process can develop within 3-5 weeks . The minimum period of hospitalization is 2 weeks .
In cases with complications, a person may lose ability to work for 1 month .
The patient's recovery occurs under the following treatment conditions:
- Bed rest;
- Use of painkillers;
- Taking sedative medications;
- Taking sleeping pills;
Various appropriate therapies may be prescribed to stimulate the healing process. Often these are metabolic and vascular therapies . If the patient is tolerant of the disease, the patient may be discharged after a week, but this happens in rare cases. Previously, we talked in detail about how long it takes to get a concussion.
Usually, following the regimen and course of treatment, there are few symptoms left, only in isolated cases. post-traumatic neurosis may appear , which contributes to the appearance of headaches, noises, dizziness and other general symptoms.
Under such conditions, doctors can prescribe vitamin complexes, sedatives and balneotherapy. Elimination of residual manifestations can last from 3 months to 1 year .
When releasing patients to continue treatment at home , doctors prescribe constant bed rest and healthy sleep.
Various decoctions of appropriate herbs are allowed to be drunk as sedatives:
- motherwort;
- peppermint;
- Melissa;
- mistletoe and others.
It is also mandatory to adhere to a strict diet . In case of traumatic brain injury, fried foods and table salt are excluded from the diet.
Medical specialists recommend minimizing all mental work during this period.
How to provide first aid?
After a head injury, a child must be seen by a doctor. The victim must be laid on his side on a horizontal surface, with his head turned towards the ground, his leg and arm slightly bent. Cold and an ice bag are applied to the site of impact. If there are open wounds, they are treated along the edges with hydrogen peroxide.
If it is clear from the symptoms that the child has suffered a concussion, the temperature should not be brought down with medication. In case of a head injury, it is generally not advisable to give the victim any pills until the doctors arrive.
The patient should not be allowed to sleep. If the child is conscious, talk, ask how he feels, clarify the details of the incident.
Diagnostics
In a hospital setting, it is determined how severe the patient’s injuries were. To clarify the diagnosis, you should go through:
- MRI and CT scan of the head. Helps assess the condition of soft tissues and detect displacement of brain structures.
- Neurosonography (for children under one year old with an open fontanel). Allows you to identify ruptures of blood vessels and the presence of hematomas.
- X-ray of the head. It is carried out in order to determine whether there are fractures of the skull bones.
If the victim has increased intracranial pressure or a very high temperature, he undergoes a lumbar puncture (measuring the pressure of cerebral fluid in the spinal column) to exclude the development of meningitis.
Treatment of concussion with fever in children
The principles of therapy for mild or moderate hyperthermia due to TBI are the same for adults and children. In the case of younger patients, treatment is best done in a hospital setting so that health workers have the opportunity to monitor the situation.
In the case of children, treatment is best carried out in a hospital setting.
Treatment of concussion, which is accompanied by fever:
- compliance with the regime - rest, bed rest, diet, stress prevention, exclusion of physical and mental stress, protection from irritants;
- taking diuretics to help prevent and eliminate cerebral edema;
- inclusion of NSAIDs in drug therapy in case of severe headaches or suspected inflammation;
- the use of sedatives and nootropics to relax the patient, accelerate the restoration of damaged neural connections, and improve vascular function;
- taking vitamin and mineral complexes to trigger the regeneration of the nervous system, maintain the heart muscle (potassium supplements), and strengthen the immune system.