What pills to take for a concussion and how long does it take to fully recover, how to provide first aid - these are the first questions for victims with a head injury. Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is one of the most common injuries that a large number of people face every day.
Treating a concussion at home is strictly not recommended. Taking medications without a prescription from a qualified specialist can cause complications and lead to serious consequences, which can then be very difficult, and in some cases even impossible, to reverse. The first thing to do if you have a concussion is to seek medical help. The sooner the patient is hospitalized in the hospital, the sooner and more effectively he can recover.
First aid
The cause of a concussion can be any blow to the head, or even an unfortunate fall on the buttocks. Such damage can occur both at work and at home or during exercise in the gym. When an accident occurs, it is very important to provide first aid to the victim and immediately take him to the hospital for further treatment.
A concussion is characterized by symptoms that can manifest themselves both immediately and after some time:
- Headache;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Dizziness;
- Impaired coordination of movements;
- Partial loss of vision;
- Hearing impairment.
If the injured person is unconscious, the first thing to do is call an ambulance. Upon the arrival of doctors, it is necessary to accurately describe all the details of the incident, since in order to prescribe the correct medications it is necessary to know all the details of what happened.
You should also indicate the presence of psychological illnesses in the patient and information about the use of alcohol, drugs or other similar drugs. Subsequently, upon arrival at the hospital, the patient will be prescribed diagnostic procedures, the optimal course of treatment and suitable pills for concussions. If first aid is provided in a timely manner, the consequences can be avoided and you will soon return to your previous lifestyle.
The advisability of taking diuretics
Taking diuretics is advisable in cases where arterial hypertension is observed or there is a risk of cerebral edema. In this case, removing excess fluid from body tissues will be very helpful and may even save the patient’s life.
What medicine to take for a concussion, provided that a diuretic effect is needed? The two most popular drugs, whose effectiveness has been tested over the years, are Furoseimd and Diacarb. Helps remove fluid from brain tissue during injuries, hematomas, and intracranial pressure.
In some cases, traumatologists and neurologists prescribe Diacarb even to children with similar symptoms:
- headaches and dizziness caused by injuries or ICP;
- nausea and swelling after head injury;
- loss of consciousness and suspected cerebral edema.
There is no point in using diuretics on your own after receiving a head injury - this can cause even more harm to yourself by disrupting the water-salt balance of the body.
Medicines
The first medications prescribed to a patient are neuroprotectors. They normalize the metabolic rate in brain tissue, which promotes proper nutrition of cells and their restoration. Another function of neuroprotectors is to eliminate pathological changes in neurons and protect them from insufficient blood supply. At the initial stage of treatment, the following pills for concussions are often prescribed:
- Semax;
- Ceraxon;
- piracetam;
- picamilon;
- Cerebrolysin;
- encephabol;
- nootropil;
- Lucetam;
- glycine;
- alvesin;
- methionine
The patient may also be prescribed painkillers for a concussion:
- sedalgin;
- pentalgin;
- analgin;
- baralgin;
- maxigan.
In case of mood swings, the patient may also be prescribed sedatives:
- carvalol;
- valocordin;
- valerian;
- motherwort.
The attending physician determines which medications to prescribe for a concussion based on the type and severity of the injury, the patient’s age and state of health. In some cases, magnesium is prescribed. In adults, the recovery period takes longer than in children. With age, the body's supply of its own vitamins and cells that promote rapid regeneration decreases.
Dehydrants can also be used during treatment after a concussion. These medications help get rid of excess water in the body, which helps relieve brain swelling. The most commonly used drug is called Diacarb. Diuretic medications are also used, which also remove excess fluid from the victim’s body:
- arifon;
- lasix;
- aldactone;
- veroshpiron;
- furosemide (tablets or injections);
- hypothiazide;
- indap;
- indapamide.
Among various remedies, for such damage, Mexidol is also prescribed to improve blood circulation. In order for medications for concussions to show the expected results and not cause side effects, it is important to warn the doctor in advance about possible allergies to certain drugs, if any.
The final stage of the treatment course of therapy involves vasotropic drugs. They act on the walls of blood vessels, strengthening them and making them more elastic. This prevents pressure from a possible hematoma. They also eliminate vascular spasm, improve the movement of oxygen and red blood cells through the circulatory system and stabilize metabolism in the walls of blood vessels. Based on the situation, doctors may prescribe a combination of medications. In this case, patients drink both vasotropic and nootropic drugs at the same time.
Concussion in children
The clinical picture of a functional disorder is determined by the age factor. With a mild concussion in infants and children under seven years of age, changes in impaired consciousness do not appear. Only observed:
- Paleness of the face.
- Rapid breathing and pulse.
- General weakness of the body.
- Drowsiness.
Infants have disturbed sleep for 2-3 days, exhibit restlessness, regurgitation during feeding, and other behavioral disorders. At this age, children cannot explain their own condition, so parents should be careful. Children are especially prone to such injuries due to their hyperactivity. Impaired coordination (for example, a child ate independently with a spoon, but at some point was unable to pick it up normally) is a reason to contact a neurologist. Often in children, concussions are asymptomatic.
If a child receives any head injury, it is important to immediately consult a doctor, at least for preventive and advisory purposes. If this is not done, the consequences can be hidden and severe. These include:
- disruption of cellular metabolism;
- microscopic tears in the gray matter in the cerebrospinal fluid;
- damage to blood vessels;
- dysfunction of transport of oxygen, minerals and nutrients
- hemorrhage, etc.
Any medications for a concussion should be given to a child only according to the decision of a neurologist and strictly in the indicated doses.
Vitamins
When treating a concussion, you need to take the vitamins and minerals necessary for the body. It is recommended to drink the following drugs for concussion:
- folic acid;
- phosphorus;
- magnesium;
- vitamin B.
The appointment must be carried out strictly according to the schedule prescribed by the attending physician. It is Pyridoxine (vitamin B) that very actively promotes the metabolism of amino acids, enzymes and helps the synthesis of neurotransmitters. Vitamins allow magnesium to be better absorbed in the intestines and transferred to the necessary cells. The combination of all components has a noticeable effect on the rapid restoration of damaged brain cells, thanks to which the patient recovers much faster.
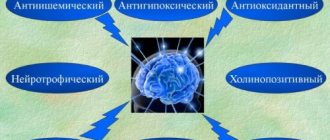
Mexidol mechanism of action
The mechanism of action of Mexidol is due to its antioxidant and membrane protective properties.
The drug reduces the formation of peroxide substances that destroy cell membranes, which leads to increased oxygen delivery to tissues and preservation of tissue structures.
Mexidol activates the following enzymes: superoxide dismutase, calcium independent phosphodiesterase, acetylcholinesterase. This improves the transmission of nerve impulses at synapses and binding to ligands. Mexidol increases the formation of neurotransmitters, in particular dopamine.
The drug triggers glycolytic reactions and ensures the oxidative processes of the Krebs cycle during tissue hypoxia, which supports the formation of ATP and creatine phosphate at the required level.
Dosage, release forms and manufacturers
The drug is produced in two dosage forms: tablets and injections for intramuscular or intravenous administration. Highlight:
- packs of 5 ampoules with 5 ml of the drug;
- packs of 5 ampoules with 10 ml of product;
- tablets of 125 mg, produced either in blisters of 10 pieces, or in plastic jars of 90 pieces.
Several pharmaceutical companies are involved in the release of Mexidol on the domestic market: Pharmasoft, ASI-pharma, Ellara, etc. The medication is also separately produced for use in veterinary practice, but it is absolutely not suitable for people!
Further prognosis for concussion
Favorable long-term results are observed in 89-90% of victims. For those who were hospitalized immediately after the injury and followed the doctor's instructions, complications are less than 2%.
Hospital patients are more responsible in following the doctor’s prescriptions and recommendations, while patients who refuse to be admitted to a hospital often violate the treatment program and do not comply with the regimen, especially against the backdrop of rapid improvement in well-being. Therefore, they have a higher risk of developing complications.
Instructions for use
Instructions for use of Mexidol tablets:
- The drug is taken orally, 3 times every 24 hours, 125-250 mg.
- The maximum daily dose is 800 mg (that is, 6 tablets).
- Duration of treatment with Mexidol: from two to six weeks.
- When relieving alcohol withdrawal, treatment lasts from five to seven days. When stopping treatment, the dose of the drug is gradually reduced over 2-3 days.
- The initial dose of Mexidol: 125-250 mg (that is, 1-2 tablets) 1, 2 times a day, during treatment the dose is gradually increased until the therapeutic effect is fully sufficient.
- For coronary heart disease, the indications for a course of treatment range from one and a half to two months.
For a second course of treatment with Mexidol, the best time is spring and autumn.
Mexidol effect
The main therapeutic effect of Mexidol is the protection of tissues from toxic forms of oxygen. Ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate stabilizes cell membranes by suppressing oxidative processes. As a result, cells retain their structure under conditions of prolonged pathological exposure. Improving membrane transport allows normalizing the functions of brain neurons.
All neurons are isolated by a special membrane that protects the internal structures of the cell from negative external factors.
The result of treatment with the drug is the following effects:
- increasing the body's resistance to stress;
- improvement of memory, attentiveness;
- reduction in the number and severity of seizures;
- normalization of cholesterol levels in the blood;
- increasing resistance to aggressive factors;
- improving metabolism in brain cells;
- normalization of cerebral circulation;
- optimization of blood properties, blood thinning;
- reduction of the phenomena of general poisoning.
"Mexidol" in complex therapy for myocardial infarction improved its collateral circulation in the ischemic zone and increased the resistance of myocardial cells to hypoxia. This multifaceted action of the drug has allowed it to be prescribed for a variety of indications in the clinic of internal medicine.
Contraindications and side effects
Like many domestic “broad-acting” drugs, contraindications exist because the drug has simply not been studied in certain situations, and this is written directly in the instructions. In relation to Mexidol, these are conditions such as:
- pregnancy;
- breastfeeding period;
- childhood.
Also, the drug cannot be used for various “acute failures” of organs associated with the metabolism and excretion of the drug (renal, liver).
Side effects are rare. This may be nausea, headache, dry mouth, drowsiness or, conversely, insomnia. Even more rarely, an allergic reaction occurs.