How exactly does pinching occur?
Everyday stress and physical labor leave a certain imprint on the state of the bone structure. Up to a certain point, the patient may not notice the body’s signals about the destruction of the vertebrae, but in a certain situation the pain will become stronger and more painful.
In this situation, the patient needs urgent medical help, since it is impossible to make a diagnosis on your own. As the pain intensifies, degenerative processes may develop in the back or neck over several months.
It is believed that it is the chest area that is most susceptible to pinching. During this process, the roots are compressed by the discs, which provokes severe pain. The sensations become so unbearable that the patient may notice a violation of breathing functions.
For reference! Most often, people between forty and sixty years old suffer from this pathology.
Why is it formed
Provoking causes should be sought in the individual structural characteristics of the body and the patient’s lifestyle. Pinched heart muscle cannot manifest itself without concomitant pathologies, so if this symptom occurs, you need to undergo a detailed examination.
The main reasons for the formation of the disease include:
- exacerbation of neuralgia of the thoracic spine due to physical labor,
- the formation of intercostal neuralgia due to frequent lifting of heavy objects,
- natural age-related changes,
- wear and tear of bones and cartilage tissue,
- osteochondrosis,
- displacement of discs due to compression of nerve fibers,
- swelling of the protrusion of the intervertebral disc,
- intervertebral hernia,
- protrusion of the intervertebral disc between the vertebrae,
- congenital pathologies,
- acquired postural disorders,
- scoliosis,
- muscle hypertonicity.
In addition, the risk group includes athletes who expose their back to prolonged and heavy loads. In the future, inflamed muscles will provoke the formation of severe pain.
Also, pinched intervertebral disc can occur against the background of the development of benign and malignant tumors. The growth of the tumor becomes the main cause of compression of nearby tissues.
Chest pain often occurs due to prolonged depression, stress, or some other mental disorder.
A sedentary lifestyle and a sedentary profession can provoke the formation of an unpleasant sensation.
If you have any diseases in the heart or blood vessels, it is important to monitor your overall health. Diseases in this area can cause not only pinched nerves, but also other complications. The process is possible due to impaired blood circulation between the vertebrae. Lack of nutrition in the spine leads to accelerated tissue degeneration.
Pinched nerve in the thoracic region: symptoms, treatment, prevention
Home » Diseases » Neuralgia » Pinched nerve in the thoracic region: symptoms, treatment, prevention
885 0
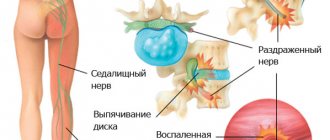
The most susceptible to nerve entrapment are the cervical and lumbar spine. In the thoracic region, nerve pinching occurs much less frequently due to its inactivity. This occurs in people aged 30 years and older.
The fact is that with age, a person’s bones wear out and become thinner. Therefore, the intercostal nerve roots, which are located between the intervertebral discs, may become compressed by these discs or vertebral bodies.
This pinching is accompanied by a sharp aching pain in the chest and back. The pain may get worse when you make any movement or try to sneeze or cough.
What causes infringement?
The main cause of pinched thoracic nerve is considered to be intercostal neuralgia. Its aggravation can be caused by too sudden a movement, lifting an unbearable weight, or incorrect rotation of the body.
Nerve entrapment in the thoracic region and intercostal neuralgia are often confused with cardiovascular diseases due to similar symptoms. But with neuralgia, unlike other diseases, it is not possible to get rid of pain with the help of conventional analgesics. To determine an accurate diagnosis, you need to see a doctor and undergo the necessary examinations.
Other reasons why chest pain often occurs:
- The presence of a disease such as osteochondrosis can also cause a pinched nerve. With osteochondrosis, the vertebrae are displaced and the nerve is pinched. Disc protrusion or intervertebral hernia may occur.
- Congenital or acquired abnormalities in the structure and function of the spine can cause nerve compression. One example is a disease such as scoliosis.
- Hypertonicity of the back muscles. Usually occurs in people who play sports or undergo heavy physical activity. The muscles spasm and pinch the nerve endings.
- Tumor and inflammation of the spinal column caused by various factors can also cause pinching of the thoracic nerve.
- People with an unstable psyche, subject to frequent stress and depression, often have the problem of pinched nerves.
Older people and athletes are most susceptible to pinched nerves. Or people whose work requires heavy physical activity. And also people whose lifestyle, on the contrary, is sedentary.
Infringement of the nerve of the thoracic spine occurs only in mature and elderly people. Infants are not susceptible to pinched nerves in this part of the spine.
Most often, due to birth injuries or improper handling of a newborn, a pinched nerve in infants occurs in the cervical spine.
What it looks and feels like
ATTENTION!
Orthopedist Dikul: “Penny product No. 1 for restoring normal blood supply to joints. Your back and joints will be the same as when you were 18 years old, just apply it once a day..." Read more »
When a nerve is pinched in the chest, the following symptoms are observed:
- pain and discomfort appears in the spine in the chest area;
- the pain worsens when trying to sneeze or cough;
- in some cases, fainting and memory loss are possible;
- blood pressure is unstable;
- possible stomach pain, reminiscent of gastritis or ulcer pain;
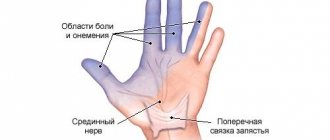
- numbness in the hands or wrists;
- the pain is felt even when breathing, and intensifies when inhaling;
- possible loss of sensitivity in the skin of the back;
- weakness and lethargy, reluctance to live an active life;
- stiffness and pain in the chest area that does not go away with the use of painkillers.
How to distinguish from heart problems and other diseases
Very often, a pinched thoracic nerve is confused with heart disease. The symptoms of these diseases are indeed somewhat similar. However, you can try to determine the cause of the pain yourself.
When a nerve is pinched, the pain can be prolonged and not stop day or night. If the heart muscle is pinched, the pain is paroxysmal and goes away over some time. Usually accompanied by a decrease or increase in blood pressure.
For neuralgic diseases, taking conventional analgesics or heart medications does not help. When palpating the intercostal areas, the pain intensifies. In case of cardiovascular diseases, pain can be relieved with the help of special medications or analgesics.
With neuralgic diseases, pain can radiate to the arm, lower back, shoulder, under the shoulder blade or neck. In heart disease, pain is localized only in the chest and heart.
With neuralgia, the pain intensifies when moving the arm, head, rotating or turning the body, sneezing and coughing, taking a deep breath and any change in body position. In heart disease, stiffness in the chest is permanent and does not change when changing body position or when inhaling and exhaling.
First aid - what to do if there is a sharp pinching in the chest
A pinched nerve can occur suddenly and in any, even the most inappropriate place and situation. In this case, you must first call a doctor and provide first aid to the victim before he arrives.
To do this, you need to lay the patient on a hard surface, lay a soft blanket or blanket on top of it and ensure his immobility. The patient should lie in the position in which the least pain is felt. In this case, it is necessary to free his chest from tightly squeezing clothing and provide access to fresh air.
Typically, a pinched nerve is accompanied by severe unbearable pain, so you should try to numb the pinched area with analgesics. Due to the suddenness of the pinching, the patient may experience not only unbearable pain, but also nervous shock. In this condition, the patient needs to be given sedatives.
Upon arrival of the doctor, it is necessary to tell about all the medications that have already been given to the patient. Hospitalization occurs only in the most complicated cases. Usually the doctor numbs the area of pain, taking into account the medications already taken, and recommends further examination.
Establishing diagnosis
If you have severe chest pain, you should seek help from a specialist. In order to determine the cause of the pain and prescribe the correct treatment, the doctor will prescribe the necessary examinations of the heart and spine.
To check your heart function, your cardiologist will order an electrocardiogram (ECG) and an ultrasound (ultrasound).
The spine is checked using x-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Only with the results of these studies in hand will the doctor be able to accurately diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Set of measures
Treatment for thoracic nerve entrapment depends on the cause of the compression of the spine. The primary goal is to release the pinched nerve and get rid of the reasons that caused it to be pinched. After this, you need to restore the functions of the released nerve.
For effective treatment, drug treatment is used. It includes taking the following medications:
- Sedatives. They have a calming effect on the patient and help restore sleep.
- Muscle relaxants. Help relieve muscle spasms and eliminate pain.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. Help relieve inflammation from the affected area.
- B vitamins. A lack of B vitamins in the body leads to a malfunction of the nervous system.
The following therapy methods are also used:
- Physiotherapy - electrophoresis with the addition of anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
- Physiotherapy. Taking into account the severity of the disease and damage to the thoracic region, the specialist determines the degree of load from special exercises.
- Acupressure. With this procedure, blood circulation in the affected area is improved. This leads to an acceleration of the nerve recovery process.
- Acupuncture. Acupuncture also helps improve blood circulation and completely relieve or reduce pain in the affected area.
Folk remedies available for use at home can also be an effective addition to traditional methods of treatment for pinched nerves in the thoracic region.
There are many such recipes in folk medicine, let’s look at some of them:
- garlic oil is diluted in 0.5 liters of vodka and the affected area is rubbed with this mixture;
- a hard-boiled egg is cut and applied to the sore spot, held until it cools completely;
- pour boiling water over a tablespoon of peppermint leaves and drink half a glass of this decoction before bed;
- horseradish leaves are applied to sore spots and wrapped with woolen cloth on top.
Hidden and obvious consequences
The possible consequences of a pinched nerve can be devastating. Moreover, if you do not pay attention to this problem for a long time and do not consult a doctor.
This threatens with complications such as disc protrusion, intervertebral hernia, and impaired movement functions (complete or partial paralysis).
There is also a malfunction in the body's immune system, which allows various viruses to attack unprotected cells in the body. Pressure surges and general malaise can cause disruptions in the functioning of internal organs.
Initial and relapse prevention
In order to avoid primary or repeated pinching of a nerve in the chest, the following rules must be followed:
- healthy lifestyle - sports (swimming), walks in the fresh air, morning exercises;
- proper nutrition - fruits, vegetables, foods containing calcium and magnesium;
- timely treatment of diseases that provoke neuralgia;
- alternating rest with physical activity;
- posture control – avoid staying in one position for a long time;
- avoid heavy lifting;
- do not be exposed to hypothermia.
A pinched nerve does not go away on its own. In order not to subject yourself to severe long-term treatment and surgical intervention, it is necessary to consult a doctor in a timely manner. Only in this case can you hope for a positive outcome of the disease.
osteocure.ru
Symptoms
If the muscle under the shoulder blade is pinched, pay attention to the additional clinical picture. The manifestation of inflammation is always accompanied by a mass of unpleasant symptoms, including:
- severe pain in the chest area,
- pain in the heart,
- breathing disorder,
- inability to support limbs,
- inability to fully move,
- when you try to stand up or bend over, there is a sharp pain,
- numbness of the upper extremities,
- discomfort in the stomach area,
- sensory disturbance,
- change in blood pressure,
In particularly severe cases, the patient may lose consciousness.
When the nerve is compressed, strong and shooting pains in the heart are formed. When taking a deep breath, the patient complains of a significant deterioration in health.
Unpleasant sensations in the spinal column can radiate to the ribs, arms, neck and lower back. There is discomfort in the stomach. Patients characterize these symptoms as signs of an ulcer or gastritis.
Symptoms of a pinched nerve are sometimes so severe that the patient cannot move for several hours.
Symptoms and treatment for a pinched nerve in the thoracic spine should be determined by a qualified physician. You, in turn, need to tell the doctor about all the signs that are bothering you at the moment.
Pinched nerve in the thoracic region: symptoms and treatment
Home → Home treatment → Neurology → Pinched nerve
A pinched nerve in the thoracic region is a condition in which acute pain occurs in the chest and thoracic spine, causing a number of other symptoms. Often, compression of nerve endings in this case occurs against the background of other pathologies. Without proper treatment, a pinched nerve can lead to serious consequences and mobility will be significantly limited.
Some experts say that most often this disease begins to manifest itself in people over thirty years of age, although for various reasons it can be encountered at a young age. At the same time, the main problem in diagnosing this disease is that the pain syndrome usually radiates to other organs, as a result of which the causes of pain are often sought in the gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular system.
Once a pinched nerve in the thoracic region has been identified, treatment should not be delayed. The longer the nerve endings are compressed, the greater the likelihood of their complete irreversible damage, permanently impairing mobility in the thoracic region.
Causes
A pinched nerve occurs due to its compression by bones and joints, which occurs due to the anatomically incorrect position of these elements of the musculoskeletal system. Most often, compression occurs in the thoracic spine. The following factors usually lead to compression:
- Intercostal neuralgia. It usually occurs due to sudden unsuccessful movements, turns of the torso, and incorrect, unevenly distributed physical stress on the thoracic spine.
- Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, exacerbation of this disease. With degenerative changes due to osteochondrosis, disc protrusion occurs, the vertebrae are displaced, this leads to compression of the nerve endings, resulting in a pinched nerve in the thoracic region.
- Spasm, hypertonicity of the back muscles in the thoracic region. In this case, tense, spasmodic muscles pinch nerve endings; muscle spasms can occur due to physical exertion; most often, this problem occurs in athletes.
- Various spinal injuries, the occurrence of tumors of the spinal column. With various injuries and tumors, displacement of the vertebrae and spinal discs often occurs, as a result of which the nerve endings are compressed.
Also, experts often highlight the age factor, since with age the bones become weaker, and various diseases of the joints and spinal column occur. Therefore, older people are advised to pay more attention to the prevention of this disease and other similar pathologies.
Important! Also, the likelihood of a pinched nerve in the thoracic region increases during pregnancy.
Pinched thoracic nerve during pregnancy: what to do?
During pregnancy, there is a high probability of this disease occurring due to the increased load on the spine and the musculoskeletal system as a whole. If compression of nerve endings occurs, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible; you cannot treat yourself.
Since most painkillers are not allowed to be used during pregnancy, they try to relieve pain using manual methods - light massage, and try to limit mobility and stress. Any procedures for this condition can only be carried out by a specialist.
Symptoms
The main symptom of a pinched nerve in the chest is pain in the sternum, often accompanied by limited mobility, numbness in the ribs and under the shoulder blades, and sometimes a feeling of difficulty breathing. The following symptoms may also occur:
- when nerves are pinched, a sensation of pain may occur due to gastritis, in the area of the right hypochondrium, while no diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are observed;
- when the autonomic nerves are pinched, shortness of breath and arrhythmia may occur, while there are no pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
Due to the fact that the pain radiates to other organs, when these symptoms appear, a full diagnosis is required; to confirm the diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment, you need to consult a neurologist.
Typically, X-rays are required to confirm this disease; in some cases, MRI or CT is used. To exclude diseases of the digestive organs and heart, an ultrasound or ECG and other tests may be prescribed. Only after this can treatment begin.
Important! The pain in this disease increases with breathing.
How to treat pinching
Treatment is usually complex, it is important to eliminate pain and relieve muscle spasms with the help of medications, then remove the limitation of mobility and the feeling of numbness that occurs due to a pinched nerve. Treatment at home is acceptable, but it is necessary to attend physical procedures in a clinic or hospital; they cannot be performed at home.
The following methods are usually used to treat this disease:
- Drug treatment. Anti-inflammatory painkillers are usually used, for example, Nurafen, Nise, Diclofenac. In rare cases, local anesthetic blockades are used. Mirorelaxants are also used to relieve muscle spasms, and B vitamins are used for the same purpose, usually in injections.
- Manual procedures and physiotherapy. They are used to improve mobility in the thoracic region, improve circulation, and consolidate the effect of drug therapy. Typically massage, acupuncture, reflexology and other techniques are used.
- Exercises for a pinched nerve in the thoracic region are also important for a full recovery. They help restore mobility, strengthen the back muscles, and improve the flexibility of the joints and spine. Exercise therapy should not be neglected for this disease; even twenty minutes of the simplest exercises a day will help improve the condition and avoid relapse of the disease.
- Treatment with folk remedies. Traditional medicines are not as effective for this disease, but some remedies will help you recover faster from the disease. If nerves are pinched in different parts of the body, it is recommended to start eating more dried apricots, prunes and walnuts; they have a positive effect on the musculoskeletal system and nervous system. Warm herbal baths are also recommended, a bath based on oak bark is especially useful.
By combining different treatment methods, you can achieve the most pronounced positive results. The main thing is to consult with your doctor at all stages of treatment; absolute self-medication is contraindicated for this disease, as it can cause complications.
www.lechim-prosto.ru
Diagnostics
If pinched, the patient needs to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis using differential diagnostics. Such an examination will reveal all inflammation in the heart, stomach and other organs.
Diseases can be distinguished by examination using computed tomography.
If the doctor finds it difficult to make a diagnosis, then an X-ray and an ultrasound examination of the body are necessary for diagnostic purposes.
In certain cases, it is possible to establish a specific diagnosis using an X-ray image using contrast agents that are injected directly into the spinal canal.
All of these methods are necessary for visualizing the internal processes taking place in the spine. After identifying the pathology, the doctor will prescribe the necessary course of therapy. Until this point, taking medications is prohibited.
First aid
Elimination of unpleasant sensations in the back is possible only with a competent approach. Since the attack occurs suddenly, it is important to know how to relieve symptoms. Before the ambulance team arrives, the patient needs to alleviate the torment using available methods.
If pinching is possible, immobilize the patient and place him on a hard surface, be it asphalt, the floor, or a stretcher. This position will reduce pain symptoms and alleviate the person’s general condition.
Important! Do not force a certain body position, as the patient will choose the optimal position himself.
Pain can be relieved with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. To do this, give the patient Movalis, Ibuprofen or Diclofenac. Local pain can be eliminated with Ketanov ointment.
If necessary, give the patient any antipyretic.
If the patient feels like he is losing consciousness or complains of severe deterioration in health, give him a sedative. The best drugs in this area are Novopassit, Persen, Afobazol.
If you have difficulty breathing, you need to provide a flow of fresh air. To do this, unfasten the buttons and remove all chains.
Traditional treatment
At the first symptoms of a pinched nerve, you should immediately seek help from a neurologist. Depending on the severity of the disease, the patient will be prescribed medication using physiotherapy.
For reference! The pathology can be eliminated in a few weeks. During this time, the patient should take out sick leave.
Depending on the factors in the development of the pathology, the patient is prescribed the following medications:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Diclofenac.
- To relieve spasms, drugs such as Tizanidine and Tolperisone are prescribed. These same remedies are necessary for muscle hypertonicity.
- For acute and excruciating pain, powerful drugs such as Tramadol are needed.
- To improve metabolic processes, B vitamins are prescribed, for example, Neuromultivit.
- To improve blood circulation and metabolism within tissues, use chondoprotectors, for example, Theraflex or Chondroitin.
All of the medications listed can be taken only after consultation with a doctor.
Physiotherapeutic methods
After relief of the main signs of the disease, the patient should undergo a course of physiotherapy. It will be useful for the patient to undergo a course of electrophoresis, acupuncture, phonophoresis and UHF.
Also, do not forget about the benefits of therapeutic exercises. Physical education is necessary for vertebral instability. Special exercises will help strengthen the muscle corset and support the work of the back.
To achieve the desired result, gymnastics should be done every day for thirty minutes in the morning and evening.
In some cases, the doctor may recommend wearing special bandages that stabilize the body position.
Surgical intervention
In the event of a serious deterioration in health, the patient may be prescribed urgent surgery. Surgery is also necessary if drug treatment does not have the desired effect.
The operation can be of several types:
- Most often, patients undergo a discectomy, in which protruding parts of the intervertebral discs are removed.
- For large vertebral arches, laminectomy is performed.
- Spinal fusion may be performed to stabilize the vertebrae.
- If tumors are present, tumors are removed.
Pinched nerve in the thoracic spine: symptoms and treatment
If there is sudden pain between the ribs that gets worse with movement, a possible cause of discomfort is a pinched nerve in the thoracic region. Symptoms of pinching largely repeat the symptoms of intercostal neuralgia.
Causes of the disease
A pinched nerve in the thoracic region can happen to anyone, but the pathology is quite rare, unlike pinching in the cervical and lumbar spine. This is due to the peculiarity of the load distribution along the spinal column and the structure of the corresponding sections. The lower back experiences enormous stress every day, unlike the thoracic region.
The causes of pinching in the thoracic region can be:
- osteochondrosis of the thoracic region;
- severe muscle spasm;
- excessive physical activity;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- age-related changes in the body;
- stressful situations.
The most common cause of a pinched nerve is osteochondrosis or spinal hernia. Since these diseases rarely affect the thoracic region, pinched nerves in this area are also uncommon.
Professional athletes whose training involves increased stress on this area are susceptible to the disease. In this case, a pinched nerve in the thoracic spine occurs due to a decrease in the height of the gap between the vertebral discs.
A separate reason should be muscle spasm and stress. Often pinching occurs due to the simultaneous impact of these two factors. Frequent stress leads to disruption of the nervous system, including its autonomic department, which causes increased muscle tone and spasms. Pinching of the intercostal nerve occurs due to muscle spasm.
With age, the body ages. All metabolic processes slow down, including those in the nervous system. The spine weakens, the height of the discs decreases. All of these factors increase the risk of developing a pinched nerve in the thoracic region.
Pinching symptoms
The following signs are typical for pinching in the chest area:
- pain on the left side of the ribs, simulating pain in the heart area;
- increased pain when moving;
- labored breathing;
- low effectiveness of cardiac drugs;
- arrhythmia;
- stiffness of movements.
This problem is characterized by compression of the autonomic nerve, which causes cardiovascular symptoms. Since the disease often occurs in older people, incorrect self-diagnosis is possible, which results in unsystematic use of heart medications. When a nerve is pinched, such drugs are useless, since the pain is associated with compression of the nerve root, but not with age-related pathology of the heart muscle.
You can distinguish a pinched nerve from coronary heart disease by listening to your own feelings. When a nerve is compressed, the pain does not go away during the day, but its nature may change. There is a tendency for discomfort to increase during movement and exercise, which does not happen with heart disease. Cardiac medications do not improve the patient's condition, so taking them is not advisable.
Another hallmark sign of a pinched nerve is a change in muscle tone. Muscle hypertonicity may occur. If you press hard on the pinched nerve, the pain will spread to the stomach area, which never happens with pathologies of a cardiovascular nature.
A characteristic feature of the disease is increased pain when there is a load on the thoracic region, for example, while coughing, laughing or trying to take a deep breath.
If discomfort persists for a long time and treatment is not started in a timely manner, symptoms include signs of low blood pressure, lethargy and apathy, and sleep disturbances.
Diagnosis of pinching
The diagnosis is made by a neurologist after examining the patient. When pressing on certain points, an intensification of the pain syndrome spreading along the intercostal space is characteristic. If this symptom is present, the doctor will prescribe the following tests to confirm the diagnosis:
- chest x-ray;
- MRI;
- myelography;
- Ultrasound of internal organs.
X-rays and MRIs can help pinpoint the affected nerve. Myelography is prescribed if diagnosis is difficult. This is a method in which an X-ray examination of the spine is performed with the introduction of contrast.
As an additional examination, an ultrasound of the internal organs may be prescribed to exclude pathologies caused by prolonged pinched nerves in the chest.
First aid
Pinching of the thoracic nerve occurs suddenly. Sharp pain appears very quickly. In this case, you need to lie on a hard surface in a position in which the least pain is felt.
The patient must take an analgesic to relieve pain. Since trouble can occur suddenly and cause a feeling of fear for one's own life due to symptoms similar to a heart attack, the patient can be asked to take a sedative.
With severe pinching, excruciating pain is observed, which cannot be tolerated, since it is harmful to the health of the nervous system as a whole. The most correct action in such a situation would be to call emergency help at home.
Upon arrival, the doctor must be informed of all medications taken before the ambulance arrived.
Treatment of pathology
There are several ways to treat nerve compression:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- surgical intervention.
First, traditional drug treatment is carried out. For this purpose, the following groups of drugs are used:
- antispasmodics and muscle relaxants;
- drugs to improve blood circulation;
- vitamin preparations;
- sedative medications.
Antispasmodics and muscle relaxants normalize muscle tone, resulting in pain relief. However, if the root cause of the pinching is not treated, the pain will return. The main goal of treatment is to release the nerve, which can only be achieved through manual therapy or surgery. Manual therapy is prescribed only after relief of acute pain.
It is mandatory to take B vitamins and a number of microelements that strengthen the nervous system and promote the regeneration of damaged nerve fibers.
After pain relief, the patient is prescribed a course of manual therapy. It is also supplemented with physiotherapy - electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, acupuncture. Typically, in the first few procedures, electrophoresis is used in conjunction with painkillers. Painkillers are then replaced with medications that improve blood circulation. This helps improve local metabolic processes and speed up recovery.
Along with physiotherapy, the patient is prescribed a course of therapeutic exercises to strengthen the muscles of the thoracic spine. A strong muscle corset will prevent re-pinching of the nerve.
If a nerve is pinched in the thoracic region, treatment is adjusted depending on the severity of the compression and accompanying symptoms.
Prevention measures
To avoid re-pinching the thoracic nerve, regular prevention is necessary.
First of all, osteochondrosis or intervertebral hernia should be treated. It is the presence of these pathologies that is one of the most important risk factors for the development of neuralgia.
You should definitely strengthen your back muscles and correct your posture. Strong muscles ensure the correct position of the spine during any activity, and therefore reduce the risk of developing pinching.
Having excess weight increases the load on the spine, in particular on the thoracic region. Patients suffering from obesity or significant weight gain need to gradually get rid of extra pounds while doing gymnastics to strengthen the muscles of the chest and back.
It should be remembered that a pinched nerve will not free itself and the pain will not go away. Only timely treatment guarantees quick relief from painful pain and restoration of normal mobility.
Tags: Central nervous system diseases
nashinervy.ru
Forecast
The consequences of pinching can be eliminated in the shortest possible time. In the case of well-chosen treatment, all unpleasant signs are eliminated within one week. At this time, tissue tension is reduced, and the functioning of the muscles and the musculoskeletal system as a whole is stabilized.
If pathology develops against the background of more dangerous diseases, symptoms can be eliminated within one month. Rehabilitation after surgery begins after three months.
How to prevent a pinched nerve
Basic rules for the prevention of thoracic neuralgia:
- balanced diet;
- rejection of bad habits;
- moderate physical activity;
- optimal work and rest regime;
- protection against spinal injuries and hypothermia.
When working sedentarily, it is recommended to exercise regularly, warm up during the day, and use orthopedic chairs. Athletes should properly plan their training schedule and avoid overexertion. For osteochondrosis and other chronic diseases of the spine, preventive treatment is necessary; it is useful to visit sanatoriums, do back massage, and exercise therapy.
We recommend reading similar articles:
Prevention
Avoiding pinched nerves is quite simple. To do this you need to follow several rules:
- Try to maintain a normal weight.
- If necessary, get rid of extra pounds.
- Treat all infectious, viral and bacterial diseases on time.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Remember the importance of consistent physical activity.
- Do not lift heavy objects.
- Avoid carrying bags and backpacks on only one side.
- Watch your diet. Eat foods rich in vitamins, potassium, and magnesium.
- Watch your posture.
- Sleep only on orthopedic mattresses.
If you are prone to vertebral diseases, visit swimming pools. Also try to visit a massage therapist in a timely manner and do therapeutic exercises.
Causes
Many people think that intercostal neuralgia is caused by osteochondrosis. However, this is not always the case. There are other disorders that cause pinching.
A pinched nerve often leads to the following factors:
- joint dysfunction – spinal-motor sections are damaged, muscle function is disrupted;
- displacement of intervertebral discs - this process leads to severe back pain;
- reflex effects - formed when the vertebrae are displaced;
- scoliosis is an organ that, when the spine is curved, begins to work incorrectly, which is why problems arise;
- neoplasms of internal organs can move discs and the spine.
The cause of spasms and pinching may be heavy physical exertion or sudden incorrect movements. You should not lift weights, because... a hernia will also appear. To avoid problems with the musculoskeletal system, you should lead an active lifestyle, move more, and exercise moderately.
Less commonly, neuralgia can be caused by:
- diabetes;
- pathologies of the digestive system (colitis, gastritis, stomach ulcer, etc.);
- acute gastroenteritis;
- allergic diseases;
- multiple sclerosis.
Muscle spasms often appear during traumatic disorders or psycho-emotional stress. Hypothermia provokes neuralgia, which can develop into pneumonia. It is possible that neuralgia occurs as a symptom of another disease.