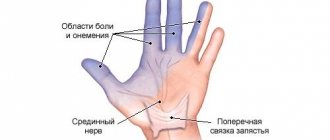
Characteristic symptoms
Signs of pathology appear depending on the location of the pinching. The most common symptom is numbness of certain areas of the skin and fingers. Painful sensations are sometimes absent.
The main symptoms of a pinched nerve in the right or left hand:
- limitation of the extension and flexion function of the hand and its fingers;
- pain - localized in the joint area and caused by a chronic disease or appears as a result of a hand injury, aggravated by sudden movement;
- poor circulation - accompanied by a feeling of numbness in the limb, which is gradually replaced by pain;
- muscle weakness or excessive muscle tension;
- numbness in the area of the little finger, ring finger or thumb, less often - all fingers at the same time.
If there is no improvement and if you refuse to see a specialist, the signs of a pinched nerve in the arm intensify. The prolonged presence of pathology can lead to necrotic processes in tissues, but this complication occurs quite rarely.
How is the problem diagnosed?
A neurologist is involved in the diagnosis of pathology and subsequent treatment . First, he collects anamnesis and records the patient’s complaints in his medical history.
The doctor identifies the problem and makes a preliminary diagnosis of median nerve neuritis during a physical examination of the affected arm.
During the examination, the neurologist asks the patient to perform a number of control exercises:
- Make a fist with your hand. The median nerve innervates the flexor muscles of fingers I-III. If he is defeated, they will not bend.
- Scratch the surface of the table with your fingernail. The terminal phalanges do not work during neuritis, so even with the patient’s hand lying on the hand, it will not be possible to perform the exercise.
- Rotate or oppose the first finger. With neuritis, it is impossible to protrude it.
- Touch the pad of the thumb with the little finger.
- Hold the paper with your thumb and index finger bent.
Thanks to the test, the doctor determines the presence of movement disorders . They arise due to paralysis of skeletal muscles - the median nerve is responsible for transmitting nerve impulses from the brain to the muscles.
The motor neurons of the nerve fiber transmit information about what movement needs to be made. With neuritis, this connection is disrupted, which leads to paralysis.
When the sensory neurons of the median nerve are damaged, numbness occurs . A neurologist can test the degree of skin receptivity by touching, pinching, or using a sterile syringe needle.
If the cause of neuritis is tunnel syndrome, then the patient experiences Tinel's symptom. In this case, during palpation or tapping at the site of the pinched nerve, acute pain is present.
To identify the cause of the development of neuritis, the patient must undergo a series of laboratory and instrumental examinations:
- Donate blood for analysis . Laboratory tests will show the presence of infection by the number of white blood cells. During the inflammatory process, their number increases.
- Hormonal studies, checking sugar levels . The cause of the development of neuritis may be a disruption of the endocrine system.
- To make an X-ray . The procedure is performed for injuries: fractures or dislocations.
- Get an MRI, CT, ultrasound . Magnetic resonance imaging helps to identify the presence of an abnormal process of the humerus and malignant tumors. MRI determines the area of pinched nerve. Using a contrast injection procedure, the condition of the blood vessels supplying the median nerve can be assessed. Similar information can be obtained using CT and ultrasound examinations.
- Electroneuromyography . Thanks to this procedure, it is possible to assess the condition of the muscles, the degree of conduction of nerve impulses along the median nerve to the skeletal muscles.
Read about the diagnosis of other types of neuritis of the extremities:
- brachial, ulnar, radial nerves;
- sciatic nerve;
- femoral, tibial and peroneal nerves.
What diseases should be distinguished from?
The clinical picture of some diseases is similar to the symptoms of median nerve neuritis. To make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis:
- Brachial plexitis . This disease also causes numbness and impaired motor activity. But unlike median nerve neuritis, brachial plexitis affects not only the hand and forearm, but also the shoulder. To clarify the diagnosis, ultrasound, MRI and CT are performed. Tests help pinpoint the area of nerve damage.
- Vertebrogenic syndromes: osteochondrosis, cervical spondylosis, herniated intervertebral discs . Due to pinched blood vessels in the neck area, the arm stops receiving nutrients and oxygen. The result is lethargy, cyanosis, paralysis or numbness of the limb. At the same time, median nerve neuritis affects only the forearm area and 1-3 fingers. In addition, with vertebrogenic syndromes, the patient complains of difficulty turning the head.
- Spondyloarthrosis . Pain from spondyloarthrosis can radiate to the arm. In this case, the patient can move his fingers and hand freely. The patient successfully passes neurological tests, which excludes the possibility of developing neuritis.
- Cervicobrachial radiculitis . When the roots of the spinal nerves become inflamed, pain is observed along the affected nerves. There is a burning sensation, pain, and numbness in the head, neck and upper limbs. In this case, to clarify the diagnosis, MRI and ultrasound are necessary. Electroneuromyography will show more accurate results.
Diagnostics
All examination methods are aimed at determining the location of the pinched nerve and the cause of the symptom. Pathology can occur in the shoulder, elbow or wrist area or as a result of the effects of spinal diseases. To obtain complete information about the condition that has arisen, several types of diagnostics are prescribed:
- medical examination - assessment of the condition of the hand, its motor activity, determination of the presence of pinching of the brachial, ulnar or wrist nerves based on the patient’s complaints and accompanying signs;
- X-ray of the arm and spine - identifying possible pathologies of the joints, including those resulting from injuries;
- MRI of the affected limb, cervical and thoracic spine - determining the location of the pinched nerve, the condition of the joints, adjacent soft tissues and blood vessels, the possible presence of tumors;
- electromyography - assessment of the degree of muscle damage;
- study of the conductivity of the radial, brachial and ulnar nerves - determination of their condition and muscle fibers of the arm, degree of functionality.
The results obtained indicate the condition of the joints of the limb and spine, the presence of degenerative processes in them, the location of the pinched nerve and the severity of the symptom. Using this information, it is determined what to do with the hand and how to treat it.
Etiology
The main cause of median nerve neuritis in 20-35% of patients is injury . A bruise, partial or complete rupture of a nerve fiber is observed in the presence of the following injuries:
- receiving soft tissue injuries of various etiologies;
- fracture of the shoulder, forearm bones;
- injury from bone fragments;
- compression of the nerve by post-traumatic hematoma;
- intra-articular fracture in the elbow and wrist;
- dislocations.
People whose profession involves prolonged flexion and extension of the wrist experience carpal tunnel syndrome.
This causes inflammation of the median nerve. The reason for this phenomenon is the pinching of the nerve fiber in the anatomical tunnel between the bones of the metacarpus, tendon muscles and the carpal ligament. Changes in these structures are possible with subluxations, tendon injuries, and rheumatism of the periarticular tissues. 1% of the world's population develops the syndrome due to an abnormal process of the humerus.
Together with the nerve, the vessels supplying oxygen and nutrients to the neurons are compressed.
As a result, with carpal tunnel syndrome, the trophism of the median nerve is disrupted, which is why the pathology has received a second name - compression-ischemic tunnel syndrome .
Carpal tunnel syndrome is typical for middle-aged women who are forced to rock a small child for a long time.
Other factors in the development of a neurological disorder may include:
- Inflammatory changes in joint tissue. Bursitis, arthrosis or arthritis may develop in the wrist and elbow joints.
- Malignant neoplasms: hygroma, lipoma, neuroma, osteoma, hemangioma. The increase in size of the tumor puts pressure on the surrounding soft tissue, including nerves and blood vessels. If the median fiber is not pinched, the tumor can compress the arteries that supply it. In such a situation, blood stagnation occurs, the trophism of the nervous tissue is disrupted, creating conditions for the occurrence of neuritis
- Disruption of the endocrine glands. Hormonal imbalance develops against the background of diabetes, hypothyroidism, and acromegaly.
- Diseases that cause structural changes in the tissues of the musculoskeletal system. In such a situation, the cause of neuritis can be rheumatism, cervical osteochondrosis, gout, or intoxication of the body.
The video will tell you how carpal tunnel syndrome manifests itself:
Therapeutic measures
All treatment procedures are aimed at eliminating signs of pinching, alleviating the patient’s condition, and restoring the conduction of nerve impulses. First of all, a course of drug therapy is prescribed, consisting of the following types of drugs:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - relieve inflammation, reduce the manifestation of pain;
- muscle relaxants - relieve muscle spasms, which alleviates the patient’s condition and normalizes limb mobility;
- painkillers - necessary for severe attacks of pain;
- warming ointments and gels - improve local blood supply, relieving muscle spasms and eliminating numbness;
- chondoprotectors, calcium preparations - prescribed for degenerative processes in the joints;
- B vitamins, magnesium - improve the condition of nerve and muscle fibers and restore their functionality.
Physiotherapy courses consist of 5–15 procedures and quickly restore pinching in the hand:
- magnetic therapy;
- acupuncture;
- laser therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- thermal wraps;
- mud therapy.
Additionally, courses of massage and manual therapy may be prescribed. Such procedures should be performed by a specialist - if you have certain skills, you can achieve a positive result after the first session.
When the main symptoms of pinching are eliminated, therapeutic exercises should begin, which consists of performing arm swings, rotational and flexion-extension movements of the hand. If your fingers are affected, you need to clench and unclench them.
During the treatment period, it is forbidden to heavily load the arm. You should not carry heavy bags, engage in active sports or do household chores that cause discomfort to the affected limb. It is allowed to resume physical activity only after the main symptoms of the pathology have been relieved.
Main causes of pinching
The main causes of pinched radial nerve are:
- Traumatic injuries (fractures, dislocations, bruises, falls, improper application of a tourniquet).
- Long-term compression as a result of squeezing (when a person sleeps with an arm under the head or torso. This is usually observed in drunk people or when very tired).
- Nerve compression due to improper use of crutches.
- The needle of a syringe hits an atypically located nerve when performing an injection.
- Compression by tumor-like formations.
More rare causes are toxic effects due to viral, infectious diseases, lead or alcohol poisoning.
Drooping of the hand when the arm is positioned horizontally is a symptom of compression of the nerve in the armpit area
Prevention
Prevention of pinched nerves in the hand is to follow these recommendations:
- Regular moderate physical activity. Helps improve blood circulation, strengthen muscles, and prevent joint diseases.
- Warm-up during sedentary work. Light exercises should be performed several times during the working day to eliminate congestion in tissues.
- Avoiding hypothermia. Often, pinching in the hand is caused by wearing clothes that do not correspond to weather conditions, or being in drafts.
- Timely treatment of joint diseases. The worsening of any diseases of the musculoskeletal system can be prevented by regular treatment - this will also relieve possible complications of the pathology.
Additionally, to maintain general immunity and improve the functionality of joints and nerve fibers, you should regularly take courses of multivitamins - this is especially true in the spring-winter season. If a nerve in your hand is pinched, you should immediately contact a specialist - this will speed up the healing process and prevent the development of unpleasant symptoms.
Causes of pinched nerve fibers
The brachial, radial, or ulnar nerve may be damaged. The localization of the lesion depends on the reasons:
- untreated injuries (knife and gunshot) or untimely identified fractures, dislocations;
- incorrectly performed surgical intervention;
- habitual joint dislocation;
- heavy load on joints when playing sports;
- excessive and prolonged tension in the muscular system of the arm;
- occupational injuries, bruises;
- carrying very heavy objects;
- “wedding night” syndrome (the partner lies on her partner’s arm for a long time);
- improper use of crutches;
- uncomfortable posture during sleep, sleeping at the table;
- compression by tumor formation;
- scars where the nerve passes;
- violation of injection technique.
Before starting treatment, the doctor must find the exact cause of the nerve compression. Analysis of symptoms, as well as anamnestic data, will help in diagnosis; additional examination methods are also needed.