Causes of neuritis
The main cause of neuritis of the hand is pinched nerve endings, against which the inflammatory process begins. Occurs as a result of limb injuries, heavy physical exertion, and improper injection technique. The following factors can also trigger the development of hand neuritis:
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Infectious diseases.
- Disorders of the cardiovascular system.
- Tuberculosis.
- Pneumonia.
- Exposure to toxic substances.
- Intoxication with alcoholic beverages.
- Disorders of the thyroid gland.
Depending on the cause, there are several types of hand neuritis. This is due to the fact that it is the work of the median nerve, ulnar and radial bundles that provide not only motor activity, but also sensitivity.
When the ulnar bundle is damaged, the sensitivity of some fingers is lost. The phalanges stop extending, and the hands look more like an animal’s paw.
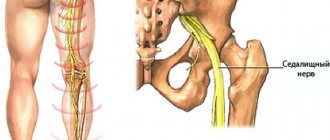
Before treating sciatic neuritis
It is very important to eliminate all negative factors before treating sciatic nerve neuritis. If you lead a sedentary lifestyle, then you should gradually, after consulting a doctor, introduce regular exercise into your life in the form of physical exercise, walking, running, etc. If you are fond of smoking or drinking alcohol, then you should completely abandon these bad habits. Balance your diet. Properly organize your sleeping and working space.
It is also important to conduct a full examination. To do this, you should consult a neurologist or vertebrologist. These doctors, after conducting an initial examination, will develop a plan for conducting the examination. This may include:
- an x-ray of the spinal column (it will allow you to determine whether there is traumatic damage to bone tissue, narrowing of the intervertebral spaces, destruction of the intervertebral joints, etc.);
- MRI of the spine, hip and knee joints (allows us to exclude the possibility of spinal canal stenosis, piriformis syndrome and a number of other pathologies that provoke sciatic neuralgia);
- biochemical blood test (diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, etc. are excluded);
- Electroneurography allows you to determine in which part of the sciatic nerve the lesion occurs, leading to an inflammatory reaction.
After all the necessary examinations, the doctor will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe an individual course of treatment.
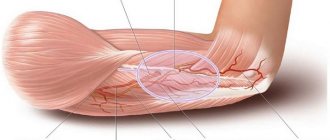
How does hand neuritis develop?
Hand damage
Neuritis is an inflammatory process that develops in the peripheral nervous system. Hand involvement most often means radial neuropathy. The disease develops against the background of compression of nerve endings, which is accompanied by pain, loss of sensitivity and some other symptoms. In some cases, severe pinching may cause paralysis of the arms.
The arms are connected to the central nervous system by the bundles of the radial, ulnar and median nerves. A disease when the pathological process spreads to several bundles of nerve endings at once is called polyneuritis in medicine.
Pathology causes dysfunction of muscle tissue, and the inflammatory process is accompanied by loss of tendon reflexes. Depending on which nerve is damaged, the functioning of a certain area of the hand or arm is impaired.
Types of radial neuritis
All neuritis of the radial nerve of the hand is usually divided into three types depending on the traumatic effect. These include:
- Axillary. Also called crutch palsy. Diagnosed in rare cases. A distinctive feature is the weakness of the flexion function of the forearm. In addition, there is a loss of extensor mobility.
- "Tennis Player Syndrome" It is characterized by injury to the posterior branch of the nerve in the elbow area. The causes of development are heavy physical exertion, when pressure was placed on the elbow. This is exactly what can be observed when playing tennis, for which this type got its name. All changes that occur with radial nerve neuritis lead to chronic disease of the nerve bundle. It manifests itself as painful sensations when moving the arm or moving the fingers.
- Nerve damage in the middle third of the shoulder, as well as on the outer back surface. Happens quite often. The causes include fractures, sleeping in an awkward position and incorrectly administered injections.
Radial neuritis in some cases may be the result of previous infectious diseases, when a person received insufficient or no treatment. Most often, due to infection, damage to the middle third of the shoulder develops.
Reasons for numb hands: symptom treatment
Many patients go to the hospital with numbness in their hands and fingers. When the hands go numb, an unpleasant short-term specific sensation occurs, which occurs due to compression of the nerve endings.
The hands and fingers become numb due to the fact that a person occupies an uncomfortable or unnatural position for a long time. As a result, pinching occurs, blood flows poorly to the arm area and the fingers go numb. You can exercise your arm to get rid of the numbness.
- Why do my hands and fingers go numb?
- Lesions of the hands and their primary causes
- Lesions of the hands and their secondary causes
- Causes of complete and partial numbness of the hands
- Causes of numbness in legs and knees
- Features of the treatment of diseases in which limbs become numb Gymnastics for numbness of the hands
- Traditional treatment methods
Why do my hands and fingers go numb?
But if your fingers and hands succumb to numbness too often, and it is accompanied by severe pain, you should immediately consult a doctor. Why is it necessary? Because frequent numbness in the hands can be the cause of a number of diseases:
- atherosclerosis;
- osteochondrosis;
- diseases of arterial vessels.
If the numbness is too long, then simple manipulation is unlikely to help you, but if the entire right arm from the elbow goes numb, then this may indicate damage to the carpal tunnel.
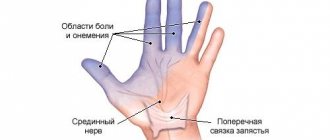
Lesions of the hands and their primary causes
Numbness of the hands and fingers is a very common phenomenon and occurs due to compression of the median nerve. And if treatment is not started on time, the consequences can be serious. As a rule, numbness spreads in turn to the following parts of the hand:
- first the fingers go numb;
- then the palm;
- brush.
Then the whole arm goes numb. And the longer a person endures pain and does not begin treatment, the stronger it will be both day and night. The pain may intensify when you raise your arms up.
Constantly being in the same and uncomfortable position causes aching pain in the hands. This may also indicate lower back pain. If the spine is damaged, then pinching of the lumbar nerve can radiate pain to the arm.
Damage to the carpal tunnel in most cases causes immobilization of the hands. The first three fingers on the hand are susceptible to damage when the middle canal is compressed. The reason for this may be prolonged sedentary work. First, the patient’s fingers go numb, and then the whole hand.
The right hand often goes numb due to a lack of vitamin B12, which responds to the functioning of nerve fibers. If it is not enough, then the following symptoms appear:
- overwork;
- feeling of weakness;
- severe pain with slight movement of the hand;
- increased irritability.
Also, my right hand is numb due to Raynaud's disease. Blood circulation is impaired, the patient feels severe and prolonged pain accompanied by numbness. The causes of this disease are as follows:
- stress;
- poisoning from alcohol or nicotine;
- hereditary factor.
Often numbness of the hand occurs due to hypothermia or prolonged exposure to the sun. The risk group is women under 30 years of age. Also, with Raynaud's disease, in addition to numbness, the fingers turn blue and become cold. If left untreated, the disease will spread to other parts of the body:
- chin;
- ears;
- legs;
- nose.
Lesions of the hands and their secondary causes
Often the cause of prolonged pain and temporary numbness of the extremities is obliterating endarteritis. It affects the vessels of the extremities. The outflow of blood is difficult, partial or complete numbness of the hand occurs. If timely treatment is not started, gangrene may occur.
Discomfort may occur due to pathological changes in the spine in the lower back.
Numbness can occur for a variety of reasons, but neuropathy is often a secondary cause. In addition to numbness, the following symptoms occur:
- tingling of the skin on the fingers;
- burning;
- itching;
- skin tightening.
Neuropathy can occur due to multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, or diabetes.
The hands often become numb due to ischemic stroke, as well as lesions of the cerebellar and vertebral arteries.
Pain often occurs against the background of hyperventilation, which is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- anxiety;
- fear;
- lack of air;
- rapid breathing.
Numbness can occur due to pinched blood vessels and be accompanied by pain and tingling.
Numbness in the hands can have different consequences. If they are not very numb, then this provokes a slight circulatory disorder, and if timely treatment is not undertaken, gangrene may begin.
Causes of complete and partial numbness of the hands
Quite often, hands go numb after sleep when they were in the wrong position. Painful sensations often occur due to compression of nerves and blood vessels by muscles. Since these vessels are responsible for the normal functioning of the hand and wrist, there may be defects in its functionality. When the nerve canal is compressed, not only the hand itself hurts, but also the entire arm from the elbow. If you have such symptoms, it is recommended to consult a doctor who will identify the source of the pain and prescribe treatment.
Sometimes a person may complain of pain in the shoulder, and the whole arm hurts along with it due to inflammation in the cervical spine. The cause may be pain in the lower back. The key reason for the appearance of the syndrome is prolonged stay in an unnatural position and stress on the joints.
But pain in the lumbar region may not always be the cause of numbness in the hands. This may be their systematic overwork. Often such symptoms are observed with osteochondrosis, so the more a person spends at the computer, the more the spine becomes tense, and accordingly, the more the lower back hurts. Sometimes the pain radiates to the following areas:
- cervical back;
- shoulders;
- hands and their numbness.
Limbs can also become numb if a person types, lifts, or carries things for several hours at a time. The blood flow is disrupted, the hands are very tired. Sometimes, after such loads, a person cannot clench his hand into a fist and do something with his fingers.
Fatigue may be accompanied by pain in the elbows, joints and wrists. Further, the pain increases, hands and fingers become numb more often. A special risk group is women from 35 to 55 years old.
Causes of numbness in legs and knees
Knees can hurt for various reasons:
- age factor and age-related changes;
- joint deformation;
- weak ligaments;
- destruction of cartilage tissue.
If they become numb, it is recommended to visit a doctor. If the sensitivity of the knee is impaired, then this may not be due to age, but due to destructive processes in the spine.
Numbness of the lower back is often observed. It is rare and does not particularly bother a person, but over time, other parts of the body, in particular the legs, begin to go numb. This may be a symptom of one or another lumbar disorder:
- vertebral displacement;
- inflammatory process;
- pinched nerve;
- osteochondrosis;
- intervertebral hernia.
The nature and duration of pain and numbness vary depending on the underlying cause. So, if your legs hurt in a dream, and there is constant lethargy in the limbs, your legs often go numb and your knees cramp, then this indicates the presence of an intervertebral hernia. The pain intensifies when a person sits or stands for a long time, when bending over and a number of other actions. Less commonly, the hips, feet, and knees may become numb.
As a rule, it all starts with numbness in the lower back. And in order to prescribe treatment, the doctor must take an x-ray of the spine, but this is not always enough to make a diagnosis. Sometimes MRI and other diagnostic techniques are required.
Frequent numbness in the legs and constant pain in the lower back may indicate radiculitis in acute or chronic form. Timely consultation with a doctor and initiation of treatment can help get rid of the disease.
Features of the treatment of diseases in which limbs go numb
So, we found out why arms, hands and other limbs may go numb. And now we will look at how to treat this disease depending on the root cause of the symptom. So, if severe pain occurs during sleep and there are signs of osteochondrosis, radiculitis or arthrosis, then treatment should begin as soon as possible after diagnosis. Only a specialist can prescribe a course of rehabilitation after illness.
First of all, the doctor prescribes medications whose effect is aimed at the following:
- elimination of pain and numbness syndrome;
- relief from muscle spasm;
- resumption of blood circulation in normal mode;
- removal of toxins.
Along with medications, the patient may be prescribed minerals and vitamins that will help eliminate the inflammatory process and restore the functioning of the damaged area.
If the shoulders, hands, knees or elbows hurt, the patient may be prescribed manual therapy, which helps prevent the subsequent development of the disease. Manipulations help prevent salt deposition in joints, they restore the elasticity of ligaments and muscles, relieve swelling, restore metabolism, blood circulation, and nutrition of the limbs.
Different types of ultrasonic influences also have a positive effect:
- laser treatment;
- magnetic therapy;
- ultrasound.
After the procedures, tissues are restored, the inflow and outflow of the blood improves.
Additional methods for treating radiculitis, osteochondrosis, rheumatism and other diseases in which the limbs become numb and sore are gymnastics and traditional medicine. They help restore immunity, strengthen muscles and overall health.
Gymnastics for numbness in the hands
Treatment of numb hands through gymnastics is very effective; it should be performed in the morning. This is the only way to prevent complete numbness of the hand and fingers. Exercises can be done without even getting out of bed:
- lying on your back, slowly raise your arms up, clench and unclench your fingers;
- stretch your arms up, clench and unclench your fingers as many times as you can at one time;
- stretch your arms along your body and again clench and unclench your fingers;
- clasp your hands and unclench them.
Traditional treatment methods
If there is numbness in the limbs, it is recommended to warm the affected areas with a compress based on pumpkin porridge. The mass is applied to the affected area, wrap it with cling film, wrap it in heat and leave it overnight.
You can use ointments and infusions made independently based on pepper, vodka, cucumbers, oil and other ingredients.
For prolonged pain and numbness, a contrast shower or bath helps. During the reception, it is recommended to stretch your fingers, squeeze and unclench them.
If your hands, or just your fingers, as well as your knees and legs go numb, then you should not ignore this symptom, especially if it recurs constantly. Without treatment, you can provoke the development of a number of serious diseases.
Symptoms of hand neuritis
Numbness of the hand
Symptoms of the disease directly depend on the degree and area of damage. Common features include:
- Loss of sensitivity. Patients often complain of numbness and tingling in the upper extremities.
- Partial decrease in strength or paralysis of muscle tissue. Atrophy may develop.
- Swelling of the skin.
- Blue discoloration of the upper layer of the epidermis.
- Thinning skin and dryness.
- The appearance of ulcers on the surface of the skin.
In cases of injury to the armpit or upper third of the shoulder, the pathology is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Partial or complete loss of sensation.
- Inability to move the index and middle fingers.
- Violation of flexion and extension functions.
- Inability to straighten the arm in the wrist area.
When the middle third of the shoulder is affected, the same symptoms are observed. At the same time, motor activity and sensitivity of the shoulder are preserved. A distinctive feature is the “falling” brush. The patient is unable to straighten his fingers at the metacarpophalangeal joints.
Treatment
The choice of treatment method for ulnar nerve neuropathies is largely determined by the reasons for their development. When the nerve is torn as a result of fractures, surgery is performed to stitch it together. After this, the patient needs rehabilitation, which can take about six months. If nerve compression is caused by other reasons, then the patient is prescribed conservative therapy, and surgical intervention is recommended only if drug and physiotherapeutic treatment is ineffective.
Conservative therapy
If the ulnar nerve is compressed, it is recommended to wear fixing devices to limit compression during movements. For this purpose, special orthoses, bandages or splints can be used. Some of them can only be used at night.
If compression of nerve fibers is provoked by habits or movements that must be performed because of their professional activities, then the patient should completely abandon them. In addition, during treatment it is necessary to avoid movements that cause increased pain or other symptoms.
To eliminate pain and signs of inflammation at the onset of the disease, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed:
- Indomethacin;
- Diclofenac;
- Nimesulide;
- Ibuprofen;
- Meloxicam et al.
For local anesthesia, a Versatis medicinal patch containing Lidocaine can be used.
In case of severe edema, diuretics (Furosemide), agents with anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory effects (L-lysine escinate) and capillary stabilizing agents (Cyclo-3-fort) are used to reduce compression.
To improve nerve nutrition, B vitamins are used:
- Combilipen;
- Neurorubin;
- Milgamma;
- Neurovitan et al.
If there are no signs of elimination of the inflammatory reaction, instead of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, a mixture of a solution of Hydrocortisone and a local anesthetic (Lidocaine or Novocaine) is prescribed by injection into the cubital canal or Guyon's canal.
In most cases, this procedure eliminates the symptoms of neuropathy and has a long-lasting therapeutic effect. Drug treatment of neuropathies is complemented by physiotherapeutic procedures:
- acupuncture;
- electrophoresis with drugs;
- ultrasound;
- massage;
- physiotherapy;
- electromyostimulation.
Surgery
If conservative therapy is ineffective and there are pronounced scar changes in the area where the nerve passes through the canals, surgical intervention is recommended. The purpose of such operations is aimed at eliminating (cutting and removing) the structures that compress the ulnar nerve.
When there is compression in the cubital canal, its plasty is performed, part of the epicondyle is removed and a new canal is created to move the nerve. In cases of Guyon's canal syndrome, a dissection of the palmar carpal ligament above the canal is performed.
Performing a surgical operation allows you to free the nerve from compression, but to completely restore all its lost functions, additional treatment is prescribed:
- medications - analgesics, drugs to improve nerve nutrition and conductivity, vitamins, diuretics;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- physiotherapy.
After the operation is completed, the patient’s arm is immobilized using a splint or splint for 7-10 days. After its removal, the patient is allowed to perform passive movements. After 3-4 weeks, active movements are allowed, and only after 2 months can weight-bearing exercises and throws be performed.
The duration of rehabilitation of a patient after such surgical interventions is about 3-6 months. The completeness of restoration of nerve function largely depends on the timeliness of treatment. In advanced cases, even surgical intervention does not allow complete rehabilitation, and some disturbances in sensitivity and movement will accompany the patient throughout his life.
Neuropathies of the ulnar nerve can be provoked by various reasons, which determine further tactics for treating the disease. The main manifestations of these neurological pathologies are the appearance of pain, paresthesia and sensory disturbances. And the effectiveness of their treatment is largely determined by the timeliness of contacting a doctor.
Diagnostics
The neurologist first establishes the symptoms and conducts an examination. Also, to determine the degree of impairment of motor activity, it is necessary to perform several tests:
- The patient should press his palms together and spread his fingers apart. With neuritis of the radial nerve, the fingers of the damaged limb will slide over the palm of the healthy one.
- The patient's injured hand should be placed on the table, palm down. As the disease progresses, he will not be able to place his middle finger on his index or ring finger.
- The patient should stand up and lower his arms along the body. With neuritis, it will be impossible to turn the injured hand forward with the palm and raise the thumb up.
Radial neuritis is diagnosed based on test results. After establishing the degree and area of localization of inflammation, the doctor determines treatment regimens.
How is sciatic neuralgia treated?
Treatment of sciatic nerve neuritis must begin with eliminating the causes that provoked it. If these are infections, then it is advisable to first conduct a course of therapy with an infectious disease specialist.
Restoring the functionality of a damaged nerve fiber is a serious task for a neurologist. He can use the following manual therapy methods in the treatment of sciatic nerve neuritis:
- manual traction – allows you to eliminate the compressive effect on the radicular nerves, their branches, and the structure of the sciatic nerve;
- osteopathy – improves the processes of microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid in the source of inflammation, thereby starting the process of axonal regeneration;
- massage occupies a separate place in the treatment of sciatic nerve neuritis, since it allows you to completely preserve muscle mass and prevent the patient from becoming disabled;
- physiotherapy accelerates the metabolic process at the cellular level;
- reflexology starts the healing process by using the hidden reserves of the human body;
- Laser exposure removes cicatricial deformities and relieves pressure from the nerve fiber.
Therapeutic gymnastics and kinesiotherapy are used in the treatment of sciatic nerve neuritis in combination with massage. This is a very effective technique, it allows you to improve axonal trophism and achieve complete recovery of the patient.
If you need safe and effective treatment for sciatic nerve neuritis, then you can make a free appointment with a neurologist at our manual therapy clinic in Moscow. The doctor will conduct an examination and examination and make an accurate diagnosis. He will then develop a personalized treatment plan.
Treatment of hand neuritis
Antibiotics
The course of therapy depends on the cause of the disease. Antibiotics are used in cases where neuritis is a complication of an infectious or bacterial disease.
The goal of treatment is to restore blood circulation in the limb. For this purpose, medications and vitamin complexes are prescribed that help normalize the functioning of the peripheral nervous system. Taking anti-inflammatory drugs such as Ibuprofen is also indicated. It helps not only stop the pathological process, but also relieve pain.
After symptoms are eliminated, patients are prescribed a course of therapeutic massage and physiotherapy. Treatment methods allow you to restore hand function. Electrophoresis and magnetic therapy are indicated .
In order not to have to visit the physical therapy room again, especially during epidemics, you can do electrophoresis at home. To do this, you just need to purchase an Elfor device. This is a device for performing galvanization and electrophoresis procedures at home. This is an indispensable thing for neuritis and neuralgia, osteochondrosis and radiculitis, as well as other diseases. The device is easy to use, everything is written in detail in the instructions.
In severe cases, when suturing of injured nerve fibers is required, surgical intervention is performed.
Treatment with folk remedies is strictly prohibited, as this can lead to irreversible processes, and it will be impossible to restore motor activity and sensitivity.
Hygroma of the wrist and hand: is treatment possible without surgery?
Hygroma of the wrist is a rather unpleasant disease. This is a pathological tumor-like formation, benign in nature, which consists of a capsule and serous contents.
Simply put, this is a cyst of the articular capsule or, as people say, a lump on the wrist.
The formation causes a lot of inconvenience, sometimes it hurts, and increases in size. The sooner you treat hygroma, the easier it will be to get rid of it.
Read more about hygromas in this article...
Causes of wrist hygroma
The insidiousness of the disease is that it can occur for no apparent reason and getting rid of it is not as easy as we would like. Factors such as:
- constant force loads on the hands;
- consequence of untreated injury;
- genetic factor - our ancestors also had this disease;
- inflammation of the joints of the hands, wrist joint;
- similar movements for certain professional skills.
It has been noticed that hand hygroma often occurs in computer scientists, typists on keyboards, and typewriters. “Office” hygiene has not been canceled, and failure to maintain the correct position of hands at a desk when working at a computer, lack of rest, hand exercises, and constant rubbing of uncovered areas of the hands on various surfaces can increase the risk of a bump.
If you dig deeper, the reason for the appearance of the cyst lies in the pathological divergence of the fibrous fibers of the joint capsule and the formation of a defect in the form of a protrusion.
The joint fluid fills the defects and over time they are more and more limited from the joint cavity. A cyst is formed filled with serous fluid.
Hygroma symptoms
With the classic course of hygroma on the hand, it does not cause a person much discomfort. You can suspect her based on the following signs:
- A round, dense subcutaneous formation appears near the joint;
- The surface of the cyst is smooth in most cases, the skin color is not changed;
- A lump on the hand under the skin can grow from 0.5 to 3 cm. It further increases due to the accumulation of fluid;
- Growth rates vary: a lump on the hand can grow rapidly in a few days, or it can “sit” in place for years;
- A volumetric formation that is not fused with the surrounding tissues, but is always fixed at the base with the joint capsule or tendon sheath;
- When pressed, pain and discomfort appear in the joint, and not in the tissues of the hygroma;
- If the tumor-like formation has grown to a large size, then the movement of fluid in it can be palpated;
- The lump on the wrist on the top of the hand is hard
- The disease is considered chronic because it can exist for more than one year.
The formation is localized in the projections of the joints of the hands.
Hygroma of the wrist joint of the hand is observed in the vast majority of cases. It grows mainly on the back of the hand.
The lump on the inside of the wrist is dangerous because it is located near the radial artery, which can be easily damaged during surgery. Hygroma on the finger is also a common occurrence and causes considerable discomfort, pain and limited mobility.
Hygroma in children
Manifestations of hygroma in children are the same as in adults. A voluminous lump forms on the finger or wrist. It is soft to the touch, you can feel the movement of the liquid contents. The color and temperature of the skin in the affected area are not changed at the initial stage.
The formation appears after injury or due to hereditary factors.
Hygroma on a child’s arm requires particularly careful handling and approach to treatment. Children have a lower pain threshold, it is more difficult for them to survive any surgical interventions, and they may be intolerant to painkillers. In addition, not every parent will agree that scars will appear on their child’s body at a young age.
In such cases, laser treatment is used to remove hygroma of a child’s wrist or finger. The method has many advantages and is successfully used not only to treat pediatric patients, but also adults.
The laser more effectively excises the capsule and remaining diseased epithelium.
Complications with this method of treatment are minimal. There is no need to worry that after the operation there will be pain, the stitches will rub, or infection will occur. The laser treatment method is considered a safer and sterile way to eliminate any pathology compared to the classical surgical method. The use of this method does not exclude the appearance of scars, but their size will be minimal.
Diagnostics
First, the doctor must listen to the patient’s complaints and examine the affected area. After these steps, a preliminary diagnosis can be made and a suitable treatment method can be prescribed. If necessary, additional diagnostic methods may be prescribed:
- Radiography;
- Ultrasound of the hygroma and tissues around it;
- Puncture of hand hygroma is prescribed in case of complications to examine the fluid contents.
Read about other modern methods for diagnosing joint diseases in this article...
How to treat hygroma on the wrist?
Indications for removal of hygroma on the wrist or finger include both an unsightly aesthetic appearance and impaired functionality of the joint, the appearance of pain, and limitation of hand movement due to compression of nerves and blood vessels. The previously popular method of crushing a hygroma is becoming a thing of the past. In addition to extreme pain, this technique carries with it the risk of complications and rapid relapse. Treatment of hygroma of the hand can be conservative or surgical.
It is worth considering that if a hygroma of the wrist has formed, treatment without surgery does not always end with success.
In 80-85% of cases, relapses occur after conservative treatment. This is explained by the fact that the capsule of the formation, which is not removed, eventually fills with liquid again. A radical method of curing a lump on a finger joint or on the wrist is surgical treatment with removal of the contents and capsule of the hygroma. But a conservative treatment method is also used in cases where the patient himself desires it or if there are contraindications to surgical intervention. Treatment of hand hygroma with traditional methods also deserves special attention.
Physiotherapeutic methods can be used as an independent type of treatment or as an addition to the main one. Often these techniques are used in the recovery period after surgical treatment. They include:
- applications in the form of mud and paraffins;
- electrophoresis with drugs (iodine);
- ultrasound therapy with hydrocortisone (steroid hormone);
- UHF therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- shock wave therapy.
You can read more about physiotherapeutic treatment methods here...
Physical procedures cannot be used if the hygroma on the arm becomes inflamed, the process of suppuration begins, or was preceded by traumatic crushing.
Educational puncture is done most often. After local anesthesia, a lump on the finger or wrist is punctured with a needle and syringe. A transparent viscous jelly-like mass is pumped out of the cyst and washed with antiseptics to prevent infection during puncture. After the procedure, a sterile bandage is applied. In some cases, several punctures are made until the formation completely disappears. How to carry out this manipulation, see the video:
Unfortunately, after a puncture, a hygroma on the palm often appears again and can transform into a multi-chamber cyst, which is much more difficult to remove.
It is necessary to get rid of the pathological connective tissue that makes up the walls of the hygroma and which secretes fluid. Only then will there be complete recovery.
Drug treatment includes a combination of puncturing the hygroma on the palm and introducing medications into its capsule. For example, they do a blockade using glucocorticosteroids. Limitations on the indications for the administration of GCS are the size of the formation up to 1 cm. After puncture, removal of the contents, and washing with antiseptics, GCS is administered (for example, a drug such as Diprospan is used). Next, the joint is immobilized with a bandage for 3-5 weeks. During this period, the walls of the capsule are overgrown with scar tissue. Sclerotherapy is carried out by the above-mentioned puncture, only at the end special sclerotic or enzymatic drugs are also administered, under the influence of which the hygroma capsule collapses, sclerosis and thus disappears.
Traditional treatment. Is it possible to cure hygroma on the hand without surgery?
Treatment without surgery with folk remedies for hygroma of the wrist or fingers is not always successful, but it also has the right to be.
You should use traditional medicine recipes only after consultation with a medical specialist.
A hygroma on the hand, treated with folk remedies actively and correctly, may decrease and heal. Compress recipes:
- Compress from celandine juice. Apply a bandage soaked in celandine juice to the previously steamed hand in the affected area, put a piece of polyethylene on top, and wrap it overnight. Such procedures need to be done from 7 to 19 times. You will need about 1 tablespoon of celandine juice.
- Cabbage compress. We knead a piece of cabbage leaf, grease the inside with honey and apply it to the hygroma of the brush, the treatment of which we want to carry out without surgery. Apply a bandage for 8-10 hours. You need to do such procedures for 10 days in a row.
- Compress from wormwood stem. Grind 2-3 young fresh wormwood stalks in a blender. Apply the paste to the hygroma on the wrist of the hand that we are treating, and wrap it with a bandage for 5-6 hours. The course of treatment is 3 weeks.
Surgery
The operation to remove hygroma of the hand can be performed under local or general anesthesia, which depends on the age of the patient, the size of the formation, its location, and the depth of its occurrence.
Surgical interventions on the palmar surface of the hand carry more risks, since in this area there are many nerve fibers and blood vessels, damage to which threatens to disrupt the motor function of the hand.
During surgical treatment of hygroma of the finger or wrist, a skin incision is made corresponding to the size of the formation. Next, the lump is carefully separated from the soft tissue and excised. Then the wound is sutured, a sterile bandage, plaster or orthosis is made for immobilization for 7 days. On day 10, the sutures are removed. How to remove a hygroma on the wrist or on another part of the hand so that the scar is minimal?
Now there are modern techniques that allow you to make an incision of a few millimeters and effectively remove the cyst.
The method is called endoscopy and is used using an endoscope.
Forecast
The prognosis for hand hygroma is favorable in most cases. Sometimes the formation can become inflamed and therefore increase in size. The disease is highly curable and relapses rarely occur after surgery. Re-formation, be it a hygroma of the tendon of 1 finger of the left hand or another part of the hand, can occur if the tissue excision was not carried out correctly.
Disease prevention
People with a hereditary predisposition to the occurrence of this disease, as well as those who have heavy force loads on their hands, should first of all think about preventing hygroma.
To avoid having to look for the causes and treatment of lumps on your fingers or wrist, you should follow these recommendations:
- Treat your hand joints with care, avoid injuries and excessive stress;
- If a heavy force load is expected, then use an elastic bandage;
- If inflammation or other changes in the area of the hand joints begin, you should immediately visit a specialist!
How to prevent hand neuritis and its prevention
As a preventative measure, various hand injuries and hypothermia should be avoided. It is also recommended to promptly treat all infectious diseases and vaccinate. In order to maintain immunity, you need to eat right, exercise, follow a work and rest schedule, and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Neuritis of the hand manifests itself with pronounced symptoms, but can be treated without difficulty. The main goal of therapy is to restore impaired blood circulation. If you consult a specialist in a timely manner, the disease goes away without a trace and there are no consequences. But you should remember that self-medication is strictly prohibited.
Causes of defeat
Damage to the median nerve is caused by the influence of internal and external factors, namely:
- Regular long-term use of a computer mouse and keyboard. Constant, identical movements while working at a computer lead to the development of a pathology such as carpal tunnel syndrome, a disease of the peripheral nervous system. The arms are in a static position of flexion or extension, blood circulation and trophism of the nervous tissue are disrupted. The risk factors here are the female gender, since the median nerve canal is anatomically narrower than in males, the third or fourth stage of obesity - the load on the upper limb increases.
- All types of arthritis. Most problems with the body begin with inflammation. The soft tissues swell, the lumen of the canal narrows, and accordingly the nerve is exposed to external pressure. In addition, due to the chronic pathological process, many tissues become sclerotic and abraded. The articular surfaces gradually grow together as the bone surface is exposed. The hand becomes deformed over time, and due to the incorrect position of the anatomical structures, the patient’s condition worsens.
- Injuries. A common problem in orthopedics in conjunction with neurology. When a hand is sprained, dislocated, fractured or bruised, the body’s adequate reaction is the expansion of blood vessels and the accumulation of fluid in the soft tissues. As in the previous case, compression of the nerve occurs. In addition, the bones are displaced and there is a risk of improper fusion, which dramatically aggravates the situation.
- The accumulation of large amounts of fluid is associated with concomitant human diseases, for example, nephrosclerosis, acute or chronic renal failure, pregnancy, menopause, lack of thyroid hormone, dysfunction of the genital organs, and so on.
- Edema is caused by specific and nonspecific pathogens (tenosynovitis). The pathology can occur as a catarrhal form, or with the formation of pus. Microorganisms reach the affected area in several ways: from neighboring anatomical structures, through the blood, and directly through the wound.
- Diabetes. The causative factor is impaired glucose metabolism and energy starvation of cells, which gradually die. The nerve fiber is destroyed.
- Genetic predisposition. If close relatives (brothers, sisters, parents) suffered from similar diseases, then there is a high risk of developing it in the person himself.
Causes of the disease
The most common provoking factor causing ulnar nerve neuritis is considered to be hypothermia. In second place is the development of complications after bacterial or viral infections, as well as:
- consequences after fractures;
- being in one position;
- circulatory disorders;
- endocrine diseases;
- anatomical disorders;
- osteochondrosis;
- intoxication.
Among endocrine dysfunctions, diabetes mellitus and thyroid dysfunction are dangerous. The disease can cause pinching of the nerve trunk along its course in the following situations:
- during a sudden change in body position;
- with incorrect posture;
- as a result of surgery;
- after resting your elbow on the surface for a long time.
Additional causes of neuritis are nerve nutritional disorders, vitamin deficiencies, complications after measles, diphtheria, brucellosis, and typhoid fever. Last but not least is reduced immunity and the factors that cause it.