Painkillers
This type of drugs can be divided into 2 types: those with a purely analgesic effect and anti-inflammatory (combining components that help relieve pain and eliminate the cause of the inflammatory process). The basis for both groups of these drugs is metamizole sodium (analgin).
Among the painkillers prescribed for neuralgia are:
- Tempalgin is a drug that has a complex effect and relieves pain in the shortest possible time;
- baralgin - blocks pain receptors. In essence, this is the same analgin produced abroad;
- diclofenac - the drug relieves inflammation, helps to quickly reduce temperature and relieve pain.
How to treat neuralgia at home. How to treat neuralgia in the acute stage
Drug treatment alone during an exacerbation may not produce the desired results. The complexity of a syndrome such as neuralgia means treatment must be complex, long-term and combined. The very first cure for neuralgia is painkillers: ointments, tablets, compresses, injections. In combination with pain relief, doctors prescribe medications:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Indomethacin);
- anticonvulsants (Carbamazepine, Baclofen, Phenytoin);
- muscle relaxants (Clonazepam, Sirdalud, Mydocalm).
Pain reliever for neuralgia
Analgesics are often used to relieve the first signs of the disease. Ortofen and Diclofenac are not recommended for use as painkillers for neuralgia. Preparations with ibuprofen and nimesulide have the best effect on the source of pain. A common method of pain relief now is the fentanyl patch. Muscle spasms are well relieved by the drug Lyrica; it is most often used in the treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. An analgesic such as Pentalgin is effective at the initial stage.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for neuralgia
The most effective pills for neuralgia are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which not only relieve pain, but also relieve inflammation. Such tablets include Indomethacin, Ibuprofen, Sulindac, Ketorolac. All these medications are irritating to the kidneys and gastric mucosa, so their use should only be prescribed by a doctor after examination.
Ointment for neuralgia
To suppress unpleasant symptoms, an ointment for neuralgia will help, the effect of which is to:
- warming tissues and relaxing them;
- improving local blood circulation;
- increasing the elasticity of diseased ligaments;
- activation of local metabolic processes.
The ointments contain anti-inflammatory and analgesic components. Ointments based on bee and snake venoms are effective. Popular ointments that are used to relieve pain and inflammation are Viprosal, Finalgon, Apizartron, Myoton. The main effect is achieved by warming the tissues, improving blood circulation and dilating blood vessels. Before using products with this composition, you should read the instructions. Such ointments, for example, cannot be used during pregnancy and lactation.
Injections for neuralgia
What to do with neuralgia if you can’t use ointments, tablets, or they simply don’t help? Drugs for neuralgia that are used for injection are effective. For severe symptoms, analgesic injections are the best way to restore mobility and normal condition to the patient. Injections of Spazgan, Baralgin, Trigan are used. It is important to remember that an injection to numb an inflamed nerve should only be given by a doctor who knows human anatomy well.
Massage for neuralgia
During the period when acute pain subsides, it is effective to do acupressure, general or cupping massage to relieve tension in the muscles. Thus, massage for intercostal neuralgia, together with acupuncture, will help improve lymph flow, relieve muscle tension between the ribs, prevent muscle wasting and promote rapid recovery and restoration of mobility. Massage in combination with physiotherapy is effective - physical therapy, which is performed under the guidance of a doctor, will help cope with pain.
Treatment of neuralgia during pregnancy
Neuralgia often develops during pregnancy. This happens due to a sharp gain in body weight or high fetal weight in the final stages. In principle, pregnant women are not recommended to take strong painkillers, but still, in case of acute pain, strictly as prescribed by the attending physician, the following drugs can be prescribed:
- voltaren,
- tizanidine,
- sirdalud,
- diclofenac.
In addition, if neuroconductivity is impaired, multivitamin complexes can be prescribed.
Set of exercises
- The patient lies on a special mat for gymnastics. Shoes and socks should be removed. You need to stretch your upper limbs up, feet down. Then pull your toes towards you, your feet pointing upward. The body can wriggle, with this exercise against intercostal neuralgia stretching the spinal column.
- Next, the patient lies with arms outstretched, shoulder girdle lowered, each foot pressed to the floor. You need to move your pelvis to the left side. Inhale, while exhaling, each knee goes to the right side, rushing together to the surface of the floor. At this moment the head looks in the other direction. This state must be fixed for 15 seconds, and also performed on the other side.
- Continue to lie on the surface of the floor, the upper limbs should be lowered so that they are parallel to the body, the soles are connected, each knee is spread to different edges. While inhaling, raise the sacrum with the lower back and chest. Move the cervical spine to relieve tension. Fix this state for up to 10 seconds, return the body to a horizontal position in the reverse order of execution. Do 4 approaches. The gluteal area should be tense and the neck should be relaxed.
- Connect the lower limbs and pull them towards the chest. Hug your knees with your palms. Inhale, as you exhale, your forehead should touch your knees. After 2-3 seconds, lower yourself to the floor surface.
Stretch your lower limbs, slightly bending them at the knee joints, pull them to your chest, and hug the popliteal area of both legs with your upper limbs
Roll on your back with caution. Repeat the exercise no more than 3 times
You should not overstrain your neck, it is unsafe. Sit in the lotus position if possible. Take the upper limbs behind the back area, each hand parallel to each other. The chest is sagging anteriorly. Raise the pelvic area while inhaling, the gluteal muscles are tense. Then slowly lower down. Perform no more than 4 times. Make sure that the cervical spine is not overstrained. Next you need to sit down. The lower back is straightened, the lower limbs are brought together, the knee joints are bent, each heel is pulled towards the gluteal area. Use your palms to fix the popliteal area. Having rounded your back, you need to lower yourself down, inhaling at the same time. As you exhale, pull your body back toward your lower limbs. Repeat the exercise 3 times. Spread the lower limbs at shoulder width, bend the knee joints, and move the upper limbs behind the back so that they lie under the shoulder girdle. Raise the pelvic area. The body with the head and hips form a straight line. Perform the exercise 4-5 times. While sitting, extend your lower limbs forward. Upper ones ─ lift up, secure in a “lock”. The back stretches upward. Each leg is completely relaxed. Stretch both arms forward. As you exhale, turn your entire body to the left side with the left upper limb abducted 180°. Also perform this exercise in the opposite direction. It will stretch the intercostal spaces well, and intercostal neuralgia will gradually disappear. The left leg must be bent at the knee joint. The right palm is located on the left knee joint, and the left palm is located on the floor surface from the side edge. Perform several smooth twists to the left side. The coccygeal area and the crown form a straight line. The thoracic spine is pulled towards the left edge and upward. This exercise is also useful for eliminating neuralgia and will stretch the chest well.
- Sit cross-legged with your arms down in front of you, resting on your palms. Lower yourself forward, relaxing your lumbar region as much as possible.
- Stand up. Soles ─ shoulder width apart. Raise your upper limbs above your head, clasping your fingers. Turn your torso towards the left edge. Hold the position for 2-3 seconds, repeat on the opposite side.
- Repeat the previous type of exercise with the upper limbs already placed on the sides.
- Spread your arms to the sides, touch one to the floor surface, and raise the other up. Position your head so as to look at the raised upper limb.
- Two hands should touch the floor, each leg straight. Stretch your back, gently bend down, fix the position for no more than 10 seconds.
This treatment at home can be performed daily to eliminate intercostal neuralgia. You just need to not be lazy and do these exercises.
{SOURCE}
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia
For diseases of this type, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are usually prescribed:
- spazgan,
- spasmalgon,
- nize,
- ketoprofen,
- pentalgin.
In addition, the following ointments are used:
- nize,
- ortofen,
- voltaren,
- diclofenac.
Sometimes, with severe inflammation of the nerve endings and the patient’s unstable emotional state, some sedatives, such as Persen or Afobazole, may be prescribed. You can additionally read how complex treatment of intercostal neuralgia is carried out on the website of a clinic specializing in neurology..
Causes
Nerve endings can become trapped in muscle fibers due to the development and progression of the following diseases:
- osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine,
- ankylosing spondylitis,
- scoliosis with curvature of the chest,
- spondylitis,
- herniated intervertebral discs,
- kyphosis in the progressing stage,
- infectious infection,
- foodborne toxic infection, incl. alcohol poisoning,
- spondylopathy,
- multiple sclerosis,
- diabetes,
- aortic aneurysm,
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, colitis, hepatitis, renal failure, etc.).
Among other reasons causing the development of the disease are:
- nervous stress,
- mechanical injuries,
- increased physical activity, especially without pre-warming the muscles,
- passive lifestyle,
- hypothermia.
After diagnostics and diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a set of measures aimed at anesthetizing the affected area of the back, releasing the nerve root and treating the underlying disease that caused the pinching.
Sedatives
Unfortunately, few specialists prescribe sedatives to their patients, although patients really need the latter. Most patients with intercostal neuralgia complain of constant bad mood, depression and dark thoughts. All this is a sure sign that the patient requires comprehensive assistance. By the way, sedatives work not only towards the psychological state of the patient.
Thanks to sedatives, a person will begin to feel calmer about the events occurring in his life around him and not react so violently even to unpleasant situations. Additionally, sedatives will help minimize persistent spasms.
They also help relax skeletal muscles, relieve nervous tension and even high blood pressure, which is usually on the list of the patient's general clinical picture. In other words, this is exactly what will help the patient relax, literally and figuratively. Without sedative medications, therapy may not be effective.
By the way, the most popular remedies with a sedative effect (based on plants - chamomile, motherwort and valerian) are not as effective as pharmaceuticals, but their undoubted benefits cannot be ruled out either. Plant-based products promote good sleep, and this is an important factor in health. Among the most popular drugs in this group is Novopassit.
Infusions, alcohol tinctures, decoctions for internal use
Decoction of willow bark. This is a good anti-inflammatory and pain reliever. You need to take 1 large spoon (tablespoon) of crushed bark and place it in a saucepan with 300 ml of water. Cook for half an hour in a water bath. Then strain. You should drink large spoons 3 or more times a day, shortly before meals;
A decoction of mint leaves has a calming effect, normalizes sleep, relieves pain, and relieves muscle spasms. To prepare, you need to take a large spoon (tablespoon) of dry mint and boil it with 200 ml of water in a water bath. Drink a third of a glass shortly before main meals;
Alcohol tincture of thyme or thyme. Take 10 g of herb per 100 ml of medical alcohol. Leave for a week, shake periodically. Strain after steeping. Place 15 or a little more drops into a cup of water. The number of receptions per day is at least three. Thyme has anti-inflammatory properties, relieves pain, strengthens the immune system;
Chamomile decoction. You should take 2 large spoons and add 200 ml of water. Brew for a quarter of an hour in a water bath. After cooling, strain. Drink 30 ml before main meals. Has a calming, antispasmodic and analgesic effect.
Prevention
A pinched nerve often occurs during a sedentary lifestyle. Intercostal neuralgia often results from osteochondrosis, lordosis, and radiculitis.
In order not to pinch a nerve and cause painful neuropathy, you should keep your posture as straight as possible, do not hunch over, and do not overwork the muscles of the lower back and back.
And yet, if a sudden attack of pain occurs, you need to switch to a lighter mode of activity, do not overcool and avoid intense physical strain.
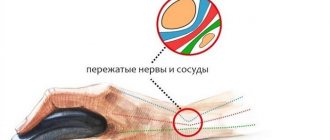
One of the reasons for pain in the rib area is pinching of the intercostal nerve (neuralgia). Painful manifestations are usually localized between the ribs on the right or left, and can also penetrate the back all the way to the lower back. This disease is not independent, but develops as a result of damage to the spinal column. In this case, damage to the nerve fibers is caused by a narrowing of the openings between the vertebrae through which they exit, due to pathological changes in the discs, the vertebrae themselves, or their relative positions. The symptoms of neuralgia are very diverse and sometimes similar to the manifestations of other diseases.
Symptoms
Intercostal neuralgia is manifested by pain, the nature and severity of which is determined by the degree of pinching of the nerve and its location. In this case, pain has a number of characteristics:
- The onset is acute, piercing, highly intense, reminiscent of an electric shock or a heart attack, which is due to the special sensitivity of the clenched fibers.
- After a few minutes, the pain decreases, but with the slightest movement it returns again or becomes wave-like.
- Most often, the pain is felt on one side of the chest, radiating under the shoulder blade or below, and when localized on the left side, it resembles a sharp tingling sensation in the heart.
- There is a close connection with inhalation - as the chest expands, the pain increases significantly.
- A burning sensation, tingling or decreased sensitivity may occur at the site of pinched roots.
Also, pain appears when there is a sudden change in posture or palpation of the ribs, radiating to the stomach, neck, shoulder or other parts.
In addition, pinching of the intercostal nerve can lead to dysfunction of nearby internal organs. Most often, tachycardia and angina pectoris develop, the acidity of gastric juice increases, intracranial and blood pressure rises, and congestion appears in the lungs. The last symptom is especially painful, since the combination of neuralgia with cough does not stop the attack and can significantly aggravate the symptoms of the disease.
To differentiate neuralgic pain in the left intercostal space from an attack of angina, you should know that the manifestations of a heart attack do not depend on the movement or coughing performed, and are also reduced when taking the appropriate medication.
However, during a heart attack, the pain is also not eliminated by a pill, so if you suspect a cardiac pathology, you need to call a doctor and do an ECG.
When the nerves of the lower ribs are damaged, symptoms of renal colic may appear. In very rare cases, signs of intercostal neuralgia resemble manifestations of diseases of the chest organs - lungs, mediastinum and others.