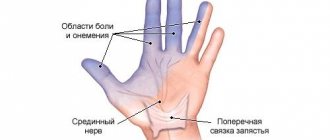
The occurrence of sudden piercing pain in the leg, which also affects the knee joint area, may indicate a pinched nerve. Sharp pain in any situation is an alarming symptom, signaling the presence of serious pathologies and requiring competent diagnosis and treatment.
But such symptoms do not always indicate extensive damage. Pain can occur when there is a local effect on nerve tissue, namely when it is pathologically pinched. The disease, in addition to painful sensations, carries a certain threat. Because if a nerve is pinched for a long time without the necessary treatment, there is a real threat of its endings dying off.
Why does a pinched nerve occur?
When a nerve is pinched, mechanical compression of the nerve fibers occurs. Under the influence of compression, the nerve becomes inflamed, which provokes negative consequences in the form of complete or partial loss of functionality of the nerve canal.
- pain syndrome develops;
- nerve conduction is disrupted;
- sensitivity is lost;
- muscle atrophy appears.
The location of the disease, accompanied by pain in the knee joint, is quite extensive. Because any group of nerves that are responsible for the functionality of the lower extremities can be pinched.
Most often, knee joint problems are associated with pinching of the sciatic, tibial, shutter, femoral or gluteal nerve . Pinching, under no circumstances, is a spontaneous phenomenon. It always signals the presence of a certain pathology, which affects the nerve in a certain way.
These may be everyday factors, such as fractures, direct injuries, or meniscus damage, as well as increased physical activity. Quite serious diseases that are located directly in the knee or hip joint, such as an oncological tumor or inflammatory processes, can also lead to pinching.
- Pathologies of the knee joint in the form of arthritis, polyarthritis, advanced stage of arthrosis. With inflammation that occurs during exacerbations of such diseases, tissue swelling and enlargement of the knee joint are observed, which provokes a negative effect on the nerve endings.
- Injuries of various locations. Trauma-related entrapment can occur for two reasons. In the first case, this phenomenon is explained by the formation of tissue swelling, which occurs subsequent to damage to the meniscus, tendons or ligaments. The second reason is direct compression of nerve fibers by fragments of bone or cartilage tissue, which occur as a result of fractures or damage, or torsion of the meniscus. To eliminate the negative effects of a torsion of the meniscus or fragments on the nerve fibers, surgery is often necessary.
- Edema. With extensive tissue swelling caused by vascular, articular, traumatic, hormonal, and autoimmune processes, a negative effect on nearby nerve tissue is observed.
- Tumor. If a tumor of various types grows in the area of the knee joint or pelvis, compression may occur on the nerves that are located in close proximity to the place where the tumor is localized.
- Excessive loads. During physical overload, not only injuries to the knee joint can occur, but also muscle spasms, which is accompanied by compression of the nerve.
- In turn, the lack of sufficient physical activity and prolonged stay in a static position, as well as the presence of excess weight, are closely related to partial dysfunction of the knee joint. Such deviations are often complicated by nerve entrapment.
Quite often, pain in the knee area, spreading throughout the entire leg, is caused by pinching of the sciatic nerve. Due to the fact that the sciatic nerve originates from the spinal column, its infringement is not associated with pathologies of the knee joint. Problems of the sciatic nerve arise as a result of any pathologies of an inflammatory, traumatic nature, localized in the lower parts of the spine.
The cause of radicular syndrome, as a result of which the sciatic nerve becomes inflamed, may be associated with the presence of hernias, protrusion, osteochondrosis, spondylosis and other pathologies of the spine. Swelling or swelling in the lower back area also affects the sciatic nerve.
Causes of pinching
The following nerves are responsible for the innervation and mobility of the knee:
- shutter;
- sciatic;
- femoral;
- gluteal;
- tibial.
This means that pain may develop in the knee joint due to a number of reasons.
Often compression occurs due to injuries or fractures that affect the areas of the nerve fibers mentioned above (pelvis, lumbar area, and others).
Also, pinched nerves in the knee can be caused by:
- arthritis, arthrosis and other pathologies affecting joints;
- osteochondrosis;
- tumor processes (benign, malignant formations, hernias);
- proliferation of bone growths (osteophytes), which leads to calcium deposition;
- overweight;
- abscesses;
- hereditary predisposition;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- autoimmune diseases and hormonal imbalances, which cause tissue swelling;
- physical overload that provokes muscle spasms.
Pinching of the knee nerve also occurs when carrying a child. During pregnancy, a woman's weight increases, and the load experienced by the joints of the lower extremities increases. In addition, after conception, a hormonal imbalance occurs, which contributes to tissue swelling. It is possible that a nerve may be pinched due to prolonged stay in one position.
The appearance of pain localized in the knee is associated with wearing tight clothing or a long course of inflammatory systemic diseases and infectious pathologies.
Common symptoms
When nerve fibers are pinched and, as a result, become inflamed, various symptoms may be observed that are characteristic of a particular nerve that has been compressed. In addition, pinching often manifests itself not only at the location of the pathology, but also along the entire length of the nerve.
- Pain in places that are in the projection of the nerve. If your knee or hip joint hurts, you can assume a pinched sciatic nerve. Sharp pain may intensify if you make certain movements with the limb or fix it in a certain position.
- Pain on palpation. When inflamed, the nerve becomes especially sensitive. Therefore, if you palpate or press on the area where the discomfort occurs, the pain intensifies significantly and becomes acute.
- Loss of mobility. When the sciatic or femoral nerve is compressed, the limb not only hurts, but also loses motor ability. You may encounter problems bending or moving your leg to the side.
- Numbness. When the conductivity of nerve impulses deteriorates due to compression of the nerve, pulling sensations can be replaced by numbness and even complete loss of sensitivity.
- Nervous tic. The leg or muscle tissue may begin to twitch involuntarily due to nerve compression. Most often, the appearance of a nervous tic is associated with damage to the sciatic nerve. Women also face such problems during pregnancy. However, with a nervous tic, it is not always possible to speak with certainty about a pinched nerve. This ailment may have other causes and treatment of a pinched nerve in such cases will not bring results.
What are the symptoms of a pinched nerve in the hip joint?
The hip joint is innervated by several nerves: sciatic, femoral, external cutaneous, obturator, superior and inferior gluteal. Depending on which one is clamped, the symptoms will vary slightly. Naturally, the main sign of a pinched nerve is severe pain. In some cases, the disease may be accompanied by fever, weakness, sweating, chills and other signs of an acute inflammatory process.
Symptoms of a pinched femoral nerve are:
- severe pain localized in the hip joint and spreading to the lumbar region and the anterior inner surface of the thigh and lower leg;
- the pain intensifies when pressing on the inguinal ligament;
- there is a violation of knee flexion;
- with prolonged infringement, atrophic changes in the quadriceps femoris muscle, numbness of the skin, and a sensation of “pins and needles” occur.
When the external cutaneous nerve is pinched, the following are typical:
- numb areas of skin on the outer thigh;
- pain is localized on the outer surface of the thigh;
- the pain is accompanied by the appearance of “goosebumps”, burning, a feeling of cold, tingling of the skin of the thigh;
- there is a disruption in the functioning of the skin, manifested by increased dryness, increased sweating, thinning or hair loss;
- pain decreases when you are in a position with bent knees;
- intermittent claudication;
- hypertension and hyperarthria;
- limitation of mobility due to pain.
Obturator nerve entrapment is characterized by:
- pain manifests itself on the medial surface of the thigh;
- pain affects the perineum and rectum;
- increased pain occurs in a sitting position, as well as when trying to move the leg to the side;
- difficulty keeping the body upright due to instability;
- spasms and convulsions that occur while walking;
- limited mobility in the hip joint reduces the amplitude of the step.
Pinching of the sciatic nerve is accompanied by:
- suddenly arising and disappearing sharp, burning pains;
- soreness along the entire leg on the affected side;
- difficulty bending the knee;
- numbness of the lower leg, buttocks and thighs;
- inability to move your toes.
When the superior and inferior gluteal nerves are pinched, the following are typical:
- pain in the pelvic region, back, leg;
- impaired ability to abduct the leg and extend the knee;
- difficulty moving and holding the body in an upright position.
Treatment of a pinched nerve
Before embarking on active therapeutic actions, it is necessary to find out exactly what influenced the unnatural state of the nerve fibers. To determine which tissues are compressing the nerve, it will be necessary to undergo an X-ray or tomographic examination. It is better to take an X-ray if there is a suspicion of compression of nerve tissue by bone structures. For soft tissue pathologies, it is better to do an MRI.
The range of treatment measures for a pinched nerve is quite diverse. With the right choice of medications and auxiliary methods, treatment allows you to quickly cope with the pathology.
Doctors often prescribe Movalis as a pain reliever.
First of all, treatment begins with eliminating pain . To relieve pain, the patient is advised to remain calm and not subject the limb to unnecessary stress that aggravates the situation. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Aspirin, Movalis are most often prescribed as medicinal pain relief for pinching. Taking such medications can quickly bring relief, but you should strictly adhere to the dosage and do not increase the course of treatment on your own.
In cases where the pain becomes unbearable, the doctor may recommend novocaine or hormonal blockade.
For muscle spasms, pain treatment involves the use of antispasmodics and meorelaxants. By eliminating muscle tension, you can unblock the nerve endings.
Physiotherapeutic procedures will also help cope with pain. Laser therapy, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis and UHF, paraffin heating will help with pinching.
Once severe pain has been eliminated, treatment focuses on unblocking the nerve tissue . If the cause of the pathology is associated with edema, inflammation, treatment involves the use of means to eliminate precisely these processes. These can be either local ointments, compresses, lotions, or anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous medications.
You can cope with a pinched sciatic nerve using massage, acupuncture, and a set of special therapeutic exercises.
For specific causes of impaired functionality of nerve endings, treatment by specialized specialists is often necessary. So, if a tumor is present, the treatment should be carried out by an oncologist. Standard treatment regimens may not be suitable in such situations.
If the pathological reaction is provoked by a meniscal injury or fracture, the help of a traumatologist or surgeon may be needed . Quite often, in case of displaced fractures and complete rupture of the meniscus with the formation of fragments and twists, the only way to get rid of the infringement is surgically.
The help of a surgeon is also needed in the presence of hernias in the spinal column, which provoke loss of motor abilities of the knee joint and limb, as well as other negative consequences.
For any type of nervous disease, vitamin treatment will be effective. An increased intake of vitamins belonging to group B into the body helps improve the conduction of nerve signals and also has an additional analgesic effect.
After eliminating negative symptoms, treatment should be continued . Further therapeutic measures are selected based on the cause that provoked the pathology. If this factor is not eliminated and the underlying disease is not treated, frequent relapses in the form of pinching are possible. Moreover, each time the symptoms will only get worse.
The lack of timely treatment for such diseases can lead to complete loss of sensitivity and immobilization of the lower extremities.
Treatment
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to undergo a high-quality diagnosis and find the root cause that led to the problem. The instructions assume complex treatment of the patient; this is the only way to achieve good results.
Several methods are used to eliminate pain and other manifestations of the disease:
| № | Method of treatment | Effect on the body |
| 1. | Anesthesia | Helps alleviate the patient's condition. |
| 2. | Anti-inflammatory drugs | Reduce inflammation and swelling, which provoke pain. |
| 3. | Physiotherapeutic procedures | Help relieve tension and swelling. |
| 4. | Massage and gymnastics | Help strengthen joints and muscles during the recovery phase |
| 5. | ethnoscience | Serves as an aid to help eliminate the cause of pinching. |
| 6. | Activity mode | Allows you to regulate the degree of load on the joints. |
| 7. | Diet | Helps restore the body, cleanse it of waste and toxins. |
Drug treatment and physiotherapy
Pain syndrome should not be tolerated; it is difficult to cope with pain on your own, which is why painkillers are used. At the same time, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed if the patient has swelling and inflammation of the nerve fibers, as well as nearby tissues.
Only a doctor should do this. The price of drugs may vary significantly, but you should not skimp on your health and look for cheap drugs, or buy only part of the necessary drugs.
Treatment begins with drug therapy
Physiotherapy helps relieve pain, relieve muscle tension, relax and calm the patient. This way you can help relieve inflammation.
Typically, mud wraps, hot baths, magnetic, paraffin therapy, etc. are used for these purposes. Procedures are chosen at the discretion of the specialist, depending on the cause of the disease.
Gymnastics and massage
Massage and gymnastics are not performed in the acute period, when the patient requires rest. Such activities are carried out already during remission. It is best to start with a massage, first relaxing, then warming and restoring.
Exercise therapy will help during the recovery stage of treatment
As soon as relief comes and there is no need to remain in bed, you must immediately move on to exercises. First, you need to start with a light warm-up and gradually move on to more intense loads.
Usually, a physiotherapist teaches a set of exercises to the patient. The video in this article shows some effective therapeutic exercises.
In addition to these methods of therapy, as in the treatment of any other disease, it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle: try to spend more time in the fresh air, eat right, take vitamin and mineral complexes, and move more. Only by acting comprehensively can you quickly solve the problem, eliminate painful symptoms and significantly reduce the possibility of relapse!
Video
Video - What to do if the pain “shoots”
Source sustavkoleni.ru
The sudden appearance of a sharp, piercing pain in the leg, which also affects the knee area, may indicate that a nerve has been pinched in the knee joint. When bending and straightening the leg, the discomfort increases so much that the gait may even change. In addition to acute pain, pinching poses a real threat to human health, and such a symptom should under no circumstances be ignored.
Reasons for infringement
The entire human body is permeated with nerves extending from the spinal cord. In most cases, knee problems are associated with pinched femoral, tibial, gluteal, sciatic or sciatic nerves. This situation always indicates a certain pathology: if a nerve is pinched, it means that some kind of malfunction has occurred in the body.
The reasons that provoke pinched nerve fibers include:
- Pathological condition of the knee joint in the form of polyarthritis, arthritis, advanced stage of arthrosis. In the acute form of these diseases, inflammation in the knee area is observed: the tissues swell, the knee joint increases in size, which leads to a negative effect on the nearby nerves.
- Various injuries. A pinched nerve as a result of injury can occur for two reasons. Severe damage to tendons, ligaments or meniscus results in tissue swelling that can impinge on nerve fibers. In the second case, a similar condition is caused by compression of fragments of cartilage or bone tissue formed during a fracture. In this case, it will be necessary to undergo many operations to restore full function of the damaged nerve.
- Tumor. When a tumor forms and grows strongly in the knee area, compression of the nerves located nearby may occur.
- Edema. Pinching of nerve fibers can occur as a result of extensive swelling of nearby tissues. Edema can be a consequence of hormonal, vascular, articular, traumatic, and autoimmune processes.
- Excessive physical activity. Under heavy loads, muscle spasms are common, causing compression of the nerve. However, a complete lack of moderate exercise, a sedentary lifestyle, and excess weight can also cause a pinched nerve in the knee area.
- Pregnancy. Weight gain during pregnancy causes significant stress on the legs, which can lead to nerve pinching. The development of this pathology is also facilitated by the changes that occur in the female body during the last stages of pregnancy.
In each individual case, a pinched nerve in the knee joint can lead to serious complications, including atrophy of the nerve fiber. Therefore, it is so important to consult a doctor in time and begin treatment.
Prevention
You can prevent recurrence of a pinched nerve by following the rules:
- You need to sleep on a hard, flat surface.
- Avoid heavy lifting and excessive physical activity.
- Do not make quick turns or sudden movements.
- Avoid hypothermia of the extremities and lower back.
- Lose weight, try to adjust your diet and eliminate salted fish, smoked foods, alcohol and caffeine.
- Every morning, do special exercises or just take a walk in the park.
- Swimming has a general strengthening effect on the body.
- Constantly monitor your posture.
A pinched nerve is an unpleasant disease that causes discomfort and pain. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner and identify the cause, the disease goes away faster, and the person returns to the usual rhythm of life without pain.
Characteristic symptoms
A characteristic feature of nerve compression in the knee joint is pronounced symptoms, which can manifest not only in the knee area, but throughout the entire length of the nerve.
The main symptoms of a pinched nerve include:
- severe, sharp pain that intensifies with movement or while fixing a limb in a certain position;
- pain when pressed, as the inflamed nerve becomes very sensitive to any external influences;
- loss of full mobility of the limb, in particular, problems arise when moving the leg to the side or bending the knee;
- numbness of the leg caused by deterioration in the conduction of nerve impulses of the damaged nerve;
- a nervous tic or involuntary jerking of a limb is associated with compression of the sciatic nerve, which most often occurs during pregnancy.
Pinched nerve in the elbow joint
As a result of a sharp impact with the elbow on a hard surface, severe pain occurs in the joint, which spreads to the hand. Similar sensations are caused by compression of the nerve in this area.
Its reasons are the following:
Repeated monotonous movements in the elbow joint and significant physical stress on it, for example, during a bench press;
Frequent fractures, bruises and other mechanical damage;
Pain when a nerve is pinched in the elbow joint is localized not only directly in the area of compression, but is also felt in the fingers. Discomfort is accompanied by numbness and stiffness. These symptoms are most pronounced after the arm has been in a bent position for a long time.
Detection of a pinched nerve in the elbow joint is possible through external examination. Additional diagnostic methods include radiography and computed tomography. Conservative treatment is usually sufficient to eliminate the disease. To do this, the sore spot is treated with anti-inflammatory ointments and gels. During the treatment period, physical stress on the elbow should be minimized and monotonous movements in the joint should be avoided. A few months later, a re-examination is carried out and if there is no improvement, surgery is prescribed.
First aid
If you experience severe pain in the knee area, as well as other warning signs indicating a pinched nerve, the following measures must be taken.
First of all, pain should be eliminated. As a rule, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are recommended as medicinal pain relief: Ibuprofen, Ketonal, Movalis, Declofenac. These medications can quickly eliminate even severe pain. If the pain is so severe that painkillers cannot cope with it, an injection of novocaine is allowed, which is injected into the gluteal muscle.
It is also very important to eliminate any physical activity and provide complete rest to the leg until qualified medical care is provided. Any overstrain when a nerve is pinched can only aggravate the situation.
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate without first consulting a doctor. Heating the knee joint can cause particular harm - this will lead to even greater swelling and compression of the nerve.
Who to contact and how to treat
Before starting treatment measures, it is necessary to find out the true reason why the nerve was compressed. This will require an x-ray or tomography. In this case, an X-ray examination is prescribed if the doctor suspects compression of the nerve by bone tissue, and an MRI will be required for various soft tissue pathologies. Only after carrying out the appropriate diagnosis will the therapist be able to tell which doctor to contact to solve the problem.
Once the acute pain has been eliminated, treatment involves unblocking the nerve fibers.
- for severe muscle spasms, antispasmodics and muscle relaxants are prescribed;
- if pinching is associated with swelling or inflammation, treatment includes the use of appropriate remedies: compresses, ointments, lotions, decongestant and anti-inflammatory medications and herbal decoctions;
- good results are achieved by such physiotherapeutic procedures as therapeutic massage, UHF, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, exercise therapy.
Only by completely eliminating tension in the muscles can damaged nerve endings be unblocked.
However, in case of serious damage to the meniscus, accompanied by the formation of torsions and fragments, it is impossible to eliminate the pinched nerve without surgical intervention. Surgery will also be required if there are hernias in the spine, which can cause problems in the knee joint.
After eliminating the symptoms of a pinched nerve, you will need to undergo a course of vitamin treatment. To speed up recovery processes, B vitamins play a special role. They improve the conductivity of nerve signals, accelerate metabolic processes, restore the full functioning of nervous tissue, and have a mild analgesic effect.
With proper and timely treatment, you can cope with the problem of a pinched nerve in a short time. The main thing is to know what to do if alarming symptoms appear, do not self-medicate and strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Source ortocure.ru
The knee joint is a complex anatomical structure. It bears a heavy load during walking, running and other active movements. Therefore, when patients ask whether a nerve in the knee can be pinched, doctors give a positive answer, which is associated with the frequent occurrence of injuries to the joint.
The sudden onset of acute pain in the knee area is a characteristic symptom of a pinched nerve. The disease develops due to the fact that the nerve fiber is subjected to compression by tissues in the periarticular area.
In addition to pain, the patient is diagnosed with a decrease in range of motion, numbness of the skin and other neurological disorders. Without treatment, nerve restoration is impossible.
For any symptoms of damage, you must contact a traumatologist or neurologist, who can make an accurate diagnosis and answer how to treat a pinched nerve in the knee joint.
Treatment of the knee joint
The disease is diagnosed through an examination, after which the surgeon takes measures to eliminate the causes of pain.
Also, diagnosis of a pinched nerve in a joint is carried out using:
- Nerve conduction studies. Electrodes are attached to the skin, after which the nerves are stimulated using weak electrical impulses. After testing, damaged nerve endings are identified.
- Electromyography, during which a thin needle - an electrode - is inserted into the muscles. The patient alternately relaxes and tenses the muscles. With this test, doctors determine whether there is damage in the nerves leading to the muscles.
- MRI of the knee joint, which can identify pinched nerves.
First of all, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory medications to eliminate pain. If the drugs do not help, strong analgesics are prescribed.
Including corticosteroid injections to relieve pain and stop the inflammatory process. If the pinching does not go away after a few weeks, surgery is prescribed.
After the main symptoms have been eliminated, manual therapy, physical therapy, and therapeutic massage are used in treatment
In order for the pain to stop completely, it is important to reduce excess weight in case of increased body weight, so that the additional load on the knee joint does not affect the condition of the knee joint. It is also recommended to exercise regularly
As a rule, if a patient has a pinched nerve in the knee area, this disease is treated fairly quickly. Pain and limited mobility are eliminated almost after the first treatment session of manual therapy, therapeutic massage or acupuncture.
Using these procedures it is possible to quickly and effectively:
- Eliminate muscle spasm;
- Release nerve endings that are pinched;
- Restore mobility to the lower limbs;
- Get rid of pain.
To prevent pinching of the knee joint from occurring in the future, complex treatment with heating, vacuum therapy, jade massage and other procedures of traditional or Chinese medicine is used.
Main manifestations
When nerve fibers are damaged, the patient always experiences pronounced clinical manifestations. Symptoms appear not only in the area of the knee joint, but also throughout the lower leg, which is associated with the characteristics of the innervation. The main manifestations of the pathology are as follows:
- sharp pain (increases with any movement);
- pain intensifies when you touch the knee (the nerve fiber becomes hypersensitive to any external influences);
- inability to abduct or flex the limb at the knee joint;
- gradually increasing numbness (appears as a result of deterioration in signal conduction along the nerve pathways);
- discomfort at the site of nerve fiber damage;
- change in gait;
- muscle weakness in the affected leg;
- loss of skin sensitivity that develops after numbness.
The clinical picture of the disease depends on which nerve fiber was damaged.
For example, when the femoral nerve is pinched, there may be disturbances in sensitivity and movement of the entire group of muscles of the leg, while with an isolated lesion of the tibial nerve, pathological manifestations affect part of the muscle fibers.
Occurrence of disease
Pathology can develop due to a large number of reasons. It is always worth remembering that only if the main cause of the disease is eliminated, the patient’s recovery is possible. Doctors identify the following risk factors for developing the disease:
- deformation of the legs and incorrect placement of the feet while walking (the load on the knee increases);
- osteoarthritis of the knee joint with deformity;
- inflammatory processes in the joint capsules (bursitis);
- hemarthrosis with a pronounced inflammatory reaction, which can cause compression of the nervous tissue;
- obesity (excess body weight increases the load on the knee);
- post-traumatic scar changes in joint ligaments;
- wearing tight clothing that puts pressure on the knee area;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system (lead to impaired trophism);
- stagnation of lymphatic fluid;
- pregnancy period;
- intense physical activity (strong muscle contraction with spasm can lead to compression of nerve fibers);
- injury to the articular joint (damage to ligaments, menisci, bones);
- malignant tumors in the knee area.
Many patients have a question about what to do if a nerve is pinched in the knee. First of all, you need to contact a medical institution. Pathology in the absence of effective therapy can lead to atrophy of the nerve trunk and disability of a person.
Home therapy
Treatment of a pinched nerve in the knee joint at home can only be carried out after consultation with a doctor. It is important to contact a neurologist in a timely manner to conduct additional research methods and make a correct diagnosis.
When attempting to independently diagnose and self-medicate, the underlying disease may progress, complications may develop, and the patient may become disabled. A sick person can carry out home treatment as an additional therapy when receiving medical care in a clinic.
At home, patients are recommended to use therapeutic exercises for pinched nerves in the knee, massage; outside the acute period, dry heat, folk remedies and some medications should be used.
Physiotherapy
Exercise therapy exercises are used as rehabilitation after the acute inflammatory process subsides. The first classes are supervised by an instructor.
Exercises while lying on your back: bicycle (simulate riding a bicycle 15 seconds forward, 15 seconds back), smoothly pulling your knees to your chest - each exercise is performed 5 times, then 10 or 15.
A gradual increase in load will help restore limb function, strengthen muscles and ligaments, improve blood circulation and relieve pain.
Example of an abdominal exercise: leg raises and hold in the air for 5 seconds. For the first time, it is recommended to perform 5-10 repetitions.
Standing exercises: clapping under the knee, raising legs at right angles, bending back and forth, squats without additional weight, over time you can move on to lunges. The frequency of repetitions becomes higher every day, this helps to quickly strengthen the ligaments and joints.
In addition to gymnastics, they use gentle stretching, slow walking with a gradual increase in distance, and slow climbs up the stairs. Such exercises will have a positive effect on the condition of the knee joint and the body as a whole.
Medication approaches
Symptoms and treatment of a pinched nerve in the knee joint are closely related in that the effectiveness of therapy depends on the timely detection of signs of pathology. When a doctor selects therapy, he focuses, first of all, on the cause of the disease, and then on the clinical manifestations.
Medicines are the basis of treatment. They are used in the following cases:
- in case of bacterial infection, antibiotics are used (second, third or fourth generation cephalosporins, protected penicillins, macrolides or fluoroquinolones);
- if severe pain or swelling develops, treatment includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ketorol, Ibuprofen, Movalis, Diclofenac and others);
- to reduce the symptoms of nerve fiber damage, B vitamin complexes are prescribed (most often injections are carried out intramuscularly) - Combilipen, Neurobion, Trigamma, Beviplex, etc.;
- for severe muscle spasms, antispasmodics (Teopek, Saracin, Solpadein) and muscle relaxants (Mydocalm) are used.
Any medication has certain indications and contraindications, and therefore they should be used only as prescribed by a doctor.
Folk remedies
The use of folk remedies is possible after consultation with a doctor. It is important to note that such treatment approaches do not have proven safety and effectiveness. People often use infusions, decoctions, and ointments. In folk medicine, the following recipes can be used:
- a powder mixture of juniper needles and bay leaves is poured with melted butter, mixed and rubbed into the knee joint. Get an excellent remedy for pain and muscle tension;
- Pounded hops are mixed with oil or a spoonful of pork fat, applied to the affected area and covered with a warm scarf;
- butter ointment and spoons of ammonia are spread on the joint and covered with a handkerchief. The mixture warms, improves blood circulation in tissues;
- a decoction of lilac buds is mixed with pork fat and used as an ointment;
- garlic oil with a teaspoon of vodka is used as a pain reliever;
- decoctions for water procedures (from calamus root, spruce or oak bark, cereal flowers, wormwood);
- A decoction of lingonberry leaves relieves pain.
Traditional treatment has an analgesic effect, accelerates healing and metabolic processes in the lesion, has an anti-inflammatory effect, relieves swelling and redness.
Diagnosis of the disease
First, the doctor interviews the patient and performs functional tests. Radiography plays an important role in making the correct diagnosis. It can be used to determine the underlying cause of pain. More testing is usually required to pinpoint the pain trigger.
It is necessary to review the patient's medical history and ask about current symptoms. The patient may provide information about past surgeries or injuries. Age plays an equally important role in the development of the disease.
Injury
After a conversation with the patient, a physical examination is carried out. There are various physical tests that can help identify knee malalignment, torn ligaments, or other pathologies.
At the next stage of diagnosis, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound examination, which allows you to see the inside of the knee. The examination makes it easy to detect cracks or tears in the menisci and ligaments. With radiography, pathologies are visualized better and more clearly than with ultrasound.
Next, CT (computed tomography) is prescribed as a research method. It helps create a more accurate picture of the affected area of the knee. The technique helps to accurately and painlessly visualize cracks, tears and deformations of the joint.
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) provides information about the inside of the joint. It visualizes soft tissues with high accuracy.
In rare cases, arthroscopy is performed to help make an accurate diagnosis. The knee is viewed using an arthroscope. This method can be used for insertion of instruments and precision treatment of the knee. With the help of arthroscopy, the doctor can restore the thinnest cracks, thereby relieving pain. This diagnostic method, which also serves to treat knee pain, is performed under local anesthesia.
Arthroscopy
However, knee pain may also indicate a neurological disorder, which can be detected and treated by a neurologist. The doctor can either rule out a nerve disorder or try to identify an underlying condition.
What is not recommended to do
When symptoms of the disease occur, patients often perform actions that are contraindicated when a nerve is pinched.
Doctors make the following recommendations:
- you should not apply anything hot (exposure to heat leads to an increase in the severity of the inflammatory reaction and swelling, which contributes to the progression of the disease);
- do not put off visiting the doctor;
- There is no need to make an independent diagnosis and treatment, as this is fraught with the progression of the pathology and the development of complications.
Following advice and timely contacting a medical facility can ensure a quick start of treatment and a person’s recovery.