Hello, dear readers of the “Medicine and Health” blog. We continue to publish articles on the issue of prevention, treatment and recovery after a stroke. So, read the new information - Repeated stroke, prognosis for life in old age.
During the first year, every fourth stroke patient experiences a recurrence of the disease. A repeated stroke increases the motor and speech complications that the patient had, worsens his condition, and increases the risk of developing dementia. The mortality rate for recurrent strokes is higher than for primary strokes.
That is why the rehabilitation of patients who have suffered such a serious illness for the first time involves not only restorative treatment, but also preventive measures. Essentially, preventing a recurrent stroke begins on the first day of the first stroke.
In the vast majority of cases, a recurrent stroke develops according to the same “scenario” as the primary one. This means that it is very important to know and take into account the reasons that caused it initially.
Let me remind you that an ischemic stroke, in other words, a cerebral infarction, occurs due to a lack of blood in a certain area due to blockage of a vessel or when it is very sharply narrowed by an atherosclerotic plaque.
The second type of stroke, hemorrhagic, occurs when a vessel ruptures due to excess blood, causing bleeding in the brain.
Prevention and recommendations
Prevention will significantly reduce the risk of relapse of the disease.
Advice from leading neurologists will help you achieve a positive prognosis. Medical recommendations that include:
- Accurate and timely administration of medications prescribed by a doctor;
- regularly visiting a specialist and undergoing relevant examinations;
- blood pressure control and timely administration of stabilizing medications;
- moderate exercise;
- giving up bad habits, rational nutrition;
- be exposed to stress as little as possible, keep yourself in a stable emotional state.
Prevention is the most effective way to avoid a second stroke and its consequences.
We should not forget that those who have experienced the first case of a vascular accident should especially carefully monitor their health and not allow habits to prevail over reason. Next time the disease may not provide another chance for survival.
Do you still think that it is impossible to cure hypertension?
Hypertension, unfortunately, always leads to heart attack or stroke and death. For many years, we only stopped the symptoms of the disease, namely high blood pressure.
Only constant use of antihypertensive drugs could allow a person to live.
Now hypertension can be CURED; this is available to every resident of the Russian Federation.
Causes of a second stroke
It is almost impossible to avoid the development of a second attack, especially if we talk about pensioners, or about unfinished rehabilitation, when brain cells have not been completely restored, and foci of inflammation have not been eliminated. One factor is enough to cause an attack. This could be a traumatic brain injury, a surge in pressure, great physical or emotional stress, the presence of chronic diseases, lack of diet and exercise. Although often the problem lies in improper blood circulation or heart disease.
Negligence towards health
If, after recovery, a person returned to his previous life, could not give up smoking and alcohol, sits a lot at the computer, his physical activity is reduced, and his blood sugar and cholesterol are exceeded, then in a couple of years you should expect a second attack. It can even be triggered by an emotional shock or a slight surge in blood pressure.
Vascular tone
Vascular tone and poor functioning of the circulatory system can be a prerequisite for the development of a stroke a second time. We are talking about atherosclerosis, arrhythmia, diabetes, high cholesterol and other pathologies. In this case, the vessels lose their elasticity, thicken or become too thin, and a lot of toxins and fats settle on their walls, which leads to thrombosis and rupture. Often, a repeated attack due to problems with blood vessels ends in hemorrhage.
Arterial pressure
Increased pressure in the blood vessels causes not only a recurrent stroke, but also a myocardial infarction, as chaotic contraction of blood vessels, stagnation and unstable blood flow to some parts of the body are observed. All this leads to thrombosis and blockage, the formation of aneurysms or lacurnas. If this was preceded by a primary attack, then the second time may result in rupture of capillaries and hemorrhage in the brain.
Summer season
Prolonged exposure to the sun, increased exercise in the heat, and even walking in high summer temperatures can also cause a stroke. The fact is that the water balance drops significantly during this period, and almost no oxygen and glucose reach the cells. Patients suffer from dehydration and swelling may occur. As a result, there is a sharp rise in pressure, the formation of blood clots, breathing problems and a repeated attack of stroke.
Therefore, it is very important to drink as much water as possible, go out less under the scorching sun and wear hats.
Heart problems
Heart problems such as arrhythmia, primary myocardial infarction, and atrial fibrillation should be treated immediately after the first stroke occurs. After all, they can be the cause of an attack a second time. This happens due to uneven blood pumping, irregular functioning of the atria, constant contraction and lack of relaxation during work. It is enough for the pressure to rise a little or a little stress to occur that a stroke develops.
To prevent another stroke, listen to your heart
People with heart problems should be especially careful about the recurrence of the disease. Repeated ischemic stroke can develop with cardioembolism resulting from atrial fibrillation or cardiac aneurysm. With this pathology, emboli are formed, which often enter the brain and lead to a heart attack.
For prevention, anticoagulants are used, drugs that inhibit the activity of the blood coagulation system, among them warfarin, Pradaxa and Xarelto , new, more advanced drugs. Please note that these medications are taken continuously and not in separate courses.
Monitor blood clotting while taking warfarin. If it appears when brushing your teeth, your urine or stool turns black, which indicates bleeding in the stomach or intestines, immediately reduce the dose of the drug and consult a doctor.
As for an aneurysm of cerebral vessels, an abnormal protrusion of their walls, it can be congenital or acquired, and is manifested mainly by headaches. As you know, the rupture of an aneurysm led to the death of the famous artist Andrei Mironov .
Therefore, if, without any apparent reason, your head begins to hurt for a long time and often, go to the doctor, he will refer you for an angiography. Now this examination is carried out on an outpatient basis. Treatment involves blocking, that is, clogging the aneurysm with special balls. But more often it is removed, since in essence it is a time bomb.
Medicines - constantly
The cause of many strokes, including repeated ones, is increased platelet aggregation, in other words, their increased ability to stick together. As a result, blood clots form. This pathology is observed to one degree or another in all types of ischemic stroke.
Small vessels with very fragile walls often grow into an atherosclerotic plaque. They bleed into the plaque and partially destroy it. A blood clot develops on the uneven surface of the plaque, clogging a large vessel.
With high blood pressure, thrombotic masses can break off and clog vessels located more distally. Narrowing of the internal carotid artery by seventy percent or more leads to so-called transient cerebrovascular accidents.
The so-called transistor ischemic attacks, which makes the risk of developing a recurrent stroke quite real. As a result of such disorders, the symptoms of which persist and disappear within a day, and therefore are called transient, not only foci of bleeding appear, but also very small hemorrhages.
This is determined by computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. In such cases, an operation is performed - the plaque is “crushed” by installing a stent, or removed. To prevent the formation of blood clots, antiplatelet drugs are prescribed, primarily aspirin, which prevent platelets from sticking together.
Regular use of antiplatelet drugs helps prevent recurrent stroke. Scientists from our Scientific Center for Neurology have proven that small doses of aspirin, on average 1 mg per 1 kg of patient weight, are effective for preventive purposes.
Recommended drugs against stroke
Depending on body weight, a person should take from 50 to 100 mg of aspirin daily, preferably in the morning, once a day. However, long-term use is known to be fraught with the development of erosive gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers.
Therefore, take aspirin as part of a combination drug that dissolves in the intestines. These are thrombo ACC (tablets 50 and 100 mg), aspirin cardio, cardiomagnyl . Medicines protect the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines from the irritating effects of aspirin.
For patients with gastric and duodenal ulcers, such drugs are contraindicated; they are prescribed dipyridamole (chimes) , which, having a less pronounced antiaggregation effect, is well tolerated and does not cause ulcers or bleeding.
Since many drugs are prescribed, as a rule, on an ongoing basis, it is important to know that their effectiveness decreases over time, and so that they do not turn into a dummy, periodically check how the blood reacts to taking them.
In addition, in approximately 20 percent of cases, aspirin does not have the necessary antiplatelet effect on the patient at all. The level of antithrombotic activity of a particular drug can be determined using a special test system, which was developed at the Scientific Center for Neurology.
Cholesterol and glucose are under control!
When a recurrent stroke occurs, the prognosis for life in old age depends on the level of cholesterol and sugar in the blood. Against the background of high blood pressure, small “infarctions” of the brain cannot be ruled out, which can also lead to a recurrent stroke.
Their development is based on the narrowing of small vessels. Therefore, along with aspirin and antihypertensive drugs, drugs are prescribed that improve blood circulation and saturate tissues with oxygen.
This is, in particular, pentoxifylline and its analogues - trental, agapurine, vasonite.
Folk remedies
Treatment can be supplemented with herbal infusions, which somewhat thin the blood.
Pour 2 tbsp. spoons of horse chestnut flowers 0.5 liters of boiling water, leave in a thermos. Strain and drink 3-4 times a day. Or prepare lemon balm infusion: 1 tbsp. spoon per glass of boiling water. Drink a third of a glass 3 times a day.
Before going to bed, drink a glass of kefir, adding ground cinnamon to the tip of a knife, which, among other things, lowers blood sugar levels.
High levels of cholesterol in the blood are another factor in the development of ischemic stroke. Atherosclerotic plaques formed on the walls of the vessel narrow its lumen and slow down blood flow.
Let me remind you which cholesterol numbers are considered normal and which are considered elevated.
- The cholesterol level is up to 5.2 mmol/l.
- A slight increase in the indicator, requiring only adherence to a diet, -5.2-6.7 mmol/l.
- Moderate hypercholesterolemia, which requires taking statins along with diet, is 6.7-7.8 mmol/l.
- Severe hypercholesterolemia - above 7.8 mmol/l.
- Finally, the desired cholesterol level for patients with cardiovascular diseases and diabetes is 4.5-5.0 mmol/l.
There is a rule: if a person has a cerebrovascular accident or has coronary heart disease and at the same time an increased level of cholesterol in the blood is detected, then for six months he must sharply limit the consumption of animal fats: butter, cheese, sour cream, sausage, lard, fatty meats and fish, rich broths, as well as eggs, liver, and other offal.
If after this the cholesterol level remains high, it is necessary to start taking statins, drugs that reduce its level. It is equally important to periodically monitor blood glucose levels.
Atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels in patients with diabetes mellitus occur 10-12 years earlier than in people with normal glucose levels. Arterial hypertension complicates the course of diabetes, which, in turn, contributes to the progression of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Increased blood glucose is often accompanied by impaired vascular tone, damage to the walls of large and small vessels and is a risk factor for the development of recurrent stroke. Be sure to check your glucose levels at least twice a year.
The main reasons for the development of pathology
As practice shows, people who have experienced a cerebral stroke, after a short time, begin to forget that until recently they were literally on the verge of death, and gradually return to their usual lifestyle, ignoring the doctor’s recommendations regarding nutrition, physical activity and refusal to bad habits. This is precisely what is often a fatal mistake.
The thing is that the first stroke causes quite serious damage to the brain vessels and neurons, so if a person’s lifestyle does not change for the better, a second stroke is not far off. In addition, non-compliance with doctors' recommendations and lack of targeted treatment for primary diseases, which largely contribute to the appearance of this dangerous condition, ultimately leads to further damage to the blood vessels in the brain. Thus, the main predisposing factors for the development of recurrent stroke include:
- decreased mobility due to paralysis and paresis;
- tendency to obesity;
- slowing down metabolic processes in the body;
- frequent stress;
- sleep disorders;
- increased blood cholesterol;
- consumption of large amounts of animal fats;
- violations of rest and work schedules.
Among other things, weather sensitivity that appears during the first attack can provoke a second stroke. In addition, any violation of the drug regimen prescribed by doctors often leads to the formation of preconditions for a recurrent stroke. In fact, according to statistics, approximately every 3rd person after an attack has a second stroke for some time.
Secondary prevention of stroke - this phrase in Russia, as a rule, means the prevention of a vascular accident in those who have already suffered it.
Indicators subject to primary control
Any person who has already suffered a similar attack should know how to prevent a recurrent brain stroke. It is important to understand that the patient’s future fate and condition directly depend on the patient’s specific lifestyle and actions. With the right approach, the likelihood of a repeat attack can be reduced to a minimum. In practice, it has been proven that a primary stroke, which did not leave severe damage in the patient’s body, if it occurs again can cause damage that cannot be corrected later. If you do not prevent a second attack, both motor and thinking abilities can be damaged.
Precursor symptoms of a recurrent disease may appear in the form of jumping blood pressure. Doctors recommend that everyone, especially elderly patients, have their own tonometer, with which they can regularly measure blood pressure at home.
The risk of recurrent stroke is especially high among hypertensive patients and people with even slight deviations from the norm. Especially careful should be those whose upper indicator often exceeds the bar of 140 mm, and the lower - 90 mm. Hg Art. If pressure surges are observed from time to time, you can take medications that would help normalize this indicator. However, if you use different drugs incorrectly, the outcome may not be the most pleasant; if any illness occurs, you must immediately consult a doctor. In some cases, atherosclerosis detected in the early stages helps doctors react as quickly as possible and prescribe the correct treatment in a hospital.
What should people at risk do?
This group does not only include stroke patients. People who experience short-term transient attacks are treated as such. To protect yourself from another cerebral infarction, the first thing you need to do is contact a neurologist. Instrumental and laboratory diagnostics will be required to adjust treatment:
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the carotid arteries and large vessels of the brain.
- Echocardiogram;
- Electrocardiogram (ECG).
- Blood lipid profile analysis.
- Coagulogram.
- Determination of the level of the amino acid homocysteine. When it increases, the risk of thrombosis and early vascular atherosclerosis increases. The risk of stroke increases by 6–8 times.
A blood test for homocysteine is not included in the examination protocol in Russia. But it makes sense to do it on a personal basis for the benefit of your own health. The examination will allow the doctor to prescribe timely treatment, which will help the patient avoid a stroke. Sad prognosis: in 70 out of 100 cases, a second stroke is fatal.
Preventive measures
To prevent a tragedy from occurring, it is important not only to undergo a full course of rehabilitation, but also not to forget about prevention and premature therapy. This often happens at home, in sanatoriums or hospitals.
The course includes taking medications, diet, exercise or hydrotherapy, giving up bad habits, treating underlying causes, undergoing quarterly examinations, and adjusting blood pressure, sugar and cholesterol levels. Although much depends on the gender and age of the patient and the area of brain damage for the first time.
Causes
In addition to the obvious reasons such as depleted brain cells, blood vessels and heart, there are simpler circumstances. For example, if a patient suffers a stroke due to excess cholesterol, the risk of a repeat event will not disappear until the level of the dangerous substance is reduced. If a patient suffers from heart disease, then it is worthwhile to work hard to prevent it, since now every time a heart problem will increase the risk.
Also, sometimes patients, having got out of the hospital ward, think that nothing threatens them anymore and that the danger has completely passed. They return to the previous way of life, which led them to the stroke, do not eliminate diseases, suffer from bad habits and do not strengthen the body with physical activity - cardio jogging or gymnastics.
IMPORTANT! Infectious diseases, especially those leading to inflammatory processes, can increase the likelihood of a stroke. Getting rid of such diseases, as well as any others that impair the immune system when a stroke is dangerously close, is necessary first of all.
Age can be a very significant reason. It is difficult to do anything about worn-out organs and organ systems; unfortunately, modern medicine has not yet reached such a level. Elderly and elderly people should be especially careful not to encounter the disease again.
Making a prognosis for a third stroke
With any illness, a person wonders when he will get better. In the case of ischemic or hemorrhagic brain damage, the patient and his relatives are interested in how much self-care skills, communication, and intellectual abilities will suffer during the illness and how quickly they will recover. The third cerebrovascular accident does not occur in the same way for everyone. For some, this can be a death sentence, and for others, a disease that will require serious treatment and long recovery. Some patients may completely lose their intellectual abilities as a result of the disease, while others may regain the skills they had before the disease.
The prognosis for rehabilitation after three strokes depends on a number of factors
Indicators that form the prognosis for the development of a third stroke:
- Unchangeable factors. These include the severity of the stroke, its type, location, and the patient’s age.
- Variable factors: blood pressure, some biochemical blood parameters, body temperature.
Control of the second group of factors creates opportunities for treating patients and gives them a chance for recovery.
The very concept of “prognosis” for a third stroke is a complex concept. It brings together the circumstances that together determine a patient's chances of life and recovery. These are the circumstances:
- Clinical outcome of the disease.
- Functional outcome.
- Prospects and duration of recovery.
- Probability of death.
- The likelihood of complications.
Based on the time elapsed since the onset of the disease, the prognosis is divided into:
- Early. This is the first month after the illness.
- Late. A month after the onset of the disease.
Early prognosis for cerebrovascular accidents
In the first hours and days, the doctor assesses the patient’s condition using several indicators:
- The number of points on the stroke scale (NIHSS scale - American National Institute of Health).
- Time from the onset of the disease.
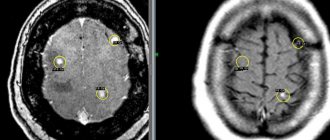
- Magnetic resonance imaging data.
- The volume of affected brain tissue on magnetic resonance imaging.
MRI will help diagnose the patient’s condition and give a prognosis for his rehabilitation.
This is, in fact, an attempt to predict whether a person will survive the first month of illness or not. The sum of points scored by the patient according to these criteria allows the doctor to make an early prognosis for the clinical outcome of the third stroke.
But there are conditions that can affect recovery. Based on research, they were determined by the National Institute of Health:
- Young age.
- Having a spouse.
- Lower body temperature in the acute period of the disease.
- Positive dynamics in the first week of the disease.
They accelerate the recovery of motor and speech skills after ischemia.
Late forecast
Using clinical data, taking into account favorable or unfavorable circumstances, a month after the onset of the disease, the doctor re-evaluates the patient’s condition. At this stage, the chances of recovery are considered taking into account the characteristics of the disease in that person. The late prognosis for patients with a third stroke will include all levels of manifestation of the consequences of the disease:
- Clinical. Movement, sensitivity, speech and vision disorders, behavioral and mood disorders.
- Domestic. Difficulty moving and self-care. Difficulty performing complex activities - driving a car, going to a store or savings bank.
- Social. After the third stroke, a person cannot perform previous social functions.
One month after the stroke, a final prognosis for its recovery can be given.
At this time, a person’s rehabilitation program is formed. They clarify the medications he will take at home. They teach relatives the specifics of care. And they voice the results that the joint efforts of doctors and the patient will lead to.
Ideally, clinical recovery should lead to complete everyday and social recovery, but this occurs only in 15% of cases.
Separately, there are signs that predict an unfavorable outcome:
- Severe disturbances of consciousness and perception.
- Persistent paralysis of the limbs.
- The appearance of urinary incontinence.
Forecast for life
The state of health after a recurrent stroke deteriorates greatly: motor functions are inevitably impaired and mental abilities fade. A person who has suffered a second attack needs help from family or medical staff for life.
The severity of the consequences largely depends on the location and volume of the affected brain tissue, the age and gender of the patient, and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
Only about 30% of older patients survive a second stroke. The life expectancy of surviving patients after an attack does not exceed 3 years on average.
Recurrent ischemic stroke in old age: life prognosis
According to statistics, after the first ischemic stroke, mortality reaches 30% during the first year. Over the next five years, mortality may reach 50% of people, and over the next ten years - only 25%.
With the development of repeated IS, these indicators for life prognosis double, especially if the patient is not young. The prognosis worsens if there are concomitant cardiovascular diseases that worsen the prognosis for survival and recovery. These diseases are:
- previous myocardial infarction
- rhythm disturbances (atrial fibrillation)
- congestive heart failure
Disease prediction
No doctor can answer the question about the patient’s further condition after a stroke; everything is very individual. But there are several signs that suggest the development of an unfavorable prognosis in an elderly person:
- Location of the lesion in the brain. If its most important centers are affected, the outcome will be fatal. The area of spread of hemorrhage, affecting the loss of many body functions. The most severe consequences are observed in patients with hypertension and atherosclerotic plaques on the vessels of the brain. A coma caused by cerebral edema sharply worsens the prognosis. A recurrent stroke usually ends in the death of the patient.
Factors that can lead to rehabilitation and recovery of an elderly patient:
- The hematoma is small in size, as confirmed by laboratory tests; The patient does not lose consciousness; Absence of heart disease, atherosclerosis of the head and neck vessels; Normal blood pressure.
Calling a doctor in a timely manner is of great importance. When admitted to the hospital within the first 6 hours, the likelihood of a favorable outcome of the disease increases significantly. The life of an elderly patient often depends on the experience and skillful actions of the specialist who comes to the call.
Typically, ischemic stroke is preceded by transient attacks. It is the recognition of the signs of these disorders and their treatment that will prevent the development of severe pathology of the cerebral blood supply. Prolonged post-stroke coma often leads to the death of the patient.
Consequences and forecasts
It is no secret that the prognosis after a recurrent stroke is disappointing. Of course, such factors as the age of the patient, the efficiency and correct actions of the medical staff, the scale of the lesions, etc. are of great importance. But still, according to statistics, about 75% of repeated attacks, in which severe symptoms are diagnosed, end in death.
The consequences of a repeat stroke are severe. Due to disorders of brain activity, patients experience the following abnormalities:
- Memory deterioration; the victim may forget even familiar things, even the names or images of relatives, the names of objects.
- Speech disorders, partial or complete. Often, patients after a stroke are unable to pronounce words normally, which is associated with damage to the corresponding parts of the brain. If the lesions are severe, speech function may be completely lost for a long time.
- Decreased motor function – control over the musculoskeletal system is impaired. With the first stroke, only fine motor skills may be affected, but with a repeated pathological process, the damage is more serious, often the patient cannot walk, hold objects, or is completely bedridden.
- Mental disorders - manifest themselves in mental imbalance, aggression, isolation, apathy, depressive disorders, etc.
- There is a decline in mental functions and intelligence.
- Damages to the nervous system take on a different nature; the functioning of the muscles responsible for the swallowing reflex is very often disrupted, which is why patients choke on food and water; in some cases, auxiliary feeding methods are necessary.
In fact, there are many more possible consequences, some of them are minor, others pose a serious threat to life. If we talk about the most dangerous consequences, after a second stroke, in addition to death, the patient may fall into a coma. In this case, predicting the exit from the unconscious state falls on the shoulders of specialists and modern diagnostic methods.
Prevention of recurrent stroke
Proper prevention can significantly reduce the likelihood of a recurrent stroke. It should begin immediately after the first blow and last at least four years.
First of all, patients need to maintain a healthy lifestyle, give up nicotine or at least reduce the number of cigarettes they smoke daily, completely give up alcohol and drugs, maintain physical activity and monitor their weight, and reduce the consumption of foods high in cholesterol.
Women who have had a cerebral hemorrhage are advised to abstain from oral contraceptives.
A key indicator by which you can determine an impending threat is blood pressure. A person who has suffered a stroke must purchase a tonometer and measure his blood pressure daily, regardless of how well he feels.
The risk group includes not only hypertensive patients, but also people with mild high blood pressure. Signs of danger are indicators of 140-180mmHg for the upper and 90-105mmHg. Art. for lower pressure.
Taking medications to normalize blood pressure, improve microcirculation of cerebral vessels and prevent cerebral hypoxia should be agreed with the attending physician and carried out in strict accordance with his instructions.
If the patient is diagnosed with atherosclerosis, diseases of the cardiovascular system, aneurysm, etc., treatment should begin immediately.
Diet and physical activity should be tailored to the illness.
Diet
The menu should be balanced and include products that normalize cholesterol levels.
The basic principles of the diet should be:
- reducing the amount of sweet, fried, flour, fatty and smoked foods;
- the predominance of raw vegetables and fruits, boiled food;
- absolute abstinence from alcoholic beverages, smoking and other bad habits;
- regular intake of microelements and vitamins.
Pomegranate, citrus fruits, kiwi and wheat germ are considered beneficial for the blood and lowering cholesterol levels.
Before breakfast, it is recommended to drink a glass of fresh juice with the addition of a few drops of flaxseed oil.
Taking aspirin helps reduce the risk of blood clots and prevent recurrent ischemic stroke. You should take it one quarter of a tablet per day. For patients with a history of stomach disease, aspirin is contraindicated; it is replaced with Cavinton, Alisate or Trental.
Stroke and its types
Stroke is an acute pathological process in which there is a violation of blood circulation in the vessels of the brain. Such disorders lead to focal lesions of the main organ, which is why the victims experience disruption of many basic body functions.
The pathology often leads to disability, in addition, the risk of death is high and the older the patient who has an attack, the higher the likelihood of the latter.
In medicine, there are two main types of cerebrovascular accidents:
- Ischemic stroke is an acute circulatory disorder associated with partial or complete obstruction of blood vessels in the brain area. This type of stroke is the most common. Due to a pathology of this nature, blood circulation in some part of the brain is disrupted or completely stopped, which leads to tissue damage and possible necrosis.
- Hemorrhagic stroke is a more severe, but at the same time rare pathology, differing from stroke in that it is not a blockage of the vessel that occurs, but a violation of its integrity, in other words, a rupture. In this case, hemorrhage in the brain is observed, which entails much more severe lesions, complications and consequences, and mortality rates among victims significantly increase.
When we talk about a second stroke, most often we mean the ischemic type of pathology, but even if the patient has fully recovered after the first stroke, the consequences of the second will be much more severe and life-threatening.
Prevention Methods
Preventive measures include the use of pharmacotherapy, exercise therapy, adherence to a specially selected diet, and treatment through physical therapy. Among the first preventive measures, the patient should keep blood pressure under control, as this will allow him to monitor not only the condition of the blood vessels, but also monitor possible manifestations of coronary artery disease.
As a result of a hemorrhagic stroke, the patient is prescribed angioprotectors, for example, Troxevasin or Detralex. The action of the components of these drugs is aimed at strengthening the walls of blood vessels. Do not overdo it in the process of lowering blood pressure, as this can trigger the formation of an ischemic stroke. To increase brain activity, Cinnarizine or Cavinton can be prescribed. The prognosis in this case can be quite favorable.
As for nutrition for secondary disease, it should include the optimal amount of fruits and fresh vegetables, juices, fermented milk drinks, which help thin the blood and prevent the formation of blood clots. It is worth including foods that normalize cholesterol levels in your diet.
During the recovery period, it is important to take care of physical activity, but at the same time it should be optimally enhanced. . Many patients often wonder how long do people live after a second stroke? Let's start with the fact that not in all cases patients have the opportunity to survive, even if this happened, the body suffers serious disturbances and changes
With a second stroke, the consequences are usually irreversible. After 2 strokes, they may be less pronounced than after subsequent ones, especially if treatment was started in a timely manner. Currently, the manifestation of the disease has increased significantly, when strokes are repeated and at the same time the number of patients who then fall into a coma and never come out of it increases. It is good if the patient manages to live in this state for some period of time. When a diagnosis such as a recurrent stroke is made, the consequences can be not only partial disruptions of individual systems, but also the entire organism.
Diagnostics and prevention
If an illness such as a stroke recurs, the outcome of the situation depends only on the speed of action of the people around the patient. If a repeated attack occurs, you should know that its symptoms will completely coincide with those signs that accompany the initial attack. As a rule, the patient experiences nausea and noticeable dizziness. In addition, a person may feel severe weakness, his speech and vision will deteriorate, and part of his face will recede. To help a person, you should not look for manifestations of all these symptoms; it is enough to detect at least one similarity. The assistant’s main task is to sit the patient up or give him a horizontal position, which will allow the pressure to be measured. If this indicator exceeds 160 mmHg. Art., you shouldn’t delay, you need to call an ambulance.
Signs of a second stroke
The signs of a second stroke are no different from the first, although they develop much faster, and most often the acute phase occurs suddenly. We are talking about migraines or severe headaches, loss of consciousness, speech and memory disorders, problems with motor skills and coordination of movements, paralysis and numbness of the limbs. In this case, a person faces stroke of ischemic, hemorrhagic, spinal and subarachnoid type. All this can be accompanied by hemorrhage and flooding of the entire space of the brain.
Ischemic lesion
Ischemic damage develops due to blockage, thrombosis of blood vessels and oxygen starvation of nerve cells, which begin to die within four to six hours. In this case, the patient loses consciousness, experiences a headache, speech and memory disorders, trembling in the hands, hesitation when walking, and may vomit.
A crooked smile or errors in speech can also indicate the onset of an attack, so it is important to go to the hospital immediately.
Hemorrhagic lesion
In this case, neurons and cells suffer much more, since hemorrhagic damage is accompanied not only by necrosis of brain tissue, but also by hemorrhage, rupture of blood vessels, and penetration of red blood cells through the walls of the heart. Development into the acute phase occurs in just a couple of hours, and often leads to cerebral edema, coma or death. The second attack is especially dangerous for pensioners, since most do not survive it, and the consequences are incurable.
Symptoms of a stroke
Hemorrhagic and ischemic types of pathology usually manifest themselves in different ways. Hemorrhagic stroke generally develops rapidly; after a capillary rupture, a person can even lose consciousness. The first signs in older women and men are:
- the occurrence of a severe headache. The painful sensations will be pronounced, and they will not be alleviated even after taking modern anabolic steroids;
- speech dysfunction, severe hoarseness;
- heavy and rapid breathing;
- a sharp jump in blood pressure;
- redness of the skin;
- cardiopalmus;
- severe vomiting;
- paralysis of facial muscles.
Depending on the area in which the hemorrhage is localized, a person’s vision or hearing will also be impaired. In severe cases of stroke, the possibility of seizures and falling into a coma cannot be ruled out.
Ischemic stroke manifests itself differently:
- the patient develops a severe headache accompanied by vomiting and nausea;
- motor functions are impaired . Many people find it difficult to lift an arm or leg because it becomes almost impossible to control the limbs;
- the temperature during a stroke in an old person rises to 39 degrees ;
- double vision;
- sudden loss of memory and sensitivity;
- problems with facial expressions , it becomes difficult for the patient to smile or wince.
Signs of such a disorder begin to develop gradually, the most acute phase lasting 6 hours after the attack itself.
Experts assure that the symptoms of stroke in older women are not as intense, since the female body is more resilient and strong.