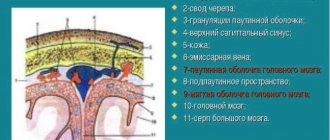
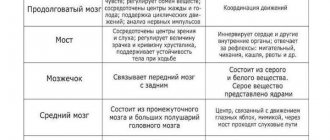
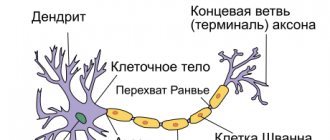
Is it all so harmless?
A group of British scientists from the University of Oxford conducted their own study, analyzing medical statistics collected over the past 30 years (from 1985 to 2015). The study involved several hundred people aged 40 and older. This data included not only how much alcohol they drank regularly, but also CT scans of their brains.
Question and answer Alcohol consumption in Russia. Infographics
For the purity of the experiment, scientists randomly selected from a list of approximately 550 men and women without obvious alcohol dependence and conducted several surveys with them, testing their memory and intelligence over the past five years. At the same time, people continued to lead their normal lifestyle. After this, the researchers combined the data obtained and tried to understand how alcohol affects the “external” manifestations of the human brain and its internal structure.
Contrary to generally accepted ideas about the benefits of moderate alcohol consumption, British scientists managed to prove the opposite. Even small portions of alcohol - less than 70 grams per week - do not lead to any noticeable improvements in brain function, but, on the contrary, slow down its functioning. They published their findings in the respected medical scientific journal BMJ on June 6, 2021.
How does alcohol affect the brain? Worse than you could imagine
Sometimes you can hear people who abuse alcohol say that their brains have completely drank. Most often this happens due to their inappropriate behavior, illogical decisions, immoral and unexplainable actions, not only while intoxicated, but even sober. Alas, the crude description of a “drunk brain” is not a figure of speech. Alcohol has a destructive effect on all human organs and systems. But the effect on the brain is especially clear.
A drop to defeat
A slurred tongue, an unsteady gait, defiant behavior that is not characteristic of a person when sober - all these are external manifestations of the brain working under the influence of alcohol.
The more you drink, the more noticeable they are. A person in a state of strong alcoholic intoxication makes a repulsive impression on others. But the external manifestations of the harmful effects of alcohol cannot be compared with what happens inside the body, in particular, with the brain.
The blood supply to the brain occurs many times more actively than to other organs. Ethanol penetrates into gray matter cells within minutes of consumption. It has been proven that any exogenous (coming from outside) dose of alcohol is toxic to the brain because it damages the membranes of neurons and can lead to cell death. You must understand that even one drop of alcohol has a damaging effect. In this case, a small number of neurons die. But the higher the dose, the more “victims”.
Alexander Alishevich , chief physician of the City Clinical Narcological Dispensary in Minsk:
— In general, the brain is a target organ that immediately suffers when drinking alcohol, just like the liver. But the liver has a colossal resource for regeneration and is capable of resisting and neutralizing the toxic effects of ethanol for quite a long time. The brain is not. Relatively speaking, under certain circumstances, 1/8 of the healthy part of the liver is enough to restore the normal functions of the organ. And if neurons die, there is no chance of recovery.
To be fair, the expert notes, neurons still have some ability to resume functions. In this case, we are not talking about the appearance of new cells to replace the dead. If the neuron survives, it takes approximately 7 years to restore its damaged substances. Compare: internal epithelial cells in the intestines are renewed within a few days. The brain is the most “long-lasting” tissue in the human body in terms of self-healing, and only if the cells affected by the attack remain alive. When drinking alcohol (especially more frequently and in large quantities), there is no talk of saving brain cells.
Exhaustible resource
At birth, the human nervous system contains a fantastic reserve - an average of 100 billion neurons. Over time, neurons wear out, “age” and, having served their purpose, die. Their supply is not renewed. But this natural decline was initially taken into account by nature when forming brain potential. The quantitative composition of neurons is also influenced by external factors, for example, high body temperature during viral and bacterial diseases, stress, intoxication... In particular, alcohol intoxication, which occurs when drinking alcohol, is called the main cause of mass death of brain cells.
Microscopic studies show that in place of neurons killed by ethanol exposure, so-called foci of cellular devastation and/or connective tissue scars are formed. Healthy parts of the brain shift to fill the void. As a result of numerous atrophic and dystrophic changes, the brain of a drinking person decreases in volume and seems to shrink.
Alcohol intoxication also leads to irreversible vascular changes and impairs cerebral circulation. Venous blood stagnates in the veins of the brain, which provokes the development of thrombosis and increases the risk of micro-strokes (minor hemorrhages). There is an opinion that in people who abuse alcohol, strokes (acute cerebrovascular accident) occur almost 5 times more often.
Typically, the greatest losses from ethanol exposure are suffered by neurons in the frontal lobes of the brain. These are centers that are responsible for motivation, planning, goal-directed behavior and provide the ability to solve problems and achieve goals, overcome difficulties and develop. Alcohol abuse leads to disruption of these functions. Over time, a drinker develops so-called “alcoholic automatism” - a type of behavior based on standard, stereotypical thoughts, actions, words, which gradually become scarcer and narrower. Roughly speaking, a person stops developing as a person, and the process of degradation begins. The result of many years of alcohol consumption can be dementia (dementia), alcoholic epilepsy, encephalopathy and a number of other neuropsychiatric disorders.
Alexander Alishevich:
— Scientists believe that in the absence of external damaging factors, the number of neurons deposited at birth, taking into account their natural decline, would be enough for one thousand years of brain functioning at full capacity. Alcohol abusers often damage their brains for 40-50 years. In my practice, there was a young man who was assigned to a boarding home for the disabled due to dementia that developed as a result of alcohol abuse. He was 33 years old. So “drank your brain” is not a figure of speech, but a harsh reality with prolonged and systematic use of alcohol.
Subscribe to our Telegram channel, Facebook groups, and stay up to date with the latest news! Only interesting videos on our YouTube , join us!
How exactly does alcohol harm the brain?
According to British scientists, consumption of even small portions of alcohol, equivalent to one bottle of beer per week, leads to atrophy of the memory center in the brain and a deterioration in its functioning in general.
Question answer
Why do some people drink more alcohol and others drink less?
As researcher Anya Topivala noted, drinking more than 140 grams of alcohol already has a negative effect on brain function, let alone people who regularly exceed this figure. According to her, those who drank this amount of alcohol had a more “loose” hippocampus, the memory center, than their non-drinking peers, and performed worse in tests of memory and intelligence. In addition, other regions of the brain atrophied, including the white matter in the cerebral hemispheres, and they could also name fewer words per letter than abstainers.
According to scientists, the relationship between these disorders and their progression in those studied is directly related to the increase in the amount of alcohol they drank, which indicates a direct connection between alcohol and atrophy of the nervous system. This, according to scientists, should be taken into account by all health services in the world when formulating strategies to combat alcoholism and its consequences.
The effect of alcohol on the female brain?
Complications caused by drinking alcoholic beverages are more serious in the fairer sex than in men.
It has been experimentally proven that ethanol behaves much more aggressively towards the cells of a woman’s body than towards the cells of a man. Organs and their functions are more susceptible to the negative effects of alcohol. The destruction of the liver, damage to the heart muscle and cells of the nervous system occurs faster.
Having carried out a comparative analysis of the results of studies of the human brain using MCT, scientists have established the fact that the negative effects of ethanol manifest themselves in the fact that the brain decreases in size.
The degree of such a decrease is the main indicator that organic changes are present in the brain cells. And the longer the experience of drinking alcohol, the higher these indicators.
In addition, the results of the experiments showed that both women and men who suffer from alcohol addiction face certain problems when they have to learn something or remember any information. All this occurs due to frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Note that the male representatives who participated in such an experiment had twice as much experience of regular consumption of large amounts of alcohol than the fairer sex.
It turns out that the negative effects of ethanol on both the male and female brains manifest themselves in the same ways. But it is necessary to take into account that women took exactly half as much alcohol. From all this we conclude that ethanol has a stronger effect on the female brain.
In contrast, two articles were recently published in an American publication discussing the role of gender in the effects of ethyl alcohol on the body.
The authors came to the opposite conclusion, that is, according to them, ethanol has the same effect on everyone without exception. This means that experiments of this kind need to be continued in order to find out the specific effects of ethyl alcohol on a woman’s brain cells.
Chemical relaxation
Doctors recommend that it calms the nervous system and dilates blood vessels. Drink.
film "The Diamond Arm"
To answer this question, you first need to understand why people take drugs. Drugs are substances that are similar to neurotransmitters in the brain. After taking a dose, a drug addict modifies brain activity, trying to somehow solve his problems.
Each type of drug “solves” its own type of problem. What problems does vodka “solve”?
The brain is designed in such a way that when a person has a desire, the brain is tuned to receive this desire. There is interest, excitement, anticipation.
When a person gets what he wants, he experiences satisfaction and peace of mind.
Let's assume that a person does not believe that he will get what he wants. At this moment, a contradiction occurs in the brain:
- Part of the brain is wired to receive desire.
- Part of the brain resists this.
This state of affairs is not very pleasant. Normally, you need to turn on your thinking and choose one or another option.
What should an alcoholic do in this situation? At the moment when a person gets what he wants, a special neurotransmitter is synthesized in the brain - gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). It is at the moment of GABA synthesis that a person moves from a feeling of anticipation to a feeling of satisfaction.
Vodka is an aqueous solution of ethanol. The structure of ethanol is similar to the structure of GABA. As soon as a person drinks an ethanol solution, the body mistakenly believes that ethanol is a neurotransmitter, so it sends it directly to the brain.
Ethanol binds to the endings of neurons and burns them out. Internal psychological tension disappears. According to the subjective perception of the alcoholic, “the problem is solved.”
This is where the myth comes from that alcohol supposedly “calms the nervous system.” In fact, it does not reassure, but deceives. When a person gets sober, he sees that the problem is not solved. On the contrary, it has only intensified. And this is another reason to drink.
A single dose of ten grams of ethanol burns out about one hundred thousand neurons. The problem is that neurons with burned out endings can no longer function normally. Which neurons are burned out first?
This is the most interesting thing. Questions of desires and goals are questions of a person’s personality. That is, vodka burns out, first of all, a person’s personality.
Personality is contained in the frontal lobes of the brain. There is no point in counting how many years it will take for vodka to burn out your entire brain; you need to know how many years it will take for vodka to burn out your personality.
This is similar to the following problem. A terrorist has hijacked a plane and is killing one person every hour. When will he kill everyone? It would seem that the answer is hundreds of hours. But no. A terrorist entered the cockpit and killed two pilots. The rest will break on their own.
Same with alcohol. It burns out the personality, and then the person will ruin his life himself. And you don’t have to wait three thousand years for this.
According to statistics, a person who is a “cultural drinker” burns out his personality in about seven years. What's happening to him?
Scientists have calculated how long it takes the brain to recover after drinking
Author:
Kolechnik Dmitry
2 minutes
57627
Alcohol has a quick effect on the brain, as most of us know. But not much is known about how the brain recovers from binge drinking and how long it takes. All cognitive functions do not return to normal immediately.
Scientists from the British University of Bath analyzed a number of studies that examined brain dysfunction on the second day after drinking alcohol. The authors looked at hourly changes in brain function. With a few exceptions, all of these studies have shown that our cognitive abilities, such as attention and memory, remain impaired even when our blood alcohol levels are no longer detectable. The results of the study were published in the journal Addiction.
“Decreases in these abilities involve reduced concentration, focus, memory, and reaction time,” says study author Craig Gunn, from the Department of Psychology at the University of Bath.
Scientists have studied how exactly our bodies and brains counteract the physiological effects that accompany heavy alcohol abuse. In the United States, this is considered drinking more than four standard drinks for women, and five for men. A standard dose of an alcoholic drink contains approximately 14 ml of pure alcohol.
Alcohol is a powerful diuretic, causing the body to lose a lot of fluid, up to four times more than what was consumed while drinking, leading to dehydration. To compensate for the loss of fluid, the body's organs pull in as much fluid as they can, causing the brain to become dehydrated. As a result, the meninges practically shrink.
As all this fluid is eliminated from the body, magnesium, potassium, sodium, and other nutrients needed for the smooth functioning of the brain's cognitive functions are also washed away. And washed out nutrients are not immediately replaced with new ones after alcohol leaves the body, and depleted membranes are also not immediately restored. Recovery from an ethyl alcohol attack takes time.
The brain will not be able to get back into shape for many more hours, in some cases it lasts more than one day. Until this happens, attention, memory, reaction time and decision-making will not work at full capacity. The results of the study show that it is completely unrealistic to return immediately to your usual activities and work as usual.
“Our results show that a hangover can have serious consequences for everyday activities, such as work skills, driving skills, concentration and memory,” said lead author Sally Adams from the University of Bath.
The study offers two main findings. The most obvious is that drinking too much alcohol is simply a bad idea for many reasons, including the price it takes on our brains and bodies. And, secondly, it would be foolish to think that we can tolerate drinking without serious consequences, which are by no means limited to headaches and nausea.
In other words, drinking alcohol affects a person over a long period of time. This is not only the time he is drunk, but also the time needed to recuperate, and our brains recover more slowly than we think.