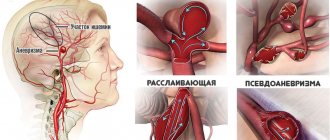
Blockage of blood vessels supplying blood to the brain occurs due to metabolic disorders, diseases and pathological conditions. These include stenosis (persistent narrowing of the vascular lumen) and the presence of foreign, atypical particles in the bloodstream, including blood clots (thrombi). Atherosclerotic damage to the arteries, accompanied by the formation of cholesterol plaques on the inner surface of the vascular wall, ranks first among the causes of mortality and disability in the population. Atherosclerosis affecting the brachiocephalic arteries is the leading cause of ischemic stroke.
Characteristic
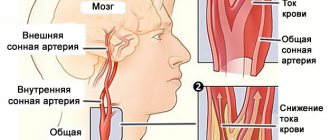
Blocked blood vessels cause the development of life-threatening conditions such as cerebral infarction and stroke. Mortality from stroke is about 30-70% of cases. Brachiocephalic arteries (carotid, vertebral) are the main routes through which blood flows to the parts of the brain.
Statistics show that atherosclerotic damage to the brachiocephalic arteries, which lie in the neck and supply the brain, is asymptomatic in 30% of cases. In 60% of patients, atherosclerosis of the neck vessels is manifested by repeated ischemic attacks (TIA). Damage and narrowing of the carotid arteries occurs with equal frequency on one side and on both sides. Insufficiency of cerebral blood flow correlates with the degree of stenosis (narrowing) of the carotid artery bed.
Stenosing lesions of other brachiocephalic arteries (subclavian, vertebral) are more often detected on one side. Compensatory mechanisms maintain the possibility of blood flow for a long time even in the case of significant narrowing of the lumen. Studies show the presence of blood flow in unilateral stenosis of the subclavian or vertebral artery in a volume reaching 75%.
Common localization of cholesterol plaques: the mouth of the vertebral, middle, and anterior cerebral arteries, as well as bifurcations (bifurcation areas) and siphons (segment bends) of the carotid arteries. For example, the localization of cholesterol plaques in the bifurcation zone of the carotid artery is detected in 70% of cases in the general structure of lesions of the great vessels supplying the brain.
Carotid-vertebral stenosis, which is multiple lesions of the arteries of different basins, is diagnosed in 57% of cases. Isolated damage to the walls of the carotid arteries occurs with a frequency of 24% of cases, and in 18% of patients the pathology is bilateral.
Causes
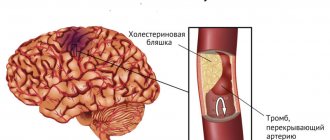
Atherosclerosis is the leading cause of clogged cerebral vessels. The disease is associated with disorders of protein and lipid metabolism. The pathology is characterized by the formation of atherosclerotic plaques from lipid fractions; localization of deposits in the vessels of the neck and head leads to disruption of cerebral blood flow. Damage to the carotid arteries of atherosclerotic origin is often combined with their pathological tortuosity. Other causes of cerebral vascular obstruction:
- Lipohyalinosis. Thickening of the vessel wall associated with the proliferation of hyaline (protein, glassy) tissue.
- Fibrinoid necrosis. Death of cells and vascular tissues caused by biological factors.
- Microatheroma. The formation of small cysts on the inner walls of arteries.
- Thrombosis. Formation of blood clots that interfere with normal blood flow.
- Embolism. The presence of foreign particles in the bloodstream that interfere with normal blood flow.
It depends on the type of disease what the vessels are clogged with - an embolus, a thrombus or a detached fragment of a cholesterol plaque. Clogging of the vascular lumen occurs against the background of its narrowing, provoked by the above reasons.
Provoking factors: angiopathy (impaired nervous regulation of vascular wall tone), arterial hypertension, history of diabetes mellitus. Angiopathy, in turn, correlates with pathologies such as liver, kidney and heart failure.
Factors that can provoke the development of stenosis of the main arteries include an unhealthy lifestyle, bad habits, and unhealthy diet, which leads to an increase in the concentration of cholesterol in the blood. A condition where the vessels supplying blood to the brain are clogged is often accompanied by characteristic symptoms, which makes it possible to suspect and promptly treat the pathology.
Signs of cerebral vasoconstriction
There can be many reasons for the narrowing of blood vessels in the brain. But, you should pay attention specifically to the forms of the already established disease: initial and chronic. It is difficult to judge which of them is most dangerous for the human body. Because the chronic form can plague a person for years, and the initial form can lead to death at the very first stage.
That is why it is so important not to miss the first “bells” of the onset of the disease.
So, the following signs should alert you:
- functional disorders of the central nervous system (fatigue, migraines, unexplained irritability, tearfulness, overexcitation, touchiness);
- incipient memory problems (short-term forgetfulness, inability to remember what happened a few minutes ago - the name of the program, the location of the keys, etc.);
- change in gait (a person shuffles his feet or minces heavily);
- the appearance of a false urge to urinate;
- loss of coordination of movements, loss of balance;
- development of dementia;
- malfunctions in the functioning of internal organs located in the pelvic area.
Symptoms
Symptoms of blockage of blood vessels supplying the brain depend on the nature of the damage to the vascular wall. In 29% of cases, ischemia of brain tissue is asymptomatic. 60% of patients experience transient ischemic attacks (TIA) and cerebral symptoms:
- Pain in the head area.
- Dizziness, impaired motor coordination.
- Nausea, sometimes with bouts of vomiting.
- General and muscle weakness.
- Decreased performance, increased fatigue.
- Mood swings, irritability.
- Deterioration of cognitive functions (memory, mental activity).
- Convulsive attacks of the generalized (general, widespread throughout the body) type.
If the vessels supplying blood to the brain tissue are clogged, patients experience symptoms: frequent changes in blood pressure, short-term sensitivity disorder, impaired motor function in the extremities.
Severe occlusion (obstruction) of the vessels supplying the brain leads to the development of a stroke; in this case, signs of clogged elements of the cerebral circulatory system are represented by persistent neurological symptoms of a focal type. Symptoms of clogged cerebral vessels depend on the pool in which the disturbance occurs. Signs of damage to the carotid vessels (carotid arteries) include:
- Numbness, paresthesia (sensitivity disorder) in the extremities.
- Transient speech disorders.
- Hemiparesis (paresis, muscle weakness in one half of the body).
- Deterioration of visual acuity.
Damage to the arteries of the vertebrobasilar area (subclavian, vertebral) is manifested by pain in the head area, dizziness, gait disturbance, and inability to maintain balance, which leads to falls and fainting. Many patients simultaneously experience visual dysfunction - blurred, blurred images, diplopia (double vision).
Episodes of stroke in 25-77% of cases develop against the background of atherosclerotic damage to the brachiocephalic vessels without previous neurological symptoms, which makes surgical treatment of confirmed asymptomatic atherosclerosis justified.
Observation of patients in whom cerebral atherosclerosis occurs without obvious manifestations confirms the occurrence of a history of TIA in 4% of cases within 2 years after diagnosis. In 10% of patients with diagnosed atherosclerosis, a history of TIA appears within 5 years.
Diagnostics
The attending physician will tell you what to do if the vessels of the neck and head are clogged, based on the results of a diagnostic examination. Determining the patient’s neurological status and collecting anamnesis are the primary diagnostic measures. Consultations with doctors - neurologist, cardiologist, vascular neurosurgeon - are shown. Instrumental diagnostic methods:
- MRI, CT.
- Angiography.
- Doppler ultrasound.
- Duplex scanning.
- Electrocardiography.
Instrumental research methods aimed at studying the vascular bed make it possible to identify the nature of the disorders and the exact localization of the pathological focus. A blood test shows the concentration of cholesterol and glucose.
Preventive measures
Prevention of blocked arteries in the brain involves avoiding situations that may trigger the occlusion. However, this is not always possible; the list of risk factors is quite extensive.
In case of surgery, a medical specialist must ensure the quality of the artery blockage, such as cauterization. You can reduce the likelihood of developing arterial embolism if you follow all the requirements of your attending physician and monitor your well-being.
You can also reduce your risks by reviewing your diet. It is recommended to give preference to vegetable fats in food. Include more fruits and vegetables in your daily meals. Quitting drinking alcohol and smoking will also reduce the risk of vascular occlusion.
Treatment
Your doctor will advise you on what to do if the blood vessels supplying the brain are clogged. Treatment is prescribed taking into account the nature and extent of damage to the cerebral circulatory system, the patient’s age, and the presence of concomitant chronic diseases.
To prevent pathology, doctors recommend leading a healthy, active lifestyle, giving up bad habits, establishing a daily routine, organizing a nutritious diet low in trans fats and saturated fats, high in plant fiber, vitamins, and microelements.
Drug therapy
When the vessels supplying blood to the brain are blocked, treatment is carried out with pharmaceuticals - statins (lower cholesterol concentrations), cerebral blood flow correctors (improves blood microcirculation), anticoagulants (prevent the formation of blood clots), thrombolytics (dissolve blood clots). In the presence of heart disease, medications are prescribed to correct cardiac activity.
Surgery
When symptoms of blockage of blood vessels supplying the brain appear, diagnostics and adequate surgical treatment are carried out, which is considered the most effective (in comparison with drug methods). If the vascular lumen is narrowed by more than 50%, surgical intervention is recommended to prevent the development of a stroke. Methods of neurosurgical treatment:
- Carotid endarterectomy (removal of atherosclerotic plaque from the artery cavity).
- Endovascular stenting (removal of emboli and thrombi that obstruct blood flow, followed by installation of a stent in the artery cavity, which prevents narrowing of the lumen).
- Bypass surgery, prosthetics of brachiocephalic arteries (restoration of the circulatory network).
- Correction of deformations of elements of the circulatory system of the brain.
- Extra-intracranial microanastomosis (creation of an artificial connection between the temporal and middle arteries for chronic occlusion of the internal carotid artery).
Surgeries for revascularization (restoration of the vascular network) of the brain are considered as a prevention of ischemic stroke and as a method of treating chronic cerebral ischemia.
Traditional methods
If blood vessels are clogged, you need to do classic and acupressure massage in the neck, shoulder girdle and head, which will help improve cerebral blood circulation. To achieve results, an integrated approach is required - using several methods of stimulating cerebral blood flow simultaneously.
If the main arteries supplying blood to the brain are clogged, use products made from garlic. It is eaten in crushed form, adding to various dishes to taste. Garlic contains adenosine, a nucleoside that has cytoprotective (protects cells from damage) and anti-inflammatory effects.
A tincture is prepared from garlic, which cleanses blood vessels, strengthens the immune system and increases vitality. Take 350 g of garlic, chop it, and squeeze out the juice. The concentrated juice is diluted with medical alcohol in a ratio of 1 to 1. The solution is poured into a dark glass bottle and left for 10 days in a cool place.
The tincture is taken three times during the day, successively increasing the dosage by 1 drop. For example, in the morning of the 1st day, drink 1 drop of tincture diluted with water or milk in a volume of 50 ml. At lunch, drink 2 drops, diluted in the same way, in the evening - 3 drops, in the morning of the next day - 4 drops.
The medicine is continued to be taken according to the regimen, gradually increasing the volume to 25 drops. Then continue to drink 25 drops three times a day until the medicine runs out. If cerebral vessels are clogged, traditional healers recommend taking decoctions and infusions prepared from medicinal plants. Several recipes:
- Recipe 1. Bay leaves (7 g of dry raw material) are poured with water (0.5 l), boiled for 5 minutes, infused in a thermos for 4 hours. Drink between meals, taking a few sips.
- Recipe 2. Rose hips (2 tablespoons of dry raw materials) are mixed with crushed pine needles (5 tablespoons), poured with water (0.7 l), boiled for 10 minutes, infused in a thermos for 6 hours, filtered. Drink the entire amount throughout the day. Course – 30 days.
- Recipe 3. Horse chestnut (50 g of crushed raw materials) is poured with vodka (0.5 l), infused for 2 weeks, left in a dark place, shaking the bottle regularly. The finished tincture is filtered and taken 3 times daily, 30 drops each. Course – 30 days.
It is useful to drink green and herbal tea with honey and lemon. A mixture is prepared from lemon, orange and honey, which improves the condition of the vascular wall. Fruits, taken in groups of 2, are thoroughly ground in a blender. Add honey (2 tablespoons) to the resulting gruel, mix, leave for 24 hours, and store in the refrigerator. Use 2 tbsp. spoons of the product three times daily before meals.
Types of blockages
There are two types of vascular embolus in a patient: endogenous and exogenous.
Endogenous blockages are those that are created directly in the patient’s body. These include:
- Adipose tissue.
- Thrombus.
- Malignant neoplasms.
- Cancer metastases.
- Accumulation of pus during inflammatory processes.
The development of endogenous vascular emboli in a patient can be triggered by injury, surgery or an infectious disease.
Exogenous emboli are air bubbles that enter the patient’s blood during mechanical trauma, injury or medical manipulation.
Note! According to parasitologists and phlebologists, the percentage of blood vessels blocked by worms is rapidly growing. Migrating throughout the body, they can cause enormous harm to the body, blocking arterial and venous passages and thereby disrupting the circulation of lymph and blood.
The situation is complicated by the fact that oxygen starvation, which occurs when blood vessels are blocked, provokes severe intoxication of the body and often causes the death of the patient.
Consequences and prognosis
The prognosis of life depends on the nature of the disease, the degree of stenosis and the severity of cerebral blood flow disturbance. Important prognostic criteria: the extent of damage to cerebral vessels, involvement of several areas in the pathological process, atrial fibrillation and other heart pathologies in the anamnesis.
The vessels of the head and neck become clogged due to many diseases. Narrowing of the vascular lumen by 90 percent correlates with acute insufficiency of cerebral blood flow, which leads to the development of stroke.