Causes of pain in the back of the head on the left side of the head
Pain and discomfort are not a separate disease, so there are many reasons why the left back of the head hurts. The simplest ones are fatigue, lack of sleep, strong emotions, high air pollution. They pass immediately after rest and creation of comfortable conditions. Also, this symptom may indicate a number of diseases of the cervical spine, blood vessels and nerves, which require timely diagnosis and treatment.
Diseases of the cervical spine
If the occipital part of the head on the left hurts, it is important to conduct an examination of the cervical spine. It is here that the important vertebral artery passes, which carries blood to the head and nourishes nerve tissue. Pathological formations in the vertebral area, bone calluses, muscle spasms lead to compression and a decrease in blood flow to the brain.
- Osteochondrosis is a chronic disease of the intervertebral discs and joints associated with a slowdown in metabolism and blood circulation. It often occurs in older people, but can also result from injuries and diseases of the spine at any age. The cartilage becomes thin and inelastic, and the process of deformation of the vertebrae and the formation of bone calluses begins.
- Protrusion – protrusion of intervertebral discs in any direction. The pathological process goes through several stages, the last of which is a hernia. It occurs with rupture of the dense fibrous membrane and release of the cartilage contents. In advanced cases, treatment requires surgery.
- Displacement of the vertebrae - often due to injuries and falls, but can also be a consequence of weak ligaments. The process is accompanied by acute pain in the neck, compression of blood vessels and nerve roots. The pain in the occipital part of the head on the left is sharp, throbbing, intensifies during movements and turns of the head. It goes away if the normal position of the vertebrae is restored, but it is important to prevent them from being displaced again.
Treatment tactics for various diseases of the cervical spine will differ. It is important to eliminate the cause of compression of blood vessels and nerves, restore normal blood supply and innervation of tissues. For most patients, massage, gymnastics, and taking muscle relaxants and antispasmodics are sufficient, but in some cases surgical intervention may be necessary.
Muscle diseases in the neck area
Muscle spasms and inflammation of soft tissues are one of the reasons why the left back of the head hurts. Discomfort spreads to the neck and occipital region, and can affect the entire surface of the head. During diagnosis, a number of muscle pathologies in the cervical region can be determined, which cause an acute headache in the left occipital region.
- Myositis is inflammation of the muscles. The process can be of traumatic or infectious origin, or result from hypothermia of the neck and head. The pain is acute and persists even at rest, and the skin over the affected area becomes inflamed and acquires a red tint. For most patients, anti-inflammatory and analgesic ointments are sufficient for treatment.
- Muscle strain is a micro-tear of fibers. This damage occurs as a result of sudden movements of the neck, falls, or prolonged exposure to an uncomfortable position. The most dangerous is a complete rupture of the muscle - it must be restored surgically.
- Myogelosis is a disease in which painful lumps form in the muscles. They limit the mobility of the cervical spine, compress blood vessels and nerves, and lead to the formation of ischemic areas in the brain. For treatment, muscle relaxants, massage and physiotherapy sessions are prescribed.
One of the reasons why the left occipital part of the head hurts is a sedentary lifestyle, working at a monitor. Lack of movement causes muscle spasms, slow blood circulation, and ischemia of brain tissue. Doctors at the Clinical Brain Institute recommend periodically warming up during the working day to maintain vascular health.
Nerve diseases
If the back of the head on the left side of the head hurts severely, this may be a manifestation of neuralgia. The pain is acute, throbbing, and persists both during movement and at rest. Its source is the greater occipital nerve, which originates from the second cervical root and passes under the base of the skull. Painful sensations can be caused by the following pathologies:
- neuritis - inflammation of the nerve;
- mechanical compression, pinching of nerve fibers;
- incorrect posture;
- diseases of the cervical spine associated with anomalies in the location of the vertebrae;
- abnormal physical activity.
Neuralgia can occur in acute or chronic forms. It is often shooting and has a high intensity. When the greater occipital nerve is damaged, it spreads to the neck and back of the head. Treatment depends on the cause of the pain. In case of mechanical compression of the nerve, it is important to restore its conductivity; in case of infectious diseases, a course of antibacterial therapy is prescribed. At home, you can additionally use ointments with the addition of painkillers and anti-inflammatory components.
Vascular diseases
Pain in the back of the head on the left side of the head is a reason to undergo a vascular examination. Spasms, inflammatory and dystrophic processes lead to deterioration of blood circulation. Areas appear in the brain that are deficient in oxygen and nutrients. There are a number of diseases that manifest themselves as pain in the left or right back of the head, associated with pathologies of the vascular system.
- Hypertension is a chronic increase in blood pressure. It often manifests itself in older people, and can also be associated with abnormalities in the structure of blood vessels, physical activity, and metabolic disorders. The walls of the arteries gradually stretch under blood pressure, becoming thin and inelastic. Hypertension is one of the main risk factors for the development of hemorrhagic stroke.
- Hypotension is a decrease in blood pressure. Its causes include heart disease, insufficient vascular tone, anemia and other factors. If the condition occurs frequently, you must follow a special diet and take medications to increase your blood pressure. Long-term oxygen deficiency negatively affects brain function, leads to headaches, and can provoke an attack of ischemic stroke.
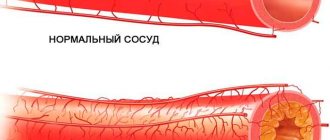
- Atherosclerosis is a disease of large arteries associated with impaired lipid metabolism. Excess cholesterol and some fractions of lipoproteins accumulate on the inner wall of blood vessels, forming deposits and plaques. Detecting this disease at an early stage will prevent its further development. In the later stages, atherosclerosis is dangerous due to the complete blocking of the lumen of the vessel, as well as rupture of its walls.
Fluctuations in blood pressure and vascular disease are one of the risk factors for stroke. This is a dangerous condition that represents an acute cerebrovascular accident. An attack occurs either when an artery ruptures, or due to a prolonged lack of oxygen in certain areas. The treatment and rehabilitation regimen depends on the type of stroke and the size of the affected area, as well as the age of the patient and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Other reasons
If the left side of the back of the head hurts, it is worth undergoing a detailed diagnosis and determining the exact cause of this symptom. During the examination, it is important to indicate all the conditions for the appearance of painful sensations, as well as additional complaints. Discomfort can be associated with a variety of diseases and conditions, including:
- migraine;
- prolonged fatigue, stress and insomnia;
- poor nutrition, excessive consumption of fatty and salty foods;
- sedentary lifestyle.
In most cases, pain in the back of the head on the left goes away after proper rest. Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain recommend that you seek examination if painful sensations occur frequently or are acute.
Origin of the painful syndrome: types of diseases
The causes of the pathological condition can be different:
- diseases of the cervical region of the spinal column: spondylitis, osteochondrosis, migraine, spondylosis, etc.);
- neurosis of the occipital nerve endings;
- diseases of the cervical muscles: myogelosis, myositis;
- hypertension, intracranial pressure;
- overstrain of cerebral vessels;
- prolonged stay in the wrong position;
- muscle strain during exercise;
- pathologies of the maxillotemporal joints;
- stress and depression.
Regardless of the reasons behind headaches, they cannot be ignored, as they can significantly worsen the quality of life, as a result, a person becomes irritable, nervous, and indifferent to problems.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
A disease of the spine in which rapid destruction of the vertebrae of the neck and intervertebral capsules is observed. The pathological process can simultaneously affect several different parts of the spinal column.
The main causes of osteochondrosis:
- Sedentary (office) work.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Alcohol abuse, smoking.
- Excess body weight.
- Incorrect posture and body position during rest.
- Hereditary predisposition.
The first signs of the disease are a headache in the back of the head; some patients believe that they are simply overtired. Failure to provide medical care in a timely manner can lead to irreversible processes in the body.
Cervical spondylosis
A disease of the spinal column resulting from the degeneration of ligament cells into bone tissue. Growths form, neck mobility decreases, patients note stiffness when bending their head. There are constant throbbing headaches from behind, spreading to the eyes and ears (they intensify with movement).
Spondylosis develops in older people and in those whose activities involve sedentary work.
Cervical myositis
An inflammatory process occurring in skeletal muscle tissue. It affects several groups of bone tissue at once. In addition to internal problems, the patient may have changes in the skin.
Causes of myositis:
- pathologies of an infectious nature;
- systematic hypothermia of the body;
- injuries, sprains and muscle cramps.
The disease is accompanied by dull pain in the neck, gradually spreading to the back of the head. To make a diagnosis, an x-ray examination is performed.
At the initial stages, treatment of pathology is carried out with the help of anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics and anthelmintic medications. Physiotherapy and massage are indicated. In advanced forms of myositis, surgical intervention is required.
Hypertension and neuralgia
High blood pressure is almost always “adjacent” to bursting, throbbing pain in the left or right side of the back of the head. Often the patient feels unpleasant discomfort upon waking up. Headaches may be accompanied by heaviness, dizziness, tachycardia, and general malaise. As you move, the intensity of the spasms increases. Often, after vomiting, the symptoms of migraine disappear.
The inflammatory process of the occipital nerve is the main companion to osteochondrosis, as well as other diseases of the cervical spine. Neuralgia can occur due to hypothermia.
The disease makes itself felt by burning, strong paroxysmal spasms in the back of the head, spreading to the neck, ears, back and jaw. Any movement, coughing, sneezing, increases discomfort. At rest, the pressing, dull pain persists.
Intracranial pressure
If you have this pathology, your head hurts constantly. Attacks become more frequent at night and in the morning, accompanied by a feeling of nausea and vomiting. Patients experience unstable blood pressure and fainting.
Occupational pain and stress
Such discomfort can bother people who are forced to spend a lot of time at work in one position, in which the neck muscles are constantly under tension. Very often, office workers and drivers have headaches in the back. The nature of the sensations is prolonged, dull attacks that are relieved by rubbing the back of the head, neck and turning the head.
When stressed, the body's internal systems work under tension, the blood pulsates, and can increase blood pressure. All this can cause an unpleasant, painful pulsation in the back of the head.
Migraine cervical
The most common disease in which the patient complains of the following symptoms:
- Pain in the forehead, temples, and back of the head.
- Fog before the eyes.
- Extraneous sounds in the ears.
- Lack of attention.
The pain intensifies with pressure on the vertebral artery. Only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis.
A thorough, comprehensive examination will help determine why your head hurts. Based on its results, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment.
Examination methods
If the occipital part of the head on the left often hurts, it is important to undergo a full diagnosis. During the initial examination, the therapist prescribes additional examinations from specialized specialists, as well as the necessary tests:
- blood tests to determine its composition, identify viral and bacterial infections and obtain other indicators;
- X-ray or MRI of the cervical spine if disease in this area is suspected;
- examination of the vessels of the neck and head using Dopplerography - ultrasound diagnostics using a contrast agent;
- MRI, CT scan of the brain is an accurate, informative technique for detecting neoplasms, hemorrhages and other pathologies that can cause headaches;
- specific examinations by a neurologist, traumatologist, ophthalmologist and other specialized specialists according to indications.
The Clinical Institute of the Brain has all the necessary conditions for diagnosing diseases that are accompanied by headaches. Accurate test results, high-quality modern equipment, many years of experience of specialists are the main advantages of the center.
Treatment
Treatment is prescribed depending on the patient's primary diagnosis. Cephalgic syndrome, which is not accompanied by neurological symptoms (convulsions, confusion, speech, hearing, vision disorders, numbness of the limbs, muscle weakness) and fever, usually does not pose a threat to health and life.
Non-drug therapy for primary forms of cephalgia involves creating conditions for the patient’s physical and mental peace. Drug treatment is carried out to stop the attack. For cephalalgia of moderate intensity (no more than 7 points on an analogue scale) with an attack lasting no more than 24 hours, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Non-opioid analgesics (Paracetamol, Analgin).
- Combined analgesics (Sedalgin-Neo, Solpadeine, Migrenol, Pentalgin).
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ketorolac, Ketoprofen).
Combined analgesics are not taken for a long time (no longer than 7 days per month) in order to avoid the development of abuse headaches associated with taking medications. If the intensity of painful sensations exceeds 7 points, and the duration of the attack is longer than 24 hours, triptans are prescribed (contraindicated in basilar and hemiplegic forms of migraine, ischemic heart disease, arterial hypertension, cerebrovascular pathologies with the threat of ischemic stroke).
The group of triptans includes the following drugs: Sumatriptan, Zolmitriptan, Naratriptan. If necessary, add antiemetic drugs (Metoclopramide, Domperidone). In secondary forms of cephalalgia, treatment is focused on the primary pathology. In complex therapy, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs, angioprotectors, cerebral blood flow correctors, and medications that normalize blood pressure are used. If necessary, surgical intervention is performed.
Headache treatment
The treatment regimen is selected for each patient individually. It is prescribed taking into account the exact diagnosis, the general condition of the patient and the presence of concomitant diseases, as well as other factors. The main condition for successful treatment is strict adherence to all recommendations at home and carrying out all necessary procedures:
- taking medications – the doctor may prescribe medications to improve blood circulation, painkillers, antibiotics and drugs to correct blood pressure;
- proper nutrition - the diet should contain enough vitamins and microelements, and the consumption of fatty foods, salt and spices, and semi-finished products should be limited;
- physiotherapy – a set of techniques to improve nutrition and blood supply to tissues in diseases of the cervical spine;
- massage, therapeutic exercises - are prescribed additionally for spinal curvatures, osteochondrosis and other disorders.
If you have a headache in the back of the head on the left, it is important not to self-medicate. Rest, fresh air, head massage are the simplest techniques that will help get rid of discomfort in the absence of serious illnesses. In other cases, it is important to follow doctors’ orders and undergo periodic examinations.
How to get rid of headaches in the occipital region?
The same principle applies - treatment is determined solely by the factor that led to the manifestation of the pain syndrome. That is:
Help with migraines
In the event that the cause of the headache attack is migraine, then it will be necessary to take any of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - nimesulide, dicloberl or xefocam, as well as a specific anti-migraine drug - Rapimiga or Antimigraine 100. Ideally, use these drugs on stage of the onset of the aura, in this case it will be possible to avoid the manifestation of a headache altogether.
Important! If you feel a sudden pain in the back of your head on the left, then hurry up and sit down. Standing or lying down in this case is equally dangerous - this is explained by the peculiarities of blood circulation. It would be a good idea, by the way, to apply pressure to the temples.
Treating an attack of hypertension
Do you have a headache after your blood pressure rises? In this case, you should immediately take a rapid-acting antihypertensive drug so that the crisis is not complicated by a cardiovascular accident. It is best to administer an intramuscular solution of 25% Magnesium sulfate, this way you can reduce your blood pressure within a few minutes and forget about the headache. Are you afraid of injections? In this case, you can take a tablet of the drug Kaptopress - after half an hour you won’t even remember the pain. A hypertensive crisis is sometimes accompanied by pulsation of the cervical and temporal vessels.
This is interesting! Regarding why migraine headaches occur. In fact, everything is very simple. There is a rush of blood to the vessels of the brain, which become overfilled and put pressure on the receptors. That's the whole mechanism.
Help with intoxication
In the event that the headache is the cause of fever and a consequence of intoxication syndrome, then it will be somewhat more complicated. It will be necessary to reduce the temperature by taking NSAIDs and go to see a doctor so that he can exclude the manifestation of a serious infectious pathology.
Prevention methods
To prevent diseases of blood vessels and nerves, pathology of the cervical spine, as well as to prevent stroke, you should follow simple recommendations from doctors every day:
- when working sedentarily, regularly do simple exercises for the back and neck;
- lead an active lifestyle, carry out daily exercise necessary for health;
- create a complete diet with a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals;
- give up bad habits: smoking and drinking alcohol.
Headache in the left occipital part of the head is a manifestation of a number of diseases of the cardiovascular system, nerves and spine. The Clinical Brain Institute has all the conditions for diagnosing and treating this condition in an inpatient or outpatient setting. The center is equipped with modern devices for analyzes and examinations, and is also staffed by experienced specialists of a narrow and broad profile.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 5/5 — 2 votes
Share article on social networks
Diagnosis of the disease
Regardless of the patient’s condition, diagnosis of the disease is the most important and primary part of treatment. The nature of the symptoms that patients complain about is the basis for correct diagnosis.
Among the doctors, go through:
- ophthalmologist;
- therapist;
- neurologist;
- otorhinolaryngologist;
- take general blood and urine tests.
In this case, an MRI or X-ray may be prescribed. Tell your doctor if you feel pain in the back of your head on the right side or pain in the left side of your head—the specific symptoms and treatment are closely related.