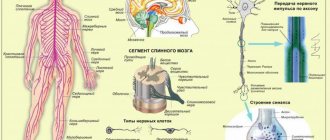
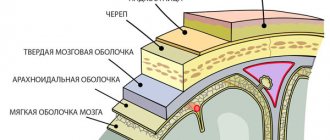
Cystic formations are often diagnosed pathologies of the central nervous system, which cause dizziness, a feeling of fatigue, headaches and other symptoms that bother the patient. After consultation with a specialist, diagnosis shows the formation of an arachnoid or retrocerebellar cerebrospinal fluid cyst of the brain.
Untimely diagnostic measures lead to the destruction of neural connections, which is fraught with neurological disorders. In the article we will analyze in detail the reasons for the development of the anomaly, signs and treatment and preventive measures of retrocerebellar neoplasm.
The formation of a head tumor causes dizziness, a feeling of fatigue, and pain in the head.
What is a retrocerebellar cyst of the brain?
With a disappointing doctor's conclusion, patients often wonder about the diagnosis of a head tumor. It is a cavity containing a capsule with liquid exudate. The pathology forms at the site of necrotic nerve cells in any part of the brain. In most cases, MRI shows the location of the tumor in the posterior fossa behind the cerebellum.
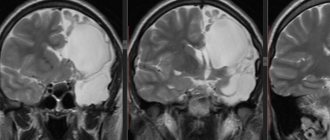
The image shows a retrocebellar arachnoid cyst with obvious enlargement of the posterior fossa (white arrows).
Retrocerebellar cysts are asymptomatic for a long time, but over time the pathology progresses, compressing neighboring organs - parts of the brain, which is often dangerous with serious complications - symptoms of neurological deficit.
What is the danger of pathology?
A patient who has been diagnosed with a cerebellar cyst of the brain must understand how dangerous the disease is.
Adults suffer from increased intracranial pressure, frequent headaches and loss of consciousness. Complications contribute to the development of oxygen deficiency and necrosis of brain tissue.
A lesion of this nature may be accompanied by symptoms:
- hearing and vision loss;
- motor dysfunction;
- pain in the parietal and back of the head;
- speech disorders, unclear diction, “speaking”;
- frequent occurrence of seizures.
Classification of neoplasms
Tumors, which are usually benign, are classified based on location:
- Liquor retrocerebellar cyst - located deep in the brain, containing liquid exudate. It often appears as a result of damage to the skull and intracranial formations, operations, and cerebral hemorrhage.
- Arachnoid retrocerebellar cerebrospinal fluid cyst - forms more often, in contrast to cerebrospinal fluid cyst. It is formed on the surface of the hemispheres of the main organ of the central nervous system and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Most often diagnosed in childhood due to intracranial pressure, inflammation, brain and cranial injuries.
What do arachnoid and retrocerebellar cysts look like?
Treatment options depend on the location of the retrocerebellar cysts. Moreover, the following subtypes of cystic formations are distinguished:
- Congenital (primary) - appears in the fetus during embryogenesis.
- Acquired (secondary) - occurs as a result of damage to brain structures, traumatic brain injury.
A retrocerebellar tumor forms in affected areas of the brain. To determine the type and parameters of the anomaly, the patient needs to undergo an examination.
Causes of the disease
Most often, a retrocerebellar tumor is formed due to disturbances in intrauterine development or appears as a result of difficult childbirth. With a congenital anomaly (as well as with an acquired one), instead of healthy tissue, a cavity is formed, filled with cerebrospinal fluid or protein fluid from the serous membranes.
Most often, a retrocerebellar tumor is formed due to disturbances in intrauterine development or appears as a result of difficult childbirth.
Secondary retrocerebellar neoplasm is diagnosed as a result of the following pathologies:
- hemodynamic disturbance;
- damage to the skull and brain structures;
- brain surgery;
- infections, inflammations.
Scientists hypothesize that the presence of a retrocerebellar cyst is often due to a hereditary factor—close relatives are diagnosed with the same disease. In this case, the primary cystic formation rarely progresses and does not interfere with normal life activities. An exception is if, in addition to the retrocerebellar formation, organic damage to the central nervous system is noticed.
Cyst sizes: which ones are dangerous?
In children, a cyst can be dangerous if its diameter is more than 30 mm. Typically, neurologists refer for an EEG (to check the bioelectrical activity of the brain) when they detect a cyst with sides, for example, 32x18x14 mm. If a retrocerebellar cyst appears congenitally, and not as a result of injury or neuroinfection, the formation is considered a developmental option and does not require additional examinations or special treatment.
A retrocerebellar cyst in adults, if it does not damage surrounding tissues, is not considered a disease. A dangerous sign is a constant increase in the size of the cyst. Take into account the education parameters established during the initial diagnosis. If a cyst measuring 23x22x36 mm is discovered for the first time, and a repeat MRI reveals its increase to 23x35x46 mm, a clear growth of the formation is noticeable. It is these cysts that are dangerous.
A small cyst is considered normal (a development option) and does not require attention. Its presence is not taken into account when diagnosing diseases.
A retrocerebellar cyst of the brain can provoke dysgenesis of the lower parts of the cerebellar vermis, the left or right cerebellar hemisphere, a local upward displacement of its tentorium, a slight deformation of the cortical plate of the occipital bone, and moderate compression of other adjacent brain structures.
The presence of these deviations does not affect life. You need to pay attention not to the size of the retrocerebellar cyst, but to the neurological symptoms and its dependence on the cyst or other pathologies.
How to react if the cyst grows?
Changes in the size of the retrocerebellar cyst occur from infancy to adulthood. Normally, education increases in accordance with a person’s height.
In adults, the cyst should not increase, but there may be minor changes in its size and shape. Such changes are considered a variant of the norm. When comparing indicators, pay attention not only to size, but also to volume.
For example, if you encounter this situation:
| MRI time | Cyst size | Cyst volume |
| First examination | 19x26x41 mm | 20.25 cu. cm |
| One year later | 25x35x21 mm | 18.37 cu. cm |
| 2 years after diagnosis | 29x18x37 mm | 19.31 cu. cm |
There is no need to worry - this is normal. Despite the constant change in proportions, the volume of the cyst is stable.
The cyst has grown since the last examination: what to do?
If a slight growth of the cyst is diagnosed (up to 0.2-0.3 cm), there is a possibility of measurement error. A re-examination is required in 3-6 months. There is no point in doing an MRI earlier, since changes in the size of the cyst will not occur in less time.
Diagnostic methods
For an accurate diagnosis of retrocerebellar formation, you should consult a neurologist. When diagnosing, the doctor relies on the patient’s anamnesis and complaints. However, symptoms are not absolute proof of a retrocerebellar cyst, so specialists examine the patient using the following methods:
- MRI of the brain with contrast - determines the location, parameters, structure, differentiates between benign and malignant formations.
MRI of the brain.
- Dopplerography of the vessels of the head and neck excludes cerebral circulation disorders.
- Ultrasound of the heart - detects disturbances in heart rhythm, determines the presence or absence of heart failure.
- Blood clotting test.
- Determination of cholesterol concentration in the blood.
- Study of markers of autoimmune diseases.
- Puncture of cerebrospinal fluid - to identify neuroinfections.
Diagnostic measures
Making a diagnosis is one of the most important components of tumor therapy. If done incorrectly, there is a high probability of death. Thus, in the case when an oncological tumor is confused with a similar cyst, a surgical operation may be prescribed, which in no case should be done in the event of dangerous tumors.
First, the specialist interviews the patient, drawing up a complete picture of the patient’s clinical symptoms. After this, MRI, CT and ultrasound are mandatory, and ultrasound must be carried out with intravenous administration of contrast agents, which helps determine whether the patient has a benign or malignant tumor. The specialist also prescribes other examinations to reliably determine the cause of the formation of the pathological neoplasm. It is important to do this right away in order to begin treatment and eliminate the negative impact of the root cause of the disease.
Features of therapy
When diagnosing a retrocerebellar cyst, the patient is registered at a dispensary and the progression and severity of symptoms are monitored. If the tumor parameters do not change, there are no characteristic symptoms, there is no need for surgical intervention - only observations and conservative methods are sufficient.
Drug therapy
Therapeutic measures will only help at the beginning of the disease if there is no progress. Non-surgical therapy is based on the following areas:
- Treatment of arterial hypertension - drugs Berlipril, Captopril.
- Normalization of blood clotting with anticoagulants - Aspirin, Pentoxifylline.
- Reducing blood cholesterol levels.
- Improved blood circulation.
Homeopathy is effective only as a complement to the main treatment of the cyst. Alternative medicine also does not contribute to cystic resorption, but is used as a symptomatic aid.
In case of infection, antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and immunomodulators are prescribed to increase the body's protective functions.
Surgery
If it is not possible to stop the cystic growth with therapeutic methods, surgery is prescribed. Before surgery, specialists assess the extent of the lesion and choose the most appropriate method, taking into account the location and parameters:
- Endoscopy - a special device is used to excise the formation and pump out liquid exudate.
An operation to excise the formation and pump out liquid exudate from the brain.
- Creation of drainage - selected when there is a constant flow of fluid into the cavity.
- Craniotomy is a radical method that involves removing the cyst and adjacent tissues.
Attention! After surgery, patients need to rehabilitate - to normalize the functioning of the brain.
Prognosis, possible complications
In the absence of therapy, the patient's condition, if the tumor progresses, will worsen. As a rule, this leads to severe pain, which most often ends in rupture of brain tissue. The patient will begin to bleed, which is accompanied by inflammation, which ultimately causes death. This is the main danger of retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst of the brain.
However, even with proper treatment and surgery, the patient may experience complications. The prognosis of the disease is usually positive if the patient fulfills all the requirements of specialists. Complications may be the following:
- high blood pressure;
- headache;
- decreased immunity, malaise;
- dysfunction of sensory organs, motor and speech functions;
- epilepsy, seizures;
- hyperactivity or developmental delay in children;
- psychological disorders.