Tunnel syndrome (compression-ischemic neuropathy) is a complex of diseases of the peripheral nerves caused by impaired nutrition of nerve fibers, which leads to a decrease in sensitivity in the problem area. This condition manifests itself in the upper and lower extremities. When selecting treatment, it is important not only to establish the localization of compression-ischemic neuropathy, but also to differentiate this condition from other pathologies.
Manifestations of tunnel neuropathy
The nature of the manifestations of upper limb tunnel syndrome is determined by the localization of the processes that caused damage to the nerve cells. Based on this feature, the following forms of neuropathy are distinguished:
- carpal tunnel syndrome;
- pronator teres syndrome;
- ulnar nerve tunnels;
- radial nerve tunnels.
In most cases, damage to these nerves provokes dysfunction of the hand and fingers.
Upper extremity nerve compression
One of the most common (diagnosed in 50% of cases) is carpal tunnel syndrome. Those at risk for developing this type of neuropathy include women over 50 years of age and people who constantly experience stress on their upper limbs.
The median nerve, compression of which causes carpal tunnel syndrome, runs along the palm. This channel transmits impulses responsible for the sensitivity of the first three fingers of the hand. In addition, the median nerve is responsible for their mobility.
The development of carpal syndrome begins with a loss of sensitivity, which is observed after prolonged stress on the limb. At rest, pain and other symptoms characteristic of tunnel neuropathy disappear. Later clinical phenomena are a constant concern.
After limb numbness and pain become chronic, movement disorders occur. In the absence of adequate therapy, the wrist muscles atrophy. In advanced cases, carpal tunnel syndrome extends to the shoulder joint.
An important diagnostic sign of neuropathy affecting the carpal tunnel is that the intensity of pain at night is more pronounced than during the day.
Elbow (ulnar) syndrome is characterized by compression of the nerve located in the so-called Guyon's bed. In this part of the upper limb there are fibers that are responsible for the sensitivity and motor activity of all fingers.
The following symptoms indicate ulnar syndrome:
- intense burning pain;
- paresthesia (tingling, goosebumps);
- decreased mobility;
- deterioration of fine motor skills.
These symptoms appear predominantly in the little finger and ring finger. As compression progresses, muscle fibers atrophy.
The development of cubital tunnel syndrome is accompanied by compression of the canals running through the supramuscular-ulnar groove.
This type of neuropathy is also considered one of the most common. With cubital syndrome, the clinical picture is similar to the manifestations of compression of the ulnar canal nerve. However, numbness and pain in this case occur when the patient keeps his arm bent for a long time. In addition, pain may occur on the back of the hand.
Neuropathy of the radial nerve, which lies in the armpit, is characterized by impaired motor function of the hand. With this disorder, problems with abduction of the thumb and flexion of the others are also noted. Developing in the area of the elbow joint, radiation syndrome can cause a decrease in sensitivity in the back of the shoulder.
Compression of the nerves of the lower extremities
In addition to the above, there are other tunnel syndromes that affect the lower limbs or muscle beds. The latter type of violation is extremely rare. Muscle tunnel syndrome occurs due to problems with blood circulation in certain areas. Such a lesion is localized mainly on the lower extremities and manifests itself in the form of the following symptoms:
- intense pain;
- redness of the compression site;
- swelling of the problem area;
- muscle paralysis;
- decreased sensitivity or complete numbness in the interdigital space of the foot;
- decreased motor activity.
Among the tunnel syndromes of the lower extremities, the most common are the following:
- Roth's disease;
- femoral nerve;
- sciatic nerve;
- peroneal nerve;
- tarsal syndrome.
Roth's disease develops due to compression of the nerve running in the subcutaneous layer of the thigh. Carpal tunnel syndrome that occurs in this area provokes pain, a sensation of “pins and needles” and tingling in the problem area. The intensity of symptoms increases during movement.
Femoral nerve tunnel syndrome manifests itself in a similar way. The difference is that in this case, pain and paresthesia are localized in the perineum, legs and feet. Subsequently, there is a decrease in sensitivity and weakness of muscle fibers, which atrophy over time.
With neuropathy of the sciatic nerve, burning pain is noted, which is localized in the lower leg and foot in the right leg. Numbness, paresthesia and decreased Achilles reflex are also possible.
Tunnel (fibular) syndrome of the peroneal nerve is characterized by deterioration of mobility (flexion dysfunction) of the foot and fingers. Skin sensitivity decreases in the problem area. The pain from this neuropathy is localized near the fibula.
Tarsal syndrome develops when the tarsal canal (located near the ankle) is compressed. The main symptom indicating this form of neuropathy is pain in the foot, occurring mainly at night. As compression develops, discomfort occurs during movement.
Carpal tunnel syndrome calculator
The more “Yes”, the greater the likelihood of CTS
- Do you feel tingling or numbness in your palms or fingers?
- Do you feel a burning sensation?
- Do you feel itching on your palms and fingers?
- Do symptoms get worse at night?
- Have you ever woken up from sleep feeling the need to shake out your hand?
- Do you feel uncomfortable when working with objects?
- Can you tell the difference between hot and cold?
- Was the dominant side affected first?
- Have you ever had a wrist injury that caused swelling?
- Did you have problems with fluid retention during pregnancy or menopause?
- Do you have a stressful job?
- Are you experiencing shooting pains that radiate from your forearm to your shoulder?
- Do symptoms originate in the little finger?
Causes
The causes of the development of tunnel syndrome are often due to trauma to soft and bone tissues in the area of nerves: fractures, bruises, long-term wearing of a cast, etc. Some types of work activities lead to similar violations. Carpal tunnel syndrome is often diagnosed in miners, musicians, and loaders. In this case, compression of the nerve is observed only on one side (for left-handers on the left hand, for right-handers - on the right).
Possible causes of neuropathy include:
- connective tissue pathologies;
- hormonal imbalance;
- endocrine diseases;
- metabolic disease;
- thickening of the nerve, which is caused by pathological processes;
- prolonged muscle strain (sitting in one position).
A relationship has been established between neuropathy and a hereditary predisposition characterized by narrow canals. Tunnel syndromes develop due to congenital anomalies of the structure of the lower or upper extremities. Medical procedures can cause nerve compression. Frequent intravenous or intramuscular injections made into the same area provoke swelling of the local tissues, which compresses the canals.
Those at risk for developing neuropathy include people on a strict diet. A lack of nutrients leads to a decrease in the volume of subcutaneous tissue, which performs a shock-absorbing function and protects nerve canals and bones from impacts.
In addition, systemic diseases contribute to the development of tunnel syndromes: diabetes mellitus, renal failure, arthritis, and blood pathologies.
What is carpal tunnel syndrome?
Carpal syndrome is a disorder of the peripheral nervous system. The wrist is surrounded by a very large amount of fibrous tissue. First of all, it plays the role of support for the joint.
The median nerve provides sensation to the index, middle and thumb. Carpal tunnel syndrome is the most common disease in the world. Surgical intervention for this disease is performed very often and is one of the most common diseases.
The disease occurs very often in people who perform monotonous work. In women, the syndrome is detected much more often than in men.
Main symptoms
With tunnel syndrome, symptoms mainly manifest themselves in the form of pain of varying degrees of intensity and paresthesia. The feeling of discomfort becomes most pronounced at night or after physical activity.
As compression-ischemic neuropathy develops, the intensity of general symptoms increases. The pain acquires a burning character or manifests itself in the form of an electric “lumbago”. This symptom is due to both compression of the nerve canals and the course of the inflammatory process. In advanced cases, pain occurs due to muscle spasm.
Also, with tunnel syndromes, there is a decrease in motor activity of the fingers, hands, and feet (depending on the location of the neuropathy). Over time, there is numbness in the problem area and atrophy of muscle tissue. In case of compression of the arteries, the skin turns pale, the body temperature in the affected area decreases and swelling occurs.
Possible complications
Without adequate treatment, if constant trauma to the area of the pinched nerve persists, complications of carpal tunnel syndrome naturally appear:
- amyotrophy;
- persistent contracture of the hand.
The muscle tissue innervated by the affected nerve stops contracting.
Over time, such an immobilized muscle decreases in size, atrophies, and becomes very weak. It will be much more difficult to cure such a condition; it will require long-term rehabilitation - physiotherapeutic methods and physical therapy.
Contracture is the immobility of the joints of the hand, their constant forced position. For example, when the ulnar nerve is damaged, the hand takes the shape of a “clawed paw”. Without proper treatment, this hand position will remain forever. Without nervous regulation, muscles literally freeze and lose their ability to contract.
Sometimes surgery is necessary to treat persistent contracture.
Diagnostics
Tunnel neuropathy is diagnosed based on the collection of information about the patient's condition. When the canal running in the upper limbs is affected, characteristic clinical phenomena occur. But in case of compression of the nerves in the legs, additional examination is required.
To diagnose compression of the canals, specialized tests are used to evaluate the motor activity of the limbs and the changes that occur. Electroneuromyography is also prescribed (the speed of impulse transmission along the nerves is analyzed).
When selecting treatment tactics, the pathologies that provoked compression are taken into account. When diagnosing diseases that cause carpal tunnel syndrome, ultrasound, MRI, CT and other techniques are used.
Treatment
In the treatment of compression-ischemic neuropathy, a set of measures is used aimed at restoring the function of the damaged nerve and eliminating symptoms. For this purpose, medications, special exercises, physiotherapy methods and surgery are used.
Drug therapy
Since it is necessary to treat nerve compression over a fairly long period of time, the patient needs to limit the motor activity of the injured limb for the allotted period.
Due to the fact that tunnel neuropathy provokes pain, at the initial stage of therapy the following is prescribed:
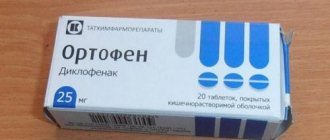
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The drugs are used for carpal tunnel syndrome in the treatment of concomitant diseases. In this case, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen and other medications that suppress inflammation are prescribed.
- Analgesics. They also help reduce pain intensity.
- Anticonvulsants, antidepressants. Prescribed in special cases when pain occurs against the background of neuropathic changes.
Depending on the characteristics of the development of tunnel syndrome, therapeutic therapy can be supplemented with injections of an anesthetic (novocaine) and hormones or hydrocortisone. This approach is used for intense pain that analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs cannot cope with.
In addition, other drugs are introduced into drug therapy that relieve concomitant disorders (edema, decreased tissue trophism), as well as eliminate diseases that caused compression.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy methods usually complement drug treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome. For compression-ischemic neuropathy the following are indicated:
- phonophoresis with dimexide;
- electrophoresis;
- cryotherapy;
- flucturization.
If necessary, other procedures are prescribed that improve trophism (darsalization, massage) and stimulate tissue restoration (ultrasound, mud therapy).
Treatment with folk remedies and exercise therapy
You can treat carpal tunnel syndrome with folk remedies if they are approved by your doctor. It is almost impossible to get rid of neuropathy on your own, especially in advanced cases. At home, treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome is carried out using decoctions of:
- nettle;
- birch buds;
- rosemary;
- rosehip;
- horsetail.
These decoctions have an anti-edematous effect. To reduce the intensity of pain, compresses with alcohol are used (alcohol is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:2) and tincture of birch buds (a tablespoon of buds is mixed with 500 ml), which is rubbed into the problem area.
If carpal tunnel syndrome develops during pregnancy, treatment is not always required. Neuropathy often disappears within a few months after delivery.
The list of exercises for carpal tunnel syndrome is selected taking into account the location of the compressed nerve. If the carpal tunnel is affected, it is recommended to periodically squeeze a rubber ball in your hands or apply pressure with your thumb on others. Gymnastics for carpal tunnel syndrome will not get rid of the disorders, but it will reduce the intensity of the general symptoms.
Surgery
Compression neuropathy is usually treated with medications and physical therapy.
Surgery will be required when bones put pressure on the nerve or a narrow canal is identified. In both situations, reconstructive therapy methods are used.
Prevention
Prevention of carpal tunnel syndrome involves reducing the load on the hands and lower limbs. It is also important to avoid trauma to soft tissues and promptly treat inflammatory and other diseases that provoke neuropathy. In addition, it is important to exclude exposure to provoking factors. If necessary, it is recommended to perform surgery to widen the nerve canal.
With tunnel syndromes, pain of varying degrees of intensity occurs and sensitivity in the upper or lower extremities decreases. The appearance of neuropathy is caused by compression of nerve canals caused by fractures, bruises or inflammatory diseases.
How is the assessment carried out?
Testing occurs by lightly pressing on a nerve to cause a tingling sensation in a specific area of the body. The doctor may use a special hammer.
Based on the presence of pain in the patient, the neurologist diagnoses a disorder in the functioning of the peripheral nerve.
To successfully complete the test and obtain a reliable result, the patient remains static during the procedure.
After identifying the area of damage, the doctor, using the tip of the index finger or a reflex hammer, determines whether the patient has Tinel syndrome. He is obliged to take into account any pain that the patient tells him about.