Increased intracranial pressure is one of the dangerous pathological deviations of the body's functionality. Such a diagnosis sounds like a death sentence. But such a pathological deviation should not cause fear; it does not in every case “speak” of serious violations. To understand what intracranial pressure can lead to, a serious diagnostic examination will be required.
Methods for determining intracranial pressure
The level of intracranial pressure can be assessed in the following ways:
- insertion of a catheter into the lumen of the spinal canal or ventricles of the brain, followed by attachment of a pressure gauge that works in a similar way to a mercury thermometer;
- the use of both computer and magnetic resonance imaging methods;
- ultrasound examination of the brain (synonym: neurosonography) in children under 1 year of age;
- echoencephaloscopy;
- examination of the fundus picture with the definition of a typical clinic - papilledema, blurred contours, pallor.
Before measuring intracranial pressure, it is important to decide on the research method. In infants, preference is given to neurosonography and echoencephaloscopy. Patients who have suffered an acute cerebrovascular accident are prescribed a tomographic examination and an assessment of the condition of the fundus by an ophthalmologist.
Types of drugs
There are two types of drugs for intracranial pressure: some relieve symptoms of the disease and improve the patient’s quality of life. The second is to eliminate the root cause of the pathology. For effective treatment, these two groups are combined, providing lasting results and long-term reduction in ICP.
All drugs that reduce cranial pressure are potent and, if used incorrectly, can cause serious harm to human health, therefore they are prescribed strictly according to medical indications, a regimen developed by a doctor.
Medicines without lifestyle correction are ineffective, but treatment is always multi-vector and aimed at improving:
- liquor flow;
- microcirculation of the brain;
- decrease in the volume of free fluid in the bloodstream.
This helps get rid of pathological symptoms:
- lack of normal peripheral vision;
- morning cephalgia;
- pastiness of the face, neck, head;
- nausea;
- fatigue;
- mood swings.
Medications to treat intracranial pressure should never be taken independently.
Causes leading to increased intracranial pressure
Conditions that cause high intracranial pressure include:
- increase in brain volume due to edema, inflammation;
- the formation of a large amount of cerebrospinal fluid with hydrocephalus;
- the presence of a space-occupying formation (tumor, hematoma, foreign body) in the cranial cavity;
- an increase in blood content in the dilated vessels of the brain during poisoning and intoxication.
The main diseases accompanied by an increase in ICP:
- cerebrovascular accidents of various origins (ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes);
- traumatic damage to brain tissue (concussion and brain contusion);
- inflammatory changes in the membranes during meningitis, encephalitis and ventriculitis;
- intoxication with salts of heavy metals, methanol or ethyl alcohol, vapors of toxic gases;
- tumors not only of the substance, but also of the membranes of the brain, sub- and epidural hematomas;
- developmental anomalies (Arnold-Chiari, Dandy-Walker);
- benign intracranial hypertension;
- hydrocephalus.
It should be noted that symptoms of increased intracranial pressure in infants in 90% of cases are caused by birth trauma.
Indications and contraindications for osteopathic therapy
Here is just a small list of body ailments for which a specialist appointment is indicated:
- various injuries;
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- dysfunction of childbirth;
- pain of various etiologies;
- pain in internal organs;
- states of the nervous system;
- curvature of posture;
- intracranial vascular disorder;
- increased intracranial hypertension;
- pregnancy planning.
Contraindications for manipulation:
- strokes, heart attacks;
- bleeding in the brain;
- cardiac, renal, hepatic, respiratory failure during decompensation;
- infections in the acute stage;
- open form of tuberculosis;
- untreated hematomas;
- mental illness;
- blood diseases;
- oncology, tumors.
The doctor will not be able to immediately cure high blood pressure and pain in adults and children, but after an acute period of the disease, during the rehabilitation stage, he will help to recover faster. In our Center, every visitor is treated with close attention and care. An individual approach and an atmosphere of trust between doctor and patient are proof of successful healing.
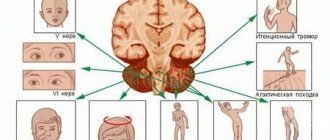
General symptoms characteristic of intracranial hypertension
In the case of increased intracranial pressure, symptoms are characterized by diversity and polymorphism. The clinical picture of the disease in children and adults is different. The leading signs that accompany an increase in ICP are:
- headache that occurs mainly in the morning upon awakening, localized in the frontal, temporal, and occipital regions, having a pressing or bursting character;
- nausea and vomiting;
- drowsiness;
- impairment of memory, attention and thinking;
- dizziness;
- rise or fall in blood pressure;
- bradycardia - rare pulse;
- sweating;
- visual impairment due to swelling of the optic nerve papilla up to blindness.
Symptoms of intracranial pressure in children
Increased intracranial pressure in children, symptoms of which can appear in the first minutes and hours after birth, often leads to the development of serious complications. Knowing the key signs of the disease, it is possible to establish the correct diagnosis in the early stages and prescribe the correct treatment for the child (see increased intracranial pressure in infants). Symptoms indicating the presence of high ICP in children include:
- bulging of the large and small fontanelles, as well as their pulsation;
- divergence of the skull bones with an increase in the size of the sutures;
- change in the child’s behavior: drowsiness, lethargy or, conversely, irritability, tearfulness;
- chin tremor;
- repeated vomiting (“fountain”), which does not bring relief;
- visual impairment;
- oculomotor disorders in the form of strabismus, limited range of motion of the eyeballs;
- impaired level of consciousness; in severe cases, a coma may develop;
- convulsive syndrome;
- increase in head circumference;
- decreased strength in the limbs up to complete immobility;
- regurgitation when eating.
There are two possible options for the development of the clinical picture of intracranial hypertension:
- sudden onset of symptoms of the disease with impaired consciousness to the level of deep coma; the probability of death is 92%;
- gradual appearance of symptoms of the disease.
Modern diagnostic methods
Increased extracranial pressure is very difficult to diagnose. This happens because there are still no methods for measuring intracranial pressure in a safe way. Today doctors resort to several options for confirming this diagnosis:
- Fundus examination. This is currently the only non-invasive option for accurately diagnosing the presence of high blood pressure. During the examination, the ophthalmologist notes characteristic changes in the fundus. Such unambiguous signs include swelling of the eye discs, congested and tortuous eye vessels, multiple micro-effusions of blood on the retina, low pulsation or its complete absence in the retinal vessels. Only after the ophthalmologist confirms the presence of this problem will the neurologist prescribe treatment.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. This type of diagnosis is more intended to identify the causes of ICP. This may be a search for tumors, blood clots, edema or other pathological changes.
- CT scan. This technique records changes in the skull and is used extremely rarely in the early stages of diagnosis.
- Ultrasound of the head. This study is carried out in children whose fontanel has not yet healed. This method is absolutely harmless and easy to carry out, but, unfortunately, the results obtained this way are not always correct.
- Performing a spinal puncture. This manipulation can only be performed in a hospital. At the level of the lumbar spine, a needle is inserted between the membranes of the spinal cord, and fluid is allowed to flow freely through it. Based on the flow rate and composition, the doctor diagnoses the presence or absence of high blood pressure.
- A series of manipulations associated with penetration under the patient’s skull. These procedures are performed only on those patients for whom intracranial pressure indicators are vital. Such surgical interventions are performed extremely rarely.
What is hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus is an excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the cranial cavity and is accompanied by increased intracranial pressure. The following conditions lead to hydrocephalus:
- increased formation of cerebrospinal fluid (the fluid that surrounds the brain) with tumors of the choroid plexus;
- the formation of obstacles to the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid;
- inflammatory process in brain tissue.
Symptoms of hydrocephalus in children
The leading sign characteristic of hydrocephalus in a child is a progressive increase in head size up to the age of two years. The main symptoms of hydrocephalus in newborns, caused by increased intracranial pressure, include:
- intensive head growth by the end of the first month;
- sparse hair;
- disproportionately large forehead;
- exophthalmos - protrusion of the eyeballs;
- progressive decrease in visual acuity due to developing atrophy of the optic nerves;
Hydrocephalus in children of other age periods is accompanied by neuroendocrine disorders, delayed psychomotor development, and head twitching with a frequency of 2-4 times per second.
Symptoms of increased intracranial pressure in adults
With increased intracranial pressure, symptoms in adults develop gradually in most cases. A headache with the following parameters comes to the fore:
- character - pressing, bursting, squeezing, occasionally - pulsating;
- time of occurrence - in the morning after waking up, which is associated with an increase in ICP;
- provoking factors - horizontal position of the body, coughing, sneezing, straining, hyperextension of the head;
- accompanying symptoms - nausea and vomiting, noise in the head;
- is not relieved by taking analgesics.
In second place in frequency with increased intracranial pressure is autonomic dysfunction syndrome, which is accompanied by:
- fluctuations in blood pressure and pulse during the day;
- disturbance of intestinal motility with the development of constipation or, conversely, diarrhea;
- hypersalivation - increased salivation;
- moisture of the skin, especially in the area of the palmar and plantar surfaces;
- attacks of suffocation;
- dizziness;
- feelings of fear, anxiety, irritability, apathy, drowsiness;
- pain in the heart and abdomen.
Much less frequently, increased intracranial pressure may be accompanied by the development of stroke-like conditions that threaten the patient’s life. In such cases, the following symptoms are observed:
- disturbance of consciousness up to coma;
- severe dizziness and instability when walking;
- decreased strength in the limbs;
- speech function disorder;
- uncontrollable vomiting;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs in the form of incontinence or retention of urine and feces;
- dysfunction of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
Traditional methods of treatment
Most doctors approve of the use of herbal medicine for high intracranial pressure and agree that diuretic herbs can best relieve pain and reduce blood pressure.
To relieve pain, you can use 3 large lemons (unpeeled) and 3 peeled heads of garlic. Scroll the ingredients through a meat grinder and dilute the mixture in 1.25 liters of water (preferably boiled or filtered). Stir and leave for 24 hours in a dark place. Then the mixture must be strained and refrigerated. Take 1 tablespoon for 3 weeks every day before breakfast.
It is possible to effectively reduce pain and get rid of all the unpleasant symptoms of increased intracranial pressure over a long period of time (about 1 year). To do this, you need to drink raw chicken eggs during the first 10 days of the month, and from the 11th day take a break until the end of the month. Repeat the procedure every month.
To quickly get rid of pain caused by intracranial hypertension, when pain occurs, you need to chew raisins and peppercorns for 5-7 minutes. Spitting occasionally. Take 1 tbsp. mint, St. John's wort, sage, horsetail and valerian.
Stir the herbs and pour 2 cups of boiling water. Place on the fire and simmer for approximately 20-30 minutes. Cool and let sit. This collection will help get rid of pain if you take it 30 ml three times a day. You can give children 1 teaspoon, but only with the permission of a doctor. Valerian can be replaced with motherwort.
A mulberry decoction will help reduce not only intracranial pressure, but also arterial pressure. To prepare it, you need to take several mulberry branches and cut them into small pieces, the leaves themselves should be chopped.
15 gr. Pour this mixture with a liter of chilled clean water, put on fire and boil for half an hour. Then let it brew for another hour. Take 1/2 cup of tincture half an hour before meals three times a day. You can recover and get rid of pain within 1-3 months.
In addition to various tinctures and decoctions, there are more effective quick ways to relieve pain. For example, inhale essential oils (orange, peppermint, rosemary) when pain occurs. Or brew a bag of bay leaves (about 20 leaves) and breathe in the steam for half an hour. If dizziness occurs, the procedure should be stopped.
If pressure and pain in the eyes occur due to overwork, wearing lenses or poorly chosen glasses, eliminate the influence of irritating factors. Relax in a dark, cool room. To restore eye tone, you can perform therapeutic ophthalmic exercises.
Eye exercises:
- Move your eyes up and down 6 times, close your eyes and repeat this exercise.
- Without moving your head, look left and right 6-8 times, then repeat the exercise with your eyes closed.
- Starting from the upper right corner of the room, draw an imaginary circle with your eyes, then in the middle of the room - a circle, a triangle. Repeat with your eyes closed.
- Draw a figure eight, an infinity sign, open and closed eyes with your eyes.
Perform the exercises while standing or sitting without moving your head. It is recommended to perform the complex daily.
Lemon juice with honey
Take one lemon. Cut it. Squeeze out the juice thoroughly. Add 2 tablespoons of honey and one hundred milliliters of water. Mix all ingredients thoroughly and drink. The treatment period is twenty days. After ten days there is a break.
Pollen with honey
Used for head massage. Take 2 parts of flower pollen, add honey. Mix the ingredients and leave for 72 hours in a place where sunlight does not penetrate. Then rub the mixture in small portions into the back of your head, the back of your neck and the bridge of your nose. Then wrap your head with a towel. Carry out the procedure every day for a month.
Plantain
Take three spoons of dry plantain, pour half a liter of boiling water over them and leave for thirty minutes. Drink fifty grams of decoction three times a day.
Sources: med.vesti.ru, net-boly.com, bolitgolova.net, bolitgolova.info, neuroplus.ru, etodavlenie.ru, uaua.info
Eye clinics
- Voronezh
- Ekaterinburg
- Izhevsk
- Kazan
- Krasnodar
- Moscow
- Nizhny Novgorod
- Novosibirsk
- Permian
- Rostov-on-Don
- Samara
- Saint Petersburg
- Ufa
- Chelyabinsk
Facebook Comments
What is benign intracranial hypertension?
Benign (idiopathic) intracranial hypertension is one of the most poorly studied pathological conditions in modern neurology and neurosurgery. This disease is typical for overweight women and children. Numerous studies have failed to establish the cause.
With benign intracranial hypertension, the same symptoms that are characteristic of increased intracranial pressure are observed. It should be noted that with this disease spontaneous recovery occurs several months after the first manifestations.
Complications that can result from increased intracranial pressure
A life-threatening condition is a sudden increase in intracranial pressure, leading to death if not treated appropriately. Other complications associated with high ICP include:
- pinching of the cerebellum in the foramen magnum, which is accompanied by respiratory failure, decreased strength in the limbs, and disturbance of consciousness;
- epileptic syndrome;
- decreased vision up to blindness;
- mental dysfunction;
- ischemic or hemorrhagic strokes.
Modern methods of treating increased intracranial pressure
Treatment begins after identifying the cause that led to the development of the disease.
Stage one - Elimination of the cause of the disease.
- In the event that an intracranial formation has led to an increase in intracranial pressure - a tumor, hematoma, aneurysm, after appropriate additional examination, emergency surgery is performed (removal of a space-occupying formation).
- In case of excessive secretion of cerebrospinal fluid with hydrocephalus, shunt operations are performed, the purpose of which is to create an additional outflow path for cerebrospinal fluid, which leads to a decrease in intracranial pressure.
Stage two - Drug correction of the level of intracranial pressure. For this purpose, the following groups of drugs are used:
- osmodiuretics (mannitol, glycerol), the action of which is aimed at reducing the amount of cerebrospinal fluid;
- loop diuretics (furosemide);
- hormonal drugs (dexamethasone);
- diacarb;
- neuroprotectors (glycine).
Stage three - Medication manipulation. Ventricular puncture and decompression craniotomy are designed to reduce the volume of cerebrospinal fluid in the cranial cavity. Stage four - Diet therapy. The amount of liquid and salt entering the body is limited, which corresponds to diet No. 10, 10a. Stage five - Using techniques of manual therapy, hyperbaric oxygenation, controlled arterial hypotension, hyperventilation.
Extremely rarely, during enhanced treatment, decreased intracranial pressure may occur, the symptoms of which are:
- drowsiness;
- weakness;
- headaches that get worse with head movements;
- dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting.
Treatment of increased intracranial pressure should be comprehensive.
Traditional treatment of pathology
It is best to treat a patient with blood pressure in a hospital setting.
At home, it should be prescribed based on the results of diagnosing hypertension. After a TBI, the patient should be given complete rest, offered light food, drink more fluids, and take anti-inflammatory drugs. In situations of hematomas and brain tumors, surgery is required.
Similar measures should be taken for hydrofecal cerebral effusion. To drain excess fluid during ICP, a catheter is installed. Liquor should be removed several times depending on the child’s growth, and the latter should be constantly monitored. Gradually, interference with blood pressure will disappear.
Treatment with medications during pathology is prescribed to make you feel better:
- hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- agents that protect neurons - affect blood flow and gas exchange in the brain;
- diuretics - for the outflow of excess contents;
- osmodiuretics - reduce the volume of cerebrospinal fluid.
However, the drugs affect the intracranial disorder signal itself, and not its cause. At the same time, an important stage of treatment is the treatment of the pathogenesis of intracranial pressure.
What to do if you have symptoms of increased intracranial pressure?
Below is an algorithm of actions that all patients with symptoms of increased ICP should follow.
- Calm down. It must be remembered that currently there are many methods that allow normalizing the level of intracranial pressure without threatening life.
- Make an appointment with a neurologist, who will prescribe a list of examinations (CT or MRI, ultrasound, radiography, examination by an ophthalmologist).
- Strict adherence to all doctor’s recommendations (following a diet, taking medications, and, if necessary, surgical treatment). Failure to comply with prescriptions may result in death.
Complications
Chronic increased intracranial pressure, contrary to popular belief, tends to progress. Without proper treatment, the disease can lead to serious consequences leading to disability.
Such complications include:
- stroke;
- impaired coordination of movements as a result of damage to the cerebellum;
- impaired reflexes, arrhythmias as a result of compression of the brain stem;
- paralysis;
- speech disorders;
- psychical deviations;
- blindness;
- epilepsy.
A common result of the development of the disease is death. However, a benign form of the disease is also quite rare, in which the symptoms of increased ICP go away on their own, without any treatment.
Associated with the presence of this form of the disease is the misconception that the disease goes away on its own. But that's not true. The fact is that, as a rule, the benign form of the disease is typical only for young women, who are often overweight.
So you shouldn’t rely on the fact that you have a benign form of the disease. It is best to consult a doctor.
Increased intracranial pressure: facts and figures
- The leading cause of increased ICP in children under 1 year of age is hydrocephalus.
- Idiopathic intracranial hypertension occurs with an incidence of 1 to 2 cases per 100,000 population.
- Even 200 years ago, scientists drew attention to the problem of increased intracranial pressure; The issue has not yet been fully studied; research continues.
- There are several dozen medical associations around the world that deal with intracranial hypertension.
- Every tenth child seen by a pediatric neurologist has a high level of intracranial pressure.
- The number of people suffering from increased intracranial pressure is approaching 100,000,000.
- According to evidence-based medicine, herbal preparations do not have any effect on the level of ICP and, accordingly, cannot be used for treatment. Similar information is available for homeopathic medicines.
- Patients who have managed to normalize the level of ICP should visit a doctor once every two years in order to prevent the development of relapse of the disease.
Author:
Selezneva Valentina Anatolyevna physician-therapist
How is blood pressure treated today?
Depending on what caused the patient to experience such a symptom as a feeling of squeezing and increased pressure - the individual characteristics of the body, concomitant pathologies or ear inflammations, treatment will be selected.
In order to effectively equalize ear pressure without causing any complications, diagnosis and therapy are carried out on a case-by-case basis. Taking into account factors such as the duration of these symptoms and the general well-being of the patient, the doctor makes a decision on conservative treatment or surgical intervention, which will help quickly get rid of the disease.
Having diagnosed the pathology that has caused the disturbing symptoms, the following treatment may be prescribed:
- Drugs whose essence is to lower total blood pressure (antihypertensives). They are also good for relieving congestion.
- Antibacterial therapy. Used for acute and chronic otitis media to relieve inflammation.
In the case of a neuroma of nerve cells in the ear, there is a high probability that the doctor will have to resort to surgical treatment methods.
Another way to get rid of the problem is irradiation. However, it is rarely used due to widespread side effects. Radiation therapy is indicated only when the tumor is difficult to reach with a scalpel or is large in size.
If there is pressure on the ears due to a seasonal cold, then no particularly serious treatment is required. Often, therapy consists of prescribing medications aimed at relieving the symptoms of the disease.
As soon as its main manifestations can be eliminated, the patient ceases to be bothered by discomfort in the ear. However, severe forms of colds can lead to a lot of complications, which will be difficult to cope with without antibiotics.
The pressure caused by wax plug in the ear is restored by getting rid of the plug. This is done either mechanically, or the sulfur is dissolved using special means. It is recommended that you seek medical advice before removing the plug.
On a note! The whole range of measures aimed at treating atherosclerosis consists of correcting the diet, combating bad habits and radical changes in lifestyle in general. In addition to this, the patient is prescribed a number of drugs that lower lipid levels in the body.