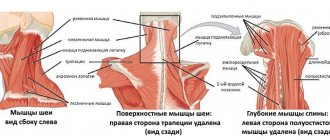
What is pain?
If we characterize this feeling, then it is, first of all, a discomforting sensation, which is characterized by reflex changes in the functions of internal organs. It is associated with actual or potential tissue damage and is accompanied by emotional distress. Pain may be caused by activation of the peripheral nervous system or result from damage to the brain, spinal cord, or peripheral nerves. If pain persists for a long time, it is characterized by changes in physiological parameters. What are the types of pain in the temples and the back of the head? What is the reason for this?
If the pain is caused by hypertension
Most often, discomfort in the occipital part is caused by increased pressure values. This is due to the fact that hypertension generally occurs more often than hypotension.
Usually, with high blood pressure, pain is localized not only in the back of the head. However, here they are most pronounced.
With hypertension, discomfort from the back of the head moves to the temples, crown and forehead. At the same time, it has a pulsating character. For this condition, mild pain is more typical. There is often a burning sensation in the back of the head.
In this case, the discomfort increases in a lying position. The pain becomes acute when coughing, sneezing, as well as during mental and physical stress. The most pronounced discomfort is observed in the morning, and in the evening it becomes weaker.
Usually this unpleasant sensation is caused by a deterioration in the outflow of blood from the skull. In this case, the elements of the circulatory system in the head, overflowing with blood, expand and begin to put pressure on the nerve endings and nociceptors. This causes discomfort, expressed in the form of throbbing pain.
Sometimes, with hypertension, pressing pain may also occur. Such discomfort occurs when the patient’s blood pressure significantly exceeds normal levels. In this case, there is a weakening of the compensatory spasm of the arteries, which protects the capillary bed from damage as a result of overflow.
To determine at what pressure the back of the head hurts, you need to pay attention to the accompanying symptoms. Hypertension has a number of characteristic symptoms.
Symptoms of hypertension:
- Increased heart rate;
- Feeling of nausea;
- Floaters in the eyes;
- Hot flashes in the facial area;
- Redness of the skin;
- Breathing disorders.
Chronic hypertension may also cause swelling of the face and limbs. This indicates the advanced stage of the disease.
Features and types of pain
The pain may be:
- Primary character.
- Secondary.
Migraine, pain from overwork, pain in the head, in which the brain is not damaged, are primary. Secondary pain is pain that is a symptom of a disease. For example, pain after a head injury, due to vascular disease, infectious diseases of the nose, throat, ears, and so on.
It is worth paying attention to the intensity of the pain in the temples and the back of the head, its duration.
- Pain that occurs periodically or is chronic most often cannot be a signal of dangerous infections. This is a sign of chronic diseases.
- Rapidly increasing pain that occurs unexpectedly and is very severe is most likely a sign of a dangerous disease. Possible meningitis, tumor or hemorrhage, and so on.
Pain can also be:
- Blunt.
- Harsh.
- With a burning sensation.
- Compressive.
- Pulsating.
- Constant or periodic.
Depending on the type of pain and the nature of its manifestation, the doctor prescribes an examination.
Characteristics of pain with low blood pressure
The patient's hypotension is characterized by 100/60 mm Hg. Art., can be chronic and episodic. The development of hypotension is related to internal processes occurring in the body: hormonal imbalances, chronic fatigue, lack of sleep, infectious diseases.
See also: How to measure blood pressure at home?
With hypotension, pain is localized in the occipital or parietal region. Occipital pain with low blood pressure is dull and squeezing in nature. Features of low blood pressure: drowsiness, frequent yawning, the appearance of black spots before the eyes, loss of consciousness, vomiting.
Diagnostics
If you often have headaches in your temples and back of your head, you should consult a general practitioner or neurologist. During the examination, the doctor will find out the nature and duration of the pain. The following examinations may be prescribed to determine the cause:
- X-ray computed tomography of the brain. Examines the cranial cavity for deviations from the norm in development, circulatory disorders, and new formations.
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and spine. Examines not only the brain, but also the spinal cord for the presence of tumors, lesions after a stroke, trauma, hernia and much more.
- Magnetic resonance angiography. An examination that evaluates the condition of blood vessels, veins, and arteries detects changes in the aneurysm.
- Blood pressure monitoring. This study reveals hidden arterial hypertension, which can cause pain in the temples and back of the head.
- Blood tests are done to detect infection or inflammation.
- It is necessary to undergo an examination by an ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, or dentist. Perhaps the cause of the pain is associated with disease of the ears, eyes or teeth due to an existing chronic infection.
What causes hypotension?
Patients with low blood pressure are called hypotensive. The causes of this disease may be related to various factors. Physiologically, this process is associated in most cases with pathological vasodilatation. The work of the heart continues at the same pace, blood flows at the same speed, but due to the increase in the capacity of the vessels, the pressure steadily decreases. The opposite situation is less common. The vessels remain the same, but for certain reasons cardiac functions are reduced. In this case, the head also hurts, the pressure decreases. Here are the main causes of low blood pressure:
- chronic heart failure;
- neuroses and depression;
- blood loss, incl. internal;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- disorders of the thyroid gland;
- pregnancy.
Hypotension is often caused by a condition called chronic fatigue syndrome. However, the opposite situations are also known, when CFS is a trigger for hypotension. In addition, headaches with low blood pressure are often observed among athletes, residents of hot latitudes and employees of hot shops. Often the development of hypotension occurs due to a genetic predisposition. If parents have low blood pressure and headaches, then there is a high probability of developing this pathology in children.
Strong pain
If severe pain suddenly appears in the back of the head and temples, this is a very dangerous symptom. It is necessary to urgently consult a doctor. This may be a sign of the following conditions:
- meningitis;
- development of sepsis;
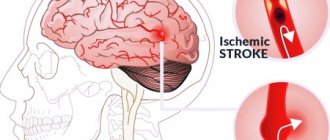
- stroke;
- cervical migraine.
It is necessary to carefully monitor the accompanying symptoms:
- dizziness;
- increased temperature;
- vomiting;
- sand in the eyes;
- increased blood pressure.
Very often, severe pain can be a symptom of a hypertensive crisis.
If the back of your head hurts and radiates to your temples, this does not exclude a problem with the cervical vertebrae or occipital neuralgia. Due to inflammation of the nerves, the symptoms mentioned above are possible. Occurs as a result of hypothermia. A dull ache persists for a long time between attacks of severe pain. The back of the head becomes very sensitive.
Be careful, pain in the temples can cause hearing or vision loss, behavioral changes, and the development of depression.
What pressure does pain in the back of the head indicate?
Head pain in the occipital area most often occurs in the morning, almost immediately after waking up, and less often develops in the afternoon or evening. Doctors identify 3 main causes of the pathological condition:
- rise in blood pressure;
- decreased blood pressure;
- increased intracranial pressure.
If the pressure is high or low, then the signs of occipital pain may be similar, but there are also some distinctive features in the nature of the sensations. It is imperative to take into account the pressure at which the back of the head hurts in order to eliminate discomfort and effectively prevent new attacks.
Vascular and infectious diseases
One of the most common diseases is migraine. It is characterized by the development of throbbing pain on one side, as well as the following symptoms:
- photosensitivity;
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- sound sensitivity.
Pain can appear for no reason and disappear just as suddenly.
Hypertension is one of the diseases that causes headaches in the temples and back of the head. Particularly pronounced at high blood pressure. Characterized by pressing, throbbing pain, as well as:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- dizziness;
- reel;
- noise in ears.
Infectious diseases include not only meningitis, but also acute viral infections and dental diseases. The blood thickens, making it difficult for it to supply the brain with oxygen. The resulting gum gum on the left side can easily cause pain in the left temple and back of the head.
Painful sensations with low blood pressure
Many, experiencing pain in the back of the head, believe that the cause lies in hypertension. At what pressure exactly does this unpleasant sensation appear?
Constant fatigue, stressful situations, hormonal imbalances, the consequences of infectious diseases - all this can cause a sharp drop in blood pressure.
Hypotension leads to a number of changes within the body. Pain appears in the back of the head or in the temporal part of the head.
Most often they are dull and do not go away for a long time. Attacks of pain intensify with a sharp turn of the head.
At the same time, the following symptoms occur:
- Nausea occurs.
- It is impossible to concentrate on faces and objects around.
- Dizziness.
- Due to insufficient oxygen.
In extreme cases, low blood pressure can gradually lead to fainting.
Blood pressure can be normalized with the help of special medications. Additionally, hot, strong coffee or a bar of chocolate helps normalize blood pressure.
To eliminate pain with low blood pressure, proper rest is important. It is recommended to additionally massage the cervical-collar area.
Low blood pressure in adolescents is caused by increased workload and frequent stress. For your age - your stress.
If for adults the situation is unpleasant on a global scale, then for a schoolchild it may be due to problems in studies or conflicts among friends.
Pain in the back of the head due to hypotension can be eliminated with the help of painkillers. But if the symptom repeats within a short time, then you need to consult a doctor.
The cause of the appearance may be vegetative-vascular dystonia. This disease has the following symptoms: nausea, dizziness, frequent pressure changes within one day.
Additionally, people who suffer from this disease have a manifestation such as an increase in body temperature to 37 degrees.
Psychogenic and neurological causes
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is usually characterized by pain that is localized on one side, but can radiate to the occipital region.
Neurological diseases are characterized by sharp pain in the back of the head and temples, alternating with dull pain.
It is worth noting that diseases of the vascular nervous system, disorders of the cervical spine, and atherosclerosis are aggravated by nervous and physical stress. Often, pressing pain in the back of the head and temples bothers children at the end of the school year. Since the body is weakened and there is a lack of strength for the active functioning of the brain vessels. Vascular pathology may also contribute to this, but this condition is also typical for adults. When overexerted, there is a feeling of pressure on the back of the head, temporal region, and possibly tingling. The pain is moderate, with no vomiting, nausea or chills. Pressure readings remain within normal limits.
Very often, throbbing pain in the temples and back of the head can be a symptom of hormonal changes in the body. This can occur in pregnant women, teenagers, and women.
This may also be the first symptom of intoxication in the body. Since a large number of dyes and preservatives are currently added to food and medicines. It is a known fact that eating chocolate and cocoa can also trigger a migraine or headache.
Treatment of pain in the back of the head
Occipital pain syndrome, which does not correlate with dangerous pathologies in the body, can be easily relieved at home using medications and even folk recipes. Depending on the nature of the discomfort, you can use the following first aid measures:
- For high blood pressure, lower blood pressure by taking an antispasmodic drug – “Papaverine”, “Spazmalgon”. If the condition is accompanied by obvious swelling, then you should take a diuretic medicine - Furosemide or Hypothiazide. Also, a good effect in this state is a foot bath with warm water, drinking warm, but most importantly not hot, hibiscus tea;
- When the pressure decreases, the optimal actions to increase it would be: taking a drug with caffeine in the composition - “Kofalgin”;
- Painful sensations associated with overwork: take a sedative, for example, Valerian, Motherwort, lightly massage the neck and head using aromatic oils - lemon balm, lavender, rosemary;
- Traumatic pain: provide the victim with as much rest as possible, immediately call an ambulance;
- Neurological discomfort: take an anesthetic drug - “Pentalgin”, “Nurofen”, apply a warm compress with mustard plaster to the back of the head.
The main rule for any type of pain syndrome is to ensure peace, access to fresh air, and silence. It is recommended to turn off the TV and other devices, dim the lighting, close the curtains in the room during the day, and open the window slightly.
Causes and treatment
Often, for neurological pain, massage may be prescribed, which is prohibited for hypertension. This once again confirms the need to clarify the causes of violations.
Also, for pain in the back of the head, the doctor may prescribe physiotherapy procedures:
- UV exposure;
- electrophoresis;
- laser exposure;
- magnetotherapy.
Such methods are good for pain in the back of the head associated with a pinched artery or nerve.
For hypertension, physical therapy has a good effect, but the exercises must be selected by a doctor, otherwise the risks of complications increase. Proper exercise removes blood stagnation and restores vascular tone.
Tying your head improves blood flow. For this effect, you will need to tie your head tightly with a headscarf or scarf. This will remove congestion and reduce the intensity of pain. Warm baths or mustard plasters for the legs will be useful - they dilate the vessels of the lower extremities, which compensates for excess blood.
Remedy – compress or headband
When the cause of occipital pain is a decrease in pressure, it is useful to drink hot coffee with something sweet, best of all with a piece of dark chocolate.
The listed methods will help relieve pain during its periodic development in the case of a known cause of attacks. It is better to discuss the use of medications with your doctor in advance.
If the etiology of pain has not been established, then you need to go to the doctor. There is a risk that a dangerous disease is developing, which needs to be treated in the early stages, avoiding complications.
Preventive measures
To prevent headaches in the occipital area, you can use the following methods:
- try to correctly compare the work and rest regimes;
- do exercises in the morning and warm-up throughout the day, you should definitely set aside some time for this;
- review your diet, add fresh fruits and vegetables to it;
- drink less alcohol and be sure to quit smoking.
The methods listed above help make pain attacks less frequent and less severe.
Exercises to prevent pain
If you experience pain in the back of your head, you should immediately pay attention to their strength and what is causing their occurrence. Constant discomfort may be a consequence of overwork, poor lifestyle or sedentary work, and not a disease. To be sure of this, you should visit a doctor and undergo an examination and receive recommendations for relieving pain in the back of the head. The condition should not be neglected, because the symptom of pain may also indicate a dangerous disease.
Treatment
First of all, it is worth noting that if you are bothered by pain in the temples and back of the head, you can only determine the causes of this condition together with your doctor. You should not self-medicate. It is necessary to undergo a full examination for effective treatment.
However, there are several recommendations that need to be taken if pain occurs in the temples and in the back of the head:
- Try to relax and take a comfortable position.
- It is better to retire to a dark room. Give your eyes a rest.
- If possible, go out into the fresh air, especially if you have been indoors for a long time.
- It is allowed to use a cold compress on the forehead and temples.
- Drink mint or chamomile tea.
- Perform a light head massage in the temporal region.
- Take a drug that will relieve pain or relieve spasms, for example Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Tempalgin.
If the pain does not go away, then you need to call a doctor.
For pain caused by osteochondrosis, the following are indicated for treatment:
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Massage.
- Therapeutic exercises after relieving pain symptoms.
Primary headaches
The most common cause of headaches in the back of the head and temples is primary cephalgia. It is easily corrected with analgesics, proper rest and regulation of the emotional background. People of all ages are susceptible to the appearance of this group of cephalalgia.
Muscle tension headaches
Tension pain can be episodic, occurring less than 15 days a month. The chronic form is diagnosed when headaches recur for more than two weeks in a 30-day period.
The nature of the pain is moderate, bilateral, often starts from the back of the head and gradually compresses the entire head like a “hoop”, radiating (radiating) to the temples and neck area. Sometimes there is intolerance to light, loud sounds and nausea. Basically, cephalalgia appears after sleep and is present all day, intensifying and subsiding.
Provoking factors:
- emotional stress;
- tension in the muscles of the neck and back of the head;
- physical inactivity.
Tension headaches are more susceptible to females and can also occur in childhood. People who lead a sedentary lifestyle and work with small objects are at increased risk.
To correct and prevent an unpleasant symptom, you need to regulate your emotional background and include moderate physical exercise in your daily routine. Frequent use of analgesics, which increase the intensity of cephalalgia during subsequent manifestations, is not recommended.
Migraine
Migraine headaches often begin in the occipital region and are localized at the temples, forehead and around the eyes. It has a pulsating, pressing and one-sided character. Migraine attacks are accompanied by nausea, sensitivity to light, sound and smells. In some cases, vomiting, dizziness and fainting occur.
Factors that provoke migraine:
- fasting, alcohol, food additives;
- excessive workload, lack of sleep, excess sleep, sex;
- stress, anxiety;
- menstruation, menopause, pregnancy, contraceptives;
- bright light, stuffiness, altitude, weather factors.
For minor manifestations of migraine, head massage, gymnastics, contrast showers and sleep will help relieve attacks.
As an ambulance for severe migraine attacks, aspirin-containing drugs will help, preferably in soluble form. If migraine attacks are accompanied for a long time and the intensity of the headaches does not decrease, hospitalization of the patient is indicated.
Overuse headache
This type of cephalalgia occurs with excessive use of certain medications. Depending on the drug, it can be unilateral or bilateral, have a compressive, pulsating nature, and sometimes accompanied by vomiting and nausea. Localized at the temples and back of the head.
Drugs that provoke overuse cephalgia:
- analgesics;
- nonspecific anti-inflammatory drugs;
- ergotamine derivatives;
- triptans;
- opioids;
- serotonin agonists.
In this case, gradual complete withdrawal of the drug taken is the only effective treatment method. At the same time, antidepressant therapy is prescribed under the supervision of the attending physician.
Cluster headache
This type of cephalalgia occurs in series several times a day over a long period. The attack begins with a blocked ear and acute intracranial pain behind the eyes. It is characterized by severe stabbing pain that affects one side of the face. Painful sensations gradually spread to the forehead and temple. In this case, the face turns red, sweats, the eye on the affected side becomes bloodshot and vision blurs.
During the cluster period, headache attacks can occur from 1 to 10 times a day and appear at the same time. This type of headache most often occurs between the ages of 20 and 40 years, 5 times more often in males.
Presumably cluster cephalgia is a cyclical disorder associated with the human biological clock. The exact cause of a headache attack is not known.
At the first sign of cluster headache, you should consult a neurologist. Correction of cephalgia includes procedures for inhalation of 100% oxygen and taking strong drugs, including ergotamine and somatostatin.
Folk recipes
There are also traditional methods for treating headaches. Here are some of them:
- It is recommended to make a compress on the back of the head from a cabbage leaf; before doing this, the leaf must be crushed.
- You can make a compress from grated horseradish or onion.
- For headaches, it is recommended to drink tea from a collection of herbs, which includes peppermint, linden, and meadowsweet.
- Rub your palms vigorously and place one on the back of your head and the other on your forehead for a few minutes.
- You can cut an aloe leaf lengthwise and apply it to your temples for 30 minutes.
- Viburnum berries are very popular. They are ground with honey and taken 4 times a day, a tablespoon.
- Add a tablespoon of apple cider vinegar to a liter of cold water. Dampen the cloth and apply to your forehead.
- It is useful to drink tea made from rose hips, chamomile and honey.
Migraine in the cervical region
A special type of headache. In the overwhelming majority it is inherited . Predominant cases occur in the female half of the population. Vegetative-vascular dystonia can also cause this complication.
As a rule, it affects one side of the head and manifests itself in the form of frequent seizures and strong pulsation. By pressing on the neck area, the occipital pain sharply worsens. It also intensifies with movement, running and fast walking.
Symptoms
Symptoms indicating migraine:
- Occipital stitching pains;
- Frequent vomiting, nausea;
- Loss of coordination/dizziness;
- Drowsy , lethargic, depressing, depressive state of health;
- Irritability for no good reason;
- Experienced aversion to certain odors;
- Intolerance to loud sounds;
- Discomfort from bright light;
- Gastrostasis (cessation of digestion of food, respectively, and medications that can eliminate the signs of migraine).
Types of migraine
There are 2 types of migraine:
1) With an aura;
2) Without aura.
The first type is associated with the appearance of an aura 15-20 minutes before an attack of illness. Sometimes these are hallucinations, both auditory, tactile and visual. Read more about how to avoid a migraine attack with aura.
The second type is classic, differs:
- abdominal pain;
- cramps in the abdominal region;
- paleness of the skin;
- diarrhea;
- vomiting, nausea;
I experience this type of migraine mainly at a young age. As the body matures, attacks decrease in their contrast and intensity.
Prevention
To prevent headaches, you should follow a few simple rules:
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, do not overcool, walk in the fresh air every day.
- If you work at a computer, take a 15-minute break every hour. The screen should be located at eye level, and the height of the chair should be selected correctly.
- If you are hypertensive, regularly monitor your blood pressure, take medications, and visit a doctor.
- Avoid conflict situations, learn to cope with stress, and relax.
- Sleeping on an orthopedic pillow and mattress will help your spine to properly relax.
- Ensure the freshness and purity of food products.
If you have a headache in your temples and the back of your head, you shouldn’t ignore it. It is necessary to consult a doctor in a timely manner to find out the cause and undergo treatment.
Causes of high blood pressure
High blood pressure occurs against the background of one or two main components: lifestyle and primary diseases. The first one is being overweight. In most people, obesity is accompanied by hypertension, although this is not an axiom. In turn, obesity is a consequence of excessive or improper nutrition and insufficient physical activity. Smoking has a significant impact. Headaches with high blood pressure are not uncommon for smokers.
Concomitant pathologies include kidney disease, adrenal gland disease and diabetes mellitus. Hypertension is often caused by dysfunction of the cardiovascular system. Eating too salty foods leads to vasospasm and a significant increase in fluid in the body. And perhaps the most important culprit of hypertension is high cholesterol in the blood, leading to atherosclerosis. Cholesterol deposits inside the vessels lead to a pathological decrease in the lumen and, as a result, chronic high blood pressure. We must not forget about genetics, since hypertension is a hereditary disease. People who have hypertension among their relatives need to especially closely monitor their health.
Diagnosis of the causes of pain in the back of the head
If occipital pain is not the exception, but the rule, then you should not ignore this symptom, temporarily eliminating it with pills. After all, its cause may lie in serious diseases. Therefore, patients with this type of discomfort need to see a doctor and undergo an examination, after which the correct diagnosis will be made.
Diagnosis of the causes of headaches:
- First of all, you need to go to see a therapist. The specialist will examine the medical history and interview the patient about the presence of any associated symptoms.
- Next, a visual inspection will be carried out. The doctor will measure the patient's blood pressure.
- If it is suspected that the pain problem lies in a blood pressure disorder, the patient is usually referred for daily recording of blood pressure readings. This makes it possible to determine the stage of hypertension or hypotension.
- If cervical osteochondrosis is suspected, an x-ray of the cervical spine is performed.
- Examinations such as CT, MRI and ultrasound are also used. These diagnostic methods allow you to study in detail the condition of the head and neck tissues and blood vessels.
- In order to confirm or exclude the presence of intracranial pressure, a lumbar puncture is prescribed.
- Blood and urine tests are also indicated.
After the doctor makes a diagnosis, he will prescribe treatment for the patient. After completing a course of drug therapy, headaches should completely disappear.