Why do I see double?
In medicine, the symptom of double vision is called diplopia. It is characterized by incorrect perception of an object, in which a person sees two images at once instead of one. The picture can be duplicated both horizontally and vertically. In the first case, the images are side by side, and in the second, they appear one above the other. Normally, a healthy person perceives the world around him using binocular vision.
From each eye, certain signals are sent to the brain, which are then superimposed on each other, which allows you to perceive a complete stereoscopic image. With diplopia, the brain receives an incorrect signal, so it cannot correctly compare information. As a result, a person observes two images at once instead of one. The symptom is often accompanied by dizziness, severe headache, and in some severe cases, attacks of nausea.
In addition, a person often experiences difficulties when moving, since it is difficult for him to navigate in space due to incorrect assessment of distances to objects. Some people confuse diplopia with blurred vision. However, in the second case, we are talking more about blurring the contours of objects and the appearance of shadows. Fogging does not cause two overlapping images.
Double vision may appear periodically, for example, with visual fatigue, a sharp turn of the head or direction of gaze at a certain angle. In some cases it is observed systematically. Sometimes a symptom occurs one-time, for example, during alcohol intoxication or taking certain medications.
If a person notices that he has double vision for a long period of time, he should seek help from a doctor.
In order to get rid of this unpleasant symptom, you need to determine the cause of its occurrence. A comprehensive examination will be required, since diplopia can occur due to a variety of factors: pathologies of the visual and central nervous system, as well as various diseases.
Symptoms of double vision:
- A person sees two duplicate images of one object (not to be confused with blurriness and unclear perception of contours);
- Images appear double vertically or horizontally;
- There is dizziness and headache;
- With severe double vision, attacks of nausea are possible.
What is double vision?
Diplopia or double vision is a phenomenon of subjective sensation manifested by the doubling of objects that a person is looking at. The phenomenon can be a symptom of a disease or a temporary manifestation of a condition. Several objects or one can double, temporarily or permanently, in bright light or more in the dark. These characteristics depend on the cause. Diplopia caused by overstrain and eye fatigue can go away on its own, but often requires further examination and treatment.
Content:
- What is double vision?
- Causes of double vision
- Symptoms of double vision
What are the reasons for dizziness and double vision?
Depending on the symptoms of the disease, it is customary to distinguish between monocular and binocular types of diplopia.
Monocular diplopia
In this case, double vision persists, even if you look with only one eye and close the other. Often this process is associated with damage to the cornea or lens, as a result of which the image is projected twice onto the retina. In addition, it can occur with various inflammatory eye diseases, as well as cataracts, astigmatism and dry keratitis. Monocular double vision is less common than binocular double vision and has characteristic symptoms, so it can be diagnosed quite easily and quickly by specialists.
What eye diseases lead to monocular diplopia?
- Problems associated with the cornea: scarring, infectious diseases (keratitis), keratoconus (thinning and curvature of the cornea), pterygium (pterygium in the area of the inner canthus).
- Cataract. The most common cause of double vision is clouding of the lens. In this case, the symptom is especially pronounced when reading. Lens luxation. This pathology leads to visual distortions and double vision. In this case, surgical treatment is usually required.
- High degree of astigmatism.
- Dry keratitis. Drying of the cornea sometimes leads to monocular double vision. In this case, the use of special moisturizing drops is indicated.
Binocular diplopia
The most common is binocular diplopia, in which a person sees several images of one object only if he looks with both eyes at once. As a rule, if you close one eye, the double vision immediately disappears. Binocular double vision can occur due to various visual pathologies, one of which is strabismus. In this case, the patient experiences a deviation in the visual axis of one of the eyes, caused by weakening of the muscles that are responsible for the correct movement of the eyeball. If the oblique muscles do not work correctly, vertical double vision occurs, and if the rectus muscles work abnormally, horizontal double vision occurs. Many people are interested in what disease can cause binocular diplopia. Let's look at the common causes of this double vision.
Why can you see double?
- Strabismus;
- Diseases of the thyroid gland, which contribute to the weakening of the motor eye muscles;
- Hypertension and other vascular disorders - a sharp change in blood pressure or cerebral circulatory disorders (stroke);
- Diabetes mellitus - can cause damage to the nerves responsible for proper eye movement;
- Myasthenia gravis is weakening and wasting of the eye muscles due to a neuromuscular autoimmune disease;
- Multiple sclerosis is a pathology in the functioning of the central nervous system (CNS), in which the cells of a person’s spinal cord and brain are “attacked” by his immune system.
- An aneurysm is a pathology that occurs when part of an artery (blood vessel) dissects;
- Brain injuries (including concussion);
- Feverish conditions caused by various viral infections;
- Eye surgeries.
The image also doubles in cases of severe intoxication of the body caused by excessive alcohol consumption or nitrate poisoning. In addition, the symptom may occur due to taking certain medications (anticonvulsants, antiepileptics) and visual fatigue. In these situations, diplopia is temporary and goes away on its own over time.
List of reasons
When a person experiences dual vision of objects, it means that one eye does not fixate on the object in sync with the other.
The causes of diplopia are:
- Weakness or paralysis of the muscles involved in eye movement.
- The optic nerve is affected by an aneurysm.
- Head injuries leading to items 1 and 2.
- Tumors and hematomas, due to which the eyeballs cannot move freely.
- Intoxication with drugs or alcohol.
- Mental neuroses.
- Consequences of surgical treatment of the brain or eyes.
The condition of double vision in one eye can be permanent or temporary. In the second case, the symptoms disappear on their own. This usually occurs after abuse of drugs or alcohol.
Why do I see double in contact lenses?
It happens that when putting on contact correction products, you feel dizzy and see double. If such a symptom occurs when you first put it on, it is likely that the problem is related to the incorrect selection of optical products. Before purchasing lenses, you should definitely undergo an examination of the visual system in an ophthalmologist’s office to select diopters, curvature and other optical parameters.
If ghosting occurs when using scheduled replacement lenses after cleaning, the problem may be due to a change in their structure. For example, when left in a solution for a long time (more than 3 days), optical products can be chemically modified and partially change their parameters. In this case, you will have to replace the optics with a new one. Remember that when using scheduled replacement models (two weeks or more), special attention should be paid to the rules of care. If you do not want or for some reason cannot systematically clean your lenses, we recommend choosing one-day lenses, for example, 1-Day Acuvue TruEye or Alcon Dailies Total 1. Models designed for daily replacement are the most practical, simple and safe to use.
If you feel like you are seeing double vision while wearing contact correction devices, make sure that it is actually diplopia and not blurred outlines of objects, lack of contrast, or other symptoms of blurred vision. In any case, you should consult an ophthalmologist.
Treatment
Therapy for monocular double vision is divided into conservative and surgical.
Conservative
Gentle methods are:
- Exercises. Visual gymnastics helps to straighten a squinting eye by training the intraocular muscles, as well as expand the field of vision.
- Prismatic correction using lenses and glasses. Various types of corrective lenses are used depending on the type of disease.
- Treatment of the underlying disease: stroke, myasthenia gravis, multiple sclerosis, etc.
Video: Diplopia. Help with Eastern medicine
Diagnostics
During the examination, such characteristics as the area of distribution (one or both eyes), the direction of the split image (vertical, horizontal, simultaneously in both directions) are revealed. The doctor finds out the features of the course - intermittent (intermittent) or constant nature of the symptoms, the presence of painful sensations, the correlation of pain with the movements carried out by the eyeballs. Diagnostics includes activities:
- Assessment of cranial nerve functionality.
- Assess neuromuscular transmission, identifying muscle weakness that correlates with double vision.
- Assessment of neurological status (reflex reactions, motor activity, maintaining balance, gait, sensitivity).
An ophthalmological examination involves a visual examination to determine visual acuity. During the examination, the doctor pays attention to the symptoms - ptosis (drooping of the eyelid), exophthalmos (protrusion of the eyeballs in the forward direction). Motor activity of the eyeballs is often accompanied by nystagmus. Disorder and uncoordinated movements (multidirectional gaze) of the eyeballs are often observed. Instrumental research methods:
- Ophthalmoscopy (the condition of the retina and lens is revealed).
- Electromyography (assesses the function of nerve impulses in muscle tissue).
- CT, MRI (the morphological and functional state of organs and systems is determined).
An MRI examination often shows damage to the orbit or parts of the brain (stroke, infection, ruptured aneurysm). In Graves' disease, palpation of the neck reveals an increase in the size of the thyroid gland. Pathologies of the thyroid gland are characterized by the appearance of pretibial myxedema - a change in the structure of the skin.
There is erythema (specific redness) in the area of the palms, the skin is moist, which is associated with hyperhidrosis (increased sweating). Typical signs: hyperpigmentation, sagging, swelling of the skin of the eyelids, dystrophic changes in the area of the nail plates. Unfavorable prognostic criteria: involvement of the pupil in the pathological process, cranial nerve dysfunction, neurological symptoms, exophthalmos.
If Graves' disease is suspected, a blood test is taken that shows the concentration of hormones (thyroxine, thyrotropin) produced by the thyroid gland. With an intermittent (intermittent) course, there is a high probability of developing neurodegenerative processes (multiple sclerosis).
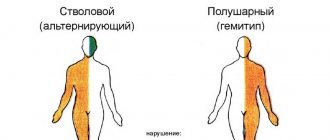
Manifestation of a pathological condition
Signs of the onset of the disease will be shown depending on the location of the lesions
. Thus, with changes in the oblique muscles of the visual organ, the visual organ begins to double in the form of the location of one object above another.
In a situation where the rectus muscles are damaged, the image will be presented in a parallel form. In addition, diplopia manifests itself in several stages of eye disorders perpendicular to the damaged muscles.
As a result, there is a noticeable restriction of eye mobility with the possibility of its complete exclusion. Often, patients bend over and turn the head to relieve this condition.
Signs of diplopia, as a rule, are: double vision, difficulty reading the location of objects, dizziness.
In this case, 2 identical images can have different brightness and contrast
. In addition, double vision is noted horizontally in one picture or vertically, located at a special angle relative to the second image.
Depending on the disease, symptoms characteristic of these factors may appear.
Does prevention help?
Double vision, as a disease, is unpredictable in its development. Therefore, it is not advisable to carry out preventive measures. But you can lead a healthy lifestyle, take care of your health and, of course, your eyes, to greatly reduce the risk of diplopia.
This article briefly talks about diseases that can cause objects or objects to double when viewed. Only a timely visit to an ophthalmological institution can protect you from unnecessary and dangerous consequences.
Don't forget to share the article with your friends on social projects. I recommend subscribing to site updates in order to promptly learn about the release of new useful materials.
A neurological symptom in which the image of objects blurs and seems to split into two is often associated with a state of intoxication, and is the subject of jokes and anecdotes. In fact, a double picture can be a symptom of serious pathologies.
Double vision can be caused by diseases of the eye itself (or both), or it can be a symptom of a general disease of the body. In any case, if you see double, then the person experiences panic, tension, which is accompanied by headache and dizziness. What causes such visual impairment and what can be done about it?
In some cases, this can only be treated with surgery. Conservative treatment and homeopathic remedies are effective when pathological vision is caused by a general disease.
Photo 1: Double vision has a medical name - diplopia. This pathology can be congenital or acquired. Source: flickr (sameer).
Diagnostic procedures
To be sure of the diagnosis or to understand the causes of double vision, the doctor prescribes a number of tests and diagnostic procedures. The main goal is to make an accurate diagnosis. Often the examination will concern the following procedures:
- Conducting an ultrasound of the eyes;
- Cordimetry;
- Visual acuity and field of vision;
- Electromyography;
- Slit lamp examination;
- Conjunctival analysis;
- Visiometry;
- Four-point color text;
- Light refraction analysis;
- Ophthalmoscopy, indirect and direct.
It is important to conduct a comprehensive examination; a cover test is often prescribed. This is an assessment of the current state and analysis of events in the past. The doctor will have to find out whether there have been any injuries, whether the situation is appearing for the first time or constantly, how the patient feels while tilting his head, whether there is double vision when closing one of the eyes, and what other problems exist.
What is visual diplopia?
In a healthy person, visual images from both eyes are transformed equally. The image arrives at the corresponding parts of the retina, from where it enters the visual cortex of the brain in the form of a nerve impulse for analysis. Here information is processed, and at the output we get a complete perception of the world.
If this path is disrupted, the image is projected onto the wrong places (several points on the retina instead of one), then the person experiences double vision and diplopia occurs. It manifests itself as double vision, one object is seen as two, which causes a person a lot of problems.
Additionally, read the article about monocular diplopia (in one eye).