Every third representative of the adult population suffers from hypertension, and by the age of 65, every second person faces this problem. For a healthy person, blood pressure is considered normal from 110/70 to 130/80 mmHg. Art. The diagnosis of hypertension is usually made when the level exceeds 140/90. The symptoms of hypertension are quite varied: dizziness, drowsiness, difficulty breathing, nausea and even loss of consciousness. A sharp increase in pressure is also often associated with headaches, and most often it appears in the back of the head. During periods of sudden pressure surges, the risk of heart attacks and strokes increases. Why pressure surges occur and how to prevent the development of hypertension, AiF.ru told osteopath Vladimir Zhivotov.
Development mechanism
Stroke is a pathological condition that is accompanied by a sudden and severe disruption of blood circulation in any part of the brain. Since neurocytes (cells of the nervous system) are very sensitive to oxygen and energy starvation, when there is a power failure, they die. According to the development mechanism, there are 3 types of stroke:
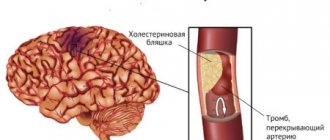
- Ischemic stroke - blood flow sharply decreases due to a decrease in the diameter of one of the arteries of the brain. Over a short period of time, oxygen starvation develops, followed by cell death. In the absence of help, irreversible changes occur. The pathological process occurs against the background of increased pressure, which provokes spasm of the arterial vessels of the brain or damage to the covering of the atherosclerotic plaque (occurs in atherosclerosis) with subsequent formation of a blood clot. If the reading is above 160/100 mm Hg. Art., the risk of violations increases significantly.
- Hemorrhagic stroke - hemorrhage occurs directly into the brain tissue, which leads to the subsequent death of neurocytes. The pathological condition develops over a short period of time, so it is rarely possible to avoid irreversible changes. Hemorrhagic stroke with low pressure develops against the background of a change in condition and a decrease in the strength of the vascular walls.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage - blood enters the space between the arachnoid and pia mater of the brain. This leads to a volumetric process, as a result of which the tissues experience mechanical compression, leading to local disruption of blood circulation and nutrition with subsequent death of neurocytes. The pathological process develops over a relatively long period of time, which should usually be enough to provide qualified assistance and prevent irreversible changes.
The division into species depending on the mechanism of development has an important justification. Depending on the pressure at which a stroke occurs, treatment approaches are fundamentally different. Regardless of the origin of the pathological condition, the risk of developing a vascular accident in the brain increases significantly against the background of arterial hypertension (high blood pressure).
Statistics
Unfortunately, the statistics are not reassuring. All over the world, stroke is the second leading cause of mortality; in Russia, every year 450,000 thousand people suffer this terrible disease and 39% have a fatal outcome, 13-16% of patients recover, and the rest are fighting for life, trying to avoid repeated strokes and recover. musculoskeletal activity, speech, memory and psychological state. The age of the patients is different, older people are more susceptible to stroke, but young people should not relax, a stroke can strike anyone. Symptoms of heart attack and stroke are described on this website.
It is a fact that 80% of strokes and heart attacks are preventable. You just need to eat right, maintain regular physical activity and refrain from smoking. It is necessary to monitor cholesterol and diabetes levels, and periodically check for cardiovascular diseases, especially if the patient is at risk.
When should you reduce?
Blood pressure is the force with which blood presses on the walls of the arteries, stretching them. This is a very important hemodynamic indicator, on which the speed and volume of blood flow in peripheral tissues depends. What pressure can be caused by a stroke is determined by several factors:
- heart rate and amplitude;
- total volume of the vascular bed;
- volume of circulating blood.
An increase in blood pressure can occur due to increased heart rate, spasm of arterial vessels (decreased vascular volume) or an increase in the volume of circulating blood (fluid retention in the body). The normal pressure level is different for each person, but it should not exceed 140/90 mmHg. Art. Arterial hypertension increases the risk of developing a cardiovascular accident, which includes cerebral stroke and myocardial infarction. If the reading is more than 180/100 mmHg. Art. the likelihood of ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke increases several times.
How to stabilize?
Rehabilitation time is divided into three periods.
- The first one lasts from six months after the attack. It is considered the most favorable time to restore the patient. Rehabilitation measures cannot be postponed under any circumstances. It is at this time that the body is most susceptible to recovery.
- The second is from six months to twelve. If you start rehabilitation during this period, the chances of recovery are reduced, but only slightly.
- The third - a year after the attack. Recovery occurs rather slowly and full results are not always achieved.
Causes
Brain stroke is a polyetiological pathological condition. This means that its development is provoked by several reasons, which include:
- Atherosclerosis is the main cause of cardiovascular disease. The pathological condition is characterized by the deposition of cholesterol in the walls of arterial vessels with the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. They reduce the lumen of the artery, due to which blood flow in the tissues worsens. Against the background of increased pressure, damage to the covering of the atherosclerotic plaque often occurs, which provokes the intravascular formation of blood clots with subsequent blockage of blood vessels.
- Hypertension - a prolonged increase in the level of systemic blood pressure causes a number of changes in the vessels of the brain, leading to a deterioration in blood flow in the tissues. Also, the pathological condition provokes the rupture of atherosclerotic plaques with the formation of blood clots. High blood pressure during stroke in women is often recorded during the postmenopausal period, which is associated with hormonal changes in the body.
- An increased tendency of blood to clot is a factor leading to spontaneous intravascular formation of blood clots (thrombosis). Clots with blood flow move in the vascular bed and clog the arteries, followed by a sharp cessation of blood flow in them.
- Thrombophlebitis is an inflammatory process in the venous vessels with a predominant localization in the lower extremities, which is accompanied by the spontaneous formation of blood clots.
- Malformation of arterial vessels is a congenital pathology, which is characterized by the formation of a “tangle” of arteries of various sizes in one place. At the same time, most of the vessels have low wall strength, which leads to their damage and the development of hemorrhage. The likelihood of this outcome is higher with high blood pressure.
- Congenital disorders in the walls of arterial vessels, which are accompanied by a decrease in the strength of their walls, are one of the factors in the development of hemorrhagic stroke in adults, less often in children.
Knowledge of the reasons for the increase in systemic blood pressure and the development of cerebral stroke is necessary for choosing measures aimed at preventing the pathological condition.
Female sex hormones estrogens protect arterial vessels from the appearance of atherosclerotic plaques. All problems with the heart, blood vessels, and an increased likelihood of developing a cerebral stroke in women occur during the decline of reproductive function with a decrease in the level of estrogen in the blood.
Is high and low blood pressure dangerous?
On the first day after the onset of a stroke, high blood pressure can be regarded as a compensatory reaction, much worse if it remains elevated by the end of the first week. This is regarded as a sign of an unfavorable outcome, permanent disability, and severe neurological disorders.
This is due to the fact that during this period the most dangerous complication is cerebral edema with subsequent wedging of the stem part into the foramen magnum. This displacement leads to critical respiratory failure and the development of acute heart failure with cardiac arrest. Even in the absence of death of the patient, high hypertension provokes:
- acute encephalopathy;
- recurrent stroke;
- spread of the ischemic focus;
- intracranial hemorrhages (especially during thrombolytic therapy).
The absence of an increase in blood pressure or even a decrease in it in the acute stage of the disease should alert the doctor. Arterial hypotension with a sharp disturbance of cerebral circulation must have a reason:
- major stroke;
- brain stem damage;
- cardiogenic shock accompanying myocardial infarction;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- blockage of the pulmonary artery (thromboembolism);
- severe dehydration (vomiting, diarrhea, diabetic coma, diuretic overdose), bleeding;
- reaction to infection entering the blood (sepsis), intoxication;
- dissecting aortic aneurysm;
If the cause of vascular insufficiency has not been established, and the diagnosis of stroke is considered confirmed, then solutions (Infezol, Reopoliglyukin) are administered to improve hemodynamic parameters, and sometimes an injection of Dopamine is required .
Blood pressure after stroke
Pressure after a cerebral stroke has a great influence on subsequent tissue regeneration, the effectiveness of treatment, and the duration of the early and late recovery period. In the first minutes of providing qualified assistance, a medical professional measures hemodynamic parameters, which makes it possible to make a forecast regarding the further normalization of brain functions, as well as select adequate treatment. Therapeutic measures depend on the results of measuring blood pressure and pulse:
- The indicator is above 180/100 mmHg. Art. – measures aimed at lowering the level of systemic blood pressure are required, since there remains a very high risk of ongoing disruption of blood flow involving a large volume of tissue.
- The indicator varies between 140/90-160/100 mm Hg. Art. – correction of blood pressure cannot be carried out, since if the indicator decreases excessively, blood perfusion in the brain tissues sharply decreases, which leads to the progression of ischemic stroke even after a hemorrhage in the tissue.
- The indicator is less than 110/70 mmHg. Art. – depending on the general condition of a person who has suffered a cerebral stroke, measures aimed at increasing the level of systemic blood pressure may be required. This will make it possible to improve blood perfusion in brain tissue and their nutrition.
When providing assistance, pay attention to the heart rate. Typically, there is an increase in heart rate during a stroke, while the amplitude of heart contractions decreases, as a result of which blood flow in peripheral tissues worsens.
Signs
It is easy to suspect a cerebral stroke based on the following clinical manifestations of a cardiovascular accident:
- Pointed, intense headache in the area of development of the pathological process is a symptom that usually occurs with the development of a hemorrhagic stroke.
- Impaired consciousness of varying severity - depending on the degree of brain damage, a stunned state or a complete lack of consciousness is possible (a person may suddenly fall), even to coma.
- Severe nausea, which is accompanied by periodic vomiting that does not bring relief.
- Change in skin color - in most cases, the facial area acquires a bluish tint (cyanosis); pallor is less common.
- Development of tonic-clonic convulsions of striated skeletal muscles of varying severity. A person may fall unexpectedly (the fall is accompanied by involuntary muscle contraction).
- Focal neurological symptoms - depending on the location of a sharp circulatory disorder in the brain tissue, there is a deviation (deviation to the side) of the tongue, a decrease or complete loss of all types of skin sensitivity in certain areas of the body, weakness in the muscles or a complete inability to move them, speech impairment, facial asymmetry, different pupil diameters. Focal symptoms usually appear on one side of the body. With a volumetric stroke of the brain, impaired muscle movements (paresis or paralysis) can be detected in both arms and legs.
The appearance of several signs of the development of a cerebral stroke requires immediate assistance with the initiation of adequate therapeutic measures.
Preventing a re-strike
To avoid a second attack, you need to adjust your lifestyle. To do this, you need to follow the following instructions:
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- monitor body weight (reduce it if you are obese);
- do not overstrain the body, and especially do not strain it sharply - all loads should be gradual;
- avoid nervous tension, if necessary, take sedatives containing only natural ingredients;
- normalize your diet (meat and fish should not be fatty, eat more vegetables and fruits, eliminate salt and sugar, steam foods, you can also bake or boil them);
- stop taking hormonal contraceptives;
- start taking anesthetics, anti-inflammatory, hypnotics and diuretics only after consulting with your doctor.
Stroke, both ischemic and hemorrhagic, has serious negative consequences. These include the following: paralysis, slurred speech, memory loss, persistent anxiety and death. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly carry out preventive measures that will help protect you from pathological attacks.
source
Symptoms of changes in pressure levels
To provide assistance, it is important to understand what blood pressure accompanies the development of the pathological process. If it is not possible to directly measure hemodynamic parameters (there is no tonometer), then you need to pay attention to the clinical signs of arterial hypertension or hypotension:
- High blood pressure is accompanied by a headache with a predominant localization in the back of the head, less often the crown. Visual acuity often decreases, “spots” appear before the eyes, general weakness, and unpleasant sensations in the heart area are troubling. Over time, signs of high blood pressure increase, and then stroke symptoms appear.
- Stroke with low blood pressure - the pathological process is often accompanied by dizziness, the head may hurt in the forehead, temples, and the pain is pulsating in nature. Against the background of dizziness, tinnitus appears, which increases as blood flow in the brain tissue deteriorates. In such cases, the pressure needs to be increased.
- Stroke with normal blood pressure often occurs in young people. The cause is almost always a decrease in the strength of the walls of arterial vessels. Against the background of normal health, the clinical picture of a hemorrhagic stroke suddenly appears, and the person loses consciousness.
Low blood pressure after a stroke is considered an unfavorable prognostic criterion, in which deterioration of blood circulation in the brain despite therapeutic measures may have a progressive course. It is usually recorded when there is a repeated circulatory disorder.
Diagnosis and treatment
To determine the level of systemic blood pressure, a digital or dial tonometer is used. If there is no device, then pay attention to clinical symptoms and focus on assessing the frequency and strength of heart contractions. Hemodynamic correction is carried out depending on the severity of changes:
- For high blood pressure in men and women, parenteral forms of antihypertensive drugs are prescribed, which can reduce the level within 10-15 minutes. For this purpose, magnesium, papaverine with dibazole, and diuretics (furosemide) are administered. If it is not possible to give an injection, then you need to take tablets or drops orally (Captopress, Farmadipin).
- With low blood pressure, the patient is prescribed injection drugs that increase arterial tone and heart rate (cordiamin, dexamethasone).
If, due to low pressure, it is not possible to administer drugs, then the patient is placed on his back with his legs elevated (a bolster can be used). This will increase blood flow to the brain tissue.
The pressure indicator during cerebral stroke has an important influence on the choice of therapeutic measures. The indicator must be measured using a tonometer. If there is no device, then hemodynamics are roughly assessed based on clinical signs, including complaints that preceded the development of a stroke.
Prevention
Scientists have found that more than 80% of strokes could be prevented by taking preventive measures. Proper stroke prevention should consist of the following points:
- Regularly check and maintain pressure. High blood pressure can cause premature stroke.
- Maintaining blood sugar levels. With diabetes, it is almost impossible to control blood pressure.
- Controlling cholesterol levels.
- Switch to proper nutrition. You need to add vegetables and fruits, legumes, lean meat and fish to your diet. It is also important to give up salty, sweet and fatty foods.
- Doing physical exercise. Exercising for 30 minutes daily will reduce the risk of heart disease and obesity, and, accordingly, stroke.
- Rejection of bad habits. Just one year after quitting smoking and drinking alcohol, the risk of stroke is reduced by half.
If you have hypertension, it is important to strictly follow your doctor's recommendations and not skip medications. Even if the pressure has returned to normal, treatment cannot be stopped.
To prevent stroke, you need to spend more time in the fresh air and avoid stress and nervous breakdowns. It is also necessary to undergo periodic examination by a doctor. All the previously proposed measures will help eliminate the risk of stroke.
source