Features of pathology in a child
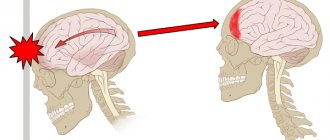
Paralysis is the complete loss of muscle strength in a muscle or group of muscles.
This condition is not an independent disease, but is considered only a consequence of any disease, that is, its symptom. It occurs in males and females of all ages.
The following classification of paralysis is distinguished, based on the prevalence of the process:
- monoplegia – paralysis of one limb on one side of the body occurs;
- paraplegia - paralysis of two limbs of the same type, for example, both arms;
- hemiplegia – paralysis develops in the limbs on one side;
- tetraplegia - four limbs are simultaneously affected.
Depending on the origin of paralysis, the following forms are distinguished:
- central (spastic) paralysis – characterized by increased tone in paralyzed muscles;
- peripheral (flaccid) – characterized by a decrease in tone in the affected muscles, as well as the development of their hypotrophies and atrophies.
The causes of paralysis are varied. We offer to your attention the following:
- ACVA (acute cerebrovascular accident);
- tumors of the brain and spinal cord;
- brain and spinal cord injuries;
- infectious diseases of the nervous system, for example, tick-borne encephalitis;
- demyelinating diseases - are associated with the destruction of the protein that ensures the conduction of nerve impulses through fibers - myelin. Such diseases include: multiple sclerosis, multiple encephalomyelitis and others;
- immunoinflammatory diseases, in particular Guillain-Barré syndrome;
- myopathies – diseases based on congenital or acquired metabolic disorders in muscle tissue;
- myasthenia gravis – a disease characterized by pathological muscle fatigue;
- poisoning, in particular with alcohol, industrial poisons, salts of heavy metals, nerve poisons.
The prognosis largely depends on the factor that caused the development of paralysis. In most cases, it is possible to achieve complete or partial restoration of muscle strength. However, in some cases, muscle paralysis cannot be corrected. It is also important to remember about possible complications, in particular the formation of contracture and ankylosis of the joints.
Motor neurons are located in peripheral nerves. These cells are equipped with long processes (axons) that transmit signals from the nervous system to the muscles. Thanks to these structures, a person has the ability to make movements.
In acute flaccid paralysis, motor neurons and axons are affected and gradually destroyed. The flow of signals from the nervous system to the muscles stops. As a result, the person cannot move the affected part of the body. Over time, muscle atrophy occurs, tendon reflexes are lost, and muscle tone deteriorates. Weakness of the limbs increases and progresses.
If the motor function of the affected area is completely lost, then doctors call this pathology paralysis. If movements are weakened and difficult, then experts talk about muscle paresis.
The following pathological conditions do not include flaccid paralysis and paresis:
- movement disorders after injuries and injuries (including birth injuries);
- paresis and paralysis of the facial muscles.
It is also very important to differentiate this pathology from paralysis resulting from damage to the central nervous system.
Flaccid paralysis is more common in children than in adults. A child is much more susceptible to infection with enteroviruses. Polio is quite rare these days. The main danger to a child is represented by other types of enteroviruses that affect peripheral nerves.
Manifestations of flaccid paralysis in children are the same as in adults. However, the child more often experiences damage to the neurons responsible for the functioning of the respiratory and swallowing muscles. Sick children breathe quickly and shallowly, which leads to hypoxia. As a result, frequent headaches, lethargy, and difficulty falling asleep occur. The child finds it difficult to swallow and often chokes on food. Children often lose weight due to lack of nutrition.
Diagnostics
In order to begin effective treatment of leg paralysis and return motor activity to the limbs as soon as possible, you will need to consult not only a therapist, but also a neurologist. First, specialists will collect anamnesis to identify concomitant diseases, injuries to the skull and spine, and the presence of psychotraumatic situations in the patient’s life.
After this, the following examinations may be prescribed:
- Clinical tests of blood and urine. This is a standard test that must always be taken, regardless of the nature of the disease.
- A CT scan of the brain and skull will reveal any changes in the condition of the tissues that may be caused by tumors or other diseases.
- MRI of the brain and spinal cord is used in cases where CT results are insufficient. This method also allows you to evaluate changes that have occurred in tissues.
- X-rays are done only when necessary and help to recognize previous injuries, as well as determine changes in tissues.
- Neurosonography is prescribed to determine the functioning of not only the brain, but also other systems located in the skull.
- Leg reflexes must be checked. This study is carried out by a neurologist.
- If the patient has injuries to the spine or skull, a consultation with a neurosurgeon will be required.
- In some cases, consultation with a psychotherapist may be necessary. This is especially true when paralysis of the legs occurs after experiences and severe stress.
The above studies will help identify the cause of leg paralysis. The patient will be prescribed a treatment regimen, which may include not only drug therapy, but also special exercises. In some cases, surgery may be required on the damaged nerve.
Forms of limb paresis
5 gradations of paresis, based on muscle strength, which was identified during a neurological examination:
- 5 points - muscle strength is completely preserved (no paresis);
- 4 points - muscle strength is slightly reduced when compared with previously existing strength;
- 3 points - muscle strength is significantly reduced when compared with previously existing strength;
- 2 points - the muscle contracts in the absence of the ability to resist gravity (for example, a person bends his arm at the elbow lying on the table, but cannot do this if the arm is hanging down);
- 1 point - individual muscle bundles of the muscle contract unproductively (the entire muscle does not contract);
- 0 points - no muscle strength (presence of plegia, which is an extreme degree of muscle weakness. This condition does not belong to the concept of “paresis”).
Paresis of the limbs, depending on the origin, can be:
- central (spastic), associated with the occurrence of disturbances in the pyramidal tract (which ensures the conduction of motor impulses) in the area running from the cerebral cortex to the motor neurons (nerve cells through which muscle movement is ensured). These disorders are combined with an increase in tone that occurs in paretic muscles;
- peripheral (sluggish), associated with the fact that the nuclei of the cranial nerves or motor motor neurons and the nerves that go from them to the muscles are affected. This condition is combined with a decrease in tone that develops in paretic muscles and their thinning (atrophy).
Forms of limb paresis:
- monoparesis - when muscle strength is reduced in one limb;
- hemiparesis - when muscle strength is reduced in the limbs on one side;
- paraparesis - when muscle strength is reduced in the arms or legs;
- tetraparesis - when muscle strength is reduced in all limbs.
Etiology
Peripheral flaccid paralysis is not an independent disease. Most often it occurs as a complication of infectious pathologies caused by enteroviruses. In most cases, this type of movement disorder develops after polio.
In the past, this dangerous viral disease was widespread. It often led to death and disability of the patient. Nowadays, thanks to mass vaccination, only isolated cases of pathology are observed. However, the risk of infection cannot be completely excluded. An unvaccinated person has a high risk of infection.
The polio virus is transmitted in several ways: airborne droplets, contact, and through utensils. In addition, the microorganism can live in the environment for several days. Children under 15 years of age are especially susceptible to infection.
The virus enters motor neurons and causes dystrophic changes in them. The nerve cell dies and is replaced by glial tissue. Subsequently, a scar forms in its place. The more motor neurons that die in polio, the faster acute flaccid paralysis develops.
Poliomyelitis is the most common, but not the only cause of this pathology. Flaccid paralysis can also develop as a result of other diseases:
- Inflammatory process in the spinal cord (myelitis). In half of the cases, this disease is caused by an infection. Its causative agents can be enteroviruses, mycoplasmas, cytomegaloviruses, as well as the causative agent of herpes. Sometimes inflammation occurs after an injury. But even in this case, the cause of the pathology is microorganisms that have penetrated the spinal cord through the wound. With myelitis, the supply of impulses from the central nervous system to the peripheral nerves is disrupted, which becomes the cause of paralysis.
- Poly- and mononeuropathies. These diseases are also caused by various viruses. With polyneuropathy, a large number of peripheral nerves are simultaneously affected. Mononeuropathy is characterized by pathological changes in neurons in a separate area, most often in one of the upper limbs.
- Guillain-Barre syndrome. The disease occurs as an autoimmune complication after viral pathologies: mononucleosis, mycoplasmosis, cytomegaly, infection with Haemophilus influenzae. The infectious process leads to disruptions in the functioning of the immune system. Protective antibodies begin to attack peripheral nerve cells, which leads to flaccid paralysis.
- Coxsackie virus infection. In most cases, this microorganism causes a disease that occurs with fever, rash and inflammation of the oropharynx. However, there is another strain of the virus that causes inflammation of the skeletal muscles. The consequence of this pathology can be acute flaccid paralysis in children. Adults are infected much less frequently.
Currently, a new type of enterovirus has emerged (type 70 strain). Most often it causes a severe form of conjunctivitis. But there are also atypical forms of the disease, which are similar in symptoms to polio. This pathology can also cause damage to peripheral nerves.
Causes of limb paresis
The causes of limb paresis include the development of an acute disorder of cerebral or spinal circulation (stroke), including hemorrhage in the brain or spinal cord.
Paresis occurs due to disruption of the central or peripheral nervous system. In the first case, paresis is called central and is more often unilateral, that is, either the right or left foot is affected. The causes of central paresis may be:
- Stroke.
- Encephalitis.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Tumors of the brain or spinal cord.
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
- Spinal cord or brain injuries.
- Intervertebral hernia.
Peripheral paresis occurs due to disruption of the peripheral nerves - tibial or peroneal, which is most often the result of:
- Diabetes mellitus
- Alcoholism.
- Injuries.
Difference from central paralysis
It is necessary to distinguish between flaccid and spastic paralysis. These two pathological conditions are accompanied by impaired motor function. However, they differ in etiology, pathogenesis and symptoms:
- The spastic form of the pathology occurs due to damage to the central nervous system. Acute flaccid paralysis is characterized by damage to the peripheral nerves or roots of the spinal cord.
- In spastic paralysis there is no damage to motor neurons.
- In the peripheral form of paralysis, there are no flexion and extension reflexes, and muscle weakness is noted. With a pathology of central origin, the muscles are tense, involuntary muscle contractions are noted, and reflex movements are preserved.
- Central paralysis can impair movement throughout the body. In the peripheral form, there is a deterioration in motor function in a certain area.
Only a neurologist can differentiate these two forms of paralysis on the basis of a comprehensive examination.
Symptoms
Paralysis can be caused by various reasons, which is why its symptoms can have a different nature and various localizations. The most common changes occurring in the major structural component of the nervous system during paralysis may include:
- degeneration (nerve tissue dies and new ones do not form);
- destruction (in this case the conduction of nerve impulses is disrupted);
- neuroinflammation;
- vascular obstruction, plaque formation, risk of thrombosis;
- development of sclerosis;
- the appearance of demyelination - a pathological process of destruction of the myelin sheath of the nervous system.
With this disease, there are other symptoms: headaches, migraines, fever, lump in the throat, partial loss of vision, nausea and vomiting, increased fatigue, muscle pain or weakness, involuntary urination, inability to control bowel movements.
If we consider paralysis from an anatomical point of view, we can divide them into two forms: the first are caused by destruction of the central nervous system (cerebral and spinal), the second - by peripheral nerves.
Symptoms of central paralysis
The symptoms of central paralysis are very diverse: some signs are immediately detected in their pure form, others are confusing due to their combination with some signs of peripheral paralysis. But both are accompanied by sensory changes and atrophy, and pathologies of vascular tone.
During the genesis of an illness of this type, the entire body is exposed to suffering, and not individual parts of the musculoskeletal system, for example, muscles.
Absolute tendon reflexes are preserved and may even intensify, and accelerated spasms of the muscles of the paralyzed limbs are noted. Abdominal reflexes are the opposite: they are reduced or disappear on the paralyzed side.
Symptoms
Symptoms of limb paresis may include the appearance of weakness in any muscle or muscle group and associated phenomena:
- change in gait if weakness develops in the muscles of the pelvic girdle. A person shifts from one foot to another, the gait resembles a “duck”;
- foot drop when lifting the leg in case of weakness of the extensor muscles of the foot. With each step, a person tries to raise his foot higher so that it does not touch the ground. A “chasing” or “cock-like” gait develops;
- hanging head forward if weakness develops in the back muscles of the neck;
- the appearance of weakness in the arm muscles, when a person has difficulty raising his arms, holding objects in his hands, or holding his arms suspended;
- the appearance of weakness in the leg muscles and the associated inability to walk. A person has difficulty getting up from a sitting position.
Impaired motor function most often appears suddenly and increases rapidly. The following symptoms of flaccid paralysis can be distinguished:
- impossibility or difficulty of movements;
- severe muscle weakness in the affected area;
- lack of response of paralyzed muscles to mechanical stress;
- asymmetrical lesion;
- muscle atrophy (a paralyzed leg or arm becomes thinner than a healthy one).
If paralysis develops against the background of polio, then the patient’s general signs of infectious pathology disappear. Usually, shortly before the onset of movement disorders, the temperature drops, muscle pain and spasms subside.
A fairly common form of pathology is lower flaccid paralysis. It is characterized by damage to the spinal cord roots. As a result, the patient experiences paralysis of one of the lower limbs. Most often, the innervation of the muscles of the feet is disrupted. A person cannot move his feet and it becomes very difficult for him to walk.
Depending on the severity of nerve damage, signs of paresis may be expressed to varying degrees. And it also matters which nerve damage led to the paresis. If the tibial nerve is damaged, the work of the toe flexors and plantar flexion of the foot are disrupted, and it becomes impossible to bring the foot inward. The patient cannot stand on his toes, and the fingers take a “claw-like” position.
Pathologies of the peroneal nerve are primarily manifested by foot drop and the inability to walk on heels.
An intervertebral hernia can lead to compression of the radicular artery and disruption of the nutrition of the corresponding nerve root. If these are the roots of the lumbar region, then so-called paralyzing sciatica may occur: sharp pain in the lower leg, and then weakness of the extensors of the foot. The most noticeable sign of foot paresis is the “cock gait” (steppage).
The patient raises his legs (or leg) unnaturally high, bending them at the knee joint so as not to touch the ground with his drooping foot. Due to paresis of the extensors of the foot and impaired sensitivity, the patient does not feel how he places his foot on the surface. This often causes the feet to roll inward or outward, dramatically increasing the risk of injury.
Symptoms and causes
Nerve damage and subsequent paralysis of the legs have the following symptoms:
- The first suspicion of the onset of the disease is loss of sensation in the limbs. When touched or changes in temperature, the patient does not feel anything. At the same time, the mobility of some muscles begins to deteriorate.
- The next stage is characterized by the fact that the paralyzed limbs do not react in any way to pain.
- After this, the blood supply to the muscles is disrupted, and symptoms of trophism appear in the affected limbs. All this leads to slow vascular atrophy, which ultimately negatively affects the entire cardiovascular system.
- If the lesion has affected a significant number of nerve centers, then the patient loses control when performing acts of defecation and urination.
- When paralysis of the legs is temporary, the victim may feel either slight weakness in the muscles or completely lose the ability to move independently.
Paralysis of only one limb may occur. As a rule, this condition is typical for patients who have had a stroke.
Another consequence of a stroke is complete immobilization of one side of the body, including not only the arms and legs, but also the face.
In addition to the manifestations described above, symptoms of paralysis of the lower extremities may vary depending on the underlying cause that provoked them:
- Spastic paralysis. Occurs when the central motor neuron is damaged. In this case, the muscles are in hypertonicity, and new reflexes arise in the tendons.
- Flaccid paralysis of the legs. In this case, the victim’s muscles are too relaxed. This lesion is deeper than spastic and most often occurs when the spinal cord in the lumbar spine is affected.
The following unfavorable factors and diseases can lead to the occurrence of pathology:
- Injuries of the spine, brain and spinal cord received mechanically, as well as their fractures of varying degrees of severity.
- Poor circulation in both the brain and spinal cord.
- If there are disturbances in the functioning of the body's metabolic processes. This often occurs in muscle fibers.
- Diseases that negatively affect the conductivity of nerve fibers. Typically this is Alzheimer's disease.
- Inflammatory processes of a purulent nature that occur in the brain and spinal cord after injuries and injuries, as well as unqualified medical care.
- Damage to the nervous system due to severe diseases. The most striking example is botulism, which occurs after eating poorly sterilized canned food.
- Diseases that affect motor neurons. This may be multiple and atrophic sclerosis, muscle fiber atrophy.
- Epileptic seizures and strokes of varying severity.
- Inflammatory diseases that specifically affect the brain. As a rule, this is encephalitis or meningitis.
- If the patient has tumors of any nature in both the brain and spinal cord.
- Past psychological trauma and severe stress, which can also cause temporary paralysis of the legs.
The reasons described above and their abundance may cause some difficulties in diagnosis and require extensive research. When the cause is established, neurologists develop a treatment regimen that is strictly individual in each specific case.
Treatment of foot paresis
In the case of a traumatic lesion of a peripheral nerve, it is sutured, in case of a stroke, restorative therapy is carried out, and if a tumor is detected that is compressing the nerve structures, surgical intervention is performed. Along with etiotropic treatment, symptomatic therapy should also be carried out, because
In case of cerebrovascular accident, it is necessary to normalize blood pressure and prescribe medications that improve cerebral blood flow and metabolism (nootropics, angioprotectors).
For infectious lesions of the brain or spinal cord, antibiotic therapy is prescribed.
When diagnosing botulism, anti-botulinum serum is administered.
If myasthenia gravis is detected, medications that improve neuromuscular conduction are prescribed.
If the cause of limb paresis is poisoning, then it must be treated by administering solutions and vitamins B, C, A.
Since paresis is not an independent disease, it can be cured only by establishing the exact cause. If the cause is diabetes, then first of all it will be necessary to correct this disease. In case of nerve injury, surgical intervention is indicated, as well as in case of tumors or intervertebral hernias.
In some cases, for example, with the progression of neurological diseases, it will not be possible to completely get rid of paralysis. In general, to treat foot paresis, the following methods are used:
- Use of medications.
- Therapeutic exercise and massage.
- Wearing orthopedic aids.
- Physiotherapeutic methods.
Horse's foot in a child
Drug therapy:
- Muscle relaxants. These substances are used for spastic paresis, when an increase in the tone of the foot muscles is accompanied by a decrease in strength. Lioresal, Sirdalud, Dantrolene are used.
- Vasodilators. These medications improve blood flow in the area of the affected nerve and accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissue. Nicotinic acid and Theophylline are prescribed.
- Nootropics. These are drugs that improve the nutrition of the brain and nerve tissues (Piracetam, Phenotropil, Nootropil).
- Complex preparations containing B vitamins.
Exercise therapy (physical therapy) is an important and integral part of restoring normal foot function. Muscle strength is assessed using a 5-point system. At the same time, 5 points means strength is preserved, there are no violations, and 0 points means lack of muscle strength, paralysis (Lovetto scale).
Before the patient begins training, the doctor determines the strength of the foot muscles
Correctly and regularly performed exercises not only help restore mobility and sensitivity, but also help avoid muscle atrophy and foot deformation, and also improve metabolic processes in tissues and strengthen ligaments and tendons.
Gymnastics may include the following groups of exercises:
- Exercises based on balance reflexes. From a standing position, the patient leans or even falls backward. The instructor stands behind and protects against a complete fall. While kneeling, the patient leans back, maintaining balance and not touching his buttocks with his heels.
- Exercises to promote passive dorsiflexion of the feet. They are performed using an exercise bike, and the feet can be fixed to the pedals with a special strap.
- The patient walks on skis with weights attached to them at a distance of approximately 15–20 cm. This promotes dorsiflexion of the foot due to gravity. The technique of the exercise is important: the patient should “walk” on skis, and not ride on them.
- Walking in special shoes without heels. Or you can use orthopedic shoes, where the sole is made in such a way that the toe is higher than the heel.
- Alternate walking on heels and toes.
- Jump alternately on both legs.
It is strictly forbidden to perform the complex without the supervision of an instructor, as there is a high risk of falling and injury.
A foot massage gives good results, and it is performed simultaneously on both feet by two massage therapists. After the operation, a set of exercises is compiled in accordance with the stages of rehabilitation (postoperative period, early recovery, late recovery) and depends on the volume of surgical intervention and the general condition of the patient.
Special structures (orthoses) help keep the leg in the correct physiological position. Orthoses for the treatment of foot paresis can be different:
- In the form of two cuffs. One cuff is attached to the arch of the foot and has a hook. The second cuff is attached in the ankle joint area and has an elastic band that is put on a hook. This design can be used under any flat-soled shoes.
- Carbon holder, which is a special design consisting of an insole, a back bar and a shin clamp.
- A hard plastic bar that is located along the shin. This strip is attached to the sole using elastic bands.
The type of orthosis is selected for each patient individually. This benefit helps a person lead a more fulfilling lifestyle, as it makes walking noticeably easier. In addition, serious complications are prevented - neuritis and arthritis, which often occur with atrophy of the foot muscles.
Orthosis for drop foot
Treatment Options
The following point should be immediately mentioned: if paralysis of the legs is caused by severe stress or prolonged experiences, then the treatment of such a patient is carried out exclusively by a psychotherapist. In this case, not only psychotherapy itself may be required, but also the use of sedatives, and in more complex cases, antidepressants and tranquilizers. All these measures help relieve tension after the experiences, and the patient will gradually return to physical activity.
In other cases, when leg paralysis is caused by diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system, therapy may include the following components:
- Drug treatment. As a rule, patients are prescribed drugs that improve the conduction of nerve impulses, as well as reduce muscle tone when it is excessively increased. It is important to remember that in this case you cannot self-medicate: the drugs used to treat leg paralysis have a large number of side effects, and an incorrectly selected dosage will only worsen the patient’s condition.
- Folk remedies. They are not able to radically affect the condition of muscles and nerves. However, decoctions and tinctures from medicinal plants can support the body's defenses and give it strength. This treatment is recommended as an additional treatment; it cannot be the main one.
- Physiotherapy . It is prescribed even for particularly severe damage to nerve endings. Specially selected exercises will help keep the body in good shape and contribute to the normal functioning of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. For milder versions of leg paralysis, such exercises will help keep the limbs in the correct position, preventing them from bending.
- Special massage. Designed to relax overstrained muscles and improve tissue nutrition. It has proven itself well both in treatment and during rehabilitation activities. Even if only one limb is affected, the procedure is performed on both to prevent a significant change in tone in them. In addition to professional massage, the patient’s relatives are taught light options for this effect, so that the patient can also receive massage at home.
- Surgical intervention. The need for it appears if the cause of paralysis of the legs is tumors, crushing, compression or rupture of a nerve. In this case, the neurosurgeon eliminates the root cause that led to the appearance of paresis. Such interventions can also be resorted to in cases where conservative treatment has proven ineffective.
- Psychological help. The new state in which a person finds himself can cause suffering and develop into neuroses and depression. The right psychological attitude and support will give the patient an incentive to continue treatment, not to mope, which will ultimately have a positive effect on his well-being and help restore normal mobility of the limbs as soon as possible.
In addition to the therapeutic measures described above, a patient with paralysis of the legs requires careful care, and often bed rest. Due to immobility, a person cannot take care of himself as before, this leads to deterioration in hygiene, and as a result, can cause the development of bacterial infections. In addition, a bedridden patient must be regularly turned over, bed and underwear changed, and washed. All this is one of the stages of treatment and helps to avoid deterioration of the patient’s condition and prevents the appearance of bedsores.
Therapy must be comprehensive, and the patient’s relatives are obliged to ensure that all its components are fulfilled. If this is not done, the patient’s condition will remain unchanged; in some cases, a relapse for the worse is possible.
It is quite difficult to give a prognosis for the disease, since much depends on the degree of damage to the nerve fibers, how many of them have ceased to perform their functions normally. An important role is played by the root cause of paralysis, as well as the psychological mood of the patient himself.
Massage for paresis
Thanks to massage when paresis of the lower extremities occurs, blood circulation improves and muscle spasms relax. In addition, with the help of massage for paresis, degenerative changes that occur in muscle tissue are prevented. The massage must be performed on both legs at the same time, so the procedure must be carried out by two massage therapists.
First, two feet are massaged, then two thighs, etc. Thanks to this procedure, spasticity and synkinesis are significantly reduced. In addition, the patient must be trained to relax spastic muscles independently. In case of increased tone in the leg muscles associated with a change in body position, the patient should bend in the lower back.
First aid
In case of sudden damage to the limbs, you must promptly consult a doctor. To do this, the first thing you need to do is call an ambulance. By waiting for a medical team, you can alleviate the patient’s situation.
- If the head, neck or back is injured (or there is a suspicion of injury), the victim should not be moved under any circumstances. The exception is a mortal threat to life - fire, flood, natural disaster.
- Fixation of the spine. To prevent further damage, it is necessary to position the victim’s head in line with the body, using available means.
- Do not give drink. Under no circumstances should you give water until specialists arrive.
Complications
If left untreated, flaccid paralysis causes severe complications. This pathology can lead to the following dangerous consequences:
- Ankylosis. Lack of movement in a paralyzed limb leads to fusion of bones in the articular joints.
- Muscle contractures. Over time, the muscles in the affected area shorten and harden.
- Persistent muscle weakness. Peripheral paralysis is accompanied by a sharp decrease in the tone of the muscles of the neck and limbs. Without treatment, muscle tissue atrophy becomes irreversible.
If the patient has already developed such complications, then it is no longer possible to restore motor function using conservative methods. In most cases, it is necessary to resort to surgical treatment methods.
Gymnastics for paresis
Therapeutic exercises can be prescribed to the patient even in the presence of deep paresis. With its help, the vestibular apparatus, cardiovascular system, and musculoskeletal system are supported - ligaments, muscles, joints, bones. Thanks to special exercises, pain is reduced, blood pressure is normalized, and dizziness and nausea can be dealt with.
Special gymnastics for paresis consists of performing passive movements. It is important that two limbs are used simultaneously, regardless of the number of limbs affected. The movements should be performed in the same volume and in the same direction, and the pace should be quite slow. To avoid overwork, each exercise is performed no more than 3-5 times.
Classification and types of paralysis
In terms of origin, there are two types of paralysis:
- peripheral (another name for it is flaccid);
- central (aka spastic).
Peripheral is expressed by the destruction of motor neurons innervating muscles, or nerves connected to muscles. As peripheral destruction develops, the tone of the paralyzed muscles decreases, they become thinner and exhausted, which creates complete atrophy.
Central have their own distinctive ability - increasing muscle activity in paralyzed areas and damaging the area above the motor activity of neurons.
There is another classification of paralysis - in terms of the number of affected limbs:
- monoplegia – paralysis of one of the limbs;
- hemiplegia – damage on one side only;
- paraplegia is partial paralysis of the legs or arms (only the upper or lower limbs are affected);
- tetraplegia affects all limbs; it is paralysis of the legs and arms.
Drug therapy
Treatment of flaccid paralysis requires an integrated approach. The main goal of therapy is to restore the normal functioning of motor neurons. Patients are prescribed nootropic and antioxidant drugs in high doses:
- "Piracetam."
- "Actovegin".
- "Mexidol".
- "Trental."
- "Cerebrolysin".
These medications help normalize metabolism in damaged nerves and protect neurons from harmful effects.
A course of injections of the drug “Proserin” is shown. This remedy improves signal transmission from neurons to muscles and helps increase muscle tone.
Be sure to prescribe a course of vitamin therapy. It is necessary to take high doses of drugs, most often the drugs are administered intramuscularly. For treatment, vitamins B1 and B12 are used, which have a positive effect on the condition of the nervous tissue.
Physiotherapy and rehabilitation
Restoring movements is impossible without physiotherapy. This is the main part of the treatment of peripheral paralysis. It is impossible to get rid of motor dysfunction using medication alone. It is necessary to develop damaged muscle groups to avoid their complete atrophy.
Patients are prescribed galvanization sessions. Electrodes are applied to the affected areas and a low-voltage constant electric current is applied. This helps improve tissue metabolism and restore damaged neurons, as well as increase muscle tone. Baths with mineral waters are also shown. This allows you to influence peripheral nerves through skin receptors.
Such procedures are allowed to be carried out only after the acute symptoms of the infectious disease have been relieved. Galvanization and water treatments are quite effective, but the process of restoring movement takes a long period of time.
Massage for flaccid paralysis helps restore muscle tone and prevent muscle atrophy. The impact on the affected areas should be quite intense, using kneading and rubbing of the damaged muscles. But it is very important to prevent injury to muscle tissue. Therefore, this procedure should only be trusted by a qualified specialist. It is useful to combine classical and acupressure massage.
Exercise therapy for flaccid paralysis is a mandatory part of treatment. However, it must be taken into account that patients have weakened muscles and joints. Therefore, at the initial stage, passive movements using support are shown. For example, the patient rests the affected foot on a special box and tries to bend the leg.
Gymnastics in water is very useful. Exercises for the limbs can be combined with medicinal baths.
If hand movements are impaired, the patient must be taught simple household skills. For this purpose, tables with special stands are used in physiotherapy rooms. The patient learns to fasten buttons independently, press the switch button, and turn the key in the lock. Modeling from plasticine helps restore fine motor skills of the hands.
It is recommended to wear orthoses during rehabilitation. This will help maintain the injured limb in an optimal position.
Treatment
The primary task that the attending physician sets for himself is to eliminate the cause of the disease. In all cases, without exception, symptomatic drug treatment, exercise therapy, as well as therapeutic massage are carried out, which will help speed up the recovery of motor reflexes. For each individual case, its own program is selected, including both medications and preventive exercises.
In the treatment of this dangerous disease, the main emphasis is on physical therapy. During exercise, it is very important to position the affected limb correctly so that contractures do not appear. Physical education includes vigorous and passive exercises aimed at restoring motor skills and healthy muscle tone. You need to do gymnastics carefully, moderately, following all the doctor’s instructions.
Before a gymnastic set of exercises for peripheral paralysis, it is necessary to do a special massage. With the gradual revival of motor functions, active movements are added to the complex aimed at strengthening muscles, normalizing tone and straightening gait. Great success in treatment can be achieved if you add water activities to this complex. They can be done in the bathroom, or you can sign up for the pool. Water helps reduce stress on the joints, so the healing process will speed up and will not be as painful.
The drug course of drugs is selected individually by a neurologist. Dibazol, Proserin, Mellictin and intramuscular injections of vitamin B1 are usually prescribed. In case of a dangerous form of paralysis, corticosteroid drugs and salicylates are added to this complex. In extreme cases, electrotherapy is used. For vascular disorders, there are special drugs to improve the metabolic processes of the brain and saturate it with oxygen.
Spastic paralysis is treated with datrolene in combination with imidazoline and gabaleptin benzodiazepines. There are cases in which Botox is used, which can help damaged muscles relax and return to their former shape. In the case of spastic paralysis, surgical intervention is also possible. But to resort to this last resort, at least 6 months must pass. If no changes in a positive direction are observed during this period, the surgeon gets down to business.
It must be remembered that the main thing for the patient is movement. If the patient cannot do this on his own, he needs help, because the more a person is in motion, the faster he will recover.
When you stay in bed for a long time, blood circulation is disrupted, which leads to frequent dizziness and fainting, the respiratory system, cardiovascular system, joints suffer, skin condition deteriorates, and much more.
It is imperative to actively engage your lungs and perform simple breathing exercises, constantly warm up your body with massage and strengthen it with physical exercise.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the cause of the paresis. If the cause is injury, the prognosis is almost always favorable and the function of the foot can be restored in full. In case of neurological diseases, the main task will be to prevent the progression of paresis and its transition to paralysis.
In order to avoid paresis, it is advisable to follow a number of simple preventive measures:
- Get rid of bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol).
- Walk, bike, ski more.
- Regularly undergo medical examinations, and if diseases are detected, treat them in a timely manner.
- Use quality shoes.
Thus, foot paresis, which is a manifestation of a large number of diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system, is not life-threatening. But if left untreated, it can significantly limit motor activity and even lead to disability. Complex treatment (medicines, physical therapy, restorative procedures, wearing orthoses) in the early stages can completely restore the muscle strength of the foot.
The prognosis of the disease depends on the degree of neuronal damage. If diagnosis and treatment were carried out in a timely manner, then it is quite possible to restore movement. However, this will require long-term complex therapy and rehabilitation. Typically, the process of restoring motor function takes about 2 years. After surgical treatment, movements return to normal after about 1 year.
In advanced cases, it is no longer possible to restore movement even with surgery. If a patient has lost more than 70% of neurons, then such changes are considered irreversible.
Causes
According to statistics, about 2% of the population experience discomfort in the lower extremities when moving. Every year, just over 1 million people injure their backs to some degree. And these numbers are growing every year.
When the capabilities of full motor skills are weakened, and not completely lost, we can talk about paresis. Paresis and paralysis are similar in one thing - they occur when human nerve cells are damaged, when two parts of the motor system responsible for coordination are affected. Complete paralysis can be caused by the following factors:
- spinal and head injuries;
- intoxication with substances: heavy metals and their salts, poisons of various origins, alcohol, narcotic substances, medications, etc.;
- cancerous formations;
- infectious diseases that entail negative consequences in the functioning of the whole organism;
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- botulism (manifested by disturbances in the respiratory system, gastrointestinal disorders, abdominal pain, slurred speech);
- poor nutrition, unhealthy lifestyle;
- alcohol and drug abuse;
- hereditary changes in the body that affect the functioning of the nervous system and are accompanied by poor coordination of movements.
People who have suffered birth trauma can also suffer from paralysis. This, among other things, is a common cause of cerebral palsy.
There are several ailments of unknown origin (for example, Charcot's disease), which manifest themselves as motor impairments; they have very negative consequences. There is a high probability that paralysis may be the result of neurosis and have a psychogenic nature of origin. Such patients definitely need psychological help from a professional.