Rating: No rating
Unfortunately, central nervous system disorders in newborns are not uncommon. Up to 50% of all children are exposed to this disorder to one degree or another.
Today we will talk about perinatal damage to the central nervous system (CNS) in newborns, we will tell you what symptoms this disease is characterized by, what methods exist for diagnosing and treating damage to the central nervous system, and we will also understand what the consequences of this disease may be.
What is PPCNS?
The very phrase perinatal period suggests that perinatal damage to the central nervous system develops in an unborn or newly born child.
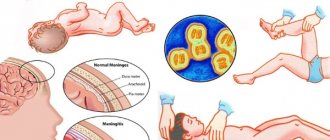
Perinatal damage to the central nervous system (PPCNS) is not one, but several diagnoses that imply dysfunction in the brain of a newborn child and can lead to persistent neurological consequences at an older age (for example, cerebral palsy, cerebral palsy). The entire perinatal period is divided into three stages:
– from the 28th week until the moment of birth, the antenatal period lasts;
– the process of childbirth itself is called the intranatal period;
– the neonatal period is the period of time from the moment of birth to the 7th day of life inclusive.
In modern medicine there is no exact name for the disease when the central nervous system of the fetus is affected, there is only a collective one, it is called PPCNS or perinatal encephalopathy. Perinatal damage to the central nervous system in newborns is manifested by disturbances in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system, speech and mental disorders.
With the development of medicine, this diagnosis has ceased to be used for children older than one month. After a month, the doctor must make an accurate diagnosis of the child. It is during this period that the neurologist accurately determines how badly the nervous system is damaged. Prescribes treatment and ensures that it is chosen correctly.
What are the causes and risk factors for PPCNSL?
The reasons why perinatal damage to the central nervous system may develop are quite varied, among the most popular:
– somatic disease of the mother, which is accompanied by chronic intoxication;
– the presence of acute infectious diseases or chronic foci of infection while the expectant mother was carrying the child;
– if a woman’s nutritional process is disrupted, or she is not ripe for pregnancy and childbirth;
– disruption of uteroplacental blood flow during pregnancy;
– changes in metabolism also entail a disorder of the nervous system in the unborn child (increased bilirubin levels, neonatal jaundice);
– in case of severe toxicosis, both at an early stage and at a late stage, or the appearance of other problems with bearing a child;
– the environment is an important factor in the development of the disease;
– the appearance of pathology during childbirth - this may be weak labor, accelerated labor;
– if a child is born prematurely, then his body is not fully developed, therefore, against this background, a disturbance in the functioning of the central nervous system may appear;
– Children who have a hereditary factor are at greatest risk of developing central nervous system lesions.
All other causes of PPCNS are situational and, to a greater extent, their occurrence is simply impossible to predict. There are several ways of development of perinatal damage to the central nervous system in newborns, depending on the cause and subsequent symptoms, the analysis of which allows us to make an initial diagnosis:
– If a lack of oxygen is clearly detected while the baby is inside the mother’s body (hypoxia), then hypoxic damage to the central nervous system is diagnosed.
– During childbirth, the baby’s tissue structure may be damaged (this can be either the brain or the spinal cord). In this case, we are already talking about a traumatic lesion of the central nervous system, resulting in changes in the functioning of the brain.
– In case of metabolic disorders, metabolic and toxic-metabolic lesions may appear. This may be due to the use of alcohol, medications, or nicotine during pregnancy.
– Changes in the central nervous system in the presence of infectious diseases of the perinatal period.
What is perinatal CNS damage?
Perinatal lesions of the central nervous system, abbreviated as PPCNS, are a number of pathologies that are related to disruptions in the functioning of the brain and developmental abnormalities in its structure. Similar deviations from the norm are observed in children during the perinatal period, the time frame of which ranges from the 24th week of pregnancy to the first 7 days of life after birth, inclusive.
Currently, PPCNSL in newborns is a fairly common phenomenon. This diagnosis is established in 5-55% of children. The wide range of indicators is due to the fact that often lesions of the central nervous system of this kind resolve easily and quickly. Cases of severe forms of perinatal damage occur in 1-10% of children who were born on time. Premature babies are more susceptible to the disease.
What are the types of PPCNS syndromes?
PPCNSL is conventionally divided into several periods, depending on at what stage the disorder was identified and how it manifested itself.
– The acute period lasts from 7 to 10 days, it is extremely rare, but it can last up to a month.
– The period during which recovery occurs (recovery period) can last up to 6 months. If the child’s body recovers slowly, this period may take up to 2 years.
Pediatric neurologists distinguish the following types of perinatal lesions of the central nervous system, depending on the accompanying symptoms and syndrome:
– Violation of muscle tone. This syndrome is diagnosed according to deviations from the norm depending on the age of the infant. In the initial period of a child’s life, it is quite difficult to diagnose this syndrome, since in addition there is physiological hypertonicity (physiological stiffness of the newborn’s muscles).
– Nervous-reflex excitability syndrome is a syndrome associated with sleep disturbances, trembling of the chin, and the child flinching at any rustle or touch. This syndrome can be diagnosed only when somatic diseases of the newborn (for example, intestinal colic) are excluded. When examining such a child, the neurologist determines an increase in tendon reflexes, as well as an increase (revitalization) of the newborn’s automatisms (Moro reflex).
– Nervous system depression syndrome. This syndrome is the opposite in its characteristics to the previous one. It is diagnosed in children who are not active in the first months of their lives, they sleep a lot, they have decreased tone, they cannot hold their head up, and they have difficulty grasping their hands.
– An unfavorable prognosis for the child if intracranial hypertension syndrome develops. Its main signs are increased excitability and nervousness, while the fontanel begins to swell and thicken. Frequent regurgitation appears. Upon examination, the neurologist notices excessive growth of head circumference, possible divergence of the sutures of the skull, Graefe’s symptom (the “setting sun” symptom).
– One of the most dangerous and severe conditions in PPCNS is convulsive syndrome, which is one of the most serious manifestations of perinatal damage to the central nervous system.
In addition, any attentive mother can notice deviations in her child’s health much faster than a neurologist, if only because she monitors him around the clock and more than one day.
In any case, a baby living for the first year with any (even minimal, but not passing) deviations in health requires repeated consultations with specialists at the medical center, inclusion in the medical examination program (i.e. close observation by a neurologist and, if necessary, additional examination , such as ultrasound of the brain, electroencephalography, blood testing to determine the compensatory potential of the nervous system, etc.). Based on the findings received, the center’s specialists develop a development plan for such a child, select an individual scheme for preventive vaccinations, introduce complementary foods into the diet, and carry out therapeutic measures if necessary.
What are the symptoms and diagnostic criteria for PCNSL?
– Not every mother who does not have a medical education will be able to distinguish and determine at first glance that her child has a perinatal lesion of the central nervous system. But neurologists accurately determine the disease by the appearance of symptoms that are not characteristic of other disorders.
– when examining the baby, muscle hypertonicity or hypotonicity may be detected;
– the child is excessively restless, anxious and excited;
– the occurrence of trembling in the chin and limbs (tremor);
– the appearance of seizures;
– when examined with a hammer, a violation of the reflex sphere is noticeable;
– the appearance of unstable stools;
– heart rate changes; the appearance of irregularities on the child’s skin.
As a rule, after a year these symptoms disappear, but then appear with renewed vigor, so this situation simply cannot be neglected. One of the most dangerous manifestations and consequences of PPCNSL in the absence of a response to symptoms is the suspension of the development of the child’s psyche. The speech apparatus does not develop, and there is a delay in the development of motor skills. Also, one of the manifestations of the disease may be cerebrasthenic syndrome.
Classification of the disease
In modern medicine, it is customary to classify deviations in the normal functioning of the central nervous system in accordance with the reasons that caused this or that pathology. In this regard, each disorder has its own forms and symptoms. There are 4 main pathological types of central nervous system lesions:
- traumatic;
- dismetabolic;
- infectious;
- hypoxic genesis.
Perinatal lesions in the newborn
Perinatal lesions of the central nervous system are those that develop during the perinatal period, the main part of which occurs in the prenatal period. The risk of depression of the central nervous system in a child increases if during pregnancy a woman suffered:
- cytomegalovirus infection (we recommend reading: symptoms and consequences of cytomegalovirus infection in children);
- toxoplasmosis;
- rubella;
- herpes infection;
- syphilis.
The baby may receive intracranial trauma and injuries to the spinal cord or peripheral nervous system during childbirth, which can also cause perinatal lesions. Toxic effects on the fetus can disrupt metabolic processes and negatively affect brain activity.
Hypoxic-ischemic damage to the nervous system
Hypoxic-ischemic damage to the nervous system is one of the forms of perinatal pathology, which is caused by fetal hypoxia, that is, insufficient oxygen supply to the cells.
A manifestation of the hypoxic-ischemic form is cerebral ischemia, which has three degrees of severity:
- First. Accompanied by depression or stimulation of the central nervous system, which lasts up to a week after birth.
- Second. In addition to depression/excitation of the central nervous system that lasts more than 7 days, convulsions, increased intracranial pressure and autonomic-visceral disorders are added.
- Third. It is characterized by a severe convulsive state, dysfunction of the brain stem, and high intracranial pressure.
Disease of mixed origin
In addition to ischemic genesis, hypoxic lesions of the central nervous system can be caused by hemorrhages of non-traumatic origin (hemorrhagic). These include hemorrhages:
- intraventricular type 1, 2 and 3 degrees;
- subarachnoid primary type;
- into the substance of the brain.
How is PCNSL treated?
To restore the basic functions of the central nervous system, as well as to reduce the manifestation of neurological symptoms, the baby is prescribed a whole range of medications. Treatment can include, for example, nootropic drugs that can restore trophic processes in the brain - piracetam, Cerebrolysin, Cortexin, pantocalcin, solcoseryl and many others. In order to stimulate general reactivity, a newborn child is given a course of therapeutic massage, special gymnastics, and, if necessary, a set of physiotherapeutic procedures (for example, electrophoresis and microcurrents).
If parents detect at least one of the signs of central nervous system damage, they should immediately consult a doctor. Do not forget that the development of each child is an individual process. Such individual characteristics of a newborn child in each specific case play an important role in the process of restoring the functions of higher nervous activity.
Restoration of cognitive functions
An important stage of post-stroke therapy is the rehabilitation of cognitive functions: restoration of memory, attention, and intellectual abilities. Violations of these functions largely determine the patient’s quality of life after a stroke; they significantly worsen the prognosis, increase the risk of recurrent stroke, increase mortality, and increase the severity of functional disorders.
Severe cognitive impairment and even dementia can be caused by:
- massive hemorrhages and extensive cerebral infarctions;
- multiple heart attacks;
- single, relatively small infarcts located in functionally significant areas of the brain.
Cognitive dysfunction can occur at different stages of recovery, both immediately after a stroke and in a more distant period. Long-term cognitive impairment may be caused by a parallel neurodegenerative process, which intensifies due to increasing tissue ischemia and hypoxia.
Rehabilitation of cognitive functions is carried out with the participation of a neuropsychologist
More than half of patients who have suffered a stroke develop memory disorders in the first 3 months, but by the end of the first year of rehabilitation the number of such patients decreases to 11–31%. Thus, the prognosis for memory recovery after a stroke can be called favorable. In patients over 60 years of age, the risk of memory impairment is significantly higher.
Memory restoration requires consistent sessions with a neuropsychologist and occupational therapist, as well as independent active work - performing special exercises on thinking, attention, memorization (solving crossword puzzles and memorizing poetry). Often, patients after a stroke are additionally prescribed medications that stimulate higher nervous activity.
To restore movement in paralyzed limbs, electrical stimulation of the neuromuscular system and sessions with an occupational therapist are indicated.
A prerequisite for an independent life for a patient is the successful restoration of everyday skills, which will allow the patient to return home from a clinic or sanatorium, eliminate the need for the constant presence of a nurse or relatives, and also help the patient quickly adapt and return to normal life. The direction of rehabilitation that adapts the patient to independent life and everyday activities is called occupational therapy.
To restore cognitive functions after a stroke, medications are used that correct cognitive, emotional-volitional and other mental disorders:
- metabolic means:
Gliatilin
After a stroke, the Italian drug Gliatilin has proven itself to be effective in restoring cognitive functions. A course of treatment improves the condition of the central nervous system, allowing for rapid restoration of memory, thinking, speech, swallowing reflex and restoration of other functions of daily activity. Gliatilin has a positive effect on the transmission of nerve impulses, protects brain cells from damage, which prevents the risk of recurrent stroke. It is also available in the form of an oral solution, which is very convenient for use if you have difficulty swallowing. The drug is well tolerated by patients; it is contraindicated for use in people with hypersensitivity to choline alfoscerate.
- neuroprotective agents (Citicoline, Ceraxon);
- drugs that affect neurotransmitter systems (Galantamine, Rivastigmine).
In addition to drug therapy, patients suffering from post-stroke memory and attention disorders are given psychological and correctional classes individually or in groups.
What are the dangers and consequences of PPCNS?
There is an opinion among experts that if the central nervous system of the fetus has been damaged, it cannot be completely restored. But practicing neurologists say the opposite. They say that if the disease is treated correctly and in a timely manner, it is possible to achieve partial or complete restoration of the functions of the nervous system. But even despite such an optimistic forecast, if you look at all possible diseases of a child associated with the nervous system, then 50% of their total number leads to disability, while about 80% of it is allocated to perinatal damage to the central nervous system.
Perinatal encephalopathy is a number of diseases (deviations) of the central nervous system in newborns. The disease can manifest itself in different ways, and therefore it is very difficult to diagnose, especially in infants. Related to this is the fact that the symptoms of encephalopathy are often regarded by pediatricians as signs of completely different diseases. As a result, treatment of the disease is not given the necessary attention at an early age, when the likelihood of a complete recovery is greatest. A progressive disease as the child grows up is often also diagnosed symptomatically, and appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Getting rid of PEDs without osteopathic influence on the root causes of the disease is, if not completely impossible (after all, the body is a self-regulating system that is quite capable of coping with a number of serious diseases), then it is significantly difficult. Of course, other treatment methods should not be neglected - as practice shows, complex procedures are the most effective.
Symptoms and consequences of perinatal encephalopathy
Symptoms of the disease manifest themselves differently at different periods of a child’s life. To simplify classification and improve diagnosis, it is customary to distinguish three main periods of PEP: acute (during the first month of life), recovery (up to 1 year, less often up to 2 years - mainly in premature infants) and outcome of the disease. There is a possibility that the child’s body - as a self-regulating system, from the point of view of osteopathy - can fully recover and neutralize the symptoms of the disease by adapting to them. This does not mean complete recovery, since the effects of AEDs may appear at a later age. Therefore, if you suspect a disease, you must immediately show the child to an osteopathic doctor, who can make the correct diagnosis and prescribe competent, adequate treatment aimed at ridding the body not of the consequences, but of the causes of the disease.
Main symptoms of perinatal encephalopathy
During the acute period of disease development, the following are observed:
- CNS depression syndrome. Characterized by general lethargy of newborns, reduced response to external stimuli, and the presence of spontaneous motor reflexes;
- comatose syndrome. It usually develops quickly and suddenly, causing unconsciousness in the child. May manifest itself in acute disruption of vital body functions;
- increased neuro-reflex excitability. Manifests itself in the form of tremor of the limbs and an abnormally excited reaction to external stimuli;
- increased cranial pressure with subsequent hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome and a disproportionate increase in skull size;
- convulsions.
During the recovery period, these symptoms may be added to:
- motor disorders. They manifest themselves in different ways, but the common thing is that the child does not fully or partially control his movements;
- psychomotor development delay (PDD). Manifests itself in delayed development, speech problems, memory impairment, problems with attention, etc.;
- epileptic seizures.
Signs of the disease can appear both in combination and individually. And at different ages. If at least one symptom is detected, it is recommended to contact an osteopathic specialist for a more detailed examination.
The outcome of the disease can be:
- recovery;
- minimal brain dysfunction;
- mental retardation;
- cerebral palsy;
- neurotic diseases;
- epilepsy;
- hydrocephalus.
As practice shows, with mild forms of perinatal encephalopathy, the likelihood of complete recovery is quite high. Especially with the right osteopathic treatment, which can be combined with other methods of influencing the child’s body.
In more severe forms, longer treatment will be required, which, due to various factors, may not be 100% effective. Some problems with memory, attention, and coordination of movements in a child can persist both for a long period and throughout life. But osteopathy contributes, if not to a complete cure, then to a significant minimization of the symptoms of perinatal encephalopathy.
Treatment methods depending on symptoms
Treatment of any pathologies of the central nervous system in newborns must be carried out in the first months of life, since at this stage almost all processes are reversible, and impaired brain functions can be completely restored.
In the first months of life, PPCNS is easily treated
For this purpose, appropriate drug therapy is carried out, which allows:
- improve nutrition of nerve cells;
- stimulate blood circulation;
- normalize muscle tone;
- normalize metabolic processes;
- relieve your baby from seizures;
- relieve swelling of the brain and lungs;
- increase or decrease intracranial pressure.
When the child’s condition has stabilized, physiotherapy or osteopathy is carried out in combination with medications. The therapeutic and rehabilitation course is developed individually for each case.
Intracranial hypertension
Intracranial hypertension syndrome manifests itself as an increase in the size of the head circumference of a newborn baby compared to the norm, swelling of a large fontanel and divergence of the sutures of the skull (we recommend reading: what does Komarovsky say about the fact that a newborn has a small fontanel?). The child is also nervous and easily excitable. If such symptoms appear, the baby is prescribed diuretics and dehydration therapy. In order to reduce the likelihood of hemorrhages, it is recommended to take a course of Lidaz.
Plus, the baby is given special gymnastic exercises that help reduce intracranial pressure. Sometimes they resort to acupuncture and manual therapy to correct the outflow of fluid.
The complex treatment of PCNSL necessarily includes general strengthening gymnastic exercises.
Movement disorders
When diagnosing movement disorder syndrome, treatment consists of a series of measures aimed at eliminating the problem:
- Drug therapy. Drugs such as Galantamine, Dibazol, Alizin, Proserin are prescribed.
- Massage and physical therapy. For children under one year of age, a minimum of 4 courses of such procedures are required, each of which consists of approximately 20 sessions with specially selected exercises. They are selected depending on what is subject to deviations: walking, sitting or crawling. Massage and exercise therapy are carried out using ointments.
- Osteopathy. It consists of performing a massage of internal organs and influencing the desired points of the body.
- Reflexology. It has proven itself to be the most effective method. Its help is resorted to in cases where SDN leads to a delay in the maturation and development of the nervous system.
Increased neuro-reflex excitability
One of the possible manifestations of perinatal damage in the acute phase is increased neuro-reflex excitability.
Being a mild form of the pathology, it is characterized by:
- decreased or increased muscle tone;
- extinction of reflexes;
- superficial sleep;
- causeless shaking of the chin.
Massage with electrophoresis helps restore muscle tone. In addition, drug therapy is carried out, and treatment can be prescribed using pulsed currents and special baths.
Epileptic syndrome
Epileptic syndrome is characterized by periodic epileptic seizures, which are accompanied by convulsions, which are shuddering and twitching of the upper and lower extremities and head. The main goal of therapy in this case is to get rid of the convulsive state.
Finlepsin is prescribed if a child has a convulsive syndrome
A course of the following medications is usually prescribed:
- Difenin;
- Radodorm;
- Seduxen;
- Finlepsin;
- Phenobarbital.
Minimal brain dysfunction
Minimum brain dysfunction, better known as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, is a low-symptom form of neurological disorder. Treatment with medications is mainly aimed at eliminating specific manifestations, while methods of physical influence, namely massage or physical education, can more effectively correct the pathological condition of the child.
Risk factors
Risk factors that increase the risk of developing the disease include:
- chronic maternal illnesses. Often they are not transmitted directly to the child, since they are not hereditary, but at the genetic level they cause the manifestations of various pathologies and abnormalities in the development of the fetus and the already born child;
- infectious diseases suffered during pregnancy. Untreated pathologies that can manifest themselves against the background of a general weakening of the body’s immunity due to pregnancy are very dangerous;
- poor nutrition. During the period of gestation, the mother's body must receive the entire necessary set of proteins, vitamins and minerals. Nutrition should be balanced and agreed with a doctor to avoid food allergies and digestive disorders;
- mother's age is too young. A girl’s body may simply be unprepared to bear a full-fledged and healthy child. If the expectant mother is too young or has insufficient physical development, she should be under the constant supervision of a specialist throughout the entire period of pregnancy and after childbirth;
- metabolic disorder in the mother's body. Since her body is closely interconnected with the body of the unborn child, any disturbances affect the nutrition and health of the fetus. Therefore, proper nutrition, which was mentioned earlier, is so important, as well as the trouble-free operation of the organs responsible for metabolism in the body;
- pathologies during pregnancy. Early and late toxicosis, stress, physical activity and other factors are very dangerous, which can lead to interruption and abnormal course of pregnancy;
- unfavorable environmental conditions. Unfortunately, today this factor is more dangerous than many others, because it is often impossible to avoid the effects of harmful external manifestations. It is recommended to contact specialists (including an osteopath) who will help to significantly neutralize the adverse effects of the environment;
- prematurity or postmaturity of the fetus.
- Thus, most risk factors are associated
specifically with the health of the mother. Therefore, during pregnancy, she should carefully monitor her well-being, listening to the advice of a good doctor. In parallel with other specialists, it is recommended to regularly visit an osteopath, who will also monitor the progress of pregnancy and will be able to correct possible deviations using osteopathic methods, without the use of drugs that can harm the unborn child.
The danger of perinatal encephalopathy
Like many other infant diseases, if not cured in the early stages, perinatal encephalopathy progresses with age and can manifest itself in the form of a wide variety of disorders that at first glance seem unrelated:
- frequent morbidity syndrome. These can be either frequent colds or periodic ailments associated with poor health, increased fatigue, headaches, etc.;
- chronic diseases of the respiratory system. They can manifest themselves against the background of frequent acute respiratory infections, gradually turning into a chronic form. In the absence of competent osteopathic treatment, with age they can develop into asthma and other equally dangerous diseases;
- developmental delay. They may manifest themselves in a less obvious form as learning difficulties, especially in the exact sciences and creative disciplines;
- posture disorders. Unnoticeable birth injuries and disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system, which arose during pregnancy, often later lead to curvature of the spine and the appearance of such serious diseases as scoliosis, with all the ensuing consequences, leading to the prolapse of internal organs and their partial or complete dysfunction;
- disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, the metabolic system and the circulatory system. Typically, these disorders invariably lead to other diseases, since due to impaired blood flow, various parts of the body begin to receive less oxygen, which leads to cell death and dysfunction.
Speech restoration
The greatest effectiveness in the rehabilitation of patients with speech disorders can be achieved by individual classes to restore speech, reading and writing, which are carried out jointly by a neuropsychologist and a speech therapist. Speech restoration is a long process that can take from several months to several years.
In the early stages of rehabilitation, stimulation techniques are used and the understanding of situational phrases and individual words is taught. The patient may be shown individual objects based on pictures, asked to repeat sounds, perform exercises for pronouncing individual words and phrases, then move on to composing sentences, dialogues and monologues. To do this, the patient tries to restore in memory the skills of working the movable jaw and oral cavity.
For articulation disorders associated with speech muscle disorders, perform gymnastics for the muscles of the tongue, cheeks, lips, pharynx and pharynx, and massage the articulatory muscles. Electrical muscle stimulation using the VOKASTIM method using a special apparatus that develops the muscles of the pharynx and larynx is effective.
Patients with severe paresis of the lower limb are taught to imitate walking in a lying or sitting position, and then to sit down and get out of bed independently.
How do osteopathic specialists evaluate perinatal encephalopathy?
From the point of view of osteopathy, the entire complex of central nervous system diseases, united under this term, is a consequence of mechanical disorders in the body of the fetus of a newborn child. Moreover, they can occur during pregnancy or later - during difficult childbirth and/or caesarean section. The reasons leading to the appearance of the disease are:
- dysfunction of the spinal column or its individual sections;
- disturbances in the functioning of internal organs;
- prolonged oxygen starvation;
- circulatory disorders.
But even if the fetus developed normally during pregnancy, there is a high probability of injury during childbirth, since, passing between the pelvic bones, the fetus rotates 360 degrees, which can cause disturbances in the skeletal structure and muscle tissue. The most common disturbances observed are in the position of the cervical vertebrae. In most cases, in the first weeks of a child’s growth, the effects of damage are completely neutralized by the body on its own. But this is not always the case; any changes or deviations in development can lead to complications, which subsequently provoke disturbances in the blood supply to the brain and the manifestation of perinatal disorder.
How is perinatal encephalopathy diagnosed in newborns and infants?
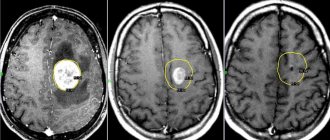
There are a number of safe brain imaging techniques that newborns can undergo. They allow you to create a complete clinical picture, determine the presence of the disease, its degree, and the nature of its course. The most informative and effective is neurosonography, which accurately detects the presence of damaged areas in the baby’s brain. In addition to this, Doppler ultrasound can be performed to assess blood flow in the vessels of the brain.
If developmental abnormalities are detected, it is recommended to undergo an electroencephalographic examination aimed at determining the degree of developmental delay. This procedure also allows you to identify foci of epileptic lesions and assess the degree of their activity and danger to the body.
In some cases, an examination by an ophthalmologist is also recommended, who will help determine the extent of the damage by assessing the condition of the optic nerves and analyzing the fundus.
Treatment of encephalopathy with osteopathic methods
A good osteopathic doctor is able to diagnose early symptoms of the disease and create a complete picture of its course. This makes it possible to prescribe competent treatment that helps the body adapt to new conditions, launch and stimulate its self-regulatory functions.
The effects of an osteopath - depending on the course and complexity of the disease - are directed primarily to the affected areas of the body in order to relieve pain and spasms resulting from improper development and disturbances in the circulatory system. In parallel with this, the specialist carries out a set of procedures to normalize brain function. Usually, various techniques of muscular-energetic influence are used for this, which allow manually restoring the balance of tension in the intracranial membranes. This helps restore micropulsations in the bones of the skull and the brain itself, and normalize blood circulation.
After normalization of brain activity, the body receives a powerful incentive to self-regulate and get rid of encephalopathy. The osteopath's further actions are to help the baby's body cope with the disease. For this purpose, manual therapy, massage, physical therapy and other techniques are used, which, in the opinion of a specialist, can help a speedy recovery.
As practice shows, perinatal encephalopathy in newborns is completely cured in 30% of cases - with early detection and proper treatment. In another 20-30% - usually in severe and moderate cases - newborns are not completely cured. Some symptoms remain, but often some of them can be corrected with complex therapy, including exercise therapy, osteopathy, massage techniques, and special education, training, etc.
Unfortunately, in many cases when perinatal encephalopathy manifests itself in the form of serious damage to the cells of the cerebral cortex, it is impossible to get rid of the disease. The reason is the death of brain cells and disruption of neural connections, which cannot be restored due to the lack or absence of physical carriers in the child’s brain. Even in these cases, osteopathy can help relieve some neurological symptoms, but complete restoration of brain activity is impossible.
It is important that possible neonatal encephalopathy is diagnosed at the earliest stages of development - in the first months of a child's life. To facilitate this, it is recommended to visit an osteopath at 3 months of life for a full examination. The specialist will prescribe the necessary tests and conduct an independent examination, which together will help detect symptoms and identify the possible presence of the disease.
Often, when PEP is detected, pediatricians advise starting drug treatment. Moreover, this must be done from early infancy. Every parent should be aware that this approach is not always effective and can most likely harm the child. The fact is that the newborn’s body is quite weak, but at the same time it is balanced and capable of adaptation and self-regulation. Exposure to potent drugs leads to irreversible changes that even an osteopath cannot neutralize. Therefore, if a child is diagnosed with perinatal encephalopathy or there is serious suspicion of its presence, it is recommended to also undergo examination by an osteopath. Osteopathic techniques are more subtle and delicate, and therefore more effective. They have a targeted effect on areas of the body and brain, the nervous system of the child, bringing it to a normal state.
Diagnostics
Any disturbances in brain activity are difficult to diagnose at an early stage. Babies are diagnosed with perinatal damage to the central nervous system during the first months of life, based on the presence of problems with the motor and speech apparatus, as well as taking into account violations of mental functions. Closer to the year, the specialist should already specify the type of disease or refute the previously made conclusion.
Disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system pose a serious danger to the health and development of the child, so it is important to diagnose the problem in time in order to carry out proper treatment. If a newborn baby behaves uncharacteristically and the first symptoms of illness appear, parents must take him to the doctor. First, he performs an examination, but such a procedure alone may not be enough for an accurate diagnosis. Only an integrated approach will identify the disease.
If there is the slightest suspicion that a child is developing PPCNS, it is necessary to immediately show a doctor
For this reason, the following clinical and laboratory tests are usually additionally prescribed:
- neurosonography (we recommend reading: what does neurosonography of the brain of newborns show?);
- CT – computed tomography or MRI – magnetic resonance imaging of the brain;
- Ultrasound – ultrasound diagnostics;
- X-ray examination;
- echoencephalography (EchoES), rheoencephalography (REG) or electroencephalography (EEG) - methods of functional diagnostics (we recommend reading: how is an EEG of the brain done for children?);
- Consultative examination by an ophthalmologist, speech therapist and psychologist.
Disease prevention
The most effective method of prevention is the mother's adherence to the regimen during pregnancy. In most cases, newborns are in good health if the mother takes care of her body (and therefore the baby). It is also recommended to regularly visit an osteopathic doctor who will help monitor your health during the prenatal period.
Attention to the health and condition of the child in the first weeks and months of his life is also very important. Any developmental deviations, anomalies and pathologies must be identified and recorded by a specialist for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Encephalopathy of a newborn is, although a very serious diagnosis, but not yet a death sentence. This disease can be treated quite effectively.