Pain in the head - or, as it is called, cephalalgia - has different manifestations. They are an alarming signal, which often forces you to put everything aside and seek medical help. The causes of pain in the head can be very different. Often it is felt even by absolutely healthy people, whose body reacts to weather changes in this way. It is very important in this case to be able to distinguish such painful symptoms from those that are a sign of serious malfunctions in the body, and to seek professional help in time.
Types of headaches
When a person suddenly has a sharp headache, this is most often explained by neurological problems or vascular dysfunction. Through numerous studies, scientists have identified about 200 types of sensations and about 45 types of cephalgia.
Severe headaches can be caused by many factors, each with varying symptoms. Eg:
- cluster pains occur more often in men and are one-sided in nature, for example, sudden cephalalgia piercing the temple in the left hemisphere for several seconds;
- cervical osteochondrosis or myogelosis causes long-term or short-term headaches that appear due to muscle spasm or compression of the vessels of the cervical region;
- inflammatory processes occurring in the trigeminal or occipital nerves cause sharp, short-term pain in the back, which can pulsate to the back of the head or intensify with movements, turning the head or tilting;
- weather dependence can provoke a condition when a person suddenly begins to have a headache due to changes in weather.
Any acute manifestations may be a sign of serious disorders in the body. It is highly recommended not to self-medicate, so as not to pose a threat to your own life.
Let's look at the most common types of sharp stabbing pain.
Symptomatic
Acute headache is a pronounced sign of the presence of an illness and unhealthy condition. Such pains are called symptomatic, as they arise due to certain disorders:
- mechanical damage to the skull;
- dysfunction of the cardiovascular system;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- infections, viruses, intoxication or poisoning cause headaches;
- metabolic or metabolic disorders, dysfunction of the facial structure, dental or cranial problems.
Each violation must be considered separately, dealing with the occurrence of prolonged or momentary sharp pain with the help of professionals.
Migraine
Migraine or hemicrania is a neuralgic disease characterized by unilateral (usually in the right half) short-term or long-term pulsation in the head.
This is one of the very common conditions that can affect both teenagers and adults. In most cases, migraine affects women, especially against the background of hormonal disorders, the onset of menopause or menstruation.
Often, such ailment begins with the appearance of precursors - sensitivity to light, sharp sounds, smells, unmotivated mood swings, depression or apathy.
Attacks can appear unexpectedly, develop rapidly within half an hour, or take quite a long time to pass. In most cases, an attack occurs when you get out of bed or at the moment when a person just wakes up.
Localization of acute headache can radiate to different points of the body - ear, eyebrow, temporal lobes, etc. The symptoms accompanying the disease are also of a different nature. It depends on the type of migraine.
For example, abdominal hemicrania is usually accompanied by vomiting, nausea, dizziness, bloating or pain in the abdomen.
The provoking factors for the appearance of migraines are considered to be neuroses, stress, disturbances in the psycho-emotional state, lack of sleep, medications, etc.
Tension headache
Such sharp and acute pain is the most common type, affecting the age group from 20 to 35 years.
Tension pain or piercing tension pains can squeeze the head in a vice, while the intensity is considered monotonous and moderate.
Tension pain can be periodic or chronic. A clear sign of tension-type headache is a nervous state, irritability, even prolonged depression.
Sharp (sudden)
Sharp pain in the temples, orbital area, in the back of the head, crown or crown, appearing suddenly, is an alarming symptom of the presence of a serious pathology and a threat to the patient’s life. Head pain of this nature is not recommended to be relieved with painkillers on your own. Regardless of the intensity of the pain, medical intervention is required to determine the cause.
Sharp, sudden pain can even be triggered by coughing, laughter, physical overload and other factors. According to statistics, in 10% of cases such pain is caused by the presence of a neoplasm or brain tumor.
Strong
Each type of unpleasant sensation has its own symptoms and development pattern. There are various manifestations of severe cephalgia:
- preliminary symptoms, after the appearance of which headache increases gradually;
- immediate development of pain, which gradually disappears;
- slow onset of pain that changes locations.
Examples of such schemes are quite varied. The basis is the intensity, duration and frequency of occurrence. In each specific case, every little thing that accompanies pain plays a role. If such manifestations occur more than 3 times a week, then this is a serious reason to consult a doctor.
Short term
Periodic attacks can be triggered not only by the presence of pathology, but also by primary causes. Eg:
- drinking a lot of coffee;
- sudden withdrawal from nicotine or caffeine;
- alcohol abuse;
- eating food with tyramine (for example, this applies to chocolate lovers);
- improper wearing of headbands, elastic bands, bandanas, braiding tight braids;
- Sleeping devices that are too soft or hard;
- overheating or hypothermia of the body.
Having eliminated the causes of this type, as a rule, short headaches disappear.
Long lasting
You rarely meet a person who suffers from the same pain in the head. Typically, cephalalgia is either alternating or mixed.
Persistent headaches have several categories:
- vascular disorders;
- pain arising from muscle tension or spinal diseases;
- neuralgic cephalgia;
- liquorodynamic GB;
- toxic poisoning causes prolonged sharp pain;
- infectious pain in the head from respiratory diseases (ARVI, sinusitis, sinusitis, meningitis, encephalitis);
- oncological headache attacks affecting the central nervous system (CNS).
Some pathologies provoke a long course of cephalalgia and can only be treated at an early stage. Timely contact with doctors can solve the problem and save lives.
Test yourself
Headaches can be of different types.
With tension pain: the pain is constant, pulling, aching, squeezing the entire head with a “hoop.”
With migraine: the pain is clearly defined, usually pulsating in nature and unilateral, predominantly frontotemporal localized. Another characteristic symptom of migraine is increased sound and light sensitivity combined with sweating, palpitations and nausea. Sometimes a migraine attack can be preceded by dizziness, the sensation of strange smells and even visual hallucinations (sparkling dots, zigzags, sparks from the eyes).
With a cluster headache: a burning, throbbing pain affects one half of the head and face (forehead, temple, orbit), it is so unbearable that it is impossible to sit or stand. During an attack, the eye may become red and watery (mainly on the side of pain), the nose may become stuffy, and the forehead may become covered with perspiration.
With high blood pressure: the pain is constant, dull, pressing, sometimes throbbing. Most often localized in the back of the head.
Associated symptoms
Sharp influxes of pain during the development of hidden pathologies or diseases are often accompanied by additional symptoms.
Main features:
- a person may feel nauseous and have a gag reflex;
- sometimes dizziness, fainting or loss of consciousness is added;
- the appearance of noise, ringing in the ears;
- visual impairment, hearing impairment;
- dysfunction of the respiratory system;
- increased heart rate, tachycardia or angina;
- pressure on the throat when it is difficult to swallow;
- manifestation of confusion, disorientation, convulsions;
- cognitive disorders.
Pain in the head that occurs during hemorrhage is particularly intense. Many characterize them as thunderous. In such cases, emergency medical attention is required.
Migraine
One of the neuralgic diseases, accompanied by severe pain in the head area -. Researchers still cannot establish the exact, true cause of its appearance. Many experts have nevertheless come to a consensus and call genetic predisposition the main factor in the development of this pathology. Moreover, the disease attacks mainly the female gender.
It has been established that seizures occur due to malfunctions of the blood vessels in the brain. This condition can be provoked by various factors, both external and pathological processes occurring in the body itself, in particular, hormonal disorders and others.
One of the factors that increases the risk of migraines is bad habits. But a violation of the diet, especially fasting, as well as an unbalanced diet are also factors contributing to the occurrence of attacks.
Unpleasant, painful symptoms can be caused by stress, emotional, physical stress, too bright light or sharp, loud sounds, noise, temperature changes.
Causes of acute headache
Acute pain can be triggered by various, even external factors:
- people with a sedentary lifestyle who spend a lot of time at the computer are at risk of suffering from cephalalgia;
- poor nutrition or the use of all kinds of diets for weight loss can cause severe attacks of pain;
- teenagers often face painful syndrome due to overwork or a difficult school program;
- sharp and sharp pains often occur during pregnancy due to disruptions of the hormonal system, toxicosis or excess body weight.
Let us consider the individual causes of cephalalgia in more detail.
Emotional experiences
Prolonged stress or severe psycho-emotional shock can trigger an attack.
Prolonged internal disharmony can lead a person to serious mental disorders. It is recommended to visit a neurologist who will select a course of necessary vitamins, sedatives or antidepressants.
Hemorrhage into the cerebellum
This part of the brain is responsible for supporting coordination, spatial orientation, and muscle tone. Accompanied by the following symptoms:
- unbearable bursting pain in the head;
- speech impairment;
- nystagmus - uncontrolled eye movement in one direction;
- dizziness, vomiting, nausea.
This is a rather dangerous pain syndrome that requires emergency hospitalization.
Cervicogenic neuralgia of the occipital nerve
This type of pathology is associated with problems of the skeletal apparatus of the spine, leading to instability and organic formations.
Injuries, postural and metabolic disorders irritate the sympathetic plexuses, arteries and venous system of the occipital nerves. As a result of inflammatory processes, piercing headaches appear, which intensify with physical activity - movement, turning the head or bending over. If this condition is not treated, it will become a chronic disease.
Chronic paroxysmal hemicrania
This pathology more often affects the female gender. The disease is characterized by multiple daily occurrence of attacks, about 15 manifestations.
It is believed that this type of migraine appears in the autumn-spring period. Headaches are characterized by attacks at night.
Acute paroxysms are very similar to cluster pain. However, they are highly sensitive to indomethacin.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
With this pathology, hemorrhage occurs under the arachnoid membrane of the brain when a vessel aneurysm ruptures.
The anomaly can be either congenital or acquired. In the latter case, the provoking factors are atherosclerosis, autoimmune vasculitis, and smoking abuse.
An aneurysm is rarely accompanied by any symptoms. A vessel may burst due to a specific reason. In this case, a sharp and acute pain occurs in the back of the head, crown area, temples, eyes and frontal lobes.
Pituitary apoplexy
The pituitary gland is an endocrine gland located in the brain. Apoplexy refers to the effusion of blood into the tissue structures of the pituitary gland.
As a result of this process, a sudden increase in the size of the gland occurs, during which adjacent vessels or nerve endings are compressed. Severe headaches are usually accompanied by blurred vision and confusion. Treatment involves surgery.
Harris migraine neuralgia
This species appears unexpectedly for no apparent reason. Severe attacks are otherwise called tension headache or cluster headache.
The pathology usually affects middle-aged men. Cutting pains usually occur at night. The location is on one side of the face, extending to the temple or eye.
Migraine cephalalgia may be accompanied by increased tearing, sinus congestion (left or right), and redness of the affected facial area.
Pathology of the autonomic nerve ganglia
Pain in the area of the facial structure associated with neuralgia of the branches of the nerves of the skull. The pathology is paroxysmal in nature.
Burning, piercing headaches occur in outbreaks, which tend to shoot through adjacent parts of the head and body. When introduced into deeper structures, pain may radiate to the temple, crown, forehead or ear.
Mental or physical stress
A sharp headache does not necessarily occur due to the presence of pathology. Mental or physical stress is also a cause of cephalalgia. This type of headache is the scourge of office workers or workaholics. Discomfort is easily eliminated by good rest and adherence to the regime.
Taking medications
Severe headaches can be caused by drug abuse. This type of cephalalgia is quite common. Another name for abuse pain.
Often occurs as a result of abandoning the usual painkillers. Sometimes acquired pathology has a complex course and long-term treatment. Therefore, drugs must be selected by a specialist and strictly individually.
Diagnostics
Based on the fact that headache is a polyetiological disease, it should be remembered that when making a diagnosis it is necessary to take into account many factors that may influence its occurrence.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Children who have previously had vision problems must undergo a full examination by an ophthalmologist. It is worth remembering that the results are highly informative after electrocardiography, ultrasound dopography of the vessels of the cervical spine and head, electroencephalogram, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging of the cerebral hemispheres, etc.
In adults, the diagnosis of headaches should be carried out somewhat differently, since the percentage of people suffering from hypertension is steadily increasing every year, and this disease has a direct impact on the occurrence of pain in the head area.
That is why, during a headache attack, it is necessary to measure blood pressure and, with the data obtained, seek advice from a specialist.
Headache massage
Headache massage is a simple and effective remedy for relieving the condition, which can be used independently.
The main methods used to identify the etiology of headaches are:
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the head and cervical regions is performed to exclude lesions of the lobes of the brain and blood vessels in these regions.
- Angiography is a method for studying the patency and condition of the vessels of the head and neck. It is often prescribed to exclude the occurrence of aneurysms, the design of blood vessels and anomalies in their structure. This study plays the greatest diagnostic role in people who experience severe pain during physical activity.
- X-rays and computed tomography are performed extremely rarely, as they have little information content and cannot fully reflect the processes occurring inside the cerebral hemispheres.
- By conducting a general and biochemical blood test, you can find out about the presence of chronic infectious processes, chronic inflammatory diseases, which can be the cause of constant headaches.
The occurrence of a headache is not always a sign of a disease of the cranial organs; in some cases, these symptoms occur when other systems are affected. That is why it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound of the internal organs, which can provide comprehensive information about the condition of the internal organs.
An electroencephalogram can provide information about brain function.
When conducting physical and instrumental examination methods, it is necessary to exclude all dental pathologies, ENT diseases, diseases of the organs of vision and blood vessels of the fundus.
Only after a detailed examination of the patient and identification of the cause of the headaches can an individual course of treatment be prescribed that will help eliminate the symptoms that have arisen.
How to get rid of cutting pain in the head?
A number of comprehensive measures will help eliminate acute and severe headaches:
- taking painkillers prescribed by a doctor;
- in case of stress, it is recommended to take a herbal medicine, for example, valerian or motherwort;
- Regular filtered water will help ease the pain; adding lemon increases the effect by an order of magnitude;
- various relaxation techniques help relieve pain;
- massage of certain points of the head or body, for example, the second metacarpal bone, located between the thumb and index finger;
- compliance with preventive measures.
If the attacks are constant, self-treatment at home will not provide the proper effect and relief. It is necessary to undergo a detailed medical examination.
Brain examination
For an initial appointment, you should contact a therapist or neurologist. The doctor will conduct a survey, give a referral to other specialists, as well as to undergo a brain examination:
- laboratory tests (blood, urine);
- MRI or CT (tomography of brain structures);
- EEG (electroencephalography) to check brain activity;
- Ultrasound for examination of blood vessels;
- REG to identify pathologies of the cervical spine and skull bones;
- fundus examination.
After identifying the cause of headache, the doctor prescribes a course of competent treatment with a long-lasting therapeutic effect.
First aid
First aid measures at home are as follows:
- taking medications or folk remedies;
- drinking plenty of water or herbal decoction;
- taking a contrast shower or a warm, relaxing bath;
- provide yourself with isolation from light or noise, lie down on a flat surface and rest;
- Hot lotions on painful areas or, on the contrary, cold compresses (for example, an ice pack) help relieve the condition;
- use of massage and relaxation techniques.
Treatment with folk remedies
Many people prefer to use folk natural remedies rather than chemical ones. Apple recipe If you have a sudden morning attack, it is recommended to eat a slice of apple sprinkled with salt. At the same time, drink plenty of warm water. The painful condition will gradually subside. Mint recipe Brew peppermint or dried lemon balm (1 tbsp) with a glass of boiling water, close the lid and let it brew for a while. Next, you need to strain the broth, adding a spoonful of honey. This is an excellent proven remedy for severe pain in the head.
Fast acting tablets
To get rid of severe acute pain in the head of a domestic nature, provoked by external factors, there are a lot of remedies that can be bought without a prescription.
| Name | Reception scheme |
| Paracetamol (Panadol, Efferalgan) | Take 1-2 tablets. 3 times a day |
| Analgin | Recommended dosage: tablets or intravenously, 1 pc. 3-4 times a day |
| Nalgesin (naproxen) | 1 capsule until pain is relieved |
Treatment
Therapeutic measures for shooting pain in the head depend, first of all, on the causes that provoke it. It should be remembered that any pathology can be treated more quickly if it is identified and treated at an early stage of development.
Unfortunately, there are also diseases that cannot yet be completely cured. One of them is migraine. The attack can only be alleviated, and not every painkiller is suitable in this case. The most effective during a migraine attack are pharmaceutical drugs from the triptan group (Zomig, amigrenin, antimigraine, imigran, rapimed, sumatriptan, relaxax, trimigren, and so on). After taking the pill, it is advisable to lie down and be in complete silence and peace for at least some time, also eliminating bright light.
In order for lumbago to appear less frequently, the influence of harmful factors should be minimized. In the case of migraines, these are overexertion, stress, overwork, alcohol abuse, smoking, uncontrolled use of pharmaceutical drugs, dietary supplements, and others.
Neuralgia requires other therapeutic measures. Most often, anticonvulsant drugs are used: muscle relaxants, vitamin complexes, including all vitamins from the B group. For topical use, ointments that have a warming effect are prescribed.
You can reduce the risk of this disease and, accordingly, eliminate pain in the head in the form of lumbago by constantly monitoring the strengthening of the immune system, preventing injuries and hypothermia. Moderate exercise, food with a high content of vitamins and microelements, giving up bad habits, and daily walks in the fresh air are very useful in this regard.
When attacks of shooting pain caused by a bacterial infection occur, complex treatment is usually prescribed. Anti-inflammatory pharmacological drugs, painkillers, and injections of vitamins, mainly B-group, are used. In some cases, if the process is particularly severe, antibiotics are prescribed. The use of physiotherapy methods is not excluded.
If the cause of the pain syndrome called cranialgia is osteochondrosis, then during the period of exacerbation it is suggested to use painkillers. If their effect is insufficient, anti-inflammatory drugs (non-steroidal) may be prescribed. You can relieve and reduce pain symptoms by using a pepper patch or an ointment with a warming effect.
Physiotherapy procedures, which are prescribed on an individual basis, are very effective for osteochondrosis and the resulting lumbago in the head area. This can be electrotherapy, ultra-high frequency or magnetic therapy.
In addition to these procedures, massage, manual therapy, and therapeutic exercises are prescribed.
At the first manifestations of cranialgia, you should immediately seek professional medical advice and help. If the pathology takes on an advanced, chronic format, then it will be much more difficult to get rid of it. A progressive disease can even lead to disability over time.
Only by determining the cause of a sharp shooting pain in the head, undergoing an appropriate examination, and then treatment prescribed by a doctor, can serious complications be avoided.
How to prevent pain
Seizures can be prevented if you follow simple rules and recommendations from doctors:
- Introduce regular sports activities into your life, such as yoga, aerobics, running or brisk walking.
- Walking in the park area in the fresh air will provide the necessary amount of oxygen.
- At work, try to take at least a minute break every hour.
- Make it a rule to drink two liters of plain water daily, this will relieve the body from dehydration.
- It is recommended to stop drinking large amounts of coffee, eliminate alcohol and nicotine.
- A properly selected diet enriched with vitamins, iron and other beneficial microelements will help avoid irritation of pain receptors in the head.
- Following a daily routine, sleeping patterns and eating patterns will greatly facilitate the task of preventing severe headaches.
On a note
Those who suffer from frequent headaches should not indulge in the following products:
- Cheese, smoked herring, chicken liver, red wine, nuts - they contain the headache-provoking amino acid tyramine;
- Chocolate – it contains the headache-causing substance phenylethylamine;
- Processed foods, especially those richly flavored with spices and sauces from Asian and Chinese cuisine (such as sauerkraut). They also contain another headache provocateur – monosodoglutamate, which is sometimes hidden under the pseudonym “hydrolyzed vegetable protein”. There is even a special term for headaches caused by oriental culinary exoticism - “Chinese restaurant syndrome”;
- Bacon, sausages, salami and other sausages. To give them a beautiful pink tint, nitrites, which are undesirable for headaches, are added to them. They are especially abundant in cheap sausages, which are usually found in street hot dogs. For lovers of this type of fast food, there is a diagnosis - “headache from walking dogs”;
- Sugar substitutes, which contain aspartame and sweetener E 961 and are purchased by people suffering from diabetes, as well as adherents of low-calorie diets. Aspartame is also often found in chewing gum, low-calorie desserts, soda, candy, yogurt, vitamins and cough lozenges.
| Drugs | ||
| Non-narcotic analgesics | Medicines for the prevention and treatment of migraine. Triptans | Other antimigraine drugs |
Remember, self-medication is life-threatening; consult a doctor for advice on the use of any medications.
Buy the printed version of the directory at kiosks in your city or order it from the editorial office by phone or email [email protected] with the mark PM (indicate your full name, postal address and telephone number in the letter).
Myositis of the cervical muscles
A sharp headache with this disease most often manifests itself in the form of pinpoint unpleasant tingling sensations spreading to the neck, forearm and chest. The disease is accompanied by the presence of an inflammatory process in the neck muscles and their thickening, as well as disturbances in the metabolic processes of the body.
The headache occurs mainly when you touch it. A complete absence of pain can be observed at rest, in a supine position.
The causes and pathogenesis of myositis have not been fully studied. The catalyst can be emotional stress, which is accompanied by severe muscle tension. Both young and elderly people can be affected by the disease.
What can cause the disease
Shooting headaches often occur in people with pathology of the cervical spine. For example, osteochondrosis with this disease has a huge risk of feeling a sensation of shooting in the neck against the background of pinched blood vessels and arteries. Where there is most curvature of the spine, such disorders are sometimes the main place for pain localization.
Migraine
This form of the disease also contributes to the development of shooting pain in the head. This is especially true for those who often experience long-term migraine syndrome. Women who have already had similar experiences in their family are more susceptible to this. Often they are the ones who are forced to suffer from unilateral neurological pain in the head.
Intracranial pressure
You can talk about this ailment with shooting pain if the sick person has ailments in the temporal region. Its strength can be different, it all depends on the level of influence of the cerebrospinal fluid on the structures of the brain. Sometimes this can cause the patient to exhibit symptoms of seizures, dizziness, nausea and a gag reflex.
Ear infection
The cause of the shooting pain in the head is quite reasonable, perhaps purulent otitis media or sinusitis. The fact is that any inflammatory manifestations in the middle ear subsequently, if the disease is not treated on time, can lead to a large accumulation of purulent formations. Thereby causing irritation of nerve receptors in a person suffering from otitis media or sinusitis, provoking a shooting headache.
To prevent this in any form of otolaryngological diseases, it is important to be treated under medical supervision. Drink antibacterial drugs aimed at eliminating pus, attend physiotherapeutic procedures in order to get rid of the inflammatory process
Trigeminal neuralgia
If, after an injury, a person’s ternary nerve is damaged, then as a result he may experience shooting pains in the head, photophobia, lacrimation, and changes in taste sensations. In this case, as a rule, anticonvulsants are prescribed to eliminate the disease. Occasionally, surgical intervention may be necessary; it is necessary in case of inserting a special plate into the area of squeezing the blood vessels.
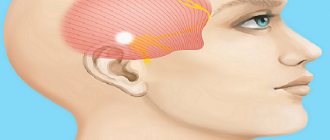
Arthritis
The symptoms of arthritis are somewhat similar to those of a migraine. However, there is a difference; arthritis; its main cause is the pathology of the temporomandibular joint. Otherwise, it is also called temporal arteritis, which occurs more often among older people. The consequence of this disease is an inflammatory process and aneurysm of the carotid artery; more often, it is this cause that causes discomfort in the temporal and occipital regions of the brain.