One of the most common complaints presented by patients to a specialist during a consultation is a complaint of a headache of one location or another, for example, on the right side above the ear.
As a rule, a person strives to get rid of discomfort on the right or left side of the head by taking a pharmaceutical remedy and forget about the unpleasant situation. But, if a headache behind the ear recurs more than 2-3 times over the last month, and gets worse when tilting the head, this is a reason to be wary and consult a specialist with a comprehensive diagnostic examination.
Many pathologies have become significantly “younger” and complaints that they have a headache on the right or left are made by children 7-10 years old, sometimes the pain radiates behind the ear. It is not recommended to brush aside such complaints from your child - many diseases make themselves felt precisely through pain in the head, and other symptoms appear later.
Types and main causes of pain behind the ears
Pain behind the ears is a symptom that requires extensive examination of the patient, establishing the cause and selecting treatment.
There are 2 types of pain behind the ears:
1) pain arising from direct damage to the organ of hearing; 2) headaches not associated with pathology of the hearing organ.
Pain behind the ears is aching in nature and persistent, can intensify with changes in body position, and be accompanied by hyperthermia, hearing loss, and asthenia of the patient.
Ear pain can be due to various reasons. Among them, the most common are:
- Arterial hypertension;
- Arterial hypotension;
- Cephalgia due to trauma;
- Hearing diseases;
- Tumors of the brain;
- Organic brain damage;
- Headaches of various origins (migraine, tension headache);
- Cephalgia due to intoxication.
Important information
Traumatic brain injuries, in which cephalalgia develops with irradiation behind the right or left ear, are often accompanied by hematoma formation and bleeding. Such injuries require immediate qualified medical care.
For ear diseases
1. Otitis is an inflammatory disease in the ear, which affects the outer, middle and inner sections. Otitis is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, sharp pain in the ear and behind the ear, radiating to the upper jaw, neck, and eyes. Later, purulent discharge appears from the external auditory canal. The inflammatory process stops within a week.
2.Mastoiditis – inflammation of the cave and cells of the mastoid process of the temporal bone. The mastoid process is anatomically located behind the ear. The most common form is secondary mastoiditis, which develops as a result of infection from the middle ear.
Symptoms of mastoiditis include:
- constant headache;
- pain behind the ear;
- otalgia (pain directly in the ear);
- hyperthermia;
- hyperemia of the skin;
- swelling behind the ear (in the mastoid area);
- purulent discharge from the external auditory canal.
3. Labyrinthitis is an inflammatory process in the inner ear. With labyrinthitis, the patient experiences dizziness, nausea, vomiting, tinnitus, and unilateral pain behind the ear. The disease is also characterized by pain, hearing loss, and even its complete loss in the diffuse type of labyrinthitis.
4. Otomycosis is a disease of the outer part of the ear. The causative agent is fungi (aspergillus, actinomycetes). The main symptoms of otomycosis are pain in the ear, decreased hearing, itching, swelling, discharge from the external auditory canal, and ear congestion. The disease develops when infected water gets into the ear cavity or during long-term antibacterial therapy in the form of ear drops.
5. Meniere's disease is a disease of the inner ear, which is characterized by an increase in the volume of endolymph and increased endolymphatic pressure. This pathology is characterized by tinnitus, dizziness, vomiting, development of deafness, and pain.
Other diseases
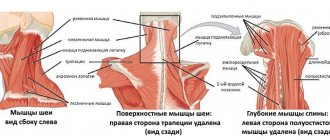
1. Cervical myositis is an inflammatory lesion of the skeletal muscles of the neck. The main symptom is local muscle pain. With cervical myositis, pain can also be localized behind the ears and is caused by inflammation of the muscle fibers of the neck and back of the head. The malaise is absent at rest and occurs with sudden turns of the head and neck, or a sudden change in body position. Cervical myositis is serious and requires medical intervention due to the possible involvement of the muscles of the larynx, esophagus, respiratory muscles and pharynx.
2. Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is a disease characterized by dystrophic changes in articular cartilage.
With osteochondrosis, compression of the neurovascular trunks occurs, which leads to insufficient supply of oxygen and nutrients to the brain cells through the blood. This phenomenon is referred to as “hypoxia” and causes headaches behind the ears and in the back of the head. Pain due to osteochondrosis can also be localized on the back of the neck and in the occipital region of the skull, radiating behind the ears and to the temporal region. In addition to the symptoms listed above, there is noise in the head, dizziness, and pain in the upper extremities.
3. Trigeminal neuralgia is a syndrome characterized by short-term attacks of intense and burning pain in the areas of innervation of the trigeminal nerve. Localization is determined by the branches of the nerve, each of which has different zones of innervation. The pain is one-sided. With trigeminal neuralgia, it can be localized along the ear and in the parotid region, and also spread to the ear itself, the upper and lower jaws, and the eyes. The localization of pain is individual and is determined by the location of the branches of the trigeminal nerve in each individual person.
4. Tumor diseases of the brain. Oncology can be unilaterally localized and cause pain behind the ear on the left or right, depending on the location of the lesion.
Rare causes
1.Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges of the brain. The course of meningitis is characterized by the occurrence of neurological and cerebral symptoms. With this disease, cephalalgia can also be localized behind the ears. Differential diagnosis is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis.
2. Lymphadenitis is an enlargement of the lymph nodes, which occurs as a complication of infectious diseases. Lymphadenitis can occur with or without the formation of purulent contents. With inflammation of the parotid lymph nodes, a headache often occurs in the parotid region, radiating to the ear. The skin over the lymph node is hyperemic and swollen.
3.Arthritis of the temporomandibular joint - inflammation of the joint connecting the lower jaw and the temporal bone. With this disease, patients, in addition to moderate pain in the parotid region, complain of joint stiffness and difficulty chewing.
4. Migraine is a form of headache. Cephalgia, as a rule, has a one-sided localization, is accompanied by nausea, increased sensitivity to external stimuli, vomiting, and is preceded by a so-called aura. With a migraine, the head may hurt in the temporal, parotid, occipital and parietal regions.
5. Oral diseases (toothache) - for example, caries. If left untreated, the inflammatory process during dental caries of the upper jaw can spread to deeper tissues and cause pain in the ear area and behind the ear.
Types of pain
Cephalgia manifests itself in the following types:
- Tension pain. A person perceives this type of pain as compression of the head, both on both sides and on one. Subjectively, it seems as if the eyes and forehead are trying to escape from the head. Typically, an attack of tension pain lasts up to half an hour.
- Migraine is a throbbing pain in the head on the right side, but the location of pain in migraine is not a defining feature. Cephalalgia extends to the eyes, mouth, jaws and neck. A migraine attack can last several hours.
- Cluster pain. This type is characterized by burning and stabbing pain on one side of the face. It is perceived as a sharp headache in the right hemisphere. Accompanied by redness and sweating on the painful side. Cluster pain is combined with nasal congestion and lacrimation. The cluster type of cephalgia is manifested by attacks that last from 15 minutes to several hours.
- Pain in the back of the head on the right may occur after drinking coffee. A large amount of caffeine affects the tone of blood vessels in the brain - this causes pain. Cephalgia can also occur with abrupt withdrawal of the drink. For example, if a person constantly drinks coffee and does not drink it one day, he risks getting headaches.
- A headache on the back of the head on the right is one of the symptoms of hypertension or high blood pressure. Most often, cephalalgia with hypertension is manifested by throbbing pain. Unpleasant sensations are accompanied by numbness, blurred vision, low performance and nosebleeds.
- Rebound pain. This type of cephalalgia appears after taking medications as a side effect. A paradoxical phenomenon: painful sensations can occur with long-term use of painkillers. The way out of the situation is to discontinue the drug, which causes a side effect.
- Dull and aching pain. Occurs with tumors in the brain. The tumor mechanically compresses areas of the brain and skull, thereby affecting the nerve endings, which leads to pain. Typically, such cephalgia appears in the morning and is accompanied by vomiting.
- Costen's syndrome. Some infectious and rheumatic diseases lead to damage to the maxillofacial joint, which is accompanied by pain on the right side. Also hurts: ear, sinus, tongue.
What is the danger?
The unilateral appearance of pain behind the ear on the left, regardless of its frequency, is alarming and a reason to seek specialized medical help. If cephalgia is accompanied by elevated body temperature and is not relieved by non-narcotic analgesics, this may indicate serious organic brain damage and requires immediate examination and treatment. The danger lies in the high risk of complications such as meningitis, cerebral edema, and cerebral hemorrhage.
Lack of treatment can lead to complications, including complete loss of hearing by the patient.
What does this give off in your head?
Typically, throbbing pain in the ear appears due to the presence of inflammatory processes. Often this is inflammation of the internal sections or the Eustachian tube.
REFERENCE. In medical science, this condition is called tinnitus.
Despite the fact that the pulsation is generally not so strong, a person still suffers from it, sleep is disturbed, attention decreases, and irritability appears.
You should definitely see a doctor, as sometimes this ear pulsation can be associated with a malfunction of the heart muscle, and this condition requires immediate treatment.
Ripple can be observed in one of the ears, or in both ears at once. It is a rhythmic noise that corresponds to the beat of the pulse.
Noise in the ear leads to hearing loss. With its duration, nervous system disorders begin. This is manifested by an aggressive or depressed state of a person.
Diagnostics
A patient who complains of pain behind the ears needs a thorough examination, since the causes of such pain are varied and also have different treatment principles.
Helpful information
To establish an accurate diagnosis, it is extremely important for the doctor to find out whether the patient has other complaints and symptoms other than pain behind the ears. The resulting picture allows us to combine all the symptoms into a single symptom complex and establish the disease.
Diagnostics is based on the following data:
- Patient complaints;
- Medical history (neck, head injuries);
- Physical examination (examination, determination of blood pressure);
- Laboratory tests;
- Instrumental diagnostic methods;
- Consultation with doctors of related specialties (general practitioner, otolaryngologist, neurologist).
Laboratory diagnostic methods include:
- A blood test (biochemical, general) is carried out to exclude pathologies of other organs;
- Analysis of cultures from purulent exudate is necessary for specific antibacterial therapy aimed at a specific pathogen.
Instrumental methods include:
- Ultrasound examination of neck vessels;
- Study of cerebral vessels;
- Magnetic resonance imaging/computed tomography to identify pathological neoplasms;
- X-ray examination (less informative);
- Audiometry is a method that allows you to measure hearing acuity and the sensitivity of the hearing aid to sounds of different frequencies. This study is carried out by an audiologist;
- Electroencephalogram;
- Otoscopy is a method in which the external auditory canal is examined, and the outer ear is also cleaned;
What to do
Pulsation in the ears is just a symptom of some disease.
Therefore, it is impossible to cure only this condition. It is necessary to identify the underlying disease.
Depending on the type of pathology, appropriate treatment will be prescribed:
- For osteochondrosis, analgesics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, and sometimes anticonvulsants are prescribed. It is important to take medications to lower blood pressure to prevent blood clots from appearing in the vessels, undergo physical therapy, etc.
- If you have a wax plug in your ear, you should go to an ENT doctor for treatment, who will rinse your ear with a furatsilin solution or saline solution.
- Diseases of the cerebral vessels will require complex and long-term treatment. The therapy is based on the use of nootropics and medications that improve blood circulation in the vessels of the brain and metabolism.
- It happens that pulsation in the ear appears due to overwork. The doctor may prescribe sedatives, breathing exercises, and strict alternation of work and rest. If there is a stressful cause, then a psychotherapist will deal with it.
- Ear diseases are usually associated with inflammation, so they often need to be treated with antibiotics.
ATTENTION. Often, as a conclusion about the cause of pulsation in the ear, the doctor indicates vegetative-vascular dystonia. But in medicine there is no such diagnosis. Therefore, you should contact a qualified specialist to determine the exact disease and only then begin treatment.
Treatment
What to do if you have a headache behind your ear on the left or right?
Drug therapy
a) symptomatic (painkillers, infusion - NSAIDs);
b) etiopathogenetic (antibacterial drugs, antiviral drugs). Antibacterial therapy is prescribed in several stages - first, broad-spectrum drugs are used (for example, third-generation cephalosporin - ceftriaxone), and after identifying the pathogen, more selective antibiotics are used to suppress the microorganisms that caused the infection.
c) immunomodulatory therapy to increase the body's defenses and strengthen the immune system.
d) Use locally of ointments and gels to relieve signs of inflammation and achieve a distracting effect;
Physiotherapy
a) exercise therapy;
b) Massage;
c) Magnetic therapy.
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment of pain behind the ear on the left is carried out in the presence of surgical pathology:
- Neurosurgical diseases (tumors);
- Head injuries (traumatic brain injury);
- Injuries of the cervical spine and neck;
- Diseases of the mastoid process (mastoiditis);
- Inflammatory diseases of the superficial tissues in the ear area, giving the clinical picture of headaches behind the ear;
- Abscesses and boils must be opened and drained;
- Myringotomy is a surgical intervention performed for mastoiditis;
- Mastoidectomy if treatment is ineffective and there is a risk of serious complications.
Other treatments
- Vitamin therapy;
- Bed rest, rest for otitis;
- Laser therapy for acute forms of otitis;
ENT pathology
Many diseases of the ENT organs begin with a rise in temperature and local pain, for example, in the ear, in the projection of the sinuses, forehead, purulent discharge joins later:
- Severe headache behind the ear, in the projection of the mastoid process on the affected side - on the right, on the left - with mastoiditis. Characteristically, the intensity of pain increases during night rest hours. The history indicates a previous history of otitis media.
- Boils of the external passage of the auricle also manifest themselves with intense pain. The entire right or left half of the skull hurts - directly depending on the location of the boil; when bending to the side, awkward movement, touching - the pain intensifies significantly. After opening the purulent cavity, the symptoms decrease.
- External and otitis media can occur in a person at any age. Children especially suffer - the slightest hypothermia or prolonged runny nose lead to inflammatory manifestations in the ear area. Patients complain that literally the entire half of the skull hurts - shooting in the ear, making it impossible to eat, sleep, or perform work duties. Accompanied by a significant rise in temperature.
- Every day you can feel pain in the ear area and with such a pathology as dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint. The unpleasant sensations are dull, aching in nature, and intensify with movements in the lower jaw, tilting the head, and physical stress on the neck.
After carrying out diagnostic procedures, the ENT specialist will recommend a number of appropriate treatment measures.
Prevention
Prevention of pain behind the ears can be divided into primary and secondary. The most widespread is secondary prevention aimed at eliminating recurrences of such pain. Secondary prevention is individual, since such pain in each person, as a rule, has its own nature of origin. Primary prevention involves the need for annual medical examinations for the purpose of early diagnosis and prevention of possible diseases.
The main methods of prevention include the following:
- Ear hygiene (ears, ear canals);
- Earwax removal;
- Oral hygiene;
- Ventilation of premises at home and at work;
- Limiting the use of headphones if you already have hearing diseases;
- Compliance with the work and rest regime;
- Regular screening of the main indicators of normal functioning of the body (blood pressure, blood glucose levels, cholesterol);
- Timely seeking medical help also helps prevent the development of pain behind the ears thanks to timely initiation of antibacterial therapy;
- Rational balanced diet;
- In the cold season - dress warmly, avoid drafts and air conditioning;
- Walking in the fresh air, doing physical activity;
- Timely treatment of colds.
Timely treatment is the key to success
A headache in the right hemisphere of the brain causes considerable discomfort, and there are reasons for this - from injuries to the crown of the head to sudden overexertion. This problem can develop into an even bigger one, since any ailment is a symptom of one of many diseases.
Ignoring the problem means an even greater burden on the body; it is better to immediately consult a doctor for timely help. Various bad factors influence the development of diseases of the human nervous system:
- constant stress;
- all kinds of chronic diseases;
- stressful and sedentary work;
- environmental contamination.
A negligent attitude towards a headache that appears on the right side is unacceptable. Hoping for self-healing or wanting to treat yourself, which you shouldn’t do, will only complicate the situation. It is important to check and confirm the presence of the disease with a specialist and make a diagnosis.
Main types of treatment:
- physiotherapy;
- manual therapy;
- acupuncture;
- drug treatment;
- physiotherapy;
- methods of extracorporeal hemocorrection;
- folk remedies.
First aid at home
If there is discomfort in the right temporal part and on the right side of the back of the head, pay attention to folk remedies:
- strong hot teas;
- using essential oils when taking a bath or going to bed;
- applying cold compresses with mint and lemon oils;
- if the right hemisphere of your head hurts, learn acupressure, take a lying position, ventilate the room.
In addition to folk remedies, use medication in the form of tablets:
- citramon;
- Nurofen;
- pentalgin;
- analgin;
- paracetamol.
Or injections:
- diclofenac;
- drotaverine;
- baralgin;
- ketarol
Scheduled visits to the doctor
If you experience constant pain with indefinite intervals between them, consult a doctor and do it regularly. It is necessary to undergo an examination every time as prescribed by a doctor.
Doctors believe that migraines should not be tolerated, therefore, if tingling in the head recurs more than twice a week, obtaining a proper medical examination is mandatory.
During pain on the right, in the back of the head or at the top, you should visit a doctor, it is better to do this in the morning.