general information
Despite the fact that a newly born baby is a defenseless creature, it already has more than seventy-five unconditioned reflexes. It is thanks to these mechanisms that a person survives and adapts to new conditions.
Each of the innate reflexes is relevant in the first three to five months. After this period, they gradually fade away, giving way to conditioned reflexes.
Every parent should know what reflexes their children have. This will help them prevent the development of serious illness.
The proboscis reflex, like the sucking one, is associated with the most important process necessary for the full development of personality - the absorption of food.
Detection of pathologies in a child
Many pediatricians believe that normally, the pulling of the lips into a tube (proboscis reflex) should disappear by the third month of life. If such a reaction is present in further development, it may indicate the presence of some lesions in the brain. Pathology may also be indicated by the asymmetry of the lips, elongated into a tube, as well as the complete absence of the proboscis reflex in the first months of life.
It should be noted that in healthy children up to one year, sometimes up to three years, this reflex was observed. In such cases, it was characterized as a protective-adaptive reaction.
Important reflexes
The main reflexes that provide a baby with a comfortable existence in the first months of his life in new conditions include:
- Sucking reflex.
- Swallowing reflex.
- Proboscis reflex.
- Ref. Babkina.
- Search refl-s.
- Upper protective refl.
In newborns
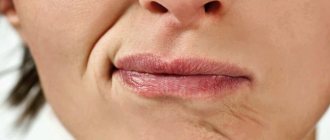
The proboscis reflex in newborns is characterized by a specific protrusion of the child’s lips. In response to the stimulus, the baby’s lips take on a specific “tube” or “proboscis” shape. This mechanism is caused by a quick, sharp touch to the actual areas of the fingers of the parent or doctor.
The proboscis reflex in newborns is caused by the automatic contraction of the orbicularis oris muscle of the newborn. The orbicularis muscle is a key muscle called the sucker.
According to experts, the proboscis reflex is relevant in the first two to three months of a child’s life, after which it fades. There is also an opinion that normally the proboscis reflex in newborns can occur until the baby reaches the age of two and a half to three years.
In this case, the mechanism is presented in the form of a protective-adaptive reaction.
In adults
The proboscis reflex in adults indicates deformation of the structures of the cerebral cortex. If such a symptom is present, the researcher may suspect:
- Traumatic brain injury.
- Stroke.
- Encephalopathy.
- Bulbar syndrome (relevant in case of damage to the tenth pair of cranial nerves).
The proboscis reflex in adults is the most common sign of oral automatism. Also, the proboscis reflex in adults can be detected with diagnosed pseudobulbar palsy. Sometimes this symptom is detected with diffuse lesions of the brain. In addition, the risk group includes mentally ill individuals and people suffering from neuropathic disorders. To avoid negative consequences, it is recommended to undergo regular examinations in a neurologist’s office. Particular attention should be paid to this mechanism.
The presence of this mechanism does not always indicate the presence of an abnormal process in the body.
A moderately pronounced proboscis reflex in adults is often caused by older people who care about their health.
Diagnostic purposes
The study of the proboscis reflex has the following goals:
- Determination of development norms. The proboscis reflex manifests itself in a newborn from the first day of life and indicates the fullness of its development. Accordingly, by testing this reflex, the doctor can conclude that the baby complies with physiological standards.
- Assessment of the neurological status of the newborn. If certain injuries occur during childbirth, the brain stem may be damaged. In such babies, unconditioned reflexes are impaired. In most cases, the proboscis symptom begins to appear by the seventh day of life, and before that it is weakly expressed or absent altogether. Based on the results of diagnosing this reflex in combination with other indicators, the neurologist assesses the child’s neurological status. What is significant in this case is the duration of the absence of manifestation of the reflex and its intensity.
- Determination of pathologies in a child. Normally, the reaction to touch in the form of pulling the lips into the proboscis disappears after the second or third month of life. If this reaction is present in the fourth month or later, this may be evidence of the presence of certain organic brain lesions. Pathology may also be indicated by the presence of a certain asymmetry of the lips when pulled into a tube or the complete absence of this reaction in the first 2-3 months of life. It should also be noted that cases of persistence of this reflex up to one year, and sometimes up to two or three years, as a protective-adaptive reaction, were also observed in healthy children.
- Detection of pathologies in adulthood. With normal development, the absence of pathologies and developmental deviations, it is not typical for an adult to display infantile reflexes, since there is no need for them. On neurological examination, a positive proboscis reflex in adults may raise suspicion for stroke, encephalopathy, traumatic brain injury, or bulbar syndrome. The reaction can also be diagnosed with pseudobulbar palsy or indicate diffuse brain damage. In healthy people, this reflex can be moderately expressed in old age.
How is it called
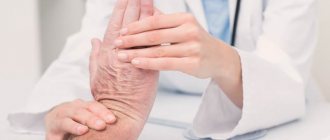
The proboscis reflex can be detected using a special neurological instrument. A specialist who wants to identify this mechanism gently taps the relevant area with a hammer. This zone is considered to be the upper lip of the subject. The area is at the level of the gums.
The response should be considered a protrusion of the lip. In some cases, the person being examined protrudes both lips. In this case, the shape of the lips takes on a characteristic shape. This is why the reflex was called proboscis.
Researchers note that the intensity of the reaction can vary greatly. Sometimes it persists for a certain time.
Sometimes, simultaneously with the protrusion of the lips into the proboscis, the lower jaw also moves. Specific movements similar to the act of swallowing are often provoked.
This mechanism is recognized by medical experts as pathological.
The presence of the proboscis reflex is noted in the presence of pathological foci on the opposite side of the posterior part of the frontal lobe.
Many researchers working on this issue, including Dr. S. Karchikyan, believe that the presence of this mechanism may be due to a high level of idiomuscular mechanical excitability. The human orbicularis oris muscle is at risk.
In addition to V. Bekhterev and S. Karchikyan, this issue was studied in detail by A. Epstein. The main theses were put forward in the thirties of the twentieth century.
Important to remember
Using important reflexes, including the proboscis reflex in newborns, the doctor checks how the baby’s central nervous system works. It is important to remember that the absence of vital reflexes may indicate the presence of a serious pathological process. This is also evidenced by the long “life” of a particular mechanism.
Diagnostic procedure
A study of the proboscis reflex is carried out by a neurologist when admitting a patient or when checking the reactions of a newborn.
Also, this procedure can be carried out by the parents of the baby if they have some concern about the child’s health. After reading the instructions below in detail, even a non-specialist will be able to diagnose. To diagnose, do the following:
- Prepare the room. The temperature in the room should be about 25-27 degrees. The lighting should be bright, but not irritating.
- Place the baby on a surface that is soft but not sagging. The child should be fed 1-2 hours before the procedure.
- Visually mark the area of the upper lip at the level of the gums. Make several light, quick taps with your index finger on this area. The baby's lips should extend like a proboscis. Often, this reaction can be accompanied by stretching of the lower jaw and swallowing movements.
Diagnostics: Children who are already able to follow the doctor's instructions are tested in the same way as adults. Neurologist checks the proboscis
reflex using a special hammer.
The patient is asked to close his eyes and place his index finger on his upper lip, which the doctor taps. There should be no reaction to these actions. If there is a reaction, the neurologist will suspect certain brain pathologies. This reflex can be observed with focal damage to the posterior part of the frontal lobe of the brain.
The proboscis reflex is one of the important indicators of the health of a newborn. It is very important to identify pathologies in a child’s development in a timely manner, and diagnosing this particular reaction can help. Sometimes, reflexes in newborns can be delayed, which can be due to a number of reasons, including birth injuries.
It must be remembered that timely detection of pathology increases the chances of successful rehabilitation in both children and adults.
The proboscis reflex is the stretching of the lips into a characteristic tube. In some cases, sucking movements are provoked. The proboscis reflex can be provoked by touching or delicate tapping of neurological instruments on the lips of the subject.
The proboscis reflex was first described by the great Russian neurologist V. Bekhterev at the beginning of the twentieth century.
When to sound the alarm bell
In some cases, important mechanisms in a newborn are turned on at the wrong time or appear very weakly. Sometimes the anomaly can be caused by injury resulting from a difficult delivery. It also happens that the “inhibition” of reflexes is associated with an individual reaction to a particular drug.
The weakness of the proboscis and other oral mechanisms is usually associated with the fact that the child born was premature or suffers from a mild degree of asphyxia.
If the baby is full, there is no need to sound the alarm, since pronounced oral mechanisms appear when he experiences a feeling of hunger.
Pathology is the complete absence of reactions. This is a significant reason for immediate rehabilitation. This manipulation should only be carried out by qualified personnel.
There are several reasons for this anomaly:
- intrauterine pathologies;
- umbilical cord strangulation;
- birth injuries.
It is important to remember that the reserves of a growing organism are practically inexhaustible. Most often, the child recovers quickly and even surpasses his peers in development.
Assessment of the proboscis reflex in newborns and other important reflexes is carried out in a well-lit and warm room. The surface should not be too soft and not too hard. The subject must be rested, well-slept and well-fed.
Rate this article:
(No votes yet)
Loading...
Related posts:
- Basic examples, signs and features of the classification of unconditioned reflexes
- Conditioned reflex: mechanisms of formation and classification of acquired reactions
- The main features of the manifestation of obligatory reflexes in newborns
- The main features of the manifestation of the Moro reflex in newborns
- What is included in the classification of reflexes?
- What are the consequences of a violation of the knee reflex of vital functions?
Diagnostics
The proboscis reflex is examined by a neurologist at an appointment with an adult patient or when checking the physiological development of a newborn or an infant in the first year of life. The study has several stages, after studying which, each parent will be able to independently check the presence of a proboscis reflex in their own child, in cases where there are any suspicions or concerns.
So, for diagnostics you should do the following:
- First you need to prepare the room in which the research will be conducted.
- A comfortable temperature should be between 25 and 27 degrees.
- Room lighting should be provided in such a way that there is light in the room, but there is no bright irritating light.
- The surface on which the baby will be placed should be pleasant, soft, but at the same time not sag.
- The child must be prepared. You need to feed him 1-2 hours before the procedure. He should be cheerful, but at the same time calm.
- Visually determine the area of the upper lip that you will need to touch.
- Make a few light tapping movements, but do not use any force.
- With a normal reaction, the baby's sponges should take the shape of a proboscis or tube. The reaction may be accompanied by simultaneous thrusting of the lower jaw forward, as well as swallowing movements.
In children who can already follow the doctor’s instructions, diagnostics are carried out like adults, that is, using a special neurological hammer. The doctor asks the patient to close his eyes, then place his index finger on his upper lip. The doctor taps it lightly with a hammer. There should be no reaction to these actions. If there is one, then the neurologist may suspect some pathology in the activity of the brain. The proboscis reflex may be a manifestation of focal lesions in the posterior frontal lobe of the brain.
Clinical manifestations
The key symptom of the disease is tics – motor and vocal. Motor tics are divided into simple and complex. Simple ones are short-lived, often specific to one muscle group, and stop quickly. Most often they can be seen on the facial muscle group:
- frequent blinking;
- grimaces on the face;
- elongated lips;
- loud inhalations through the nose;
- shoulder twitching;
- involuntary head movements;
- retraction of the abdominal muscles;
- frowning;
- teeth chattering.
Complex tics manifest themselves in some grimaces, jumping, and involuntary touching of one’s body or other people or surrounding objects. In the presence of accompanying mental or neurological disorders, tics are dangerous for a person - he can involuntarily bang his head against something, bite his lip until it bleeds, or put pressure on the eyeball.
Vocal tics include speech disorders - the pronunciation of meaningless, unnecessary sounds, coughing, mooing, and whistling.
Diagnostic measures
Tourette syndrome is diagnosed if motor and vocal tics are present. Since the genetic etiology of the disease has been determined, its symptoms are observed at an early age, at a time when children cannot independently maintain control over their condition through volitional efforts. This pathology is characterized by several stages of development.
The first stage is manifested by rare tics, with an interval of two minutes. Such manifestations are not very pronounced, they cannot always be seen by strangers, and they do not negatively affect a person’s quality of life. At this stage of lip development, a person does not make a tube as often as, for example, blinking or frowning, while he tries to disguise such manifestations. He can control his condition himself, so treatment is not indicated at this stage.
The second stage is characterized by more frequent tics - from two to four per minute. If a person stretches out his lips like a tube, begins to blink, twists his mouth in a grimace, this already becomes noticeable to others, but he can still control his condition by putting effort into it, trying to stretch his lips. There are no difficulties in communicating with other people, but sometimes the patient feels awkward.
The third stage is characterized by the appearance of five or more tics within one minute. At this stage, both motor and vocal tics appear. A person is not able to control them on his own; this attracts the attention of strangers. Tics are accompanied by strong stretching of the lips, frequent blinking, twisting of the mouth, and incoherent and meaningless sounds.
Such manifestations are often perceived by society as underdevelopment, although the sick person does not lag behind in mental development. The patient becomes complex, withdraws into himself, he finds work that does not involve communicating with people, and it is difficult to drag him out into public places. Such people are indicated for social adaptation and therapy with medications.
The most severe is the fourth stage. The tics do not stop; the person cannot cope with them. At this stage, this condition is often combined with mental disorders.
Features of the development of pathology
If a child puts his lips into a tube, the reason may be thirst or hunger that the newborn is experiencing. But if a child stretches out his lips after he has been fed, this is accompanied by additional symptoms, one may suspect that he has a rare genetic pathology - Tourette syndrome.
This disease, in which a baby stretches out its lips with a tube, was described by the French physician Gilles de la Tourette. This pathology is most often diagnosed in the practice of child psychiatrists, since such a diagnosis is made in early childhood.
The doctor determined that this pathology is more common in boys than in girls. According to the doctor's observations, this disease is genetically determined. But he could not determine the gene that carried it. It has now been established that the pathological mechanism is triggered by dopamine. It is this hormone that triggers the behavioral reactions that are present in Tourette syndrome.