What is MRI of the brain based on?
The diagnostic effect of brain MRI is based on nuclear magnetic resonance. In response to the powerful radiation created by the generator, the hydrogen atomic nuclei contained in the tissues line up along the electromagnetic field lines and begin to vibrate. Each atom becomes like a spinning mini-spinning top, emitting energy waves.
Different structures emit different amounts of energy - some give it out more intensely, while others less so. The difference is recorded by a device that takes pictures (slices) in different projections.
To do this, the patient is placed inside a tomograph in which generators maintain a high-frequency electromagnetic field. Special radio emitters generate pulses, and coils record the energy sent by vibrating atoms.
The resulting slice images are combined into a three-dimensional matrix using a special computer program, in which dark or light unhealthy areas are visualized against a gray background.
Patient reviews
The study received many positive reviews from patients. The diagnosis is painless, the time required for its implementation is no more than 30 minutes, while the information obtained during the study is extremely informative and necessary for making a diagnosis and determining further treatment tactics.
The only disadvantage of the study is its cost. Free procedures are carried out in government institutions on a scheduled basis by appointment, which sometimes lasts for months.
MRI of the brain is an important study necessary to make a final diagnosis of most neurological pathologies and determine the tactics for further patient management.
Diagnosis is painless and non-invasive, but the cost is high. After a conventional scan, additional contrast enhancement is often required.
Advantages of magnetic resonance imaging over other methods
An MRI examination gives results much more accurately than x-rays, echoencephalography (EchoEG), ultrasound and other diagnostic options. It allows you to obtain maximum data about existing tumors, diseases, post-traumatic and post-stroke changes. Unlike CT and X-rays, in this case the body is not irradiated.
Only soft tissues are visualized in the finished images. The bones of the skull are not visible, so they do not interfere with analysis and decoding.
The contrast agent used in MRI diagnostics is much less likely to cause allergic reactions compared to X-ray contrast agents used for radiography.
The principle of operation of magnetic resonance imaging
The operation of the tomograph is based on the phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance. This method of obtaining information consists of measuring the intensity of the response of the nuclei of a hydrogen atom to the influence of a powerful magnetic field. The fact is that the concentration of this chemical element in different tissues differs.
Thanks to modern technologies, it has become possible to obtain high-resolution images and display them on the screen in 3D mode. Scanning of the required area is carried out in several projections with a high slice frequency. Magnetic resonance imaging may be performed using contrast. Preparations containing gadolinium (Omniscan, etc.) are used as a dye.
The contrast extremely rarely causes allergic reactions and is excreted by the kidneys without causing harm to the body. When administered intravenously, gadolinium is distributed throughout the circulatory system and “highlights” areas of increased blood supply on the tomograph screen. This examination is indispensable in the diagnosis of tumors because they have a developed network of blood vessels.
Contrast is widely used in oncology to detect pathological tumors
How does the procedure work?
The patient removes all metal jewelry and takes out removable dentures containing metal.
The patient is placed on a movable table and secured with special belts. This measure is necessary because you will have to lie inside the tomograph, remaining motionless, for a long time.
A device equipped with wires that transmit and receive radio signals is placed on the head. The equipment is quite noisy and tires with constant clicks and whistles. Therefore, the patient’s ears are protected with earplugs. After this, the table slides into the device, and the specialist sits down at the computer, in which the transmitted data is analyzed and processed.
The technique takes pictures, the quality of which depends on the characteristics of a particular MRI scanner. The thinner the visual slices the equipment makes, the more accurate the final images will be. The duration of diagnosis is 20-30 minutes, and when contrast is used - up to an hour.
After MRI diagnostics, you can immediately return to your normal life. No side effects subsequently or during the MRI examination occur, with the exception of an extremely rare allergy to gadolinium salts.
Finished photographs are handed out printed or recorded on a magnetic medium - disk or flash card. It can be sent to email with SMS notification.
Types of MRI of the brain
- Standard - done without the introduction of contrasting solutions, but at the same time provides a sufficient amount of information.
- With contrast, before which drugs containing gadolinium salts are injected into the vein - gadopentetic and gadoteric acids, Omniscan, Magnevist, etc. These solutions penetrate into the bloodstream and, once in the rays of the MRI scanner, highlight the resulting “picture”. At the same time, the changed areas become better visible, which simplifies decoding. The technique is most often used to detect vascular abnormalities, multiple sclerosis and tumor formations. The dose of contrast agent is selected individually, taking into account weight.
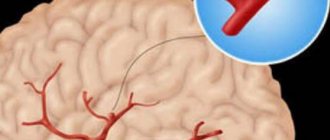
- MR angiography – is performed to assess the condition of blood vessels in atherosclerosis, aneurysms, blood clots and pre-stroke conditions. It is done with gadolinium contrast to show blood flow problems in detail.
- MR imaging of the pituitary gland, an appendage that is an endocrine gland. The pituitary gland secretes hormones responsible for reproductive function, tissue metabolism and the regulation of human growth. An examination is prescribed if an adenoma is suspected - a benign tumor that causes migraine-like pain, hormonal imbalances, gigantism, infertility, obesity and sexual dysfunction. The same method is used to identify malignant pituitary formations that have similar symptoms and are accompanied by a pronounced deterioration in health.
Indications for general anesthesia for MRI
Intravenous or inhalational sedation is only necessary for patients who are unable to hold their body still for long periods of time. Main indications for general anesthesia:
- Claustrophobia is the fear of closed spaces. Such patients, while inside the device, experience panic, which negatively affects their health and makes MRI diagnostics impossible.
- Mental disorders accompanied by unpredictability of behavior and high excitability.
- Uncontrollable involuntary head movements (swaying, shaking, tics).
- Epilepsy and other types of convulsive readiness and seizures - anesthesia is given only intravenously due to the risk of provoking a seizure attack.
- Early childhood. Small children cannot lie still for a long time in an MRI scanner, so light mask anesthesia is indicated for them.
- Severe pain syndrome, in which prolonged stay in one position causes discomfort, cramps, pain and spasms.
Is MRI harmful?
The magnetic waves created by the tomograph do not physically cause damage to biological objects. The power of an average magnetic tomograph is from 0.5 to 3 Tesla. This force is not enough to affect the health of the human body.
People often confuse electromagnetic fields and x-rays. They mistakenly believe that you can get radiation from an MRI. However, it is not. Unlike a CT scan, which emits X-ray waves, magnetic tomography does not expose the person to radiation.
It is not the scanning that can cause harm, but the procedure mode – contrast, namely: a pharmacological drug injected into the patient’s bloodstream.
There are varying degrees of side effects from contrast agents:
- Lungs: tingling, itching, feeling of heat during injection of the drug into a vein. These feelings pass quickly.
- Moderate: allergic reaction similar to hives: redness of the skin, severe itching, swelling.
- Severe: breath holding, cardiac arrest and sudden death. These side effects occur in only one case per 100,000 procedures, provided that the patient is intolerant to contrast.
Indications for magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
- Neoplasms or their metastases. Diagnosis is prescribed for persistent migraine-like pain, sudden loss of vision and hearing, auditory, olfactory and visual hallucinations, attacks of confusion, sudden reading and writing disorders, often accompanying cancer pathologies.
- Epilepsy and other diseases manifested by fainting, confusion and convulsions.
- Suspicion of single or multiple cystic cavities filled with fluid, bloody or other contents.
- Possible presence of parasites (cysticercus and echinococci) carried through the vascular bed with the bloodstream into the head.
- Inflammations – meningitis, encephalitis, arachnoiditis, myelitis. Lesions caused by infections - measles, herpes, tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis, tick-borne encephalitis.
- Rehabilitation after stroke, traumatic brain injury and surgery. Using magnetic resonance diagnostics, the doctor evaluates the effectiveness of the treatment and predicts long-term results.
- The likelihood of developing multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease and other degenerative processes.
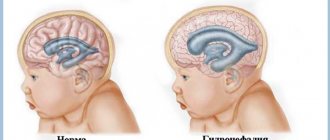
- Children are examined for congenital pathologies and hydrocephalus.
With all these diseases, life and health directly depend on a timely diagnosis. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of brain disorders in yourself or your child, you need to come to the clinic and be examined.
What the results show
MRI studies, especially those performed with contrast, reveal numerous pathological processes. In the sections, compactions, cystic cavities, and hematomas (collections of blood) are visible in detail. Scars, parasites and their cysts, foci of degeneration, sclerosis and inflammation are identified.
Vascular changes are diagnosed, manifested by impaired patency, narrowing or dilation of blood vessels, the appearance of aneurysms (protrusion of walls) and thrombosis.
The degree of tissue damage in traumatic brain injuries, hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes is determined. The affected areas look lighter and are visible even if they are small in size and have sparse neurological symptoms.
Congenital defects are determined - underdevelopment and hypertrophy of the organ, small and incorrectly located gyri, cysts, holoprosencephaly - lack of division into hemispheres. Hydrocephalus is detected - accumulation of fluid in the ventricles, which with this anomaly are greatly enlarged.
Pathological areas and neoplasms appear as dark or lightish spots of various sizes and shapes, standing out against a grayish background. Oncological seals, especially malignant ones, have blurred, uneven edges and surrounding areas of necrosis.
MR diagnostics is recommended periodically for everyone who has been treated for oncological pathologies of any location. It detects metastases, which usually accompany cancer recurrence.
Contraindications
- Installed pacemakers and other electronic devices that are disrupted by the surrounding electromagnetic field.
- Fixed dentures with metal elements present in the mouth, crowns containing metal, braces and other orthodontic structures. The metal they contain is heated by a magnet and deteriorates, damaging surrounding tissue.
- Tattoos applied to the skin, made with metal-containing ink. Due to the heat caused by the electromagnets, burns may occur in these areas. In the absence of information about the pigment. used when applying a tattoo, it is better not to risk it and do a CT scan, ultrasound or x-ray. Examination is also prohibited for any metal piercing that cannot be removed.
- MRI examinations with contrast are not performed during pregnancy or if contrast agents are intolerant. Such an examination is not prescribed for severe kidney pathologies that make it difficult to eliminate gadolinium.
Magnetic resonance imaging is a safe and highly informative procedure that detects pathologies in the early stages. Therefore, in case of migraine-like phenomena, coordination problems, a sharp decrease in hearing and vision, fainting, or progressive memory deterioration, you must definitely go to the clinic and be examined. The price of MRI diagnostics is low and quite affordable for Muscovites and residents of Moscow Region.
Get an MRI of the brain >>>
Can you get a headache after diagnosis?
If after diagnosis a person experiences malaise, weakness, nausea, vomiting, dizziness and disorientation in space, this is normal. This reaction occurs in people:
- with increased sensitivity;
- in case of violation of the rules of the procedure;
- if there are metal objects on the patient’s body or clothing.
Usually the discomfort goes away on its own, but if the symptoms do not disappear for a long time, the patient should consult a doctor.
Thus, magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is more a useful procedure than a harmful one. It cannot cause headaches or other pain in a person. It will only help the doctor determine the nature of the pain that occurs and make a diagnosis. Currently, this examination is prescribed to almost every patient who complains of discomfort in the head area.