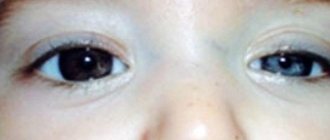
Description of the pathology
Motor neurons are located in peripheral nerves. These cells are equipped with long processes (axons) that transmit signals from the nervous system to the muscles. Thanks to these structures, a person has the ability to make movements.
In acute flaccid paralysis, motor neurons and axons are affected and gradually destroyed. The flow of signals from the nervous system to the muscles stops. As a result, the person cannot move the affected part of the body. Over time, muscle atrophy occurs, tendon reflexes are lost, and muscle tone deteriorates. Weakness of the limbs increases and progresses.
If the motor function of the affected area is completely lost, then doctors call this pathology paralysis. If movements are weakened and difficult, then experts talk about muscle paresis.
The following pathological conditions do not include flaccid paralysis and paresis:
- movement disorders after injuries and injuries (including birth injuries);
- paresis and paralysis of the facial muscles.
It is also very important to differentiate this pathology from paralysis resulting from damage to the central nervous system.
AFP in polio
The disease is characterized by rapid development, symptoms rapidly increase within 1-3 days. On the fourth day, flaccid paralysis is diagnosed. To make a diagnosis it is necessary to confirm:
- sudden onset of paralysis;
- sluggish nature of the disorder;
- asymmetrical damage to the body;
- absence of pathologies from the pelvic organs and sensitivity.
The first week before paralysis develops, there is fever, lethargy, pain, and muscle spasms. Then paralysis rapidly develops, the severity of which depends on the characteristics of the damage to the spinal neurons. With pathology, the general symptoms of polio usually subside. A gradual restoration of motor function is observed a week after the development of paralysis. The prognosis depends on which part of the neurons is affected. If 70% or more of the neurons are lost due to the disease, motor function of the affected part of the body is not restored.
The prognosis for recovery can be judged 10 days after the development of paralysis. If during this period voluntary movements of the muscles of the affected part of the body begin to appear, there is a high probability of complete restoration of mobility over time. The peak of recovery occurs in the first three months after the illness. Residual symptoms may persist for up to two years. If after 24 months the motor function of the affected limb has not been restored, residual effects cannot be treated. After polio, deformities of the limbs, impaired joint mobility, and contracture are observed.
Etiology
Peripheral flaccid paralysis is not an independent disease. Most often it occurs as a complication of infectious pathologies caused by enteroviruses. In most cases, this type of movement disorder develops after polio.
In the past, this dangerous viral disease was widespread. It often led to death and disability of the patient. Nowadays, thanks to mass vaccination, only isolated cases of pathology are observed. However, the risk of infection cannot be completely excluded. An unvaccinated person has a high risk of infection. Cases of imported infections are periodically recorded. You can also get a dangerous virus while traveling to polio-prone regions.
The polio virus is transmitted in several ways: airborne droplets, contact, and through utensils. In addition, the microorganism can live in the environment for several days. Children under 15 years of age are especially susceptible to infection.
The virus enters motor neurons and causes dystrophic changes in them. The nerve cell dies and is replaced by glial tissue. Subsequently, a scar forms in its place. The more motor neurons that die in polio, the faster acute flaccid paralysis develops.
Poliomyelitis is the most common, but not the only cause of this pathology. Flaccid paralysis can also develop as a result of other diseases:
- Inflammatory process in the spinal cord (myelitis). In half of the cases, this disease is caused by an infection. Its causative agents can be enteroviruses, mycoplasmas, cytomegaloviruses, as well as the causative agent of herpes. Sometimes inflammation occurs after an injury. But even in this case, the cause of the pathology is microorganisms that have penetrated the spinal cord through the wound. With myelitis, the supply of impulses from the central nervous system to the peripheral nerves is disrupted, which becomes the cause of paralysis.
- Poly- and mononeuropathies. These diseases are also caused by various viruses. With polyneuropathy, a large number of peripheral nerves are simultaneously affected. Mononeuropathy is characterized by pathological changes in neurons in a separate area, most often in one of the upper limbs.
- Guillain-Barre syndrome. The disease occurs as an autoimmune complication after viral pathologies: mononucleosis, mycoplasmosis, cytomegaly, infection with Haemophilus influenzae. The infectious process leads to disruptions in the functioning of the immune system. Protective antibodies begin to attack peripheral nerve cells, which leads to flaccid paralysis.
- Coxsackie virus infection. In most cases, this microorganism causes a disease that occurs with fever, rash and inflammation of the oropharynx. However, there is another strain of the virus that causes inflammation of the skeletal muscles. The consequence of this pathology can be acute flaccid paralysis in children. Adults are infected much less frequently.
Currently, a new type of enterovirus has emerged (type 70 strain). Most often it causes a severe form of conjunctivitis. But there are also atypical forms of the disease, which are similar in symptoms to polio. This pathology can also cause damage to peripheral nerves.
Virological examination
The following must be tested for the presence of the virus:
- children under 15 years of age with flaccid paralysis;
- refugees from areas with a high risk of infection (India, Pakistan);
- patients with clinical signs of the disease and their environment.
Fecal samples are required for analysis. At the beginning of the disease, the concentration of the virus in the patient’s feces reaches 85%.
Patients with polio, or patients suspected of having this disease, should be examined again one day after the initial analysis.
Symptoms of polio:
- fever;
- inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx;
- impaired motor activity of the neck muscles and back;
- muscle spasms and cramps;
- muscle pain;
- indigestion;
- infrequent urination.
Acute symptoms include difficulty breathing and muscle paralysis.
Difference from central paralysis
It is necessary to distinguish between flaccid and spastic paralysis. These two pathological conditions are accompanied by impaired motor function. However, they differ in etiology, pathogenesis and symptoms:
- The spastic form of the pathology occurs due to damage to the central nervous system. Acute flaccid paralysis is characterized by damage to the peripheral nerves or roots of the spinal cord.
- In spastic paralysis there is no damage to motor neurons.
- In the peripheral form of paralysis, there are no flexion and extension reflexes, and muscle weakness is noted. With a pathology of central origin, the muscles are tense, involuntary muscle contractions are noted, and reflex movements are preserved.
- Central paralysis can impair movement throughout the body. In the peripheral form, there is a deterioration in motor function in a certain area.
Only a neurologist can differentiate these two forms of paralysis on the basis of a comprehensive examination.
Acute flaccid paralysis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment – Healthy Family
Acute flaccid paralysis occurs as a result of damage to the peripheral nerve anywhere. AFP is a complication of many diseases, including polio.
Possible reasons
Flaccid paralysis develops due to the action of enteroviruses. Pathology occurs due to damage to neurons of the spinal cord and areas of peripheral nerves.
A common cause of development is polio.
AFP includes all paralysis accompanied by rapid development. The condition for making such a diagnosis is the development of pathology within three to four days, no more. The disease occurs in children under 15 years of age as a result of polio, and also in adults for many reasons.
Acute flaccid paralysis does not include:
- paresis of facial muscles;
- paralysis acquired at birth as a result of injury;
- injuries and damage that provoke the development of paralysis.
There are several types of AFP depending on the cause of nerve damage.
Symptoms
AFP is diagnosed if the following symptoms are present:
- lack of resistance to passive movement of the affected muscle;
- pronounced muscle atrophy;
- absence or significant deterioration of reflex activity.
A specific examination does not reveal disorders of nervous and muscle electrical excitability.
The location of the paralysis depends on which part of the brain is damaged. When the anterior horns of the spinal cord are damaged, paralysis of one leg develops. In this case, the patient cannot move his foot.
With symmetrical damage to the spinal cord in the cervical region, paralysis of both lower and upper extremities may develop simultaneously.
Before the onset of paralysis, the patient complains of acute excruciating pain in the back. In children, the pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- swallowing dysfunction;
- weakness of the muscles of the arms and legs;
- trembling in hands;
- breathing disorder.
No more than three to four days pass from the appearance of the first symptoms to the development of paralysis. If the disease manifests itself later than four days from the onset of illness, there can be no talk of an acute flaccid form.
The pathology is dangerous due to its complications, including:
- reduction in the size of the affected limb or part of the body due to the fact that the muscles are atrophied;
- hardening of the muscles in the affected area (contracture);
- hardening of joints.
In most cases, it is impossible to get rid of complications caused by flaccid paralysis. The success of treatment largely depends on the cause of the disorder and timely access to the clinic.
Types of flaccid paralysis
There are several types of pathology, depending on the cause of its development:
- polio;
- myelitis;
- polyneuropathy;
- mononeuropathy.
Paralysis in children develops due to polio caused by a virus, as well as with a disease of unspecified etiology.
Inflammation of the spinal cord (myelitis) causes a disruption in the connections between the central nervous system and the PNS, which causes paralysis and impaired sensitivity in some parts of the body.
Flaccid paralysis also accompanies poly- and mononeuropathy. These diseases are characterized by damage to areas of the peripheral nervous system.
With polyneuropathy, multiple lesions caused by viruses or infections are diagnosed.
Mononeuropathy is characterized by damage to one nerve, usually the disorder affects the radial or ulnar nerve, causing paralysis of the corresponding part of the body.
Paralytic polio
Poliomyelitis is a dangerous disease that can lead to paralysis in children. It is diagnosed in children under 15 years of age, but there are frequent cases of delayed complications of polio several decades after the illness.
The disease is accompanied by damage to the motor neurons of the anterior horns of the spinal cord, which is responsible for the development of flaccid paralysis in polio.
The routes of infection with the polio virus are from person to person and through household contact, when the patient’s saliva gets on food or utensils. At room temperature, the virus that causes this disease remains dangerous for several days.
The virus persists on the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx for up to two weeks, which makes there a high probability of infection from a sick person.
There is only one way to protect yourself from the virus – through vaccination. In rare cases, the live vaccine also causes paralysis.
Virological examination
The following must be tested for the presence of the virus:
- children under 15 years of age with flaccid paralysis;
- refugees from areas with a high risk of infection (India, Pakistan);
- patients with clinical signs of the disease and their environment.
Fecal samples are required for analysis. At the beginning of the disease, the concentration of the virus in the patient’s feces reaches 85%.
Patients with polio, or patients suspected of having this disease, should be examined again one day after the initial analysis.
Symptoms of polio:
- fever;
- inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx;
- impaired motor activity of the neck muscles and back;
- muscle spasms and cramps;
- muscle pain;
- indigestion;
- infrequent urination.
Acute symptoms include difficulty breathing and muscle paralysis.
AFP in polio
The disease is characterized by rapid development, symptoms rapidly increase within 1-3 days. On the fourth day, flaccid paralysis is diagnosed. To make a diagnosis it is necessary to confirm:
- sudden onset of paralysis;
- sluggish nature of the disorder;
- asymmetrical damage to the body;
- absence of pathologies from the pelvic organs and sensitivity.
The first week before paralysis develops, there is fever, lethargy, pain, and muscle spasms. Then paralysis rapidly develops, the severity of which depends on the characteristics of the damage to the spinal neurons. With pathology, the general symptoms of polio usually subside.
A gradual restoration of motor function is observed a week after the development of paralysis. The prognosis depends on which part of the neurons is affected. If 70% or more of the neurons are lost due to the disease, motor function of the affected part of the body is not restored.
The prognosis for recovery can be judged 10 days after the development of paralysis. If during this period voluntary movements of the muscles of the affected part of the body begin to appear, there is a high probability of complete restoration of mobility over time.
The peak of recovery occurs in the first three months after the illness. Residual symptoms may persist for up to two years. If after 24 months the motor function of the affected limb has not been restored, residual effects cannot be treated.
After polio, deformities of the limbs, impaired joint mobility, and contracture are observed.
AFP in children
Thanks to compulsory vaccination, polio in a child in our country does not pose such a danger as in India or Pakistan. But polio is not the only cause of flaccid paralysis in children.
Pathology develops under the influence of various enteroviruses. There are various neurotropic viruses that attack the nervous system and cause severe paresis with subsequent muscle atrophy.
Entoroviruses of non-poliomyelitis nature are particularly dangerous.
Treatment of AFP
Therapy is aimed at restoring the function of peripheral nerves affected by the viral disease. For this purpose, use:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- folk remedies.
The combination of these methods makes it possible to obtain a good therapeutic effect, but only with timely treatment. If more than 70% of neurons have died as a result of a viral infection, restoration of mobility and sensitivity of the affected area is impossible.
Drug therapy includes treatment with neurotropic and vasoactive drugs. Therapy is aimed at improving metabolism and conduction of nerve fibers, improving blood circulation and stimulating the activity of the nervous system.
The drugs are administered either intravenously or intramuscularly. It is possible to administer drugs using a dropper in cases of extensive neuronal damage.
Vitamin therapy is required. The introduction of B vitamins is indicated, which stimulate cell renewal and strengthen the nervous system.
During the rehabilitation period, wearing a bandage or orthosis is indicated to fix the limb in a physiologically correct position. This measure will avoid visible deformation of the joint due to weakening of the muscles.
Physiotherapy and massage
Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment help to speed up the restoration of motor activity and restore sensitivity. For paralysis, methods of electrical stimulation - galvanization, balneotherapy - are successfully used.
Such therapeutic methods improve the conductivity of nerve fibers, accelerate regeneration and cell restoration.
A course of such treatment is carried out only after the underlying disease that led to paralysis has been relieved.
To normalize muscle activity and to prevent the development of atrophy, massage is used. Patients are prescribed an intense massage, with prolonged kneading of damaged muscles and strong rubbing.
When performing a massage, it is important to remember that muscles constrained by paralysis should not be subjected to traumatic effects. The massage should be intense, but without excessive effort. Traumatic effects on the affected muscles can have the opposite effect.
To restore muscle activity, a long course of massage is indicated, up to six months. With regular procedures, the result will become noticeable after the first 5 sessions.
In addition to classic massage, good results are achieved by applying targeted pressure to painful nodes of the human body. In this case, you also cannot act directly on the stiff muscle.
This technique improves metabolic processes in muscle fibers, stimulating the rapid restoration of mobility and sensitivity.
The maximum effect is achieved by using two techniques simultaneously, alternating.
Folk remedies for a speedy recovery
Traditional methods can be supplemented with treatment, but only after consultation with your doctor. It is not possible to cure paralysis on your own using folk methods alone. Often, patients, preferring herbal treatment, ignore the doctor’s instructions, which leads to a worsening of the situation and the impossibility of further recovery with medications.
- Make a decoction of a tablespoon of rose hip root with the addition of the same amount of berries and 500 ml of water. After cooling, the broth is diluted with 5 liters of water and used as a bath for paralyzed limbs.
- Peony evasive is used to speed up recovery. To do this, you need to prepare a decoction from the rhizome of the plant, at the rate of 1 spoon of dry root per 600 ml of boiling water. After the decoction has infused and cooled, it should be taken three times a day before each meal, one small spoon.
- Fresh leaves of dye sumac are poured with a glass of boiling water and left for 2 hours in a warm place. After cooling, take the decoction in a small spoon every 5 hours, regardless of meals.
Before starting such treatment, you should make sure that there is no allergic reaction to the ingredients in the recipes.
Prevention and prognosis
The prognosis largely depends on the degree of damage to spinal cord neurons. With moderate neuronal death, it is possible to achieve restoration of motor activity, but treatment will be long-term, up to several years. In the treatment of paralysis, a timely visit to the clinic and correct diagnosis of the problem play an important role.
Preventive measures include timely treatment of any infectious and viral disease. The presence of any source of infection in the body is dangerous due to its spread throughout the body through the bloodstream, which may result in the development of inflammatory damage to the peripheral nerves.
When the first symptoms of developing paralysis appear (muscle weakness, cramps, muscle and back pain), you should immediately consult a specialist.
Source:
Flaccid paralysis or what happens in the periphery of the nervous system
Peripheral paralysis is the result of damage to peripheral neurons responsible for motor functions. This results in loss of reflexes, degenerative muscle atrophy and hypotension.
In addition, it should be noted that the process of changing electrical excitability in the affected nerves, which is called degeneration, also starts. The severity of the disease is indicated by the depth of changes in electrical excitability.
Atony and loss of reflexes occurs due to a break in the functioning of the reflex arc, and at the same time the muscles lose tone. This factor prevents the corresponding reflex from being evoked. The disconnection of muscles from the neurons of the spinal cord causes their sudden weight loss and atrophy.
From neurons that are connected to muscles, impulses responsible for normal metabolism in the area of muscle tissue flow through the peripheral nerve.
Source: https://niikelsoramn.ru/pitanie-i-diety/ostryj-vyalyj-paralich-prichiny-simptomy-diagnostika-lechenie.html
Symptoms
Impaired motor function most often appears suddenly and increases rapidly. The following symptoms of flaccid paralysis can be distinguished:
- impossibility or difficulty of movements;
- severe muscle weakness in the affected area;
- lack of response of paralyzed muscles to mechanical stress;
- asymmetrical lesion;
- muscle atrophy (a paralyzed leg or arm becomes thinner than a healthy one).
If paralysis develops against the background of polio, then the patient’s general signs of infectious pathology disappear. Usually, shortly before the onset of movement disorders, the temperature drops, muscle pain and spasms subside.
A fairly common form of pathology is lower flaccid paralysis. It is characterized by damage to the spinal cord roots. As a result, the patient experiences paralysis of one of the lower limbs. Most often, the innervation of the muscles of the feet is disrupted. A person cannot move his feet and it becomes very difficult for him to walk. The appearance of paralysis is preceded by severe pain in the lower back. In severe cases, the lesion spreads to the cervical region, and the patient's right or left arm is paralyzed.
Pathogenesis
(Guillain-Barré, Landry, Strohl, Miller-Fisher syndrome,
acute polyradiculoneuritis)
Children are affected with a frequency of 1.1 per 100,000 population. The disease is often preceded by respiratory and
gastrointestinal tract
Campylobacter jejuni (30%)
cytomegalovirus (15%)
Epstein-Barr virus (10%)
Mycoplasma pneumoniae (5%), etc.
acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (AIDP),
acute motor axonal neuropathy (AMAN),
acute motor-sensory axonal neuropathy (ASAN),
Miller-Fisher syndrome
occur without a rise in temperature against the background of a generally satisfactory condition
gradual (over 1-2 weeks) development of neurological symptoms
in children with a feverish onset of the disease, the development of paresis/paralysis occurs against the background of normal temperature
paresis/paralysis begins in the distal limbs
are symmetrical
sensory disorders of the “stockings” and “gloves” type are observed
in the CSF there is often an increase in protein numbers with normal cytosis
by the end of the 3rd week of illness, 85% of patients show signs of segmental demyelination and/or axonal degeneration in an ENMG study
Most often, post-injection mononeuropathies are observed. When collecting anamnesis, it is possible to identify a connection with intramuscular injection that preceded the development of neuropathy
Other causes are less commonly identified: falls and spinal injuries, compression of a limb by a tight bandage, pinching of a limb in a crib or playpen
Loss of reflexes, as well as hypotension, occur due to interruption of the monosynaptic stretch reflex arc, as well as disruption of the stretching mechanism of fast and slow reflexes. Muscle atrophy appears because the anterior horn ceases to have a trophic effect on muscle fibers - this problem appears several weeks after the denervation of nerve endings in the muscles has occurred and can be so severe that after several months or years only connective tissue remains in the affected muscles.
Features of pathology in a child
Flaccid paralysis is more common in children than in adults. A child is much more susceptible to infection with enteroviruses. Polio is quite rare these days. The main danger to a child is represented by other types of enteroviruses that affect peripheral nerves.
Manifestations of flaccid paralysis in children are the same as in adults. However, the child more often experiences damage to the neurons responsible for the functioning of the respiratory and swallowing muscles. Sick children breathe quickly and shallowly, which leads to hypoxia. As a result, frequent headaches, lethargy, and difficulty falling asleep occur. The child finds it difficult to swallow and often chokes on food. Children often lose weight due to lack of nutrition.
Folk remedies for a speedy recovery
Traditional methods can be supplemented with treatment, but only after consultation with your doctor. It is not possible to cure paralysis on your own using folk methods alone. Often, patients, preferring herbal treatment, ignore the doctor’s instructions, which leads to a worsening of the situation and the impossibility of further recovery with medications.
- Make a decoction of a tablespoon of rose hip root with the addition of the same amount of berries and 500 ml of water. After cooling, the broth is diluted with 5 liters of water and used as a bath for paralyzed limbs.
- Peony evasive is used to speed up recovery. To do this, you need to prepare a decoction from the rhizome of the plant, at the rate of 1 spoon of dry root per 600 ml of boiling water. After the decoction has infused and cooled, it should be taken three times a day before each meal, one small spoon.
- Fresh leaves of dye sumac are poured with a glass of boiling water and left for 2 hours in a warm place. After cooling, take the decoction in a small spoon every 5 hours, regardless of meals.
Before starting such treatment, you should make sure that there is no allergic reaction to the ingredients in the recipes.
Complications
If left untreated, flaccid paralysis causes severe complications. This pathology can lead to the following dangerous consequences:
- Ankylosis. Lack of movement in a paralyzed limb leads to fusion of bones in the articular joints.
- Muscle contractures. Over time, the muscles in the affected area shorten and harden.
- Persistent muscle weakness. Peripheral paralysis is accompanied by a sharp decrease in the tone of the muscles of the neck and limbs. Without treatment, muscle tissue atrophy becomes irreversible.
If the patient has already developed such complications, then it is no longer possible to restore motor function using conservative methods. In most cases, it is necessary to resort to surgical treatment methods.
Characteristic manifestations
Signs of peripheral paralysis:
- complete or partial loss of motor functions;
- decreased muscle tone in the affected part;
- complete or partial absence of any reaction to sudden irritation of paralyzed muscles;
- denervation atrophy is observed, that is, loss of muscle mass;
- a reaction of degeneration or degeneration is also observed.
Over time, if a person does not receive proper treatment, peripheral paralysis can develop into another form, that is, an acute infectious disease. It is often found under the name polio. It is characterized by intoxication, while the nervous system also suffers, paralysis and acute flaccid peripheral paresis develop.
This infection is initiated under the influence of a filter virus, which is quite resistant and has increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation, disinfectants and high temperature.
When the virus penetrates a neuron, a dystrophic-necrotic process is triggered, which is accompanied by the replacement of all dead neurons with glial tissue and subsequent scarring. In turn, the more neurons die, the faster paresis or paralysis occurs.
Diagnostics
A neurologist is involved in the treatment and diagnosis of this pathology. Since paralysis is usually caused by viral pathologies, consultation with an infectious disease specialist may be required.
Peripheral paralysis must be differentiated from other types of motor dysfunction. To clarify the diagnosis, the following types of examinations are carried out:
- Neurological examination. The doctor examines the patient's muscle strength, tendon reflexes, and swallowing function.
- Clinical and biochemical blood tests. The presence of pathology is indicated by an increase in ESR and an increased concentration of creatine kinase.
- Virological examination of stool. This test is performed if polio is suspected.
- Blood toxicology test. Helps distinguish peripheral paralysis from motor dysfunction caused by chemical poisoning.
- Electromyography. This test helps evaluate muscle electrical conductivity.
- Test with proserine. The test allows you to distinguish paralysis from myasthenia gravis.
Flaccid paralysis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment methods
Flaccid paralysis is a dangerous complication after infectious diseases. The pathology is characterized by the progressive death of neurons in the peripheral nervous system.
This leads to significant deterioration or complete impossibility of movement in the affected area. Most often, the muscles of the arms, legs and neck are paralyzed.
How does this type of paralysis develop? And is it possible to restore motor function? The answers to these questions can be found in the article.
Description of the pathology
Motor neurons are located in peripheral nerves. These cells are equipped with long processes (axons) that transmit signals from the nervous system to the muscles. Thanks to these structures, a person has the ability to make movements.
In acute flaccid paralysis, motor neurons and axons are affected and gradually destroyed. The flow of signals from the nervous system to the muscles stops. As a result, the person cannot move the affected part of the body. Over time, muscle atrophy occurs, tendon reflexes are lost, and muscle tone deteriorates. Weakness of the limbs increases and progresses.
If the motor function of the affected area is completely lost, then doctors call this pathology paralysis. If movements are weakened and difficult, then experts talk about muscle paresis.
The following pathological conditions do not include flaccid paralysis and paresis:
- movement disorders after injuries and injuries (including birth injuries);
- paresis and paralysis of the facial muscles.
It is also very important to differentiate this pathology from paralysis resulting from damage to the central nervous system.
Peripheral flaccid paralysis is not an independent disease. Most often it occurs as a complication of infectious pathologies caused by enteroviruses. In most cases, this type of movement disorder develops after polio.
In the past, this dangerous viral disease was widespread. It often led to death and disability of the patient. Nowadays, thanks to mass vaccination, only isolated cases of pathology are observed.
However, the risk of infection cannot be completely excluded. An unvaccinated person has a high risk of infection. Cases of imported infections are periodically recorded.
You can also get a dangerous virus while traveling to polio-prone regions.
The polio virus is transmitted in several ways: airborne droplets, contact, and through utensils. In addition, the microorganism can live in the environment for several days. Children under 15 years of age are especially susceptible to infection.
The virus enters motor neurons and causes dystrophic changes in them. The nerve cell dies and is replaced by glial tissue. Subsequently, a scar forms in its place. The more motor neurons that die in polio, the faster acute flaccid paralysis develops.
Poliomyelitis is the most common, but not the only cause of this pathology. Flaccid paralysis can also develop as a result of other diseases:
- Inflammatory process in the spinal cord (myelitis). In half of the cases, this disease is caused by an infection. Its causative agents can be enteroviruses, mycoplasmas, cytomegaloviruses, as well as the causative agent of herpes. Sometimes inflammation occurs after an injury. But even in this case, the cause of the pathology is microorganisms that have penetrated the spinal cord through the wound. With myelitis, the supply of impulses from the central nervous system to the peripheral nerves is disrupted, which becomes the cause of paralysis.
- Poly- and mononeuropathies. These diseases are also caused by various viruses. With polyneuropathy, a large number of peripheral nerves are simultaneously affected. Mononeuropathy is characterized by pathological changes in neurons in a separate area, most often in one of the upper limbs.
- Guillain-Barre syndrome. The disease occurs as an autoimmune complication after viral pathologies: mononucleosis, mycoplasmosis, cytomegaly, infection with Haemophilus influenzae. The infectious process leads to disruptions in the functioning of the immune system. Protective antibodies begin to attack peripheral nerve cells, which leads to flaccid paralysis.
- Coxsackie virus infection. In most cases, this microorganism causes a disease that occurs with fever, rash and inflammation of the oropharynx. However, there is another strain of the virus that causes inflammation of the skeletal muscles. The consequence of this pathology can be acute flaccid paralysis in children. Adults are infected much less frequently.
Currently, a new type of enterovirus has emerged (type 70 strain). Most often it causes a severe form of conjunctivitis. But there are also atypical forms of the disease, which are similar in symptoms to polio. This pathology can also cause damage to peripheral nerves.
Difference from central paralysis
It is necessary to distinguish between flaccid and spastic paralysis. These two pathological conditions are accompanied by impaired motor function. However, they differ in etiology, pathogenesis and symptoms:
- The spastic form of the pathology occurs due to damage to the central nervous system. Acute flaccid paralysis is characterized by damage to the peripheral nerves or roots of the spinal cord.
- In spastic paralysis there is no damage to motor neurons.
- In the peripheral form of paralysis, there are no flexion and extension reflexes, and muscle weakness is noted. With a pathology of central origin, the muscles are tense, involuntary muscle contractions are noted, and reflex movements are preserved.
- Central paralysis can impair movement throughout the body. In the peripheral form, there is a deterioration in motor function in a certain area.
Only a neurologist can differentiate these two forms of paralysis on the basis of a comprehensive examination.
Symptoms
Impaired motor function most often appears suddenly and increases rapidly. The following symptoms of flaccid paralysis can be distinguished:
- impossibility or difficulty of movements;
- severe muscle weakness in the affected area;
- lack of response of paralyzed muscles to mechanical stress;
- asymmetrical lesion;
- muscle atrophy (a paralyzed leg or arm becomes thinner than a healthy one).
If paralysis develops against the background of polio, then the patient’s general signs of infectious pathology disappear. Usually, shortly before the onset of movement disorders, the temperature drops, muscle pain and spasms subside.
A fairly common form of pathology is lower flaccid paralysis. It is characterized by damage to the spinal cord roots. As a result, the patient experiences paralysis of one of the lower limbs. Most often, the innervation of the muscles of the feet is disrupted.
A person cannot move his feet and it becomes very difficult for him to walk. The appearance of paralysis is preceded by severe pain in the lower back. In severe cases, the lesion spreads to the cervical region, and the patient's right or left arm is paralyzed.
Features of pathology in a child
Flaccid paralysis is more common in children than in adults. A child is much more susceptible to infection with enteroviruses. Polio is quite rare these days. The main danger to a child is represented by other types of enteroviruses that affect peripheral nerves.
Manifestations of flaccid paralysis in children are the same as in adults. However, the child more often experiences damage to the neurons responsible for the functioning of the respiratory and swallowing muscles.
Sick children breathe quickly and shallowly, which leads to hypoxia. As a result, frequent headaches, lethargy, and difficulty falling asleep occur. The child finds it difficult to swallow and often chokes on food.
Children often lose weight due to lack of nutrition.
If left untreated, flaccid paralysis causes severe complications. This pathology can lead to the following dangerous consequences:
- Ankylosis. Lack of movement in a paralyzed limb leads to fusion of bones in the articular joints.
- Muscle contractures. Over time, the muscles in the affected area shorten and harden.
- Persistent muscle weakness. Peripheral paralysis is accompanied by a sharp decrease in the tone of the muscles of the neck and limbs. Without treatment, muscle tissue atrophy becomes irreversible.
If the patient has already developed such complications, then it is no longer possible to restore motor function using conservative methods. In most cases, it is necessary to resort to surgical treatment methods.
Diagnostics
A neurologist is involved in the treatment and diagnosis of this pathology. Since paralysis is usually caused by viral pathologies, consultation with an infectious disease specialist may be required.
Peripheral paralysis must be differentiated from other types of motor dysfunction. To clarify the diagnosis, the following types of examinations are carried out:
- Neurological examination. The doctor examines the patient's muscle strength, tendon reflexes, and swallowing function.
- Clinical and biochemical blood tests. The presence of pathology is indicated by an increase in ESR and an increased concentration of creatine kinase.
- Virological examination of stool. This test is performed if polio is suspected.
- Blood toxicology test. Helps distinguish peripheral paralysis from motor dysfunction caused by chemical poisoning.
- Electromyography. This test helps evaluate muscle electrical conductivity.
- Test with proserine. The test allows you to distinguish paralysis from myasthenia gravis.
Drug therapy
Treatment of flaccid paralysis requires an integrated approach. The main goal of therapy is to restore the normal functioning of motor neurons. Patients are prescribed nootropic and antioxidant drugs in high doses:
- “Piracetam.”
- "Actovegin".
- "Mexidol".
- “Trental.”
- "Cerebrolysin".
These medications help normalize metabolism in damaged nerves and protect neurons from harmful effects.
A course of injections of the drug “Proserin” is shown. This remedy improves signal transmission from neurons to muscles and helps increase muscle tone.
Be sure to prescribe a course of vitamin therapy. It is necessary to take high doses of drugs, most often the drugs are administered intramuscularly. For treatment, vitamins B1 and B12 are used, which have a positive effect on the condition of the nervous tissue.
Physiotherapy and rehabilitation
Restoring movements is impossible without physiotherapy. This is the main part of the treatment of peripheral paralysis. It is impossible to get rid of motor dysfunction using medication alone. It is necessary to develop damaged muscle groups to avoid their complete atrophy.
Patients are prescribed galvanization sessions. Electrodes are applied to the affected areas and a low-voltage constant electric current is applied. This helps improve tissue metabolism and restore damaged neurons, as well as increase muscle tone. Baths with mineral waters are also shown. This allows you to influence peripheral nerves through skin receptors.
Such procedures are allowed to be carried out only after the acute symptoms of the infectious disease have been relieved. Galvanization and water treatments are quite effective, but the process of restoring movement takes a long period of time.
Massage for flaccid paralysis helps restore muscle tone and prevent muscle atrophy.
The impact on the affected areas should be quite intense, using kneading and rubbing of the damaged muscles. But it is very important to prevent injury to muscle tissue.
Therefore, this procedure should only be trusted by a qualified specialist. It is useful to combine classical and acupressure massage.
Exercise therapy for flaccid paralysis is a mandatory part of treatment. However, it must be taken into account that patients have weakened muscles and joints. Therefore, at the initial stage, passive movements using support are shown.
For example, the patient rests the affected foot on a special box and tries to bend the leg. Crawling on all fours is also useful. First, the patient moves the diseased limb using the muscles of the trunk, leaning on his hands.
As the movements develop, the exercises are performed while kneeling.
Gymnastics in water is very useful. Exercises for the limbs can be combined with medicinal baths.
If hand movements are impaired, the patient must be taught simple household skills. For this purpose, tables with special stands are used in physiotherapy rooms. The patient learns to fasten buttons independently, press the switch button, and turn the key in the lock. Modeling from plasticine helps restore fine motor skills of the hands.
It is recommended to wear orthoses during rehabilitation. This will help maintain the injured limb in an optimal position.
Surgical methods
In severe cases and in the presence of complications, surgical treatment is indicated. The most commonly used types of operations are:
- transplantation of healthy muscles to an atrophied area;
- elimination of joint deformation due to ankylosis (osteotomy);
- plastic surgery to thicken the lower leg (for severe muscle atrophy).
After surgery, movements are restored much faster than with conservative treatment.
Forecast
The prognosis of the disease depends on the degree of neuronal damage. If diagnosis and treatment were carried out in a timely manner, then it is quite possible to restore movement. However, this will require long-term complex therapy and rehabilitation. Typically, the process of restoring motor function takes about 2 years. After surgical treatment, movements return to normal after about 1 year.
In advanced cases, it is no longer possible to restore movement even with surgery. If a patient has lost more than 70% of neurons, then such changes are considered irreversible.
Prevention
How to prevent the death of motor neurons and the occurrence of paralysis? Most often, enteroviral diseases lead to such complications. To avoid infection, the following recommendations must be followed:
- Get vaccinated against polio on time;
- avoid contact with patients with enteroviral infections;
- strengthen the immune system;
- timely and completely cure infectious diseases;
- After suffering from polio, regularly visit a neurologist for 6-12 months.
These measures will help to avoid dangerous complications of infectious pathologies and maintain motor function.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/451317/vyalyiy-paralich-prichinyi-simptomyi-diagnostika-metodyi-lecheniya
Drug therapy
Treatment of flaccid paralysis requires an integrated approach. The main goal of therapy is to restore the normal functioning of motor neurons. Patients are prescribed nootropic and antioxidant drugs in high doses:
- "Piracetam."
- "Actovegin".
- "Mexidol".
- "Trental."
- "Cerebrolysin".
These medications help normalize metabolism in damaged nerves and protect neurons from harmful effects.
A course of injections of the drug “Proserin” is shown. This remedy improves signal transmission from neurons to muscles and helps increase muscle tone.
Be sure to prescribe a course of vitamin therapy. It is necessary to take high doses of drugs, most often the drugs are administered intramuscularly. For treatment, vitamins B1 and B12 are used, which have a positive effect on the condition of the nervous tissue.
Neuromuscular diseases
congenital muscular dystrophy
spinal progressive muscular atrophies (Werdnig-Hoffman, Fazio-Londe, etc.)
atonic form of cerebral palsy
benign form of congenital hypotension
some other diseases
Absence or decrease in muscle strength; - decreased muscle tone; - hyporeflexia or areflexia; - muscle wasting or atrophy.
Hypotonia and areflexia develop due to interruption of the arc of the monosynaptic stretch reflex and a disorder of the mechanism of tonic and phasic stretch reflexes. Muscle atrophy is caused by a violation of the trophic influence from the anterior horn on the muscle fibers, develops several weeks after denervation of the muscle fibers and can be so pronounced that after several months or years only the connective tissue remains intact in the muscle.
Restorative measures for the development of flaccid paresis or paralysis are aimed, firstly, at restoring (if possible) the function of a peripheral neuron, and secondly, at preventing the development of muscle tissue atrophy and preventing contractures.
Achieved by prescribing neutrotrophic and vasoactive drugs:
- nootropil/piracetam (capsules/tablets 0.4 g-0.8 g three times a day or 20% solution 5-10 ml intramuscularly or intravenously);
- Cerebrolysin (3-5 ml intramuscularly or intravenously);
- actovegin (5-10 ml intramuscularly or intravenously drip once or twice a day; 1 ml contains 40 mg of the active substance);
- trental (in pills, 0.1 g three times a day, or 5 ml intravenously drip once a day; 1 ml contains 0.02 g of the active substance);
- vitamin B1 (solution of thiamine chloride 2.5% or 5% or thiamine bromide 3% or 6%, 1 ml intramuscularly daily, once a day);
- vitamin B12 (400 mcg once every 2 days intramuscularly, can be taken simultaneously with vitamin B1, but not in the same syringe).
If the anatomical integrity of the peripheral nerves is compromised, neurosurgical intervention may be indicated.
This is a very important task, since degeneration of denervated muscle fibers develops very quickly and is often irreversible. By the time innervation is restored (either through natural reinnervation or through neurosurgical intervention), atrophy can reach such a pronounced degree that muscle function can no longer be restored.
Massage
It is aimed at stimulating muscles, so techniques include fairly intense rubbing, deep kneading, and impact on segmental zones. However, massage of paretic muscles should not be done with great force. The massage should be moderate and short-lived, but carried out over many months (short breaks are taken between courses).
Rough, painful techniques can cause increasing muscle weakness. They also use acupressure using a tonic technique. The toning method of acupressure is carried out by applying vibrating, short, quick stimulation with the fingertip sequentially to a number of points that stimulate the desired movement. The topography of recommended points of influence for stimulating active muscle contractions is presented in table 4.5. and in Fig. 4.6.
| Point number | Point name | Location of the point | Muscles that are stimulated |
| Shoulder girdle and upper limb | |||
| 1 | Jian-jin | On a line corresponding to the middle of the shoulder girdle, in the center of the supraspinatus fossa | |
| 2 | Fu-fen | At the inner edge of the scapula at the level of the spinous processes of the II and III thoracic vertebrae | Trapezius muscle (movement of the shoulder girdle up and back) |
| 3 | Gao-huang | At the inner edge of the scapula at the level of the spinous processes of the IV and V thoracic vertebrae | Trapezius muscle (movement of the shoulder girdle up and back) |
| 4 | Jianyu | Above the shoulder joint, between the acromion process of the scapula and the greater tubercle of the humerus | Deltoid muscle (abduction, flexion, extension, supination and pronation of the arm in the shoulder joint) |
| 5 | Xiao-le | In the middle of the back surface of the humerus 5 cun above the elbow joint | |
| 6 | Xiao-hai | On the back of the shoulder between the inner condyle of the humerus and the olecranon | Triceps brachii (extends the forearm) |
| 7 | Yang-chi | On the dorsum of the wrist joint, in the center of the wrist fold | |
| 8 | Wai-guan | 2 cun above the yang chi point | Extensor muscles of the hand and fingers |
| 9 | E-men | On the dorsum of the hand between the metacarpophalangeal joints of the fourth and fifth fingers | Finger extensor muscles |
| Pelvic girdle and lower limb | |||
| 10 | Yin-bao | On the midline of the inner thigh, 5 cun above the knee joint | Adductor muscles |
| 11 | Cheng-fu | In the center of the gluteal fold | Biceps femoris, semitendinosus and semimembranosus (shin flexor) |
| 12 | Yin-men | 6 cun below the cheng fu point (middle of the back of the thigh) | Same |
| 13 | Yin Ling Quan | On the inner surface of the tibia, at the posterior edge of the inner condyle of the tibia | |
| 14 | Yang-ling-quan | At the anterior lower edge of the head of the fibula, in line with the Yin Ling Quan point | Same |
| 15 | Tzu-san-li | 3 cun below the patella outside the crest of the tibia | Extensor muscles of the foot and toes |
| 16 | Jie-si | In the middle of the dorsum of the ankle joint | Same |
| 17 | Shan-qiu | On the inner surface of the foot, in front and below the inner ankle | Same |
| 18 | Qiu-xu | On the dorsum of the foot in front and below the outer ankle | Same |
| 19 | Pu-shen | A series of dots along the outer edge of the foot | Pronators of the foot |
Note: cun is an individual unit of measurement for each person, equal to the distance between two folds formed when bending the second and third phalanges of the middle finger on the left hand in men and on the right hand in women.
Physiotherapy
Aimed at restoring movements of weakened muscles. Initially, in the complete absence of active movements, passive movements are used in all joints of the paretic segment or limb. Passive movements are performed with a small amplitude simultaneously with the volitional sending of a motor impulse to the patient for this movement.
movements are performed in a horizontal plane, on a smooth surface. Another way to get relief is to exercise in water. The patient is taught measured muscle tension and relaxation, gradual increase and decrease of force, differentiation of different degrees of force (for this purpose, visual analogue scales and bars, dynamometers can be used to help the patient).
As muscle strength is restored, training exercises begin to be used. In order to increase the load on the muscles, multiple repetitions of the movement, an increase in the speed of movement and the length of the lever, and resistance to the movement are used (the resistance can be provided by a trainer or a partner; rubber bandages, expanders, and block exercise machines with a suspended load are also used to create resistance).
The exercise should cause some fatigue, but not overwork of the working muscles. Intense, prolonged physical activity is unacceptable, since paretic muscles are characterized by rapid fatigue, and an overdose of exercise leads to an increase in muscle weakness. The load is increased gradually as muscle strength increases.
Electrical stimulation
Electrical stimulation plays a special role in the treatment of flaccid paralysis. Electrical stimulation of motor nerves and muscles is understood as the use of electric current to excite or enhance the activity of these structures [Bogolepov V.M. et al., 1985]. Electric current, changing the concentration of tissue ions near the cell membrane and changing its permeability, acts like natural biocurrents.
The therapeutic effect of electrical stimulation is associated with increased blood flow to contracting muscles and improved venous outflow, which is accompanied by a local increase in metabolic and plastic processes, as well as an increase in the functional activity of the central nervous system. However, the therapeutic effect of electrical stimulation entirely depends on how correctly the parameters of the stimulating electrical current are selected.
The choice of exposure parameters, in turn, is determined by the degree of disruption of the muscle innervation and the condition of the muscle tissue. Therefore, electrical muscle stimulation should always be preceded by a diagnostic study of the degree of muscle denervation. The main question to be resolved is the question of the presence of a complete (anatomical or functional) or partial break of the nerve, since with a intact or only partially damaged nerve, stimulation of the muscle must be carried out through the nerve, whereas with complete denervation of the muscle it is necessary to limit stimulation of the muscle itself. This issue can be resolved using electromyography and/or electrodiagnostics.
Currently, the main diagnostic method for determining the level and degree of damage to nerve conductors is electromyography in its modern versions (stimulation, needle). Let us recall that the main electromyographic signs of partial nerve damage are a decrease in the velocity of excitation (during demyelination) and/or a decrease in the amplitude of the M-response (a sign of axonopathy), as well as changes in the structure of action potentials of motor units.
Signs of complete interruption of a peripheral nerve include the absence of an M response when the nerve is stimulated, as well as spontaneous activity recorded in the muscle at rest. Damage to a motor neuron at the level of the anterior horns of the spinal cord is characterized by the appearance of fasciculations at rest, and with active contraction - a sparse interference curve with individual high-amplitude discharges of long duration.
Physiotherapy and rehabilitation
Restoring movements is impossible without physiotherapy. This is the main part of the treatment of peripheral paralysis. It is impossible to get rid of motor dysfunction using medication alone. It is necessary to develop damaged muscle groups to avoid their complete atrophy.
Patients are prescribed galvanization sessions. Electrodes are applied to the affected areas and a low-voltage constant electric current is applied. This helps improve tissue metabolism and restore damaged neurons, as well as increase muscle tone. Baths with mineral waters are also shown. This allows you to influence peripheral nerves through skin receptors.
Such procedures are allowed to be carried out only after the acute symptoms of the infectious disease have been relieved. Galvanization and water treatments are quite effective, but the process of restoring movement takes a long period of time.
Massage for flaccid paralysis helps restore muscle tone and prevent muscle atrophy. The impact on the affected areas should be quite intense, using kneading and rubbing of the damaged muscles. But it is very important to prevent injury to muscle tissue. Therefore, this procedure should only be trusted by a qualified specialist. It is useful to combine classical and acupressure massage.
Exercise therapy for flaccid paralysis is a mandatory part of treatment. However, it must be taken into account that patients have weakened muscles and joints. Therefore, at the initial stage, passive movements using support are shown. For example, the patient rests the affected foot on a special box and tries to bend the leg. Crawling on all fours is also useful. First, the patient moves the diseased limb using the muscles of the trunk, leaning on his hands. As the movements develop, the exercises are performed while kneeling.
Gymnastics in water is very useful. Exercises for the limbs can be combined with medicinal baths.
If hand movements are impaired, the patient must be taught simple household skills. For this purpose, tables with special stands are used in physiotherapy rooms. The patient learns to fasten buttons independently, press the switch button, and turn the key in the lock. Modeling from plasticine helps restore fine motor skills of the hands.
It is recommended to wear orthoses during rehabilitation. This will help maintain the injured limb in an optimal position.
Physiotherapy and massage
Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment help to speed up the restoration of motor activity and restore sensitivity. For paralysis, methods of electrical stimulation - galvanization, balneotherapy - are successfully used. Such therapeutic methods improve the conductivity of nerve fibers, accelerate regeneration and cell restoration. A course of such treatment is carried out only after the underlying disease that led to paralysis has been relieved.
To normalize muscle activity and to prevent the development of atrophy, massage is used. Patients are prescribed an intense massage, with prolonged kneading of damaged muscles and strong rubbing.
When performing a massage, it is important to remember that muscles constrained by paralysis should not be subjected to traumatic effects. The massage should be intense, but without excessive effort. Traumatic effects on the affected muscles can have the opposite effect.
To restore muscle activity, a long course of massage is indicated, up to six months. With regular procedures, the result will become noticeable after the first 5 sessions.
In addition to classic massage, good results are achieved by applying targeted pressure to painful nodes of the human body. In this case, you also cannot act directly on the stiff muscle. This technique improves metabolic processes in muscle fibers, stimulating the rapid restoration of mobility and sensitivity. The maximum effect is achieved by using two techniques simultaneously, alternating.
Forecast
The prognosis of the disease depends on the degree of neuronal damage. If diagnosis and treatment were carried out in a timely manner, then it is quite possible to restore movement. However, this will require long-term complex therapy and rehabilitation. Typically, the process of restoring motor function takes about 2 years. After surgical treatment, movements return to normal after about 1 year.
In advanced cases, it is no longer possible to restore movement even with surgery. If a patient has lost more than 70% of neurons, then such changes are considered irreversible.
Treatment of AFP
Therapy is aimed at restoring the function of peripheral nerves affected by the viral disease. For this purpose, use:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- folk remedies.
The combination of these methods makes it possible to obtain a good therapeutic effect, but only with timely treatment. If more than 70% of neurons have died as a result of a viral infection, restoration of mobility and sensitivity of the affected area is impossible.
Drug therapy includes treatment with neurotropic and vasoactive drugs. Therapy is aimed at improving metabolism and conduction of nerve fibers, improving blood circulation and stimulating the activity of the nervous system.
The drugs are administered either intravenously or intramuscularly. It is possible to administer drugs using a dropper in cases of extensive neuronal damage.
Vitamin therapy is required. The introduction of B vitamins is indicated, which stimulate cell renewal and strengthen the nervous system.
During the rehabilitation period, wearing a bandage or orthosis is indicated to fix the limb in a physiologically correct position. This measure will avoid visible deformation of the joint due to weakening of the muscles.
Prevention
How to prevent the death of motor neurons and the occurrence of paralysis? Most often, enteroviral diseases lead to such complications. To avoid infection, the following recommendations must be followed:
- Get vaccinated against polio on time;
- avoid contact with patients with enteroviral infections;
- strengthen the immune system;
- timely and completely cure infectious diseases;
- After suffering from polio, regularly visit a neurologist for 6-12 months.
These measures will help to avoid dangerous complications of infectious pathologies and maintain motor function.
Preventive actions
In order to avoid the development of disorders, experts recommend following the following instructions:
- Seeing a doctor at the slightest symptoms of the disease or any other problems;
- blood pressure should always remain under control;
- treating infectious diseases in their early stages, preventing them from causing more serious problems;
- It is best to eliminate all bad habits - alcohol and smoking contribute to the development of many health problems, not only peripheral paralysis;
- effective prevention is maintaining a healthy lifestyle (proper nutrition, rest, adherence to a routine and physical activity).
Factors influencing the development of the disorder
Symptoms of flaccid paralysis, such as loss of motor function, are not an independent disease; they are often caused by concurrent illnesses.
Essentially, paralysis is a disorder in which a person makes involuntary movements. In some cases, patients cannot move part of the body or are completely immobilized.
Partial loss of motor functions indicates paresis. In any case, the disorder is evidence of damage to the nervous system, namely the centers that are responsible for movement and the peripheral parts. The following factors are noted as influencing the development of pathology:
- previous injuries;
- metabolic problems;
- infectious diseases (syphilis, tuberculosis, encephalitis, meningitis and polio);
- nutritional and toxic (pellagra, beriberi, heavy metal poisoning);
- oncological diseases;
- congenital and hereditary factor;
- intoxication;
- disruption of the nutrition system;
- diseases whose etiology remains unknown, for example, multiple sclerosis.