The essence of the method
Electromyography is a research method that determines the location of possible damage. If the lesions are in soft tissues, diagnosis using radiography is not carried out: EMG demonstrates the characteristic features of damage to muscle tissue and peripheral nerves.
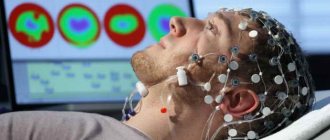
To carry out diagnostics, a device called an electromyograph is used. The device consists of an integral computer system capable of recording certain signals (biopotentials) of muscle tissue. With the help of the device, biopotentials are enhanced, which makes it possible to determine the degree of damage to muscle tissue without diagnostic surgery.
Diodes are attached to the computer system, which record deviations from the norm. Using the device, the signal is amplified, and an image is displayed on the screen showing the state of the muscle tissue and peripheral nerves of the area of the body being examined. Modern devices display images directly on the monitor, but the old generation electromyograph records the received impulses on paper.
Content:
- The essence of the method
- Type of EMG
- The feasibility of performing EMG
- Indications for the procedure
- Direct contraindications
- Possible complications
- Preparation for EMG
- Stages of the procedure
- Results
- Decoding the results obtained
During normal functioning, a certain muscle impulse is created - it is the change in impulse (deviation from the norm) that is recorded by the device during diagnosis. The doctor analyzes the resulting image, which allows you to identify damage and pathologies of muscles or nerves.
Where can I get ENMG done in Moscow and St. Petersburg?
There are many medical institutions and diagnostic centers in Moscow and St. Petersburg where you can conduct research using the ENMG method.
Here are some of them in Moscow:
- MEDSI , st. Krasnaya Presnya, building 16.
- Medic City , Poltavskaya st., 2.
- NeuroMed , Shabolovka, 34.
In St. Petersburg:
- Doctor SAN, Marata St., 78.
- Med , st. Repisheva, 13.
Type of EMG
Modern devices differ in the types of pass diodes: the range of such parts determines the accuracy of the results obtained. Two types of devices are used for superficial and local examination. Global diagnostics occurs in a non-invasive manner (non-contact) and allows you to see the activity of muscle tissue over a large area of the body. This type of diagnosis is used in cases where the cause of pain or damage within the muscles is unknown. Examination of a wide area allows us to track the dynamics in the treatment of chronic diseases.
Local EMG is carried out using the contact method: the electrode is inserted directly into the part being studied. The area of the body is first numbed and treated with disinfectants. The electrode is a thin needle that makes a minimal puncture. The invasive technique is suitable for examining a small part of muscle tissue.
The choice of technique depends on the expected problem and the doctor’s prescriptions. Indications for EMG are patient complaints, injuries and injuries that affect a person’s walking and mobility. In some cases, to accurately diagnose the problem, 2 types of EMG are prescribed at once: local and global.
Types of ENMG
ENMG research is carried out using three types of techniques, with the help of which a complete picture is created to accurately determine the pathology in the lower and upper extremities.
The functional combination of the three types makes it possible to identify diseases at the initial stage of development and promptly prescribe appropriate treatment. Patients must have x-rays, general analysis results from MRI and CT procedures, and provide a medical record.
If a patient is suspected to have only one nerve ending with pathology, he undergoes a procedure according to an abbreviated program with the preparation of a protocol corresponding to the disease.
Superficial
This technique is considered non-invasive, that is, during the procedure the integrity of the body’s structure is not violated. During a superficial examination, sensor electrodes are attached to the patient’s lower extremities.
When the device is connected, impulses begin to emanate from nerve endings that are examined without stimulation, which are reflected on the device monitor. The study is carried out to record voluntary nerve contractions and evaluate the signals emanating from them.
Superficial electroneuromyography
Needle
This is done very carefully using sensors with electrodes with thin needles installed at the ends:
- The needles of the device are inserted into the area of the plexus of the muscles of the lower or upper extremities.
- Patients may experience slight itching or a burning sensation.
- The needle method is effective for pathologies of the spinal cord and skeletal muscles, and gives a more accurate result in the diagnosis of myelopathy and inflammatory muscle diseases.
The feasibility of performing EMG
This safe technique is used to examine patients suffering from muscle pain. EMG is used as an independent or auxiliary procedure. Muscle weakness and cramps are a common reason for visiting a neurologist.
If no additional symptoms are detected in the patient, the doctor prescribes a safe and simple procedure. EMG is indicated for children and elderly people who have difficulty moving. It is advisable to conduct electromyography before competitions or heavy physical activity.
Indications for the procedure
A direct indication for EMG is pain. Sudden or frequent muscle pain is an alarming sign that should be responded to immediately. Intense muscle pain and muscle twitching require additional examination of muscle tissue. Using the EMG procedure, diagnoses are confirmed: myasthenia gravis, myoclonus or amyotrophic sclerosis. Electromyography is prescribed if the development of polymyositis is suspected.
It is advisable to diagnose muscles in case of loss of muscle tone (dystonia) or after injury to peripheral nerves. Damage to the central nervous system, brain or spine is a reason for a complete examination of muscle tissue using EMG.
Diagnostics with the introduction of diodes is prescribed for suspected multiple sclerosis, botulism, or after polio. For facial neuropathy or carpal tunnel syndrome, invasive electromyography is used. The direct indication for the procedure is diseases: micro-stroke or tremor. To safely administer Botox, EMG is used first.
The patient is prescribed the required number of procedures that do not harm surrounding tissues. The first examination occurs at the initial stage of diagnosis before treatment is prescribed. During therapy, EMG is performed repeatedly. For preventive purposes, electromyography is also used for adults and children.
Direct contraindications
In general, electromyography is a safe procedure that is prescribed to patients of different genders and age categories. EMG does not cause harm. Painful sensations during the insertion of diodes are relieved with the help of local painkillers. The diagnostic procedure is allowed even for children with muscle problems.
Contraindications to the procedure:
- infectious diseases with pronounced symptoms;
- non-infectious chronic diseases in the acute stage;
- epilepsy;
- a disease of the central nervous system that may interfere with the examination of muscle tissue;
- mental disorders (the invasive procedure is especially careful in patients with mental disorders);
- acute heart failure;
- angina pectoris;
- presence of an electrical stimulator;
- skin diseases.
In most cases, contraindications relate to the needle procedure. The technique is not prescribed to patients with diseases that are transmitted through blood - AIDS, infectious diseases, hepatitis. For people with blood clotting problems, an EMG is not recommended.
Insertion of the needle occurs with minimal bleeding, but the simple procedure can be problematic for people with bleeding disorders. Hemophilia is a direct contraindication for invasive diagnostics. Individual pain threshold is a contraindication to EMG.
Contraindications for ENMG studies
There is a category of patients for whom the procedure of electroneuromyography of the extremities is contraindicated.
These are patients diagnosed with:
- cardiovascular diseases, hypertension;
- ARVI;
- schizophrenia and epilepsy;
- hemophilia (blood clotting disorder).
ENMG is not prescribed for patients with hepatitis or HIV infection, who are undergoing physiotherapy, pregnant or breastfeeding women. To this list are added those who have trophic ulcers on the lower extremities or severe damage to the skin.
Attention! Those using an endoprosthesis and a pacemaker should know that ENMG is also contraindicated for them.
Possible complications
EMG is a safe research method. Cautions concern the healing of the wound that forms at the site of diode insertion. The hematoma formed at the puncture site heals within 10-15 days. The skin does not need additional treatment after the puncture.
If EMG is prescribed in combination with other procedures, the doctor will tell you about the restrictions and precautions after the procedure. In addition, electroneuromyography is prescribed, which allows you to fully assess the extent of damage.
Contraindications for this additional diagnostic method are the same as for electromyography.
Preparation for EMG
EMG does not require lengthy preparation. Before prescribing the procedure, the specifics of its implementation are taken into account: before electromyography, you should stop taking psychotropic drugs or medications that affect the functioning of the nervous system. Before the procedure begins (a couple of hours before the EMG), you should not eat or drink energy drinks. Avoid consumption of caffeine, chocolate and tea.
If during treatment the patient takes drugs that affect blood clotting, it is necessary to additionally consult with a doctor before the procedure. Any contraindications are taken into account before diagnosis begins. For young children, EMG is performed in the presence of their parents.
Factors influencing results
There are several factors that can influence the results of the study and make it unreliable:
- Taking medications that target the neuromuscular system. These include anticholinergics and muscle relaxants.
- Disorders of the blood clotting system.
- A significant layer of fat in the places where the electrodes are attached.
- Distance between installed electrodes.
- The accuracy with which they are installed.
- Their direction in relation to muscle fibers.
- Failure of the patient to follow medical instructions.
Stages of the procedure
The procedure is carried out in inpatient and outpatient settings. During EMG, the patient should be in comfortable conditions (sitting, standing or lying down). Before the invasive technique, the area of skin through which the diode is inserted is treated with an antibacterial agent. Antiseptics are used for processing. The healthcare worker inserts the diode and fixes it for further diagnosis.
During the procedure, the patient experiences slight discomfort - this is how the diodes read muscle tissue impulses. At the beginning of electromyography, the muscle potential in a relaxed state is read: these data will become the basis for studying muscle tone. At the second stage of the procedure, the patient needs to tense his muscles: the impulses are read again.
Cost of ENMG examination
| Name of procedure | Cost in Moscow | Cost in Russia (average) |
| ENMG of the upper extremities | From 2250 rub. | About 3500 rub. |
| ENMG of the lower extremities | From 2250 rub. | From 3000 to 4000 rub. |
| ENMG stimulation | From 3,000 to 5,000 rubles. | Expanded up to 5000 rub. |
| Single nerve study | From 1000 rub. | From 1000 rub. |
How much the ENMG service will cost depends on the choice of the type of procedure (stimulation or needle), the number of nerves and muscles to be examined. The indicated prices are conditional. Each clinic has a price list, which can be found on the official website of the medical institution.
Results
The results obtained are a snapshot (electronic image). The first to assess the condition of muscle tissue is a specialist who conducts diagnostics - a functional diagnostics doctor. Based on his conclusion, the attending physician makes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes effective treatment.
The patient does not independently decipher the results of electromyography. The diagnostician does not prescribe further therapy: he assesses the condition of the muscle and nervous tissue located in the part of the body being examined.
An electromyogram looks like a snapshot of a cardiogram. It consists of oscillations: the amplitude of the oscillations is determined by the state of the human muscle tissue. The height and frequency of vibrations are important for diagnosis.
Decoding
The electromyogram looks a little like an electrocardiogram. It detects oscillations (oscillations) with different amplitudes, frequencies and periodicities. When the muscle just begins to contract, the amplitude of these oscillations is about 100-150 μV, and in the state of maximum contraction - 100-3000 μV. These indicators directly depend on a person’s age and physical development. A thick layer of subcutaneous fatty tissue in the area of study and diseases of the blood coagulation system can distort the result.
- Myositis, muscular dystrophy and other primary muscle diseases cause a decrease in the amplitude of oscillations according to the severity of the disease (in the initial stage up to 500 μV, and in the terminal stage - even up to 20 μV at maximum excitation). On local EMG at the same time, the number of potentials is within normal limits, but their amplitude and duration are reduced.
- For polyneuropathies of any nature - toxic, metabolic, hereditary - surface electromyography records a decrease in oscillations, as well as single biopotentials of varying amplitude and frequency. On local EMG, polyphasic, relatively normal biopotentials are visualized. If most of the nerve fibers have died, muscle activity is minimal or absent altogether.
- Spinal amyotrophies on local EMG are characterized by an increase in the amplitude of oscillations and sharp waves. With surface electromyography, fasciculations are determined at rest, and with severe muscle tension - the so-called “picket fence rhythm” - potentials with high frequency and amplitude.
- Myasthenia gravis on EMG is characterized by a decrease in the amplitude of oscillations with repeated rhythmic stimulation of the muscle.
- Myotonic syndromes cause electrical activity of low amplitude and high frequency during the period of muscle relaxation after its contraction, which gradually fades away. Local electromyography records muscle hyperexcitability - the emergence of a whole series of biopotentials after the introduction of an electrode into it.
- Essential tremor and Parkinson's disease appear on surface EMG as a series of increases in oscillation amplitude and subsequent decreases. The duration and frequency of such volleys directly depends on where the pathological process is localized.