Lemtrada is an anti-multiple sclerosis drug also known as alemtuzumab. It is a monoclonal antibody that binds to certain receptors on the surface of immune cells and changes the way the immune system works so that it stops attacking nerve fibers. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) currently recommends the use of Lemtrada for relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis after two or more courses of classical treatment have failed.
How does Lemtrada work?
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the sheaths of nerve fibers necessary for the normal conduction of impulses. The disease is chronic and is currently considered incurable; doctors can only slow down its progression.
The immune system is complex. It consists of different types of cells, they “communicate” with each other and with other tissues of the body using molecular signals. There are special receptor proteins on the surface of immune cells. When they receive a signal and are activated, it leads to certain effects.
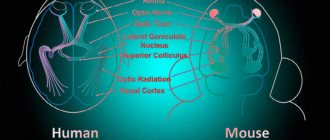
One of these receptors is called CD52 (another name is CAMPATH-1 antigen). Leukocytes that carry it on their surface are prone to aggression against the nervous system. They are credited with a leading role in the occurrence of relapsing multiple sclerosis.
Lemtrada attaches to white blood cells that carry the CD52 receptor and causes “genocide” of them. The body is cleansed of “pest leukocytes”, and gradually their place is taken by “useful” immune cells.
This mechanism of action has been studied in transgenic mice. The subtleties of how the drug works in the human body are still not fully known.
Monoclonal antibodies
Mouse, chimeric or humanized antibodies are used against various molecules, components of the immune system. But the potential benefits sometimes outweigh the toxic effects of the drugs. If substances that are not fully humanized are used, antibodies often form in the body. This leads to a lack of effectiveness of the product.
Although monoclonal antibodies have the disadvantage of being invasively administered, they are administered at longer intervals. Their disadvantage is the unexpected side effects of treatment when interfering with the fine network of immune regulation. On the other hand, selective intervention is more effective.
Many of these antibodies are used in hematology or in the treatment of other autoimmune diseases. Unfortunately, some of them are ineffective for MS.
Who is treated with Lemtrada and how?
The most effective therapy for multiple sclerosis is currently considered to be regimens using DMTs - drugs that change the course of multiple sclerosis. They usually need to be administered every few days or monthly.
When treating with Lemtrada, only two short courses over two years are sufficient:
- The first course lasts 5 days in a row. Every day the drug is administered intravenously over 4 hours, after which the patient’s condition is monitored for 2 hours.
- The second course is carried out a year later, it lasts 3 days.
The main indication for the use of Lemtrada, as we have already mentioned, is relapsing multiple sclerosis, if, despite treatment with other drugs, the patient has had a relapse within the last year or has deteriorated according to MRI results.
Alemtuzumab is sometimes used as a first-line treatment if a person with multiple sclerosis has recently relapsed or an MRI has detected active disease (new lesions in the brain).
Multiple sclerosis (MS): briefly about the disease
Despite the name, the disease is autoimmune in nature and affects young people. In this case, it is not the symptoms of intellectual impairment that come first, but neurological problems. For example, pain of unclear localization, paralysis and paresis, loss of function of the sensory organs.
| Localization of the lesion | “Scattered” speaks of non-localized damage to nervous tissue. Both the endings of nerve fibers and the neurons of the brain are destroyed. |
| Symptoms | Paresis, paralysis, tremor, cramps and other muscle cramps, fasciculations, blurred vision, unsteadiness when walking. |
| Diagnostics | Laboratory tests, antibody studies, MRI and other imaging methods, functional tests (ENMG, EEG). |
| Treatment | The use of DMTs, symptomatic therapy and hormonal drugs during an exacerbation. |
Treatment of multiple sclerosis in Russia has reached a new level. Effective first- and second-line DMT drugs have become available to patients. Now even severe forms of the disease can be controlled.
However, the use of such therapy is expensive for the state budget. Not all regions can afford modern MS medications. Therefore, attention should be paid to the development of our own domestic drugs. New domestically produced drugs are already at the stage of clinical trials.
How much better is this than classical therapy?
The results of one of the largest studies were published in the authoritative scientific journal The Lancet. The authors concluded that when treated with Lemtrada, the risk of relapse was 54.9% lower than when using a drug from the DMT group - interferon beta-1a (Rebif). It was the publication in The Lancet that largely contributed to the fact that in November 2014 the drug was approved in the United States for the treatment of multiple sclerosis.
Similar results were noted in other studies.
With regard to the risk of disability, the situation turned out to be ambiguous. In some studies, alemtuzumab was 42% better than interferon. In others, the difference was 30% - this figure could be due not to drugs, but to random reasons.
It is much more difficult to figure out what triggers the onset of such diseases.
Scientists have not yet come to a consensus on where diseases originate. However, there are two points of view regarding this issue. From one point of view, there is every reason to believe that the cause of the development of these diseases is the rare consequences of simple infections. From another point of view, there is an assumption that the development of diseases is affected by certain disturbances in the functioning of genes and their mutations. For example, scientists from Britain have found that multiple sclerosis often begins to develop in people who have an active Rab32 gene.
It should be noted that Larisa Litvinova and her colleagues determined how it is possible to stop the development of multiple sclerosis by paying attention to the brightest, most famous, most long-awaited for many people and unique of its kind process of the birth of a new body. The immune system comes to terms with its presence. It is the fetus inside a woman.
According to scientists, the fetal gene consists of 50 percent genetic material inherited from the father. It is this gene that contains the instructions by which protein molecules that are unfamiliar to the woman’s immune system are assembled. Considering the specifics of a woman’s immune system, when protein molecules enter her environment, she must begin to protect herself from the cells of the fetus. But, however, in reality this does not happen. Meanwhile, the placenta produces special hormones. These hormones affect the woman's immune system and force the immune system not to attack the cells of the fetus. Moreover, hormones also protect the fetus from various types of infections.
The hormones that develop in the female body during pregnancy have interested biologists. It is the study of the specifics of their work, the study of all their secret properties and capabilities that will make it possible to produce a medicine for multiple sclerosis. As a result of the disease, the immune system considers brain cells and other tissues to be non-native.
In an effort to find a cure for such diseases, and fascinated by the hidden properties of pregnancy hormones, Russian biologists, in order to achieve their goal, began to diligently study the interaction of these hormones on immune cells. The influence of various pregnancy hormones on the behavior of immune cells that are already familiar with real and non-real pathogens, but have never encountered them, has been fully studied. It was thanks to their observations of the reaction to hormones that Russian scientists tried to discover a substance that could suppress immune cells, but did not cause harm and did not completely suppress the immune system.
As you know, Russian biologists have recently made important steps in finding a cure for multiple sclerosis. They made the medicine and conducted a study on its effects on volunteers.
It is presented in the form of microscopic balls, which are surrounded by protection from synthetic molecules. Once ingested, they disintegrate over time. The medicine itself consists of fragments of myelin that help prevent the immune system from pushing away nerve cells. At a scientific conference held in Moscow dedicated to multiple sclerosis and other autoimmune diseases, scientists reported that the production of this medicine is progressing. In addition, other immunological factors that affect the nervous system and other organs are being studied.
Today, preparations for the next phase of clinical trials are in full swing. Scientists hope for the success of their experiments. According to scientists, with a good pace of work, the medicine may be on sale within three years.
Risks associated with drug administration
Lemtrada is not a safe drug. Treatment is associated with certain risks. Some side effects may be life-threatening:
- Autoimmune conditions in which the immune system begins to attack the body's own tissues. With immune thrombocytopenia, increased bleeding develops, with kidney damage - severe renal failure, which may require dialysis or a kidney transplant.
- Reactions to drug administration develop within 24 hours (sometimes later) after infusion and can be very severe. Alarming symptoms that require immediate medical attention: swelling of the face, difficulty breathing, severe weakness, increased or slow heartbeat, a feeling as if the heart is “freezing”, “turning over”, “jumping out of the chest”, chest pain, rash on skin.
- Oncological diseases. Treatment with Lemtrada increases the risk of thyroid cancer, melanoma, and lymphoma.
- Problems with the thyroid gland. It is possible to both increase (hyperthyroidism) and decrease (hypothyroidism) its function. “Alarm bells”: severe sweating, unreasonable weight loss or gain, rapid heartbeat, nervousness, emotional instability, increased fatigue, chilliness in the arms and legs, constipation.
- Blood problems. Due to a decrease in the number of different types of cells in the blood, some disorders develop: frequent infections, jaundice, chest pain, rapid heartbeat, dark urine.
- Severe infections. The likelihood of infection with herpes, hepatitis, and tuberculosis viruses increases.
- Lung disorders. Some patients receiving alemtuzumab develop pneumonitis, a non-infectious inflammation of the lungs.
Synthetic immunomodulators
BG00012 (FAE - fumaric acid ester) is a modified dimethyl fumarate molecule that is purer and has reduced side effects. The tablets have improved gastrointestinal tolerance. The drug affects T-lymphocytes, supports the alignment of the Th2 immune response with the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines. The drug activates the Nrf-2 pathway to protect cells from toxins, metabolic and inflammatory stress, and has a neuroprotective effect.
Approximately 10% of patients receiving BG00012 experienced elevated liver enzyme levels. The increase was 2-3 times higher than the upper limit of the standard, the indicators gradually returned to normal.
Complications occurred mainly when using the original liquid form of the drug. Now the drug is produced in capsules, which prevents its contact with the mucous membranes of the mouth, esophagus, and stomach. The medicine is not suitable for patients with stomach ulcers.
Typical side effects, occurring in more than 3% of treated patients, include:
- facial redness;
- body redness;
- feeling of heat;
- burning of the skin;
- increased sweating;
- headache;
- toothaches.
In addition, leukocytosis and cold symptoms have been reported.
It is recommended to plan pregnancy 30 days after stopping taking the drug.
What is important to tell your doctor before starting treatment?
The risk of serious side effects can be reduced by taking the drug exactly as directed and not using it on people who already have health problems. If the patient suffers from at least one of the following conditions, the doctor must know about it:
- increased bleeding;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- renal dysfunction;
- HIV;
- any infections, including recent ones;
- cancer;
- vaccination with live vaccine within the previous 6 weeks.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding are also contraindications to the use of the drug. If you take any medications, vitamins, dietary supplements, be sure to tell your doctor about it.
We offer comprehensive rehabilitation for multiple sclerosis. For detailed information call us at number. We will arrange a consultation with recognized experts in the treatment of multiple sclerosis as soon as possible.
Advances in Multiple Sclerosis Research
Scientists are studying the cause of the disease. The influence of endogenous retroviruses and the herpes virus is currently being considered. The infectious agent indirectly affects the defense system. Thus, it activates the uncontrolled process of antibody production.
New knowledge is also emerging in the field of genetic research. Scientists want to find the exact relationship between the genome and not only the possibility of disease. Now, based on the genotype, it will be possible to judge the form of the disease or the type of possible progression.
The pathogenesis of the disease is also being clarified. Now the inflammatory phase of the disease is distinguished. Then there is an active process of formation of damaging biologically active substances. Later comes the phase of neurodegeneration. It occurs when the myelin sheath and nerve tissue are destroyed. New understanding of the stages of the disease will help develop more effective treatment regimens.
Stem cells
This promising direction is still at the stage of clinical trials. In 2021, the experiment ended, in which about 200 people with severe forms of the disease took part. There have been several deaths following transplantation. But more than 50% went into remission. The disease returned in a milder and more controlled form. Research in this area is ongoing.
Monoclonal antibodies
The development of new targeted drugs is actively underway. For example, natalizumab shows excellent results in relapsing-remitting forms of multiple sclerosis. Exacerbation episodes decreased by 68%.
It should be remembered that such a strong impact on the immune system can lead to consequences. One of the side effects is the development of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. New chemical compounds with minimal risk to the immune system are being designed.
Primary progressive multiple sclerosis
Roche has developed a drug to treat the most severe form of the disease. New anti-B cell drug reduces relapse rates. In addition, the likelihood of disability in people with MS is reduced. Rituximab, an antibody to CD 20, is currently known. Ocrelizumab and epratuzumab are being tested.
Rehabilitation
Unfortunately, domestic medicine has paid little attention to auxiliary methods of rehabilitation. Kinesiotherapy, occupational therapy and physical therapy have little place in the treatment of the disease.
Kinesiotherapy should be individually selected. Exercises are chosen for each specific case of illness. Special simulators must be used in rehabilitation. They allow you not to overwork atrophied muscles. The patient accumulates adaptation to the load.
Social foundations and movements are emerging in which occupational therapists work. These are specialists who adapt the environment to the needs of a sick person. The Ministry of Health plans to introduce such a position and create a training course in the specialty.
Autovaccination
A method of T-cell autovaccination is under development. Blood is drawn from patients. Leukocytes are isolated from it. These cells are stimulated by neural tissue antigens. The cultures are then irradiated and reintroduced into the body.
After exposure to radiation, cells cannot reproduce. And the defense system recognizes them as foreign agents and destroys them. Since the patient’s T-lymphocytes have a similar structure, some of these cells are also destroyed. This suppresses immune inflammation and their aggression towards their own tissues.
New approach to treatment regimens
Today, doctors use two approaches. The first type of therapy is called escalation therapy. In this case, drugs are selected from simple to complex. For the first line, interferons and glatimer acetate are used. If they were ineffective, move on to the second line (mitotraxon, cyclophosphamide, monoclonal antibodies). The second circuit is inductive. “Heavy artillery” stops inflammation. And after that they move on to easier treatment.