The brain is the main organ of the central nervous system. It consists of a large number of neurons interconnected by synaptic connections. They are the ones who form the impulses that control the functioning of the entire body.
However, some diseases can disrupt the functioning of the brain, thus causing disruption throughout the body. Let's look at the most common brain diseases according to ICD-10.
Causes of diseases
At first, almost all brain diseases occur without visible symptoms, so they can be identified in the final stages, when it is no longer possible to help the person.
The reasons for the development of such pathologies may lie in:
- Infectious diseases, for example, AIDS, rabies, etc.
- Skull injuries.
- The effects of harmful chemicals on the human body.
- Radioactive radiation.
- Bad habits (alcohol, smoking, drug addiction).
- Unbalanced diet.
Vascular aneurysm
This head disease poses a great danger to human life. During its development, there is a loss of elasticity of the blood vessels in the brain, which is why they can rupture. And this causes bleeding in the brain.
Pathology may appear due to a hereditary or acquired defect in the walls of an artery or vein. The particular danger of the disease is that in the initial stages and until rupture, it does not manifest itself in any way. If a rupture occurs, it is very difficult to save the person, so it is very important to monitor your health and undergo regular examinations. This brain pathology has increasing symptoms. Among the main ones are:
- migraine;
- feeling of weakness even with light exertion;
- vomiting, nausea;
- negative reaction to noise and light;
- speech disorder;
- numbness of any part of the body;
- paresis and swelling;
- visual disturbances.
If such symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. If the diagnosis indicates the presence of an aneurysm, then the most effective treatment method will be surgery. This operation will strengthen the vessels and block the neck of the aneurysm.
Atherosclerosis
It is a neoplasm (plaques) in the vessels of the brain that block the flow of blood into it and, accordingly, cause oxygen starvation of neurons.
At first, it is very difficult to identify the disease, so they consult a doctor at a later date. By this time, blood clots have already formed in the vessels, some areas of the brain have undergone necrosis, cysts have appeared, and the activity of the entire organ has been disrupted.
The causes of the development of atherosclerosis are:
- high cholesterol in the blood;
- hypertension;
- the presence of chronic diseases (thyroid problems, diabetes, etc.).
Most often, such brain problems occur in old age. You can understand the development of this disease by the following signs:
- Frequent and painful headaches.
- Feeling of anxiety, fear.
- Constant ringing in the ears.
- Nervousness.
- Organic damage, that is, decreased attention, a feeling of depression, apathy.
- Insomnia.
- Frequent fainting.
- Decreased performance.
To treat atherosclerosis, drugs are prescribed that:
- Limit the intake of cholesterol into the body.
- Strengthens the body's ability to remove cholesterol.
- Reduce the symptoms of the disease.
- Normalizes fat metabolism in the body.
- Improves the condition of the walls of blood vessels.
- Normalizes blood flow in the body.
It is also very important to take preventive measures to prevent brain disease from returning. These include: proper and balanced nutrition, giving up bad habits and exercising.
Stroke
This cerebrovascular disease is the most common. It often leads to death or disability. The pathology is manifested by impaired blood circulation in the brain. There are two types of stroke: ischemic and hemorrhagic.
The first type is characterized by blockage of blood vessels, as a result of which cerebral circulation is disrupted and cell necrosis occurs in this area. In a hemorrhagic stroke, a blood vessel ruptures, resulting in a cerebral hemorrhage. The most common type of stroke is ischemic stroke, which mainly occurs in people over 60 years of age.
Predisposing factors to the development of pathology are chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart rhythm problems, etc.
Despite the fact that hemorrhagic stroke is less common, it is more dangerous for humans. People with hypertension or atherosclerosis are at greatest risk.
There are two types of signs of the disease:
- General cerebral:
- sleep disturbance;
- loss of consciousness;
- hearing impairment;
- frequent attacks of headache;
- attack of nausea, vomiting;
- profuse sweating;
- constant dry mouth;
- cardiopalmus.
- Focal signs depend on the part of the brain that is affected. If it is she who is responsible for movement, it means that the person develops muscle weakness, paralysis of the limbs, etc. The areas responsible for hearing, vision, and smell may also be affected, and accordingly, their functions will be impaired.
Causes of organic brain damage
Factors influencing the state of the central nervous system can be both external and internal provocateurs. The most common of them are:
- congenital damage to the nervous system;
- open and closed injury;
- past infections;
- general poisoning of the body with chemical compounds, alcohol, drugs;
- violation of the integrity of blood vessels, tumor processes, cancerous lesions;
- diagnosed multiple sclerosis;
- degenerative diseases.
In most cases, the development of pathology is caused by the careless behavior of the patient himself, provoking traumatic situations, abusing toxic substances, or trying to independently treat infectious diseases at home.
Migraine
It is characterized by frequent attacks of headaches that occur due to spasms of cerebral vessels. Conventional painkillers will not help here; properly selected therapy is needed.
Often, a migraine occurs on one side of the head and is accompanied by attacks of nausea and even vomiting. To cure this disease, it is necessary to undergo a series of examinations, and only after that the doctor will prescribe treatment. Sometimes a whole list of medications is required to eliminate a severe attack of pain.
Causes and symptoms
Anything can provoke the development of brain diseases: infection, head injury, genetic disruptions, delay in the development of central nervous system structures, exposure to toxic substances, alcohol, radiation exposure, poor nutrition, playing hazardous sports and neglect of basic hygiene rules, such as in case of injury organism by parasites.
But despite this, all diseases of the central nervous system have common signs of damage, which manifest themselves in specific neurological symptoms:
- headache attacks that do not stop after taking medications;
- a sharp change in behavioral and taste habits;
- problems with remembering and reproducing information;
- forgetfulness;
- deterioration of hearing, vision;
- loss of coordination of movements, tremors of limbs;
- hyper- or hypotonicity of muscles;
- numbness of a body part;
- fainting;
- convulsions;
- throwing back the head.
The neurological signs characteristic of a particular disease depend on the location of the lesion and its size, therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, a comprehensive examination of the head and its structures should be done.
Encephalopathy
This disease develops due to improper blood circulation in the brain. This may happen due to the patient’s existing atherosclerosis or hypertension. Also, brain disease can develop due to osteochondrosis, in which the vertebral discs are deformed. They are the ones who compress the arteries that supply blood to the brain.
Symptoms of the disease are neurological in nature. The onset of this head disease is associated with the patient’s usual irritability, weakness, and sleep disturbances. After this, depression and aggressive behavior develops for no apparent reason. Then there is a sharp change from increased excitability to apathy. The patient suffers from severe headaches and speech impairment.
Lack of proper treatment for encephalopathy leads to difficult-to-treat diseases, such as stroke or epilepsy.
List of diseases and their characteristics
The activity of the entire central nervous system is aimed at controlling the body. For example, any movement of the hand or wave of it is under the control of the brain, regardless of whether it was intended or happened spontaneously, at the level of a reflex.
As a result of the work of this organ, a person can talk, think, analyze and remember information. Therefore, any disorder in the organization of the brain is characterized by the development of certain symptoms.
Experts identify several groups of diseases characteristic of the central nervous system:
- Oncological. They can be both malignant and benign. These include, for example, glioblastomas and angiomas.
- Infectious. Develop under the influence of a pathogen: neurosyphilis, meningitis.
- Traumatic brain injuries: bruises, blows, concussions.
- Vascular diseases of the brain: aneurysms, hemorrhagic stroke, vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Autoimmune diseases: multiple sclerosis.
- Parasitic diseases: echinococcosis, toxoplasmosis, rabies.
- Hereditary pathologies: Recklinghausen's disease.
Although the mechanism of development of many brain diseases is poorly understood, modern diagnostic methods make it possible to identify them at an early stage of development. In this case, the main thing for the sick person is not to miss this opportunity: after all, his life often depends on how quickly treatment is started.
The most common brain diseases are:
- Encephalopathy. Characterized by the systematic destruction of brain matter. Develops against the background of a failure of intercellular metabolism. Encephalopathic changes in the structures of the central nervous system can appear against the background of inflammatory processes, exposure to alcohol, toxic substances, and vascular pathologies.
- Senile dementia of the Alzheimer's type (Alzheimer's disease). Refers to neurodegenerative diseases. Most often occurs after 65 years. As a result of the pathological process, a slow death of brain cells occurs, which leads to the development of corresponding symptoms and manifestations of the disease: dementia and impaired motor function.
- Aneurysms of the vascular system of the brain and aorta. Refers to pathologies of the structure of the body's circulatory system structures: under the influence of unfavorable factors, for example, due to surges in blood pressure and weakening of muscle tissue, the wall of the blood vessel becomes stratified, and in its place a protrusion forms in the form of a sac filled with blood - an aneurysm, which can subsequently burst.
- Hemorrhagic stroke or acute cerebrovascular accident. It develops against the background of mechanical damage to the integrity of blood vessels in the brain, resulting in bleeding. The resulting hematoma compresses and displaces the structures of the brain matter, which causes their swelling.
- Parkinson's disease. Refers to chronic neurological diseases. Usually debuts after age 65. Characterized by progressive dysfunction of the substantia nigra.
- Vegetovascular dystonia. Develops against the background of dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. It is characterized by a violation of the regulation of the tone of the walls of the blood vessels of the head.
- Oncological diseases. Sometimes tumors form in brain structures. They can be malignant or benign, be slow-growing and exhibit an aggressive distribution pattern. But in any case, their presence leads to the development of negative consequences: increased ICP, cerebral edema, etc.
- Epilepsy. It can be acquired, that is, develop as a result of TBI, or congenital. During an exacerbation (seizure), the patient cannot control his actions, and his brain refuses to work correctly: foam appears at the mouth, convulsions, shortness of breath, and the tongue sinks.
Alcoholic encephalopathy
This type of encephalopathy occurs against the background of frequent drinking of alcoholic beverages. During its development, brain damage and cell death occur. The disease can manifest itself in two forms:
- Psychologically – the patient’s memory, attention, and intelligence decrease. Frequent mood swings are disturbing, irritability and aggression appear.
- Pathological – impaired motor activity and sensitivity. A seizure or paralysis of any part of the body may occur.
Effective treatment requires intensive therapy, abstinence from alcohol and proper nutrition. In advanced cases, treatment is quite long, and symptoms may persist even after complete abstinence from alcohol.
Treatment
The method of treating brain damage depends on its type, the degree of pathological changes, and the severity of the general condition. Typically, treatment for traumatic brain injury and organ disease differs.
Traumatic brain injury
Immediately after receiving a traumatic brain injury, it is important to provide proper first aid, which will help alleviate the condition and improve the prognosis.
If there is no breathing or pulse, perform artificial respiration and cardiac massage. If these are not changed, the victim must be placed on his side, which avoids disruption of respiratory function due to vomiting.
If there is a closed injury, a cold compress is applied to the injury site to reduce pain and swelling. If there is bleeding from a wound on the skin, it is covered with a piece of gauze, and then the head is bandaged.
It is not recommended to independently remove bone fragments and other elements protruding from the wound before the ambulance arrives, because in this case the bleeding will only intensify. In addition, you can get an infection.
To correct post-traumatic disorders, the following is prescribed:
- neuropsychological treatment to restore memory, attention, and emotional state;
- taking medications to normalize blood flow in the brain;
- conducting speech therapy sessions to restore speech;
- psychotherapeutic treatment to correct the emotional background;
- a diet that includes foods that normalize brain function.
It is recommended to begin rehabilitation therapy no later than 3-4 weeks from the time of injury. Traditional treatment in such cases is not effective.
Damage of a different etiology
If brain damage is caused by an infectious agent, antibacterial drugs that are sensitive to the pathogen are prescribed. For example, for viral diseases, antiviral agents are used, for bacterial diseases, antibacterial agents are used. In combination, immunomodulators are prescribed to increase the body's protective function.
If a hemorrhagic stroke occurs, the hematoma is surgically removed. In the ischemic form of the pathology, the use of decongestants, nootropic, and anticoagulant drugs is indicated.
Mental disorders are corrected with medications (nootropics, tranquilizers, antidepressants) and non-drug (psychotherapy, etc.) methods. In most cases, they are combined.
It is worth noting that patients with acute brain tumors often have decreased memory, so they forget to take medications prescribed by the doctor. For this reason, this responsibility falls on the shoulders of relatives: they need to monitor the implementation of medical recommendations every day.
Intracranial hypertension
This anomaly indicates the development of a serious brain pathology (cyst, tumor, etc.). The most common symptoms of brain tumors, including cancer, are:
- attacks of headache;
- bluish complexion;
- lumen of the vascular network on the body;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- increased blood pressure;
- sensitivity to weather conditions.
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to identify the causes of the disease, according to which therapy is prescribed, including a specially selected diet, medication and special exercises. If the case is advanced, surgical intervention is recommended.
Malformation
This head pathology is congenital in nature, as a result of which the structure of the circulatory system is disrupted. The most important causes of the disease are: hereditary predisposition and injuries to the fetus during pregnancy.
The disease manifests itself only when the oxygen supply to the brain tissue ceases, as a result of which it cannot function properly. The only treatment used is surgery, in which the damaged area is removed or its blood supply is cut off.
Transient disorders in the brain
These are short-term disorders of the brain, which are accompanied by focal and general cerebral symptoms. A characteristic feature of such disorders is the rapid disappearance of symptoms. The reasons for such pathologies are as follows:
- minor hemorrhages;
- vasoconstriction;
- initial stage of thrombosis;
- microembolism.
Symptoms of pathology depend on their location:
- In the carotid artery - the patient experiences attacks of nausea, vomiting, and confusion.
- In the internal carotid artery, from which the ophthalmic artery arises, vision is impaired, which can lead to blindness.
- In the vertebrobasilar region - manifested by constant tinnitus, dizziness and other disorders.
Before you begin treatment for a disease, you need to diagnose it correctly. To do this, the main vessels of the head and neck are examined.
Alzheimer's disease
A rapidly developing disease in which the brain begins to overproduce a pathological protein, causing nerve cells to die. At first, the proper functioning of the organs and tissues of the body is disrupted, and then the person dies.
Like the brain diseases mentioned above, Alzheimer's disease is difficult to diagnose early on. The initial symptoms are accompanied by confusion and slight memory loss. Gradually, the symptoms increase, mental activity decreases, it becomes difficult to navigate in space and time, and constant mood swings are tormented, which develop into apathy.
After a certain period of time, the patient ceases to understand the meaning of his actions and cannot take care of himself. He is haunted by a feeling of fear, panic, and sometimes aggression, after which everything changes to peace. At the final stage of the disease, the patient ceases to recognize his surroundings, speech is impaired, he cannot move and control his needs.
An accurate diagnosis can only be made after death, during an examination of the structure of the brain.
In medicine, there are no types of medications that would help get rid of this disease or alleviate its course. During the development of Alzheimer's, it is necessary to take medications aimed at increasing blood circulation in the brain, as well as brain metabolism.
Common pathologies
There are many brain diseases, each of which is dangerous and requires urgent diagnosis and treatment.
Stroke
One of the most common and most dangerous vascular diseases. Now stroke has become significantly “younger”; it increasingly affects young and middle-aged people. Quite often, a stroke leads to death or disability. With this disease, there is a violation of blood circulation in the blood vessels of the brain. There are two types of stroke: ischemic and hemorrhagic.
The main symptoms of a hemorrhagic stroke are paralysis of the limbs, mainly on one side, and speech disorders. This type of head disease most often occurs during the day. Factors that contribute to this: severe stress, emotional stress.
Ischemic stroke often occurs at night due to disruption or cessation of blood circulation in one or more areas of the brain. As a result, these areas cease to function. List of main symptoms:
- crooked smile - due to partial paralysis, one of the corners of the mouth will remain motionless;
- motor impairment - a person will not be able to move one or more limbs due to paresis;
- speech disorders - if you ask a person to repeat a sentence, it will be difficult for him to do this, incoherent speech will be noted;
If we talk about the precursors of a pathological condition, dizziness, weakness, tinnitus or heaviness in the head may appear. If such violations are noticed, the patient should be immediately hospitalized for examination.
A brain tumor
Formations in the brain that are not specific to this organ are called tumors. Such formations lead to compression of certain areas of the brain, increased intracranial pressure and, accordingly, disruption of its functioning. There are two types of neoplasms: benign and malignant.
Symptoms:
- Head pain is the main symptom of the presence of a neoplasm. As it increases, the pain increases. The most common pain is in the morning, this is due to pressure on areas of the brain with general morning swelling of the membranes.
- Mental disorders that are a consequence of the pathological effects of neoplasms. The type of disorder depends on the location of the tumor. So, if it is located in the temporal lobe, then depression, panic attacks and memory loss are noted. The affected frontal lobe is characterized by decreased mental abilities and increasing aggressiveness.
- Paralysis, blurred vision, sensitivity to changes in temperature and pressure, as well as disturbances in gait and movement are possible.
It is very important to diagnose such brain diseases in the initial stages, then surgical intervention will help. After the tumor is removed there is every chance of recovery. In the last stages of brain cancer or with metastases, the neoplasm is not operated on; in such cases, maintenance therapy is prescribed.
Alzheimer's disease
This is atrophy of nerve cells caused by the production of a protein that is pathological for the body. This substance is in most cases deposited in the form of plaques. As a result, brain cells die en masse, which leads to disruptions in its functioning. The disease affects older people, most often women over 60 years of age.
The most common symptom is deterioration in spatial orientation. Having gone out to the store, a person cannot find his way home.
At the initial stage, memory impairments are noted, while the patient tries to use different methods to remember, not suspecting that he has a serious illness. In the final stages, the patient does not recognize loved ones and does not control his physiological processes.
Alzheimer's disease is considered incurable. A person dies after 10-13 years. The patient is prescribed medications that can improve blood circulation and general condition. There are also specialized institutions that provide comprehensive care taking into account all the features of the disorder.
Aneurysm
Refers to vascular diseases of the head, characterized by protrusion of the vessel wall, while its properties are disrupted. The disease is very dangerous because at any moment the affected vessel can burst and hemorrhage occurs. Until this moment, the disease may not manifest itself in any way, so it is very important to diagnose the pathology at an early stage.
Causes of aneurysm:
- high blood pressure;
- atherosclerosis;
- neoplasms;
- infections - tuberculosis, as well as syphilis;
- congenital pathology.
This headache may cause symptoms that are sufficiently characteristic to alert you, consult a doctor and conduct the necessary examination of the blood vessels of the brain. May cause concern: headaches, nausea, hearing loss.
If symptoms are detected, it is necessary to be examined. If an aneurysm is detected, the specialist will prescribe an operation to strengthen the damaged vessel. During surgery, the section of the vessel with the aneurysm will be removed, which will prevent its development.
Epilepsy
This is a disease caused by a disorder of the bioelectric activity of the brain. Against the background of epilepsy, there are cases of loss of consciousness and severe convulsions. Epileptic seizures are:
- local;
- generalized.
Types differ in the presence or absence of clearly defined localization of disorders. In the first case, there is a focus in one of the hemispheres, in the second, the disorders spread to both hemispheres and do not have clear focuses.
The exact causes of epilepsy are not always clear. Epilepsy is sometimes caused by traumatic brain injury or cerebral ischemia. Alcoholism is also a possible culprit for epileptic seizures. The causes of childhood epilepsy have not been established. Symptoms characteristic of epilepsy are almost impossible to confuse with another disease.
- A grand mal seizure is characteristic of the generalized type. The patient loses consciousness and falls. Respiratory cessation is observed; the person may not breathe for 5 to 30 seconds. Next comes the time of the excitement phase, severe convulsions begin. A person at this time cannot control his body. Involuntary urination and tongue biting often occur.
- Petite seizure occurs in children. In this case, the baby remains conscious, but somewhat altered. The child stops responding to his surroundings, does not answer questions, and his eyelids may twitch. Having come to their senses, the children do not remember what happened to them a few minutes ago.
- Simple local seizure. It is characterized by convulsions and loss of sensitivity in various parts of the body. The person remains conscious.
- Complex local seizure. Characterized by mental disorders, sometimes hallucinations. There is a general overexcitation of the body, anxiety, and sometimes panic occurs.
Seizures are dangerous due to the very fact of a person falling, as well as the retraction of the tongue. It is necessary to prevent the patient from falling, and to restore breathing, turn him on his side. Epilepsy can be treated by a specialist.
Atherosclerosis
In this brain disease, cholesterol plaques form in the arteries. Because of this, the lumen of the vessels is blocked or narrowed, as a result, oxygen deficiency occurs.
The symptoms of atherosclerosis are so invisible or vague that the patient seeks medical help in the final stages. In most cases, tissue necrosis already appears and blood clots form.
The main cause of the disease is elevated cholesterol levels. The disease occurs more often in older people.
The disease is treatable, the patient is prescribed medications to lower cholesterol and strengthen blood vessels. To prevent the disease, it is recommended to lead the healthiest lifestyle possible: stick to a diet, don’t smoke, give up alcohol.
Encephalopathy
This is damage to brain tissue as a result of circulatory disorders. The disease occurs due to atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension. Encephalopathy can also be triggered by osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebrae if the arteries responsible for the blood supply to the brain are compressed.
Symptoms of the disorder:
- sleep disturbance;
- irritability;
- personality changes;
- depression and constant weakness;
- pain in the head.
The patient's mood changes quickly: aggression gives way to apathy, and inappropriate behavior appears.
If the disease is neglected, brain dysfunction can become irreversible. In the final stages, epilepsy or stroke are common. To avoid serious neurological disorders, it is necessary to make a diagnosis as early as possible.
Other cerebrovascular diseases of the brain belong to the same type of pathology.
Brain tumor
This is a pathological process, as a result of which accelerated division of cells of the brain itself, its glands, membranes, blood vessels and nerves extending from it occurs. A tumor can be of two types: benign and malignant.
The main symptoms of a malignant tumor:
- Severe headaches that bother you already at the initial stage of the disease. The more the cancer progresses, the more severe the pain becomes.
- Vomit.
- Memory impairment.
- Mental disorders.
- Paralysis.
- Increased sensitivity to heat and cold.
- Visual impairment, different pupil sizes.
As for a benign neoplasm, symptoms appear when the tumor reaches a large size and compresses adjacent brain structures. In the initial stages, minor headache and dizziness are observed; in more advanced cases, symptoms similar to those of a malignant neoplasm appear.
If the disease is not recognized in time, then it is possible to shift brain structures and disrupt its functioning. In the early stages of development, the tumor can be removed, and in advanced cases, palliative treatment is carried out, which supports the vital functions of the body. Most malignant brain tumors are incurable, and after a while the person dies.
How to restore brain function?
At the initial stage, the root cause of the pathology is established, which requires prompt elimination. If exposure to infectious pathogens is detected, targeted antibacterial or antiviral agents are used. Hemorrhagic stroke involves surgical removal of the source of internal hemorrhage. Ischemia is treated with medications.
The brain in degenerative diseases cannot fully recover; prescribed drugs only reduce the rate of destruction of neural connections. The development of methods for treating Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease is still underway. Mental changes can be corrected under the influence of nootropics and psychotherapy. In case of severe disturbance of emotional balance, tranquilizers and drugs that improve sleep are recommended.
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disease characterized by a predisposition to seizures. The reason for this is a disruption of the bioelectric activity of the brain. The pathology can affect the entire brain or part of it.
People of any age are susceptible to epilepsy; predisposing factors can be head injuries, cerebral ischemia, alcoholism, etc. In children, this brain disease has no specific cause and develops as primary epilepsy.
A sign of the disease is an epileptic seizure (convulsions), which can be:
- Generalized. Affects two hemispheres of the brain.
- Local. The functioning of a certain part of one hemisphere is disrupted.
Generalized seizure
A generalized grand mal seizure is the most common type of epilepsy and is accompanied by loss of consciousness. It looks like this: the human body is in a tense state and bends in an arc, the head is thrown back, and the limbs are straightened. The patient's breathing stops, the skin becomes bluish. This phase can last up to 1 minute, and after that breathing returns to normal, and cramps of the head and limbs begin. The person does not control himself and may bite his tongue or relieve himself. After some time he regains consciousness.
Children may develop petit mal seizures, in which the child becomes unresponsive to his surroundings, his eyes become frozen, and his eyelids twitch. For such a case, loss of consciousness and convulsions are not typical.
Local attacks
They are divided into the following types:
- Simple, in which a person does not lose consciousness, but there is numbness in some parts of the body, convulsions, and trembling.
- Complex – the patient does not understand what is happening around him, hallucinations may appear.
When a person has an epileptic seizure, the most important thing is to prevent him from falling and hitting his head, and also from biting his tongue. It is best to raise the head a little and lay the patient on his side.
To prevent this condition, it is necessary to eliminate provoking factors, such as frequent stress, bad habits, etc. Constant therapeutic treatment, medication and medical supervision are required.
Common brain diseases
The list of diseases related to the brain is quite long. Ailments well known to most people:
- Alzheimer's disease.
- Aortic aneurysm.
- Stroke.
- Tumor formations.
- Alcoholic encephalopathy.
- Episyndrome.
These brain diseases disrupt the functioning of all organs and systems. Most of them are incurable.
Alzheimer's disease
This is a type of senile dementia in which memory suffers and dramatic changes in a person’s character are observed, even to the point of personality degradation. Women are more likely to suffer from Alzheimer's disease than men. The disorder often appears in old age, but can occur earlier.
The body intensively produces pathological protein. Accumulating in brain tissue, it has a detrimental effect on neurons, causing their destruction and atrophy. The examination reveals a large number of atherosclerotic plaques. A noticeable deterioration in memory is considered an alarming symptom of brain disease. Later appear:
- Mental agitation, irritability.
- Difficulty with orientation in space.
- Sudden mood swings, turning into an apathetic, depressive state.
- Speech disorder.
- Loss of household skills.
- Spontaneous urination.
- Amnesia, when a person does not recognize loved ones. Gaps in memory are short-lived and immediately fade away.
- The person becomes a burden to the family. He is unable to perform basic tasks, move independently and take care of himself.
The disease is incurable and confidently leads a person to death.
Aneurysm
Severe brain diseases associated with expansion (protrusion) of areas of the aorta are called aneurysms. Focal damage occurs in single and multiple forms. Rupture of pathological formations is the main cause of strokes.
A quarter of the victims die in the first month, and half of those who survive ruptures die in the first six months from a relapse.
The cause of the disease may be:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Congenital defects in the structure of blood vessels.
- Neoplasms.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Chronic infectious diseases.
- Closed craniocerebral injuries.
- Atherosclerosis.
The development of pathology can be provoked by:
- Smoking.
- Heavy physical activity.
- Diabetes.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
Stroke
Pathology refers to a brain disease associated with circulatory disorders. Tissues and structures are damaged, leading to dysfunction of the body. Recently, the disease occurs not only in the elderly, but also in people 20-35 years old. In order to do everything possible to save the patient during an attack, you need to know its first signs.
The causes of stroke are high blood pressure and atherosclerosis. It is divided into 2 types:
- Hemorrhagic , in which blood vessels burst and hemorrhage occurs. It is provoked by emotional overstrain and severe stress.
- Ischemic - blood circulation in a separate part of the brain is suspended or completely stopped. Oxygen starvation occurs, and the functions for which the injured part is responsible are disrupted. Most often, this type of stroke occurs during sleep.
The first signs of an attack are:
- Increasing buzzing in the ears, headaches, nausea, vomiting, lethargy.
- If you ask a person to smile, the smile will turn out crooked, since half of the body is not working.
- If you ask the patient to repeat a few words, he will start talking and drag out his words.
- During a stroke, the victim cannot raise his arms synchronously.
- During an attack, the tongue falls to one side and becomes bent.
This patient needs urgent medical attention.
Tumor formations
Tumors are the most dangerous diseases of the brain, the symptoms of which are difficult to detect and recognize in the early stages. The pathological proliferation of mutated cells provokes a rise in intracranial pressure. Common signs of neoplasms are:
- Attacks of headaches (usually morning).
- Vomit.
- Psychical deviations.
- Convulsive seizures.
- Paresis of one limb.
Symptoms of the disease appear depending on the location of the tumor. A benign or malignant tumor that has grown in the frontal part of the head impedes mental activity, leads to nervousness and unreasonable aggression.
Formations in the temporal lobes are characterized by depression, panic attacks, and memory impairment. Slurred speech, drunken gait, paresis, and blurred vision may also be observed. You can accurately determine where the lesion is located, what size it is and what type it belongs to by performing a computed tomography scan.
Alcoholic encephalopathies
In women, brain diseases caused by prolonged alcohol consumption develop faster. In alcoholic encephalopathy, severe insanity or various manifestations of psychosyndrome with systemic neurological abnormalities are noted.
The disease is caused by vitamin B deficiency, when the vascular system is severely affected. The disease is divided into:
- Acute form , in which appetite decreases, digestion is upset, and insomnia occurs. There are cramps in the limbs.
- Chronic form leading to hallucinations and anxiety. In advanced cases, coma may occur.
Women are affected by Korsakov's psychosis, which manifests itself as false memories, memory loss, and disorientation in space.
Episyndrome (epilepsy)
These are chronic brain diseases. Epilepsy has many forms and manifestations. The main cause of the disorder is a bioelectrical malfunction of the brain. Damage may affect one area or both cerebral hemispheres. Age does not matter.
The causes of morbidity in childhood are difficult to establish. For adults, head injuries and alcoholism are considered the main causes. Epilepsy happens:
- Generalized when both hemispheres of the brain are affected. Seizures are severe, convulsive, with loss of consciousness. In the first minutes, the body arches, the head is thrown back, the lips and face turn blue. Control over the body is completely lost, urination or biting of the tongue or cheek may occur. After an attack, a person feels depressed, weak, drowsy, and irresistibly tired.
- Local , in which attacks are accompanied by convulsions, numbness, distortion of the face, blue lips, loss of sensation in the arms or legs. The person remains conscious.
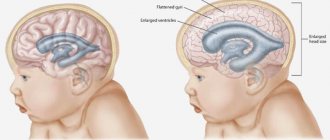
Hydrocephalus
This disease is characterized by excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. Hydrocephalus is manifested by increased intracranial pressure, headache, a feeling of constriction in the eyes, hypertension, mental disorders, seizures, etc. The reason for the development of the disease lies in the disruption of the brain's cerebrospinal fluid system. This pathology can manifest itself at any age, but children, especially premature infants, are most often susceptible to it.
Among the causes of the disease can also be identified: intrauterine infections, birth injuries, encephalitis, traumatic brain injuries, vascular disorders, etc.
The disease can be identified by the following signs:
- Headache.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Feeling of tightness in the eyes.
- Dizziness.
- Noise in ears.
- Decreased vision.
“Brain Wikipedia” against dementia, mental illness and brain “catastrophes”
: 19.02.2016
Professor Vladimir Lazarevich Zelman, a foreign member of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences and the Russian Academy of Sciences, one of the pioneers of neuroanesthesiology, a member of the International Academic Council of Novosibirsk State University, a graduate of the Novosibirsk Medical Institute, is today one of the three best American anesthesiologists.
University of Southern California (Los Angeles, USA), where V.L. Zelman heads the Department of Anesthesiology and Reanimatology and is one of the leaders in the field of neuroscience in the United States, taking part in a number of major brain research projects, such as ENIGMA. In his lecture at NSMU and in an interview with SCIENCE First Hand, Professor Zelman spoke about the most interesting results obtained by university staff in partnership with colleagues from other organizations in one of the hottest spots at the intersection of modern biology and medicine. Among them is a genetic database of the developing brain, which will allow assessing the genetic risks of diseases; a map of the location of all neurons in the brain and the “wiring” connecting them; neurocomputer technologies that allow the “power of thought” to control bionic prostheses
Over the past 25 years, brain science has advanced more than in the entire history of its study Professor Vladimir Zelman
The University of Southern California (USC), founded in 1880, is the oldest private research university in California. In recent years, according to authoritative rankings, it has traditionally been included in the top hundred best universities in the world. Currently there are over 40 thousand students studying at the university. In 1994, university professor D.E. Olah received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry
First, some statistics: according to experts, by 2050, the number of people in the world suffering from dementia - acquired dementia - may increase almost three times and reach 132 million. The most common form of dementia is associated with Alzheimer's disease, a neurodegenerative disease that develops predominantly in old age. And delaying the onset of the disease by only 5 years (from 76 to 81 years) will reduce the number of patients by half!
And this is just one eloquent example of the importance of neuroscience, which studies the brain - the physical basis of our consciousness, subconscious and mental activity, one of the most complex and most mysterious organs of the human body. The mechanisms of brain functioning have not been fully elucidated, although over the past quarter century, thanks to the emergence of new research technologies such as magnetic resonance imaging, electroencephalography, etc., more has become known about the biology of healthy and diseased brains than in the entire previous history of its study. Over the past ten years, it has become clear that at least 80% of the genes known today are expressed to one degree or another in the central and peripheral nervous system.
Investments in neuroscience are currently estimated at billions of dollars. Thus, in the last decade of the 20th century, declared the “Decade of the Brain,” the US Congress allocated about $3 billion for research in this area. For comparison, about $3.7 billion was allocated for human genome research at the same time; It is symbolic that these two most important scientific projects proceeded in parallel.
University of Southern California, where Professor V.L. Zelman has been a leader in brain research in recent years, not only in the United States, but also around the world, using a unique multidisciplinary approach to collaboratively solve the mysteries of brain disease in ways that are not possible in isolated laboratories.
So, for several years now scientists from the Institute of Neurogenetics named after. Zilka University of Southern California is conducting joint research with a group of collaborators from Yale University and the Brain Institute. Allen. Their goal is to create a complete genetic database of the developing human brain, which will allow assessing the genetic risk of various brain disorders. Today, more than 300 genetic loci associated with the pathology of the central nervous system have already been identified; in total, the unique Atlas of Gene Transcription of the Brain plans to present gene expression data for 15 brain regions in 13 age categories. Today this database is the largest in the world, and since 2011 it has been available to all interested users.
The University of Southern California has initiated the global brain research project ENIGMA, which is headed by university professor P. Thompson and funded by the US National Institutes of Health. Today, about 200 mathematicians, geneticists, neurobiologists and physicians from more than 35 countries of the world, including Russia (from Novosibirsk State University, a number of institutes of the SB RAS, the N.N. Burdenko Institute of Neurosurgery, Institute for Information Transmission Problems named after A.A. Kharkevich, etc.). The project is conducting research into the structures and functions of the brain and predisposition to diseases such as schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease, depression, drug addiction, etc. The main focus is on identifying factors that cause or, conversely, prevent a particular disease, such as lifestyle , eating habits and, of course, heredity. For example, a gene was recently discovered that is involved in the development of obesity through disturbances in the functioning of brain structures.
The human brain contains about 100 billion specialized nerve cells—neurons, each of which has about 10 thousand synapses that serve to transmit nerve impulses between cells. The different parts of our brain responsible for thinking, perceiving and feeling are connected by nerve fibers with a total length of 100 thousand miles (161 thousand km).
The most important part of the ENIGMA project is Connectome, a project to study the conduction system of the brain. The very concept of “connectome” was introduced by analogy with the concept of “genome” to fully describe the structure of connections in the nervous system. The Connectome project will create a four-dimensional (the fourth dimension is time) map of the location of all neurons in the brain and the “wiring” connecting them, describing all 100 trillion possible interactions between cells. This project, where all the results of brain imaging will be combined in a single map, can rightfully be called the “Wikipedia of the brain.” As a result, it will be possible to establish the variability and genetic predetermination of neurons, monitor their interactions in real time, and also identify the presence of neuronal pathologies.
Like any cell, each type of neuron uses a specific set of genes to create its molecular machinery; Successively interacting neurons form so-called neural circuits (the simplest example is a reflex arc). Understanding all the nuances of how neural circuits work should also help in understanding the pathogenesis of brain diseases, which will make their diagnosis more effective. After all, then it will become possible to recognize pathological processes not only on the basis of symptoms, but to search for diseases literally at the level of individual synapses.
Today, about one and a half dozen varieties of mental illnesses have been described. It is possible that in the next decade, when it becomes known at what stage and in what place genes that redirect synaptic activity in the “wrong” direction are turned on and off, the number of these diseases will increase by one or two orders of magnitude. In this case, treatment will become more personalized, and in case of early diagnosis, it will be possible to correct such “wrong” processes with complete rehabilitation of the patient.
The ENIGMA project has already collected a huge array of genetic and brain imaging data - about 50 thousand brain visualizations from 33 thousand people from more than three dozen countries around the world! Collecting such material today is not so difficult, but to decipher and interpret these huge information flows, supercomputers and bioinformaticians are required - specialists in working with “big” data. Modern science is fundamentally capable of such tasks, so it is possible that in the near future each of us will become the owner of a “flash drive” on which the decoding of not only our genome, but also our very personality will be recorded.
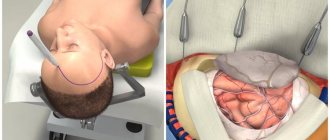
Already today, research into the brain's conduction system offers hope of making life easier for patients with serious brain damage resulting from trauma. We are talking about neurocomputer technology (the so-called brain-computer interface), which allows a paralyzed person to control “with the power of thought” bionic prostheses, for example, a mechanical arm.
Professor Zelman: “On April 17, 2012, for the first time, we performed surgery on a patient with a shot in the cervical spine, suffering from tetraplegia - impaired motor ability of all four limbs. Special electronic chips were implanted into the patient's brain, each of which has 96 sensors that read brain activity signals; Through antennas, this information is transmitted to a computer that controls the operation of a specially designed bionic arm. Currently, 6 patients have been operated on in this manner in the United States; The work is funded by the US Department of Defense."
One of the problems with such brain-computer technologies is the choice of brain signals that should be used to control bionic prostheses. According to a number of researchers, it is necessary to read the activity of nerve cells in the motor cortex of the brain, which is directly responsible for movements - in this case, feedback is formed at the level of the action itself. But there is another approach, in which preference is given not to the action itself, but to the intention to do it! The idea of installing chips in the area of the medial cortex, involved in action planning, belongs to Zelman’s colleague, Professor R. Anderson from the California Institute of Technology.
V.L. Zelman: “Richard Anderson has spent the last 25 years researching the brain in search of clusters of neurons whose activity can be used to control the movements of an artificial limb. He was sure that this did not require information about the movement itself, because each of them was provided in the connectome by hundreds of thousands of neural connections that were difficult to track. In this sense, the very intention to do this or that action is much more promising, and Anderson ultimately discovered in the posterior cranial fossa, next to the visual analyzers, the area where it is formed.”
And indeed, in the other five patients in whom the chip was implanted in the area of the motor cortex, coordination turned out to be much worse; they missed more often when making a movement, for example, when picking up a can of juice. But an even bigger problem is that so far all such bionic limbs are used only as part of experiments that sooner or later end. Chips implanted in the brain are perceived by the latter as a foreign body and ultimately become encapsulated and lose connection with neurons. However, the essence of these works is that they show the fundamental possibility of making life easier for completely paralyzed patients using a brain-computer interface.
This patient, with a chip implanted in his brain, can control an artificial arm. With its help, he can pick up not only a ball or a can of Coca-Cola, but also fragile objects such as an egg. In this case, the patient’s brain can even control the pressure that the artificial hand exerts on the object. With its help, a patient who required continuous service throughout the day can even learn to shave himself!
... Returning to Alzheimer's disease, let us recall that the brain of healthy people loses less than 1% of its weight per year, and this loss is compensated by tissue regeneration under the influence of mental activity. Symptoms of Alzheimer's disease begin to appear when 10% of brain tissue is lost, and under normal conditions this is an irreversible process. However, to date, scientists have already discovered 9 genes that can accelerate and slow down the development of this disease, including Apoe4, which is the leading risk factor for this most common form of senile dementia (substances that can transform the “aggressive” gene encoded by this gene are already being tested on animals). » ApoE4 protein into a safer isoform).
Moreover: today, scientists at the University of Southern California, together with their colleagues from Wake Forest University (North Carolina), are working on “recording” information stored in the brain, thanks to which the brain of a person suffering from Alzheimer’s disease can be “rebooted”, returning, at least temporarily, lost memories. This result, which even today seems fantastic, is only clear evidence of the successes that modern science has achieved in studying the brain, an organ that for centuries was considered suitable only for the function of cooling the blood!
Prepared by Larisa Ovchinnikova and Masha Perepechaeva
: 19.02.2016
Bone marrow diseases
Basically, this type of disease affects stem cells and disrupts their work, which leads to:
- Inconsistency in their quantity. There are many cells of one type in the body, but not enough of others.
- Varying life expectancy.
- Pathological processes in them.
All this causes disruption of the functioning of internal organs and leads to the development of such diseases:
- Leukemia - in this case, an excessive number of white cells are produced, which suppress the production of others, thereby making the body vulnerable to infections. Adults and children become susceptible to various types of viral and infectious diseases, bleeding and anemia. Their spleen and lymph nodes also become enlarged, and bruising appears on the skin.
- Myeloma – the main peak incidence occurs after 40 years of age. Such neoplasms are divided into:
- Myelodysplastic - this syndrome is characterized by the formation of pathological cells. In this case, there are fewer healthy cells and they cannot cope with viruses, infections and bleeding.
- Myeloproliferative - characterized by the production of immature cells that cannot function properly.
- Anemia – there are two types: iron deficiency and aplastic. In the first case, there is an iron deficiency, in which the bone marrow produces red blood cells that cannot perform their functions. And in the second case, the disease develops due to chemical or radiation exposure, as well as genetic predisposition.
Diagnostics
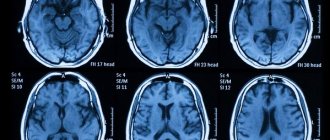
A correct diagnosis can be made only after diagnostic measures have been carried out that will help identify the type and extent of the disease. For this purpose the following is carried out:
- MRI and CT.
- Electroencephalography.
- X-ray.
- Angiography.
- Radiography.
- Blood analysis.
Any disease of the brain requires increased attention, because a person’s life depends on its proper functioning. In such cases, you should not self-medicate, as this will only worsen the patient’s condition. To treat brain pathologies, it is better to seek help from qualified specialists: a neurologist, neurosurgeon or oncologist.