Dementia or senile dementia is a serious pathology; it is a disease that significantly interferes with the life of people in old age. The disease manifests itself in patients over 65-70 years of age, which causes a decrease in social activity, problems with memory, and spatial orientation. Over time, a person becomes almost completely helpless. In the world, according to the latest statistics, more than eighteen million elderly people suffer from various forms of senile dementia.
Causes of development in women
According to research, older women suffer from dementia several times more often than men. Experts cannot explain this, but suggest that there is a connection with emotional and mental instability.
The main causes of violation are considered to be the following:
- Atherosclerotic changes in the blood vessels of the brain, provoking a disruption of its blood supply and the death of individual neurons.
- Brain injury, which leads to the destruction of neural connections and their replacement with connective tissue.
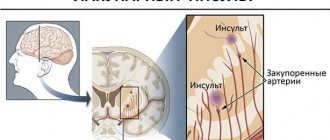
- Ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, accompanied by hemorrhage in certain areas of the brain. In this case, neurons die in large numbers, which certainly leads to disruption of thought processes.
- Atrophic changes in brain cells and disruption of their connections, as well as the conduction of nerve impulses.
- Uncontrolled use of large doses of medications over many years. Usually the cause is antidepressants, antihypertensive drugs, and drugs for the treatment of arrhythmia.
- Neurological diseases that cause regular damage to nerve cells.
The article discusses the main symptoms and signs of senile dementia.
In addition, this condition often develops in women who have more than 3 children.
This is associated with the effect of pregnancy on processes in the brain. Experts even identify the disease encephalopathy of pregnancy, which in many cases affects thought processes.
Causes
Before proceeding directly to the process of treating the disease, it is necessary to understand the causes. Factors that influence health status:
- regular pressure changes;
- tumor formation;
- diabetes;
- heredity.
All of the above points have a strong effect on the blood. As a result, the blood vessels narrow and the gray matter no longer functions normally.
Leave a request for selection of a boarding house
for an elderly person with dementia
Stages
Senile dementia (symptoms and signs in women appear with varying degrees of intensity) after the onset of the first manifestations goes through 3 stages of development.
- The initial stage is characterized by periodic deterioration of thought processes. At the same time, the general condition is not disturbed, the person accepts and understands himself, his actions, and is able to independently perform ordinary household manipulations.
- The moderate second stage is more pronounced. Sometimes a woman forgets about the basic rules of using simple objects, such as a telephone or a door lock. However, she usually follows the rules of personal hygiene and takes care of herself without outside help.
- The progressive third stage is considered the most dangerous. The patient becomes a threat to herself and others, forgets about the rules for using cutlery and other things, and relieves herself anywhere.
In the most severe cases, exhaustion of the body is observed; any disease of the internal organs can lead to death.
Treatment of senile dementia at the Alco-Center clinic
In severe stages of dementia, when the patient can harm others and himself through his actions, we recommend placing him in the hospital of our center. The same is proposed to be done in cases where relatives cannot constantly be at home caring for the patient. Treatment of senile dementia in the clinic is carried out using an integrated approach. That is, this is the treatment of symptoms of the disease with the help of medications, the creation of comfortable conditions, and caring care.
We also treat diseases that often become the impetus for the development of senile dementia. These diseases include arterial hypertension, stroke, heart attack, ischemia, etc. The patient does gymnastics according to a plan specially selected for him, and eats in accordance with the diet prepared for him. The diet includes all the necessary vitamins, microelements, and is dietary. The patient is taken for walks on the street.
The first symptoms of senile dementia
Senile dementia progresses gradually in most cases. Symptoms and signs in women do not immediately cause concern for loved ones. They are often attributed to ordinary manifestations characteristic of an elderly person.
The first symptom is memory impairment. The patient is unable to remember events that happened not so long ago. However, most often she is well versed in memories from the past, is able to talk about the smallest details and systematize her thoughts. Further, loved ones may notice a manifestation of sloppiness and a lack of interest in past hobbies.
The woman becomes indifferent, as if ready to say goodbye to life. From time to time she gets depressed.
Disorientation in time also becomes one of the first manifestations. The woman understands where she is, but is not aware of the time of day . In addition, difficulties arise when you find yourself in an unfamiliar place.
The thought process slows down. The patient spends more time solving simple everyday tasks. At the same time, such delay provokes nervousness. Another early manifestation of dementia is the refusal of habitual communication with family. The woman begins to avoid meetings and tries to remain alone.
Age-related changes in the brain
Scientists have long proven that, at its core, old age is a disease that can and should be treated. Diseases associated with various body systems often develop from a young age and can either be prevented or stopped or slowed down. The main human organ that develops and withers separately from other systems is the brain. The development of many diseases is associated precisely with the aging of the brain.
Senile dementia
A visit to the doctor to make a diagnosis of dementia of the brain
The concept of senile dementia includes all kinds of senile dementias and senile destruction of the psyche. According to scientists, senile dementia is the final stage of complete and irreversible aging of the brain. Often, the dementia of old people is ignored not only by the old people themselves, but also by younger generations, attributing it to the natural degradation of the brain, and some people even consider senile insanity to be a manifestation of character traits.
But, if you look at the results of computed tomography, you can see absolutely objective physiological changes. The ventricular system of the brain is significantly expanded. The sulci of the hemispheres and the subarachnoid spaces of the cerebrum are also expanded.
Video about brain aging and senile dementia
Late symptoms of senile dementia
As dementia progresses, symptoms become more severe. They allow specialists to establish an accurate diagnosis and determine the stage of development.
Amnestic phenomena
Memory impairment manifests itself in patients in different ways. They forget the purpose for which they go to this or that room, but do not take it seriously, considering it ordinary forgetfulness. Moreover, similar signs are observed in women who are under 65 years of age. Time orientation is greatly impaired. The patient remembers the present date for a long time, and is also unable to recognize places familiar from childhood.
Later, amnestic phenomena associated with the inability to remember faces appear. Even after several meetings and conversations with a person, a woman cannot remember him. Such a symptom should be a cause for concern.
At an advanced stage, the patient forgets the faces of relatives, and also cannot recognize her own reflection in the mirror. It is worth noting that changes occur gradually, progression takes from 15 to 20 years. When using memory enhancing products, this period increases.
Decreased mental activity
Impairment of speech and simple thought processes always accompanies dementia. At the initial stage, this is not so noticeable, but as the condition progresses, the symptoms also increase. The patient is unable to hold a pen, write or add simple numbers in her head.
Later, there is a gradual loss of the ability to acquire new skills. First, the patient stops performing her usual activities, for example, those related to her profession. After this, she loses the ability to learn anything, and also forgets the sequence of actions when performing ordinary household manipulations.
It is worth noting that the woman herself is embarrassed in the initial stages when she discovers her incompetence in a seemingly familiar issue. She tries to hide it from others and moves the conversation to another topic. Close people may mistake this for ordinary absent-mindedness, so they are in no hurry to contact a specialist.
Emotional manifestations of dementia
Senile dementia (symptoms and signs vary individually among women) is almost always accompanied by emotional disorders. At first, they are associated with the fact that the patient realizes the inevitability of such changes. She understands the complexity of the situation and withdraws into herself, trying to isolate herself from society.
When other forms of disorder occur, she breaks down, which manifests itself in depression or aggression for no reason. All character traits that previously defined personality become more noticeable. Thrift turns into greed, modesty into preventing any contact.
In addition, a woman often becomes depressed and shows indifference to things that occupied most of her time before her illness. Her mood changes frequently and unexpectedly. It is at this stage that others begin to notice that the woman is unwell.
Physical side of life
Changes in neural connections and brain function certainly lead to the involvement of motor activity centers in the process. The patient's movements become inaccurate and coordination is impaired. She quite often loses her balance and gets injured.
Since the work of all internal organs is disrupted, the body is exhausted, and the patient is weakened. She gets tired quickly and cannot travel long distances. Such changes only aggravate the emotional state, because the patient realizes her helplessness and this upsets her.
Communication and attitude to life
After the first symptoms appear, the patient’s need for communication gradually decreases. At an advanced stage, she completely refuses to contact people and concentrates on her own personality. Even if a woman expresses her thoughts, this does not mean that she is trying to communicate. It's just a way of expressing yourself.
Quite often she also talks to fictional characters, answers her own questions, laughs or gets upset. The attitude towards life changes, the patient talks about death, but it does not scare her. As a rule, at an advanced stage, the patient even strives to die in order to get rid of everything at once. She becomes dangerous to herself and others.
Forms of the disease
Senile dementia is divided into primary and secondary.
The main symptom of atrophic senile dementia is memory impairment.
Depending on the degree of brain damage, the disease occurs in the following forms:
- mild senile dementia (decrease in social activity, maintaining the ability to self-care);
- moderate senile dementia (loss of skills in using technology and instruments, inability to endure loneliness for a long time, maintaining the ability to self-care);
- severe senile dementia (complete maladjustment of the patient, loss of ability to self-care).
Depending on the etiological factor, the following forms of senile dementia are distinguished:
- atrophic (primary damage to brain neurons);
- vascular (secondary damage to nerve cells due to impaired blood supply to the brain);
- mixed.
Signs of various types of disease in women
Senile dementia (symptoms and signs in women may be combined with other conditions) rarely develops as a single mental disorder. In most cases, it is accompanied by other disorders.
Dementia due to Alzheimer's disease
More than 60% of patients diagnosed with dementia also suffer from Alzheimer's disease. The condition progresses slowly, but the main manifestations are observed in memory. Each year, thinking processes deteriorate by approximately 5%. The patient is unable to talk about recent events, remember the visual features of an object, or smells.
Memory deteriorates rapidly; over time, real memories are replaced by false ones.
A feature of Alzheimer's disease is the repression of old memories when trying to assimilate new information. In this case, all information is later erased. Additionally, speech disorders are added to the symptoms, meaningless pronunciation of phrases, conscious or unconscious repetition of the words of the interlocutor, and inability to repeat a complex word or phrase are observed.
Problems with orientation are always part of the clinical picture in Alzheimer's disease. It is worth noting that with this form of dementia, the patient’s life expectancy is reduced by several years.
How does vascular dementia manifest?
Dyscirculatory encephalopathy is the main cause of the development of vascular dementia. The disease manifests itself in patients over 60 years of age and is accompanied by classic symptoms that are observed in ordinary dementia. The patient loses her memory, ceases to navigate in space, forgets the rules for using simple household objects, and gradually withdraws into herself.
These symptoms are accompanied by physiological disorders. The patient reports headache, nausea, and bouts of vomiting. Dizziness worsens the general condition, possible short-term loss of consciousness, increased sensitivity to changes in weather conditions.
Dementia with Lewy bodies
This type of dementia is not very common. Its first manifestation is considered to be behavior disorder in the REM sleep phase. The patient talks about colorful, creepy dreams that visit her. At the same time, she makes sudden movements and can be dangerous to herself or others.
After waking up, the patient is disoriented, does not immediately understand where she is, and cannot remember how she ended up in this place. During the daytime, a woman is slow, performs the simplest actions with difficulty and gets tired quickly.
It is worth noting that such periods of decline are followed by phases of increased activity. The patient returns to her usual way of life, but closer to night she gets tired again, becomes depressed, and indifferent.
Parkinson's disease: connection with dementia and characteristic symptoms
About 5% of the total number of cases of senile dementia are due to Parkinson's disease. Symptoms usually appear in late stages in patients over 70 years of age who have a genetic predisposition to such disorders.
The main signs of the disorder will be the following:
- Muscle rigidity, accompanied by excessive tension and difficulty moving.
- Gait disturbance as a result of deterioration in coordination of movements.
- Tremor of the limbs, manifested during movements and at rest. Sometimes the tremor is replaced by hardness of the muscles when they are in constant tension.
In addition, there are classic symptoms of dementia, manifested by memory impairment and other disorders.
Frontotemporal degeneration
This type of disorder is characterized by early onset of symptoms in patients under 50 years of age. Most often, the cause is a hereditary predisposition.
The main symptoms will be the following:
- rudeness of speech and antisocial, incorrect behavior;
- sexual incontinence, lack of embarrassment;
- looseness, unwillingness to compromise;
- changes in eating habits, chewing objects unsuitable for consumption, constant smacking;
- impaired perception of the emotions of others;
- lack of desire to spend time in the company of loved ones;
- reluctance to speak or make gestures to communicate with others while maintaining the ability to speak and understand speech.
The main difference between this disorder and the classic form of dementia is the absence of orientation disorders, as well as motor disorders. The patient does not forget places and people’s faces, remembers dates perfectly, moves well, and does not get tired so easily.
In addition, this form of the disease is characterized by damage to the frontal lobe of the brain, while vascular dementia is accompanied by the presence of several foci in different areas.
Huntington's disease
This disease is dangerous for patients under 30 years of age, as it develops quickly and is accompanied by severe symptoms. Impaired memory and orientation are not considered main signs.
In the initial stages, the patient notices a change in gait, movements become sharp and not always accurate , at rest it is difficult for a woman to fix her body, the facial muscles involuntarily contract, which leads to grimaces.
As the condition progresses, the patient becomes aggressive or apathetic, sometimes becoming depressed. Hallucinations and delusions are considered dangerous symptoms. It is worth noting that the disease is hereditary in most cases; an accurate diagnosis can be made by analyzing the patient’s DNA chain.
Pick's disease
Symptoms appear after age 50. In the initial stages, memory does not deteriorate, but the patient is unstable, aggression is replaced by apathy, depression is a state of euphoria. She repeats the same jokes, phrases and stories several times, although she remembers that she has already talked about it.
The development of the disease is accompanied by the manifestation of selfishness and strengthening of basic instincts. At stage 2, other disorders appear: memory impairment, loss of the ability to read, write, speak and understand speech.
At an advanced stage, the patient becomes completely incapacitated, loses memory, orientation in time and space.
Causes and risk factors
The main cause of primary senile dementia is organic brain damage. Secondary senile dementia can develop against the background of any disease or have a polyetiological nature. At the same time, the primary form of the disease accounts for 90% of all cases, secondary senile dementia occurs in 10% of patients, respectively.
Risk factors for developing senile dementia include:
- genetic predisposition;
- disorders of systemic circulation;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- infectious diseases of the central nervous system;
- brain tumors;
- arterial hypertension;
- atherosclerosis;
- metabolic disorders;
- immunodeficiency states;
- endocrine diseases;
- rheumatic diseases;
- presence of bad habits;
- poisoning with heavy metals (in particular, zinc, copper, aluminum);
- irrational use of medications (especially anticholinergics, antipsychotics, barbiturates);
- sedentary lifestyle;
- vitamin deficiency (in particular, lack of vitamin B12);
- overweight.
Diagnostics
Senile dementia (symptoms and signs in women are taken into account when diagnosing) is not so easy to identify, especially in the early stages. Various methods are used for examination.
| Method | Description |
| General inspection | The doctor examines the skin, mucous membranes, and notes visible accompanying disorders |
| Clinical researches | A blood and urine sample is taken to identify abnormalities in the internal organs |
| Special tests to detect deviations | The specialist asks the patient to talk about recent events, repeat a few words and solve the simplest problems |
| Survey of relatives | Interviewing the patient’s relatives allows us to complement the clinical picture and clarify the nuances of behavior |
| MRI | The technique helps to see the localization of the lesion in the images, which facilitates diagnosis |
Sometimes a DNA test of the patient is required, which helps confirm or exclude a hereditary predisposition. The method is used when symptoms of genetic diseases are present.
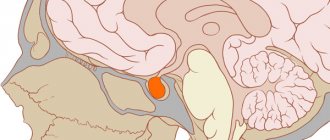
Alzheimer's disease
Schematic representation of a brain damaged by Alzheimer's disease.
This is atrophy of the cerebral cortex. Computed tomography shows obvious atrophy of the subarachnoid spaces of the cerebral hemispheres, expressed by their enlargement. There are also signs of changes in the grooves of the cerebral cortex and the ventricular system in the form of their expansion. Lack of glucose to feed the brain, which is supplied by insulin, synthesized by the brain itself. No insulin - no glucose, no glucose - the brain is starving.
The disease is accompanied by a disruption of the conductive functions of neurons, similar to an electrical short circuit. This is manifested by absent-mindedness, forgetfulness (impaired short-term and long-term memory).
The main role in the development of the disease is played by amyloid, which accumulates in the brain. At a young age, it is quickly excreted quickly, 4 hours is enough. With age, withdrawal takes longer, and for older people it takes about 10 hours.
The consequences of the development of this disease are the following factors:
- An excess of netrosamines, which are consumed together with sausages, beer, and cheeses;
- Excessive salt intake;
- Abuse of flour products;
- Excessive consumption of white sugar;
- Water fasting;
- Decreased brain activity;
- Lack of OMEGA-3;
- Herpes virus type 1;
- Oxygen starvation of the brain;
- Decreased physical activity;
- Lack of melatonin, a sleep hormone synthesized in the pineal gland of the brain. Atrophy of this part of the brain leads to hormone deficiency.
Important! The pineal gland begins to lose the ability to synthesize melatonin from the age of 30. That is why you need to take care of this from a young age, paying attention to proper and timely sleep.
Treatment
Unfortunately, senile dementia cannot be cured. A specialist can only prescribe medications that will help alleviate the patient’s condition and slightly slow down the development of dementia.
The most commonly used medications are:
- Nootropic drugs (Cerebrolysin, Piracetam, Nootropil) help restore neural connections, stimulate the function of brain cell renewal, and restore normal blood circulation.
- Drugs for normalizing blood circulation in the brain, for example, Cinnarizine, can improve the general condition and eliminate the physiological manifestations of the disease.
- Medicines to strengthen the vascular wall (Ascorutin) are indicated for patients with a tendency to fragility of blood vessels.
- Sedatives of plant origin (Persen, Novo-passit) are indicated for sleep disturbances and severe nervousness.
- Antidepressants (Amitriptyline, Anafranil) are prescribed for severe depression, lack of desire to live, and suicide attempts.
If symptoms of other diseases appear, the doctor prescribes symptomatic treatment. Usually these are antiarrhythmic, antihypertensive, diuretics, gastroprotectors, choleretic medications, hepatoprotectors.
What is dementia
A disease in which loss of mental abilities occurs and brain cells are destroyed. The cause of dementia in older people is a pathology of the nervous system, in which recovery is impossible. Neural connections in the cerebral cortex are destroyed. Because of this:
- a person forgets himself, his relatives;
- loses self-care skills;
- character and behavior change dramatically;
- without outside care becomes helpless.
Select a service for your relative | |||
| Caring for bedridden people | Disability care | Elderly care | Care after a heart attack |
Caring for older people with dementia
The patient's relatives must provide her with full and constant care. In the early stages, it is enough to remind the patient about the rules of hygiene and suggest finding certain things. As the disease progresses, it is necessary to establish complete control over the woman's life.
You shouldn't leave her alone. Later, it is necessary not only to remind the patient about the rules of personal hygiene, but also to help her perform manipulations. With complete immobility and loss of interest in life, full care is required, including feeding, combing, washing, changing underwear and bed linen, and diapers.
The most common diseases of elderly and senile people
All systems wear out to one degree or another, and which one will fail is difficult to predict. If earlier old age was accompanied by problems with joints, vision, and hearing, today ailments associated with blood circulation and digestion have taken first place.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
Statistics say that this is the most common group of pathologies. Unfortunately, in the early stages, cardiac ischemia is very difficult to diagnose, since it manifests itself without any particular symptoms. The only thing that can bother old people is shortness of breath and a slight tingling in the chest area.
Still have questions?
Send a request and we will be happy to answer them
Myocardial infarction is accompanied by painful sensations in the lower abdomen, shoulders, neck, and changes in heart rate. Sometimes it feels like a stroke. Diagnosed by a blood test, where the ESR is elevated and leukocytosis is detected.
Arterial hypertension affects people under 60 years of age. Older adults suffering from severe hypertension simply do not survive. The main symptoms are unsteadiness of gait, headache, accompanied by tinnitus, and weakness. Often this condition develops into a hypertensive crisis.
Heart failure may be associated with sclerotic changes in both the main organ and blood vessels. It is expressed by general malaise, fatigue, decreased visual acuity, disturbances in the musculoskeletal system, and ultimately a decrease in mental activity (dementia).
Cerebral ischemia is characterized by reduced blood flow and is manifested by low performance, irritability, poor sleep, inattention and absent-mindedness.
List of old age diseases associated with digestion
Troubles in the abdominal cavity can manifest themselves in the form of:
- Flatulence (bloating).
- Constipation or diarrhea.
- Indigestion.
- Stomach ulcers.
- Pancreatitis.
- Gallstone disease.
- Chronic colitis.
- Hemorrhoids.
They are dangerous because they provoke exacerbation of problems in other organs.
Insomnia
Disturbances in this area have become a classic age after 65. Drowsiness during the day gives way to wakefulness at night and in the morning. Ultimately, if appropriate measures are not taken, this can provoke more serious pathologies, even death. Over the course of a few days of insomnia, a person may:
- Develop a persistent mental disorder.
- Decreased immunity.
- Blood pressure rises.
- Neurasthenia or depression appear.
How to create safe living conditions
In the later stages, it is necessary to completely eliminate the possibility that the patient will harm herself or others. Do not allow it near a gas or electric stove, hot water, other household appliances, forks, knives. In addition, you need to remove all ropes, needles, belts, threads that could become dangerous.
It is important to prevent the patient from taking medications on her own, to exclude the consumption of alcoholic beverages. Additionally, it is important to prevent the possibility of opening windows , balcony doors, and not to allow the patient to go for a walk on her own.
Ways to combat brain aging
Ways to combat human brain diseases in old age
Today, scientists have understood exactly how to stop brain aging and have developed a number of measures necessary for this. Following the recommendations below can prolong the youth of the brain, and therefore the life of a person.
OMEGA-3 acids
These fatty acids protect nerve tissue by increasing glutathione levels. They also preserve the structure of the myelin sheath of the brain. You need to eat foods such as:
- broccoli;
- asparagus;
- fish fat;
- Red caviar;
- fish;
- olive oil;
- flax seed products, including oil;
- oils from saffron milk caps or mustard.
Melatonin
Melatonin is sometimes called the sleep hormone and is concentrated in the brain at night during sleep, between 11 pm and 2 am. You need to go to bed before 11 pm. Sleep should be complete and last 8 hours. During sleep, the brain works to restore internal organs. After that, he is engaged in formatting the memory and analyzing information. Then, it restores its energy potential.
Help to replenish melatonin:
- meat products;
- eggs;
- bird;
- dairy products;
- Walnut;
- chicory;
- buckwheat;
- bananas;
- chamomile and valerian herbs.
- vitamins B 12, D, B1.
Their deficiency can be compensated for by good nutrition, as well as by consuming vitamin complexes with a high content of this Melatonin. Vitamin D is found in large quantities in oily fish.
Coffee for the brain
Recent studies have proven the beneficial effects of coffee on the body. It reduces the likelihood of developing Alzheimer's disease by 65%. You need to use non-instant coffee.
Medications
Well-proven drugs for influencing brain cells: tenoten; glycine; aspirin; nootropic drugs; doxycycline.
Therapeutic fasting
Fasting for medicinal purposes activates the functioning of the entire body, especially the brain. It triggers the body's reserve potential, can rid the body of many diseases, stimulate the production of new stem cells and renew brain tissue. You need to gnaw wisely and rarely.
Physical activity
Gymnastics with elements of yoga and breathing exercises help prevent oxygen starvation of the brain and activate blood circulation in the vessels of the brain.
Meditation
Significantly normalizes the mental state, brings into balance all systems of the body and allows the brain to receive additional rest. Also, along with meditation, auto-training also helps.
Mental stress
Do as much mental activity as possible to exercise your brain.
You can’t let your brain sit idle. Solving complex problems, regular reading, creative activity, active communication, learning new information, new foreign languages, getting new impressions - this is what the brain needs so that it does not sleep, but lives!
Forecasts
With a sluggish course of the disease, the patient can live up to 20 years, but full control and care is necessary. With rapid progression of the condition, life expectancy is reduced to 10 years. With the development of Parkinson's disease, Pick's disease, Huntington's disease, vascular dementia or frontotemporal degeneration, the patient lives from 6 to 8 years with proper care.
The prognosis is always unfavorable because the disease cannot be treated. Senile dementia is a common and dangerous disease. Symptoms and signs appear more often in women than in men. Patients need constant supervision by a doctor and relatives.
What should relatives of a patient with senile insanity do?
The prognosis of senile dementia is unfavorable and it cannot be cured. The process of mental disintegration of the sick person lasts from one to ten years.
However, with timely diagnosis and proper treatment, the progression of the disease can be significantly stopped and the patient’s quality of life can be improved. The task of relatives is to have a patient and condescending attitude towards the elderly and provide him with comfortable conditions. It must be remembered that personality changes occur not through the fault of the elderly person, but precisely because of illness.
Regular intake of prescribed medications, as well as a comprehensive program of exercises and a properly organized daily routine, regular walks and exercises will help your patient to alleviate the course of the disease as much as possible.