What is cerebral edema?
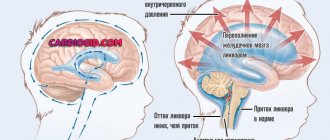
Cerebral edema is a rather dangerous complication of many intracranial diseases, characterized by diffuse saturation of brain tissue with fluid from the vascular space. Mostly this pathology is a consequence of birth trauma. Cerebral edema is a secondary sign of damage to brain tissue.
This pathology is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the brain cells, which causes an increase in brain size. With this disorder, the infant’s intracranial pressure changes and problems with cerebral circulation appear.
The outcome of such a pathology is directly determined by the speed of provision of medical care to the patient and its effectiveness. In addition to injuries during labor, other factors affecting the body can also provoke brain damage in a baby.
Clinical picture
Brain edema in children can be determined even without being a medical specialist. With swelling of brain cells, the disease will be defined by the following symptoms:
- lethargy, irritability due to light and sounds, even quiet ones, crying - all these are signs that swelling has provoked an increase in intracranial pressure;
- failure of respiratory and cardiac activity, the consequences of which can be death or disability;
- organ failure;
- convulsions;
- rapid pallor of the skin;
- fainting.
Important! The situation is worst in premature babies; the consequences of such edema in them can not only provoke a significant disruption of brain activity, but also cause the death of the baby.
Parents who strictly monitor their baby will instantly see changes in his condition. A small child, especially a newborn, never cries for no reason. At this age, the reason for his crying is health problems. Therefore, you should not ignore him and complain about his bad behavior. If he screams, there is a reason, and if any of the symptoms of brain swelling are added to the crying, then you cannot hesitate. Time is ticking now, so urgently call an ambulance to save your child.
WE RECOMMEND SEEING: Treatment of perinatal encephalopathy in children
Classification of pathology
Taking into account the pathogenetic manifestations, brain pathology in an infant is divided into several types, described in Table 1.
| Name | Description |
| Vasogenic | This type of pathology develops in a baby no later than 24 hours after injury at the site of inflammation, hematomas, neoplasms and invasive interventions. |
| Cytotoxic | This type of edema appears as a result of ischemia, hypoxia, encephalopathy, viruses and metabolic disorders in cells. A characteristic manifestation of the pathology is an increase in the volume of intracellular fluid and the development of oxygen and ATP deficiency. |
| Interstitial | This type of edema develops as a result of water entering the brain tissue through the walls of the ventricles. Typically, this disease develops simultaneously with hydrocephalus. |
| Osmotic | The provoking factor in the development of this type of pathology is improper hemodialysis, metabolic encephalopathies and water poisoning of the nervous system. |
Classification of birth injuries on video:
In addition, experts distinguish local and diffuse edema in infants. With local edema, only a separate area of brain tissue is affected, and the characteristic symptoms develop gradually. In the diffuse form of the pathology, the brain stem and its hemispheres are affected, and the clinical picture is quite pronounced. If both hemispheres are affected, a diagnosis of “generalized cerebral edema” is made.
Classification
Edema in newborns varies according to location:
- regional – a specific part of the brain is affected. The root cause is a tumor, hematoma, cyst;
- common - the entire brain is swollen. The pathology is provoked by birth trauma, asphyxia, and poisoning.
Another classification has been developed based on the root cause of the pathology:
- swelling in a child is provoked by tumor neoplasms, gas embolism of blood vessels, microembolism - this is a vasogenic type ;
- the cytotoxic type of edema is caused by insufficient oxygen supply and is characterized by an increase in the amount of fluid in the cells;
- the interstitial appearance becomes a consequence of hydrocephalus;
- the osmotic type of edema occurs due to water poisoning of the central nervous system.
Causes of pathology
The causes of brain damage in infants can be very different and are determined by pathogenesis. Sometimes the pathological process progresses so rapidly that doctors are unable to determine the true cause of the disease.
With localized edema, only a small part of the brain is affected and its main cause is the destruction of the meninges or its hemispheres. The neoplasm begins to put pressure on nearby brain structures and causes vascular circulation problems. Gradually, the pathology is complemented by increased pressure and fluid entering the cells. In infants, neoplasms can be a consequence of exposure to unfavorable factors.
One of the most common causes of brain damage in young children is trauma. After birth, the baby’s skull is quite pliable due to the fact that there are still fontanelles in the seams between the bones. Thanks to this feature, the child passes well through the woman’s birth canal, but at the same time, this factor can provoke injury to brain tissue.
During labor, injuries occur that can be caused by various pathologies in the female body. In addition, medical errors are possible, which can cause brain damage. The baby experiences hemorrhage and a hematoma forms, that is, compression of the brain develops with the danger of local edema.
Generalized edema can be provoked by ischemic brain damage in pathologies in pregnant women, which are accompanied by problems with blood flow in the veins of the umbilical cord. Ischemia of all tissues of the developing fetus and brain structures is noted. If the placenta ages too early, the movement of oxygen into the brain cells is disrupted, which affects blood flow. All this provokes the formation of edema of brain tissue.
The toxic effect of medications on brain cells can provoke generalized edema. Alcohol can cause pathology by inhibiting the normal formation of the fetal brain. If the mother is intoxicated immediately before labor, there is a high risk of giving birth to a child with alcohol syndrome.
Not the last place in the development of such pathology in newborns is occupied by such pathological processes as encephalitis and meningitis. Any inflammation is complemented by tissue swelling, so when the brain is damaged, it increases significantly in size.
Arteriovenous malformations are one of the types of congenital vascular pathology in which the normal movement of blood is disrupted. The consequence of this is the formation of aneurysms and the gradual accumulation of blood in them. If the brain stem becomes the location of such a malformation, it can cause tissue damage.
Consequences of cerebral edema in premature infants. Cerebral edema in a newborn
A health and life-threatening condition – cerebral edema in a newborn baby – is increasingly being diagnosed in babies. It is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the brain tissue. The pathology is dangerous due to its complications; surgical intervention is often necessary to solve it.
The outcome of the disease depends on when it was diagnosed and how quickly doctors began treatment. Before starting treatment and prescribing surgery, specialists identify the cause of the pathology and assess possible risks.
Symptoms
Signs of cerebral edema in newborns cannot be ignored, since this condition is accompanied by:
- An increase in intracranial pressure, due to which the child becomes lethargic, and also reacts sharply to the slightest stimuli (light, sound, etc.) and constantly cries.
- Violation of the functions of many systems and organs, which can cause the death of the baby.
- Convulsions, fainting, pale skin.
Cerebral edema is a condition that requires emergency medical attention, otherwise the consequences will be extremely severe. Pathology can be diagnosed using the following methods:
- Examination of the baby by a neurologist: the doctor evaluates the external manifestations of pathology, pays attention to the reflexes and reactions of the little patient.
- Instrumental studies: magnetic resonance and computed tomography of the brain, neurosonography, neuroophthalmoscopy, etc.
Treatment of this condition in newborns is organized in a hospital setting. Therapy is aimed at eliminating the cause of the pathology and restoring the functions of the baby’s nerve cells. If the child is not breathing, he is connected to a ventilator. The following drugs are used in treatment:
- Diuretics: help reduce swelling and remove excess fluid from the body.
- Corticosteroids: Stop the area of brain damage from further enlarging.
- Muscle relaxants: eliminate cramps.
- Nootropics: improve blood circulation and brain metabolism.
The child's condition requires continuous monitoring by a pediatrician and neurologist.
About forms of development
Depending on the factor that triggered the development of cerebral edema in a newborn, there are four types of forms of the disease. They explain the mechanism of pathology development and determine treatment tactics.
The vasogenic form is a process in which the blood-brain barrier is disrupted. Typically occurs as a result of fluid accumulation around tumors, areas of inflammation, ischemic areas, or sites of injury. A dangerous form that can lead to compression of the brain.
The cytotoxic form of edema in newborns is often the result of blockage of a blood vessel in the head. It may occur due to intoxication with substances that destroy red blood cells, so-called hemolytic poisons, and other chemical compounds. As the amount of fluid increases, the specific gravity of oxygen needed by the brain sharply decreases.
The osmotic form is a variant in which the osmolarity of the nervous tissue sharply increases. The cause of edema in a newborn may be an increase in the volume of circulating blood, encephalopathy due to metabolic disorders, errors in hemodialysis, and others.
The interstitial form is a variant in which fluid enters the tissue directly from the ventricles.
Consequences
Brain edema can provoke consequences of varying severity. The development of complications depends on the extent of the spread of edema, the general health of the child and the timeliness of treatment.
In some children who have experienced this pathology, their head circumference increases due to an open fontanel. Increased skull size does not usually return to normal over time.
Due to damage to the structures of the central part of the nervous system, the baby shows a lag in physical and mental development - he begins to hold his head, sit, walk, talk, etc. later than his peers. Edema suffered during the newborn period can provoke mental disorders in the child. The risk of developing epilepsy and cerebral palsy of varying severity also increases.
The most unfavorable consequence (with the exception of the death of the child) is periventricular leukomalacia - necrosis of the brain area.
This complication develops in premature babies, since they have underdeveloped self-regulation of the brain and blood circulation in it due to the immaturity of the organ.
Due to periventricular leukomalacia, a child's breathing, heartbeat and other body functions may be impaired. The condition of a baby with such a pathology requires monitoring and adequate treatment.
Brain edema, the causes and consequences of which we will consider in this article, is the body’s reaction to excessive stress, injury and infection. As a rule, this process happens quite quickly.
At the same time, the cells themselves and the space between them are filled with an excess amount of fluid, and the brain as a result increases in volume, which, in turn, causes an increase in intracranial pressure, a deterioration in cerebral circulation and entails cell death.
This condition, as you understand, requires mandatory and urgent medical care in order to avoid serious consequences and death.
Measures for the treatment of cerebral edema in children
Treatment of cerebral edema in a child includes the following measures:
- Elimination of cerebral hypoxia.
Intubation and mechanical ventilation as assessed by the Glasgow Coma Scale - Moderate hyperventilation
(maintaining PaCO2 at a level of 30-35 mm Hg, Fi02 at a level that provides a saturation level of >95%, Pa0290-100 mm Hg (>70 mm Hg), low PEEP levels. - Reducing ICP
: mannitol at a dose of 0.2-0.5 g/kg for 10-20 minutes. Blood plasma osmolarity should be no more than 310 mOsm/L; to maintain osmolarity, mannitol can be administered at 0.25 g/kg every 4 hours. Avoid hypoosmolarity! - Infusion therapy
at a level of 70-80% of the daily physiological requirement (but blood pressure should not decrease); provided with 0.9% NaCl solution or Ringer's solution. It is necessary to maintain sodium levels at normal levels. Avoid administration of hyperosmolar solutions. Maintaining central venous pressure at a normal level. - Maintaining normoglycemia
. - Maintaining blood pressure above normal
(using cardiotonic drugs for these purposes - dopamine, dobutamine, norepinephrine). - Hemoglobin level > 100 g/l.
- Anticonvulsant therapy:
thiopental bolus 2-5 mg/kg, then 1-5 mg/kg/h intravenously. Serum level: 40-50 mcg/ml. When blood pressure decreases, norepinephrine is prescribed. - Omeprazole
1 mg/kg/day (maintaining gastric juice pH > 4.5). - Maintaining normal body temperature
(paracetamol, metamizole, ibuprofen for hyperthermia, avoiding hypothermia). - Prescribing antibacterial drugs
. - Prednisolone
intravenously or intramuscularly at a dose of 1-3 mg/kg, dexamethasone 0.1 mg/kg (4 mg in 1 ml). - Bladder catheterization is mandatory.
Maintain diuresis at a level > 1 ml/kg/h (if necessary, using diuretics - furosemide, single dose 0.5-1-2 mg/kg; micro-jet administration up to 10 mg/kg/day is possible). Fluid balance every 4-6 hours (be aware of the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion). - When performing minimal interventions accompanied by pain (sanitation of the tracheobronchial tree, etc.), adequate anesthesia or sedation (midazolam 0.1-0.2 mg/kg intravenously or fentanyl 1-5 mcg/kg) is necessary to prevent coughing , increased blood pressure.
- Bicarbonate:
Preferably avoided due to possible paradoxical “CNS acidosis.” - Position the patient's body with an elevated head end (30°) and eliminate other causes that disrupt the outflow from the cranial cavity (for example, catheterization of the veins of the superior vena cava basin is not recommended).
If conservative treatment of cerebral edema in newborns and young children is ineffective, decompressive craniotomy is performed by removing a bone flap in order to reduce the increased ICP due to cerebral edema.
No one knows exactly what can cause a brain tumor in newborns. The development of the disease begins in young cells when their normal maturation is disrupted. Mature cells never form a tumor. What prevents cells from going through the normal maturation pathway? Experts point only to possible factors that can indirectly provoke the development of the disease:
ionizing radiation, which is used for diagnostics (can leave its “trace” for a future illness even during pregnancy); vinyl chloride, or more precisely, its evaporation (most children’s toys are now made from this material); electromagnetic fields from technology, including - from mobile phones; birth injuries to the head; heredity (the risk of developing brain cancer in a child increases if there have already been cases of this disease in the family).
Some gene diseases also increase the risk of developing a brain tumor, including:
von Recklinghausen syndrome (neurofibromatosis of the NF1 or NF2 genes); Turco's syndrome (abnormalities in the APC gene); Gorlin's disease (basal cell nevus syndrome of the PTCH gene); Li-Fraumeni syndrome (abnormalities in the TP53 gene).
In 40% of cases, these diseases are a provoking factor in the development of brain tumors in newborns.
Parents should also remember that DNA in children does not change in the womb, but to a greater extent at a very early age (during the newborn period). This can be provoked by the environment, the state of health of the child, and even his emotional background.
Causes of edema
The causes of cerebral edema may be different and lie, for example, in impaired cerebral circulation expressed by ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, in traumatic brain injury, in the presence of an intracranial cancer tumor or metastasis from tumors of any location.
Inflammatory processes in the brain or its membrane (meningitis or encephalitis), fractures of the skull vault with damage to the brain matter, as well as general diseases in the form of severe infections, cardiovascular pathologies or extensive burns can also cause cerebral edema.
In addition, even a severe allergic reaction in the stage of anaphylactic shock or drug and alcohol intoxication can provoke the development of this pathology.
Development options
The development of cerebral edema in a child can follow two patterns: focal, widespread. In the first case, an area appears in the brain that suffers from excess fluid and is unable to perform its physiological functions.
This condition can be caused by various neoplasms, such as cysts, tumors, hematomas. The development of edema in a newborn in this case occurs gradually, the symptoms increase over a certain time and, reaching their maximum, begin to fade.
There may be several foci, their location is independent of each other. In this case, the concept of “diffuse edema” is introduced.
In the second version of cerebral edema in a newborn, the damage is more extensive and can spread to the entire or almost the entire organ. Usually these are the consequences of traumatic brain injuries, general intoxication of the body, the result of various types of toxic influences (chemical or biological factors, radiation). The process develops quickly and suddenly . The symptoms are pronounced.
What is the main danger of edema?
Swelling of any tissue in the human body is a fairly common and completely natural phenomenon, which, as a rule, goes away without any special consequences. But the brain is in a limited space, in a dense cranium, which cannot increase its volume under the pressure of its tissues.
Source: https://neuro-orto.ru/bolezni/mozg/otek-mozga-u-novorozhdennyh.html
Risk factors
Experts identify various reasons that can provoke cerebral edema in a child after birth. The main provoking factors of the pathological process are:
- injuries during childbirth
- drinking alcoholic beverages during pregnancy and on the eve of childbirth
- problems with uteroplacental circulation with subsequent fetal hypoxia in acute or chronic form
- infectious diseases
- uncontrolled use of medications by a woman during pregnancy
- diseases of the vascular system of the brain, which are characterized by impaired outflow of fluid
Brain edema in young children can occur for various reasons, so it is important to identify the pathology as early as possible and select effective treatment.
Diagnosis and drug treatment
The disease is diagnosed in two ways. Firstly, this is an examination of the baby by a neurologist. The doctor checks the baby’s reaction to various stimuli, looks at his reflexes and evaluates the external manifestations of the disease. The second way is to conduct research: neuroophthalmoscopy, MRI, spinal cord puncture. Usually, to make a diagnosis it is necessary to use these methods in combination. This way you can most accurately assess the severity of the disease and the baby’s health condition. In addition, a blood test of the newborn is carried out to identify the presence of pathogens of infectious diseases.
Cerebral edema in a newborn is treated strictly in a hospital setting. It is impossible to remove it without hospitalization, since the destruction occurs too quickly. Drug therapy is aimed at restoring full oxygen metabolism in brain cells. As a rule, the child is on artificial ventilation. Treatment uses medications such as muscle relaxants, which help relieve cramps.
In addition, the baby is prescribed diuretics, which remove fluid and prevent the development of swelling, and agents that normalize blood circulation. From time to time, the method of hypothermia is used, when body temperature is artificially lowered. If drainage of fluid from the child's brain is ineffective, a ventriculostomy may be prescribed - removing excess fluid with a catheter.
Symptoms of the disease
With such brain damage, mild symptoms are noted, but the consequences can be quite dangerous.
Parents need to closely monitor the condition of the newborn, which will allow timely identification of any disturbances in his behavior. Increased pressure inside the skull, dislocation syndrome of brain structures, and various neurological changes may indicate the progression of pathology in a child.
The main manifestations of brain swelling in infants are:
- headache
- lethargy
- fatigue
- paresis and paralysis
- swelling of the optic nerve
With further progression of the disease, convulsive syndrome appears, problems with the functioning of the heart and vascular system occur, and existing symptoms intensify.
A certain clinical picture develops:
- stiff neck
- dilated pupils
- increased muscle tone
- swelling of the fontanel
- hyperthermia
- blood pressure surges
- cardiopalmus
- brain scream
- acute renal failure
In addition, characteristic signs of damage to brain tissue may be observed in the form of strabismus, deviations of vital functions and anisocoria. With edema, neuroinfection can progress, metabolic processes are impaired and neurotoxicosis develops.
Possible complications
Complications of such a pathological condition as cerebral edema in an infant can be quite serious. The most terrible consequence of the condition is the death of the newborn. If the baby has other diseases and in the absence of effective therapy, edema becomes the cause of dislocation of the middle structures and the brain stem. In other words, the medulla oblongata enters the opening of the skull in the occipital region. With such a pathological condition, the death of a child may occur unexpectedly.
In some situations, complications can be quite distant and become noticeable some time after birth. Mostly the following complications are diagnosed in the baby:
- Decreased intelligence. The reason lies in the resolution of cells of cortical structures and their death, and the degree of decrease in mental abilities depends on the severity of their damage.
- Violation of physiological functions. Mostly after such a pathology, disturbances in the extensor movements of the limbs occur. The child cannot hold his head up on his own; his sucking and swallowing reflexes are impaired.
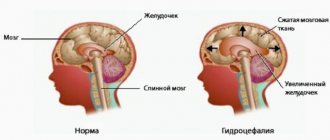
With cerebral edema with damage to the ventricular system, the infant may develop hydrocephalus. With this pathology, the outflow of cerebral fluid is disrupted, and the size of the head increases significantly.
Therapy
It is very difficult to combat cerebral edema in children. Depending on the final assessment of his condition and the severity of the disease, special therapy will be prescribed. Due to the wide range of damage that can be caused to brain activity, treatment will be highly individualized. The consequence of untimely seeking medical help can be not only the baby’s disability, but also death. It doesn’t matter whether a premature or full-term baby has an illness, doctors have one goal - to find what caused the swelling and its development, and to eliminate it as quickly as possible.
Medicines are prescribed in combination to not only remove a number of symptoms characteristic of edema, but also its very cause. Therapy is based on:
- osmotic diuretics such as Furosemide or Lasix;
- hormones;
- muscle relaxants, which will help eliminate the convulsive condition;
- corticosteroids. They will relieve swelling and stop the spread of edema throughout the brain;
- nootropics. They will help normalize blood circulation, without which brain activity will not return to normal;
- drugs to relieve specific symptoms.
In such a situation, therapy will be selected strictly individually. The child is placed in the intensive care unit, where the child’s condition is monitored minute by minute. When the child’s condition improves, examinations move to an hourly schedule. Brain parameters are strictly monitored to prevent new development of pathology. Sometimes children do not tolerate specific medications well, so the doctor will select more suitable analogues. All measures in therapy will be aimed not only at eliminating the damage caused by the tumor, but also at the restoration and development of the baby’s nerve and brain cells.
Diagnosis of cerebral edema
To determine an accurate diagnosis, a clinical examination alone is not enough. A mild form of such brain damage can be detected using some instrumental techniques.
After examining the patient, the specialist determines the diagnostic tactics and treatment regimen in each specific case.
Today, it is possible to detect brain damage thanks to several diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound using Doppler scanning mode. Thanks to this procedure, it is possible to identify various brain lesions in infants, including the accumulation of stagnant fluid in intracerebral formations. Through the use of special echo signs, it is possible to determine the severity of functional disorders. Thanks to ultrasound, it is possible to diagnose the localization of fluid in large quantities, establish periventricular edema and assess the state of blood flow in the vessels supplying the brain.
- MRI and CT. Thanks to such diagnostic methods, it is possible to achieve an accurate description of the child’s structural anomalies and pathological processes occurring in the brain tissue.
Additional diagnostic methods include studying the condition of the fundus to determine the symptoms of intracranial hypertension. It quite often serves as a consequence of such a phenomenon as cerebral edema.
How to notice and properly treat cerebral edema in newborns
There are diseases that you don’t even want to think about.
Especially if our children, so helpless and vulnerable, are in danger. At the same time, by brushing aside the obvious symptoms and hoping that the problem will “resolve” on its own, we ourselves doom the child to severe complications or, even worse, death.
Pathologies affecting the brain always raise questions about the future health and even life of the child.
Cerebral edema, which is essentially an increase in the size of the brain due to the concentration of fluid in the intercellular space, belongs to the category of secondary signs of damage. *Cerebral edema in newborns* is the most dangerous reaction of a child’s body to unbearable loads of a traumatic or infectious nature. A particular danger with edema lies in the lightning speed of development of the process.
Causes of cerebral edema in newborns
There are many conditions that can cause *cerebral edema in newborns*. In particular, it can arise due to:
- traumatic brain injury - it can occur as a result of a fall or blow;
- intracranial hemorrhage;
- infections – meningitis, toxoplasmosis, encephalitis and others;
- tumors of brain structures;
- ischemic stroke, when cells deprived of oxygen are left without nutrition;
- a sharp change in altitude - from one and a half km above sea level.
In addition to the above reasons, the development of cerebral edema can be facilitated by diseases and toxicoses suffered during pregnancy and causing hypoxia in the mother and fetus.
Another danger, threatening all sorts of complications, including cerebral edema, awaits the baby during his difficult journey through the birth canal.
Birth trauma significantly increases the risk of life-threatening cerebral edema in newborns.
Symptoms of cerebral edema
The variation of symptoms depends primarily on the causes and level of severity of the condition.
The main signs of a developing pathology, which include visual impairment, speech difficulties, disorientation, convulsions, headaches, memory loss and some other symptoms, in newborns, you will agree, are not so easy to diagnose (only convulsions can become obvious symptoms). In order to detect swelling in time, parents should exercise increased vigilance and attentiveness.
As fluid levels accumulate in the brain, intracranial pressure increases. The child becomes lethargic and weak. Swelling of the optic nerve nipple is observed.
As the process worsens, convulsions and disturbances in the cardiovascular system appear. Due to the excruciating headache, the baby simply starts screaming (“brain scream”).
Hyperthermia, a state of stupor (unconsciousness) and rigidity (compression) of the neck muscles are observed. The child suffers from convulsions, his fontanelle swells.
Further, midcerebral decompression may develop, leading to oculomotor crises, which are accompanied by dilation of the pupils and fixation of gaze. Muscle tone increases, temperature rises, blood pressure jumps, and tachycardia develops. *Cerebral edema in newborns* threatens the development of neuroinfections, brain injuries and metabolic disorders.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of cerebral edema involves the following studies:
- MRI and CT scan of the brain;
- neurological examination;
- blood test (diagnoses the cause of swelling).
Treatment of cerebral edema in newborns
It happens that a slight concussion or a mild form of mountain sickness leads to cerebral edema in newborns. Treatment* in this case may not be required - the symptoms will disappear on their own in a couple of days.
However, it never hurts to show the baby to the doctor once again. Crying and fever are already a sufficient reason to invite a pediatrician.
All other cases require mandatory and immediate medical intervention.
The treatment process is primarily focused on restoring impaired oxygen metabolism. For this, a combination of medical and surgical methods is used.
By applying the correct treatment strategy, it is possible to completely eliminate swelling, and, as a rule, initially swelling of the neck.
And if the therapy was timely, then recovery occurs quickly enough and is not accompanied by destructive changes. The following therapeutic measures help to cope with swelling:
- oxygen therapy - artificial delivery of oxygen, which enters the respiratory tract using an inhaler or other special devices;
- decrease in body temperature;
- intravenous infusions (normalizes blood flow and prevents the development of infections);
- drug therapy - selected depending on the symptoms and causes of swelling;
- surgical intervention is indicated in the most severe cases (removal of a bone fragment to reduce ICP, restoration of a blood vessel, or removal of a detected tumor).
Consequences
Of course, such a serious pathological condition as *cerebral edema in newborns* is not without consequences. As a result of the accumulation of fluid in the intercellular space, an increase in the size of the brain occurs. The latter, in turn, provokes an increase in intracranial pressure (ICP) and a deterioration in cerebral circulation, which ultimately leads to cell destruction.
Brain edema can acquire varying degrees of severity, depending on which certain disorders are formed. As a rule, the *consequences of cerebral edema in newborns* are expressed by further disturbances:
- sleep;
- communication skills;
- motor activity;
- emotional state.
And these are not all the problems that await a child who has suffered cerebral edema. In many ways, the development of complications is determined by the localization of the pathology. And if we talk about the most common consequences of cerebral edema in newborns, then these are, of course, recurring headaches.
It should be noted the influence of *cerebral edema in newborns* on the development of the child’s further intellectual abilities. So, if the cortical structures of the brain die as a result of edema, a decrease in intelligence can range from mild forms of mental retardation to serious mental disabilities. In addition to intellectual impairment, other obvious defects are possible:
- pathology of grasping and sucking reflexes;
- violation of extensor positions of the limbs;
- head thrown back reflex;
- squint and so on.
It should be recognized that the timeliness of professional assistance is the main key to minimizing future consequences. And, of course, we should not forget that with such serious pathologies, parental delay threatens the child with death.
A child who has suffered cerebral edema must continue to be monitored by several specialists at once - in addition to regular consultation with a pediatrician, he will need the supervision of a neurologist, and often a psychiatrist (if there is a delay in speech development). Mandatory sanatorium-resort treatment is recommended for the newborn and the mother.
Source: https://medikya.su/otyoki/otek-mozga-u-novorozhdennyx.html
Differential diagnosis
Differentiated diagnosis is indicated if the baby has:
- hypoxic-ischemic damage to the central nervous system
- congenital abnormalities of brain structures
- hydrocephalus
- infection during fetal development, which is accompanied by damage to nerve cells
The difficulty of differentiation lies in the fact that such diseases can be supplemented by the appearance of local edema or damage to the parenchyma already at the stage of decompensation. It is for this reason that differential diagnosis is carried out only after the acute stage of the condition has been relieved.
Drug therapy
Treatment of cerebral edema involves taking various groups of medications, which are selected by a specialist. Their main goal is to eliminate the factor that provoked the accumulation of large amounts of fluid in the brain structures. Symptomatic therapy is auxiliary and allows you to cope with the signs that arise during the pathology.
To get rid of excess fluid in the brain, the child may be prescribed certain groups of medications (see Table 2).
| Group | Description |
| Diuretics | Drugs in this group form the basis for the treatment of any diseases that are caused by the formation of edema. When taking diuretics, it is possible to achieve a pronounced therapeutic effect and improve the child’s well-being. It is possible to cope with unpleasant symptoms with the help of medications such as Lasix, Fonurit and Novurit. |
| Decongestant treatment | The drug that helps to cope with swelling is glycine. It is usually prescribed to infants along with drinks, such as juice or compote. |
| Dehydration therapy | This treatment involves intravenous administration of various solutions. Thanks to this therapy, it is possible to improve metabolic processes within cells, which restores brain function and reduces fluid volume. When treating newborns, hypertonic solutions such as calcium chloride, glucose and sodium chloride are administered. |
| Protein solutions | With the help of drugs of this group, it is possible to restore metabolic processes in tissues and have a beneficial effect on the protein balance in the child. For therapy, medications such as albumin solution are mainly prescribed, or plasma is administered. |
| Glucocorticosteroid drugs | With their help, it is possible to cope with the manifestations of cerebral edema and improve the overall well-being of the child. Typically, hydrocortisone is used for this purpose, which is selected individually taking into account the weight of the baby. |
Treatment methods on video:
In case of depression syndrome, the baby can be prescribed vitamins, among which Encephabol is considered the most effective. It has a complex trophic effect at the neural level. With the help of the medication, it is possible to normalize glucose metabolism occurring in the brain tissue. The drug has an antioxidant effect, improves the plasticity of red blood cells and increases ATP levels.
Cerebral edema in newborns - features of the development of the disease and possible complications
A health and life-threatening condition – cerebral edema in a newborn baby – is increasingly being diagnosed in babies. It is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the brain tissue. The pathology is dangerous due to its complications; surgical intervention is often necessary to solve it.
The outcome of the disease depends on when it was diagnosed and how quickly doctors began treatment. Before starting treatment and prescribing surgery, specialists identify the cause of the pathology and assess possible risks.
What is cerebral edema and why does it occur in infants?
Essentially, cerebral edema in newborns is a process in which the accumulation of fluids in the brain tissue leads to a significant increase in its volume. In appearance, the head may not have external swelling or enlarged areas, which makes it difficult to diagnose the pathology.
In addition to the trauma received during childbirth, AGM is caused by:
- intrauterine hypoxia;
- asphyxia at the time of birth (due to entanglement with the umbilical cord, penetration of amniotic fluid or meconium into the respiratory tract);
- presence of a tumor;
- microembolism and gas embolism of cerebral vessels;
- abscesses;
- infections (bacterial or viral meningitis, encephalitis).
Why does swelling develop?
Brain edema in a newborn can occur for various reasons:
- congenital infectious diseases - rubella, cytomegalovirus infection,
- TORCH complex infections;
- when entwined with the umbilical cord;
- Rh conflict leading to hemolytic disease;
- birth trauma of the skull.
The causative factor damages the substance of the brain - directly or indirectly. Brain cells respond to this by hyperproduction of fluid - they increase in size. With further action of the damaging factor, fluid accumulates not only in the cells, but also in the intercellular substance - brain edema intensifies.
Since the brain is located in a closed space, it cannot expand indefinitely. Signs of compression of the brain begin to develop. The last stage of cerebral edema in a child is the wedging of the trunk into the foramen magnum. Without emergency assistance, this leads to death due to disruption of vital functions.
Symptoms and types of pathology
The accumulation of fluid in the brain tissue of a newborn provokes a rapid deterioration of his condition. Signs of the disease include:
- bulging fontanelles;
- increase in body temperature to critical levels;
- sleep disturbance;
- strong and non-stop crying;
- refusal of food;
- clouding of consciousness;
- convulsions and seizures;
- vomiting;
- inadequate response to external stimuli;
- pallor of the skin.
Often, signs of the disease appear in the maternity hospital; if later, parents need to seek medical help as soon as possible. To clarify the diagnosis, pediatricians conduct a visual examination and prescribe instrumental types of research:
- MRI;
- electroencephalography;
- fundus examination.
After diagnostic measures, the type of disease is determined. Based on the localization of OGM, it is divided into local and diffuse. When localized, one area is affected, and in this case the symptoms appear gradually. Diffuse affects both the hemispheres and the brain stem itself, which entails pronounced symptoms and serious consequences.
Depending on the cause of the pathology, damage to brain structures can be:
- vasogenic, provoked by the presence of tumors and embolism;
- cytotoxic, formed due to asphyxia;
- osmotic, which manifests itself after the penetration of amniotic fluid into the respiratory tract.
Symptoms of pathology
Brain edema in children develops gradually. Therefore, unfavorable signs can be detected in advance:
- the child becomes lethargic, moves little, does not take the breast or bottle well;
- gradually he develops a headache - the newborn reacts to this with sharp cries;
- upon examination, you can detect bulging fontanelles on the skull;
- limbs are in a state of hypertonicity - fists are clenched, hands are pressed to the chest,
- the toes are tucked, and the legs themselves are bent at the knee and hip joints;
- you can notice the dilation of the pupils;
- the child goes from lethargic to hyperactive and screams shrilly;
- there is an increase in body temperature.
As cerebral edema progresses, the child develops convulsions, instability of breathing and blood circulation is noted, and increasing compression of the brain substance leads to impaired consciousness up to coma.
Possible consequences of AMS in children
Like any other disease, timely diagnosed and treated AMS in a newborn has minimal negative consequences. Therapy for this pathology is always carried out in a hospital setting and consists of the following:
- Reducing swelling and removing excess fluid from the body. For this, a course of diuretics is prescribed.
- Restoration of nerve cells.
- Elimination of seizures, for which age-appropriate muscle relaxants are prescribed.
- Improves blood circulation and brain metabolism. Nootropic drugs are best suited for this.
- Prevent further enlargement of the affected areas by administering corticosteroid medications.
- Restoring breathing by connecting to a ventilator (in especially severe cases).
Whatever the treatment, the consequences of an AGM will be present in the child’s future life. For example, he will be registered with a neurologist. In cases of significant developmental delays and lack of speech, you will have to be observed for a long time by a psychiatrist.
Nerve cells in the brain that die as a result of the development of the disease can significantly reduce the child’s mental abilities in the future.
How physically developed the child will be depends on the stage at which the disease was detected and what part of the brain it affected.
Sometimes, by the first year, children catch up with their peers and are no different from them either in behavior or in mastering certain skills.
Particularly severe cases can provoke the development of cerebral palsy and epilepsy. Periventricular edema leads to the development of necrosis of brain tissue. There are known cases of deaths when the damage to the child’s brain was too extensive, and treatment was untimely or incomplete.
Surgical intervention
Surgical elimination of the pathology is resorted to in the absence of a positive effect after drug therapy. In a situation where the edema is caused by neoplasms of various types, local edema is corrected during neurosurgical treatment of the tumor.
In some cases, it becomes necessary to correct the pressure inside the skull. In such a situation, the meninges are dissected through the fontanelles and decompression is performed.
Oxygen therapy
Oxygen therapy is a procedure that uses oxygen for therapeutic and preventive purposes. Under the influence of oxygen, various substances are oxidized, and the body receives the energy that is necessary to maintain its normal functioning and other biochemical processes.
The most effective method of oxygen therapy is inhalation, when the patient inhales pure oxygen or a special gas mixture through a mask. Thanks to this procedure, it is possible to get rid of headaches, increase immunity, improve the functioning of the cardiovascular system and neutralize toxins.
Alternative treatment for cerebral edema
It is allowed to treat edema using traditional medicine recipes closer to the age of one, when changes that require correction can already be noticed.
When treating children with spastic muscle lesions or hyperkinetic disorders, it is recommended to use clay, which has a lot of healing properties. You can prepare an infusion of blue clay for oral administration. It is necessary to dissolve a teaspoon of the product in 200 ml of water and drink this solution a tablespoon several times a day throughout the day. A massage with blue clay, which should be smeared on the limbs and a light massage, gives a good effect.
At home, you can do special gymnastics with rubbing the muscles with balls. This procedure should be performed every day and it is better if the mother learns it from a massage therapist.
Baths with the addition of various herbs give a good effect in treating the nervous system in young children, normalizing the function of excitation and inhibition. If a child has muscle hypertonicity, it is recommended to give him an oat bath several times a week. To do this, you need to pour the dry grass with a liter of water and add the decoction to the filled bath. In case of decreased muscle tone and decreased muscle activity, it is recommended to take baths with the addition of pine needles.
In case of severe convulsive syndrome, you can prepare an infusion of oregano herb. To do this, you need to pour 20 grams of the plant into 300 ml of water and give this product to the child 3 drops per day.
It is important to remember that traditional medicine can only be used in the treatment of cerebral edema in infants after consultation with a specialist. It is important to remember that primary medical treatment cannot be ruled out.
Prevention
Today there are no special measures that could prevent the development of pathology. Nonspecific prevention is practiced, which involves following all recommendations for a healthy pregnancy and labor.
It is important to exclude exposure to factors that could cause injury to the baby or infectious pathologies immediately after birth. An important place in disease prevention is given to proper care and prevention of various injuries.
Forecast
With cerebral edema in newborns, the prognosis is quite unfavorable, since the inflammatory process progresses quite rapidly. Often it is not possible to stop the swelling and death occurs. If a child has suffered cerebral edema, then various disturbances in motor activity, cognitive functions and other disorders are subsequently possible.
Cerebral edema in newborns is considered a dangerous pathology, which can result in the development of dangerous complications and even death. With the right approach and quick intervention, the consequences after pathology can be minimal or completely absent. The reasons for the development of such a disorder may be different, so it is important to protect the child from exposure to adverse factors.
Causes and types of cerebral edema
The most common cause of cerebral edema in a child is birth trauma. However, such generic causes do not always cause swelling. There are other factors that can provoke this serious illness:
- Encephalitis.
- Meningitis.
- Water poisoning.
- Brain abscesses.
- Various tumors.
- Fetal hypoxia, which occurs as a consequence of toxicosis in the mother.
Swelling may appear if the baby was born with asphyxia (for example, this happens when the umbilical cord is entangled in the neck), during a long and difficult birth, during which amniotic fluid entered the child’s respiratory system, as well as as a result of other injuries that occurred at birth. A predisposition to edema can also occur if the mother has a number of diseases during pregnancy.
There are two types of edema in a newborn child: regional, when only one part of the brain swells, and widespread, when the damage is extensive and covers the entire organ. Edema of the first type can be caused by hematomas, cysts and various types of tumors. Symptoms with this pathology develop quite slowly. In the second case, the cause is usually traumatic brain injury or intoxication. The symptoms in this case are most pronounced.
Depending on the underlying cause, cerebral edema in newborns is also divided into several types:
- Vasogenic. It can be triggered by various tumors, gas embolism of cerebral vessels, microembolism.
- Cytotoxic. When it occurs, the amount of fluid in the cells increases, and oxygen deficiency occurs.
- Interstitial. This type of edema develops as a result of hydrocephalus.
- Osmotic, the cause of which is water poisoning of the nervous system.
You can read lectures on the Internet that describe in detail the causes of this serious disease, as well as the symptoms that characterize it.