The radial nerve runs along the entire upper limb, from the shoulder joint to the fingertips, innervates almost all nearby muscles and is responsible for motor activity . Damages to its tissues and structures lead to temporary limitations in the functionality of the hand.
One of the varieties of this pathology is called radial nerve neuropathy - it does not pose a serious threat to health, but requires timely diagnosis and treatment.
Radial nerve neuropathy - what is it?
Radial neuropathy is a type of peripheral neuropathy and can develop even after minor exposure. Its function is to ensure flexion and extension of the arm in the area of the forearm, hand and phalanges, movement of the thumb and turning the palm with the back side up. In addition, sensory branches of the nerve provide innervation to certain parts of the hand.
The radial nerve stretches along the entire upper limb, and has several vulnerable points - on the back near the armpit, in the area of the humerus and elbow. The destruction of its structures and tissues occurs due to the inflammatory process, metabolic disorders and exposure to toxins, which causes discomfort and impaired motor functions.
According to the international classification of diseases ICD-10, neuropathy of the radial nerve was assigned code G56 - mononeuropathy of the upper limb.
For reference : the disease is considered one of the most common peripheral mononeuropathies, and occurs in patients of any age and gender.
Symptoms of the disease
Usually the disease begins with damage to one ear, and over time, hearing loss becomes bilateral. The classic manifestation of the disease is a condition in which auditory and vestibular functions are simultaneously impaired. This clinical picture occurs in a third of patients. Half of the patients first develop hearing problems. And only in some people the disease develops with a lack of coordination in space.
Main signs of the disease:
- problems with the vestibular system (loss of balance);
- feeling of stuffiness, pressure in the ears;
- hearing impairment;
- causeless noise and ringing in the ears;
- a feeling that surrounding objects are revolving around the patient;
- increased sweating;
- nausea and vomiting;
- nystagmus.
The disease manifests itself in attacks. Attacks that occur a couple of times a week or month are considered frequent, rare—up to twice a year, and episodic—every few years. During an attack, the patient can neither stand nor sit. When you try to turn your head, the symptoms become much more pronounced. At this moment, the patient needs to take a horizontal position, close his eyes and try not to move.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Another attack can be triggered by physical activity, emotional stress, being in a smoky or noisy room, or alcohol.
The attack itself can last from half an hour to five hours. For several hours, or even days, the patient feels weakness and decreased performance. If each subsequent attack becomes longer, you must urgently contact an otolaryngologist.
Causes of radial nerve damage
Due to the anatomical structure and location of the radial nerve (it is quite close to the muscles and bones), even a slight impact on vulnerable points is enough to cause damage, so there can be quite a few causes of neuropathy.
- Squeezing (compression). Often the development of pathology is caused by incorrect posture during sleep, when the arm is under the head or body for a long time. As a rule, this position is typical for people in a state of extreme fatigue or intoxication.
- Fractures and injuries of the humerus. Neuropathy of the radial nerve after such injuries develops, according to various sources, in 3-1% of cases, and the nerve itself usually remains intact - the development of the disease is provoked by scars that appear on healed tissues.
- Medical errors. Negative effects on the radial nerve can be either traumatic or associated with certain medical procedures. This may be prolonged compression with a tourniquet to stop bleeding or an error when performing injections - incorrect insertion of a syringe needle into the shoulder area can damage the structures and tissues of the nerve. This category includes the incorrect use of crutches for leg injuries - constant pressure on the armpits and forearms causes compression of the radial nerve.
- Infectious diseases . Sometimes neuropathy acts as a complication of bacterial and viral infections, including measles, pneumonia, typhus, influenza, and herpes virus.
Less commonly, the causes of pathology are intoxication with heavy metals or alcohol, hormonal disorders and pregnancy in women, benign neoplasms, diabetes mellitus, inflammatory processes in muscles and nerves.
Interesting : Radial neuropathy is most often caused by compression of the arm during sleep, which is why it is called “Saturday night palsy.”
Causes
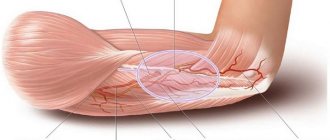
The most common cause of a neurological disorder is elbow injury . Neuritis of this etiology occurs in 28-34% of patients.
Prolonged bed rest with squeezing the arm between the body and the bed, puncture and cutting wounds, fractures and dislocations can lead to damage to the cubital canal.
In this case, there is a malnutrition and gradual destruction of the nerve fiber, accompanied by acute inflammation. In such a situation, the pathological process becomes chronic.
In some cases, neuritis manifests itself decades after the injury . This is due to the gradual progression of ligament fibrosis. Another name for the pathology is Miche's ulnar neuropathy.
Other causes of neuritis include:
- prolonged hypothermia;
- infectious lesions: diphtheria, typhoid fever, herpes virus, measles and brucellosis;
- vascular pathologies, ischemia in the elbow joint, in which the nerve stops receiving the required amount of oxygen and nutrients;
- alcohol poisoning, intoxication with heavy metal salts;
- epicondylitis, periarthrosis of the head of the humerus;
- diseases of the endocrine system: diabetes mellitus, thyroid disorders;
- compression of nerve tissue during sleep, with a sudden change in hand position;
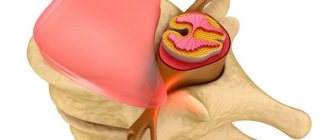
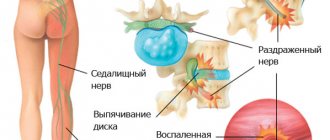
- cervical osteochondrosis, herniated intervertebral discs: lead to compression of the vessels supplying the ulnar nerve.
In children, ulnar nerve neuritis often appears in the absence of timely vaccination against measles and typhus . The cause of the disease can be hypovitaminosis, congenital pathologies of the cubital canal.
In the latter case, there is compression of the nerve in the ulnar groove by a fibrous arch stretched between the heads of the flexor carpi.
Development of the disease due to work characteristics
Neuritis, which occurs due to pinching of the ulnar nerve, develops in office workers, operators or people in industrial production. The costs of the profession force people to often rest their elbows on the table, armrests or machines.
The disease can occur with prolonged overexertion of the arms in patients whose activities involve heavy physical labor. Over time, mechanical stress leads to injury, which causes neuritis.
How does the disease manifest?
Symptoms of radial nerve neuropathy can be different - depending on the location and degree of the pathological process, the disease is manifested by disturbances in sensitivity, motor and autonomic functions of the hand.
- Motor manifestations. Patients with this diagnosis have difficulty extending the hand and elbow, and the ability to move the forearm is slightly impaired.
- Sensitive manifestations . Severe pain syndrome occurs in the area of the muscles of the forearm and elbow, manifests itself with intense movement of the hand and fingers (especially when trying to bend and straighten them), and burning pain in the area of the thumb is also possible, which spreads to the entire arm up to the forearm and shoulder.
- Vegetative manifestations. One of the symptoms of the disease is numbness and a crawling sensation on the skin; the most common is loss of sensation on the back of the hand and mild numbness of the shoulder.
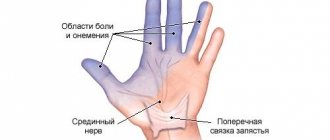
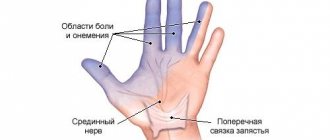
- Radial tunnel syndrome. Carpal tunnel syndrome is a neurological disorder characterized by acute pain in the back of the hand and upper forearm that occurs when trying to move the fingers or wrist.
- Impaired supination of the hand and forearm . Supination of the hands and forearms is the ability to rotate the hand so that the palm faces down, parallel to the surface of the floor or thighs. With lesions of the radial nerve, impaired supination occurs quite often.
The symptoms of the disease vary depending on the location of the pathological process - it can be concentrated in the forearm, elbow or wrist.
For reference : one of the clear signs of pathology is the so-called “dropping hand” symptom (when trying to raise the arm up, the patient’s hand will hang down).
Ulnar nerve neuritis: code according to ICD-10, massage of the joint nerve, treatment with folk remedies and exercise therapy
Ulnar nerve neuritis is a neurological type of disease.
The disease can affect the nerve of one or both arms at the same time. Symptoms will depend on the exact reasons for the development of the disease. In this article we will tell you what the general clinical picture is, what needs to be done to recover, and we will briefly consider prevention methods.
Description of the disease
The disease in ICD-10 is coded M79.2. It often makes itself felt, first of all, by weakness, when a person tries to tightly clench his hand into a fist, hold certain objects, or lack sensitivity in his fingers. The appearance of the bone also changes.
Important! Next to the ulnar nerve is the radial nerve. In this regard, the clinical picture often resembles the symptoms of radial neuralgia.
Basically, the corresponding disease affects those who spend a lot of time at the office desk. The thing is that employees often lean on their elbow. As a result, over time, the nerve is injured, which in this particular place is not very deep.
Causes of the disease
Several factors can simultaneously cause the disease. We are talking about the following:
- frequent hypothermia, human exposure to low temperatures;
- infectious factors;
- getting injured. Here, both the nerve itself and the area of the bone where it is embedded can be affected. As a result, pinching and development occurs
- diseases;
- vascular type pathology, which contributes to obstruction of blood circulation and disruption of the supply of nutrients;
- insufficient levels of microelements and vitamins;
- alcohol intoxication;
- thyroid dysfunction, elevated blood glucose levels;
- osteochondrosis;
- hernias developing in intervertebral discs;
- structural features of the muscle canal;
- staying in the wrong position for a long time.
Reference! Diseases of the elbow joint are also a cause of the disease. If the patient is aware of their presence, then the problem must be kept under control.
Symptoms and clinical picture
The ulnar nerve is responsible for the functioning of the ring and little fingers and the functioning of the muscles that flex the wrist.
In this regard, the patient immediately feels discomfort in free movement of the hand.
The clinical picture usually depends on the location of the inflammation, but pain is considered the main symptom.
She may be:
- piercing;
- sharp;
- burning;
- aching.
General symptoms:
- impaired sensitivity of the affected area;
- numbness;
- the presence of a tingling sensation;
- The most common localization of pain is in the area of the 4th and 5th fingers, as well as the palm.
Signs of improper functioning of motor fibers are as follows:
- the appearance of seizures;
- impaired finger activity;
- it is difficult for a person to form a fist or a hand;
- there is an absence of tendon reflexes;
- hand paralysis;
- muscle atrophy may develop.
Important! If timely treatment is not started, trophic disorders will appear. The skin turns blue, nails crumble, and hair falls out.
Diagnostics
The sooner the disease is diagnosed, the more effective and faster its treatment will occur.
As the pathology progresses, atrophy of the hand muscles or complete loss of all key functions may occur.
Usually doctors immediately prescribe treatment, since the little finger is retracted and the hand itself resembles a clawed paw.
To identify the disease, special tests will be required:
- the patient should place the sore hand on the table and try to move the little finger;
- you need to try to spread your fingers to the side;
- If there is a defeat, a person cannot do this. In addition, he cannot hold a sheet of paper with his index fingers.
Additional examination methods:
- Ultrasound;
- MRI;
- electromyography.
If a person experiences all the symptoms, it is better not to delay going to the doctor in order to prevent complications.
Treatment
Typically, treatment of the disease involves the use of an integrated approach. First, the cause of the pain , and then measures are taken to eliminate it. If the disease is infectious, then antiviral drugs will be needed for treatment. When blood circulation is impaired, Papaverine is needed.
Immediately after the diagnosis is made, the arm is fixed with a splint. For recovery, the hand should be in a straight position, and the fingers should be bent.
Reference! A special bandage or scarf can be used to secure the arm. It will take at least two days for immobilization.
Complex treatment involves:
- use of medications;
- physical therapy;
- massage;
- traditional medicine.
on this topic:
Medicines
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed at the first stage of the fight against the disease. In addition, they relieve pain and general inflammation. The list of necessary medications includes:
- Indomethacin;
- Diclofenac;
- Nimesupid.
To improve the response of nerve impulses, Prozerin is used. As a supplement, your doctor will help you prescribe vitamin B supplementation.
Massage
With ulnar nerve dysfunction, the temperature in the area that coincides with the affected area decreases. The objectives of massage are:
- analgesic effect;
- acceleration of conduction of all nerves;
- increased sensitivity.
The massage technique involves gradual kneading of the cervicothoracic region, and then the entire limb. Rubbing movements and light stroking are used
You also need to massage the muscles well; vibration is often used here. It is customary to massage the ulnar nerve when the arm is slightly bent at the joint. The duration of one procedure should be approximately 10-15 minutes.
Exercise therapy
After removing the main fixator, doctors recommend performing special exercises. Both active and passive movements are prescribed. The goal of therapeutic exercises is to restore muscle function.
Recommendations for implementation:
- first it is recommended to do gymnastics in water;
- the hand sinks deep under the water, and the healthy one tries to bend the phalanges one by one, lifting them upward;
- Circular movements of the hand and abduction of the fingers to the sides are carried out.
Important! It is necessary to direct efforts to develop the index and sore fingers. The first one goes down, and the second one goes up.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods are used as additional treatment.
They are generally considered to be ineffective on their own.
The most commonly used herbal infusions and compresses are:
- tying burdock, horseradish or cabbage leaves to the affected area;
- using bear cheese instead of ointment;
- apply a compress based on red clay, previously diluted with vinegar;
- Before meals, drink a decoction of leaves and raspberry stems.
When the patient begins treatment on time, the prognosis will be favorable. Full recovery should only be expected after two months. It is important that there is no relapse.
Prevention
To reduce the likelihood of illness, the following measures are taken:
- breaks in work if it involves bending or straightening the arms;
- when a person sits at a computer for a long time, his hands need to be stretched;
- Self-massage is practiced from time to time to eliminate muscle tightness, swelling or numbness.
When it comes to athletes, injuries sustained must be treated immediately, even if they are minor. Preventive measures include measures to strengthen the immune system. Particular attention is usually paid to hardening and diet.
Thus, it is better to treat ulnar nerve neuritis immediately, avoiding complications. You do not need to prescribe any medications yourself; it is better to have a specialized doctor do this. To prevent relapses, it is important to carry out preventive measures.
Source: //doktor-ok.com/zabolevaniya/perifericheskoj-nervnoj-sistemy/nevrit/loktevogo-nerva.html
Diagnostics
If you have symptoms of the disease, you should contact a neurologist, surgeon or traumatologist. To make a diagnosis of radial nerve neuropathy, a number of clinical and instrumental studies are used, which allow not only to identify the pathological process, but also to determine its localization and extent . First of all, complaints and medical history are collected, external examination and palpation of the affected limb are carried out, after which the patient is sent for further diagnostics.
Blood analysis
Clinical and biochemical blood tests are carried out to detect inflammation and infections in the body, as well as to determine blood sugar levels - neuropathy is a common disorder in diabetes. Sometimes hormone levels and a general urine test are required.
Functional tests
Functional tests for suspected radial neuropathy are performed to assess the motor functions of the limb. The patient brings his palms together with his fingers straightened so that the wrists touch each other, and then tries to spread the fingers - if the nerve is damaged, this will be difficult. In addition, people with this diagnosis cannot simultaneously press their fingers and palm onto a flat, flat surface, or move their finger away from the palm.
Electromyography and electroneurography
To confirm the diagnosis, electroneurography and electromyography are used - diagnostic methods that allow you to assess the functional state of nerve and muscle tissues. With lesions of the radial nerve, electromyorgaphy reveals a decrease in the amplitude of the action potential of muscle fibers. Electroneurography is a method of studying the passage of an electrical impulse along nerve endings - the development of neuropathy is indicated by a slowdown in this process.
Instrumental methods
Instrumental diagnostic methods (CT, MRI, X-ray) , as a rule, are indicated for fractures and mechanical injuries of the hands - they allow you to obtain images of the affected tissues and prescribe appropriate treatment. Sometimes the patient requires consultation with an endocrinologist, infectious disease specialist and other specialized specialists.
Important : differential diagnosis for this pathology is carried out with radicular syndrome, as well as lesions of the other large nerves of the upper extremities - the ulnar and median.
Causes.
“Classic” carpal tunnel syndrome is chronic.
Etiology:
- Trauma due to professional activity: repeated movements and compression of the hand or wrist; holding tools; severe flexion or squeezing of the wrist; working with vibrating tools.
- Common causes: obesity; may be temporary in pregnant women; mucopolysaccharidosis V; tuberculous tenosynovitis; diabetes; hypothyroidism; acromegaly; amyloidosis; carcinomatosis; polymyalgia rheumatica; rheumatoid arthritis; gout.
“Acute” carpal tunnel syndrome is very rare. Its symptoms arise quickly and are pronounced.
Etiology:
- Thrombosis of the median artery.
- Hemorrhage into the transverse ligament.
Treatment
Neuropathy does not pose a serious threat to health, but if left untreated for a long time, it can cause a reduction in muscle mass and problems performing simple household tasks. The therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis - hospitalization is necessary only in severe cases (serious injuries to the upper extremities and intense pain that cannot be relieved with painkillers). To treat the injury, a comprehensive approach is required, which is aimed at eliminating symptoms and improving hand function.
Therapeutic methods
The following medications are used as a conservative treatment for the disease:
- anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs (Ibuprofen, Diclak, etc.);
- decongestants and vasodilators to eliminate edema, improve blood circulation and metabolic processes in tissues;
- anticholinesterase drugs reduce the activity of a special enzyme that causes overexcitation of the nervous system, thereby improving the conduction of impulses along nerve endings;
- biostimulants and B vitamins to accelerate regenerative processes in tissues;
- antiviral and antibacterial agents are necessary in cases where the cause of neuropathy is infectious diseases.
In case of intense pain, strong painkillers (for example, Tramadol) or novocaine blockades may be required - injection of the drug directly into the affected area. To improve the effect of conservative treatment, patients are shown physical therapy and alternative treatment methods.
- Massage . Improves blood circulation and metabolic processes in the area of the affected nerve, increases muscle tone and helps accelerate regenerative processes. You can perform the massage yourself - use gentle movements to massage and knead your arm in the area of the hand, elbow and forearm, bend and straighten your fingers. When performing manipulations, the patient should feel slight discomfort; in case of severe pain, the intensity of the effect should be reduced.
- Electrophoresis . The treatment method involves introducing drugs into tissues using an electric current. Most often, for radial nerve neuropathy, prozerin, xanthinol, nicotinate and other drugs are used that improve muscle condition, and electric current provides additional stimulation of the nerves.
- Paraffin applications . Prolonged gentle heating helps eliminate inflammation and pain, improve blood circulation and remove toxins that come out with sweat and are absorbed into paraffin.
In addition to the above procedures, electromyostimulation, acupuncture, magnetic therapy, ozokerite and mud applications are used to treat radial nerve neuropathy.
For reference : acupuncture is particularly effective for this pathology - the procedure acts directly on the affected muscles and nerves, due to which the patient’s condition significantly improves.
Therapeutic exercises
A set of special exercises will help restore motor functions of the hand, increase muscle tone and avoid degenerative processes.
- Bend your elbow and place it on a hard surface so that your forearm is at a right angle. Alternately move your thumb down and your index finger down, repeat 10 times for each finger.
- Place your hand in the same position as in the first exercise. Lower your index finger down and lift your middle finger up, repeat 10 times.
- Grasp the lower phalanges of the fingers on the affected hand with healthy ones so that the thumb is on the side of the palm. Bend and straighten them 10 times, then repeat the same with the second phalanges.
- Dip your fingers into the water and with your healthy hand pull them back one by one, repeat the procedure 10 times.
- To perform the exercise, you will need a small rubber ball, toy or any other object - you need to squeeze and unclench it with your fingers at least 10 times.
Exercises should be performed 1-2 times a day for several weeks, combining the complex with physiotherapeutic methods and medications.
As a rule, radial nerve neuropathy responds well to conservative treatment, and hand function can be restored within 1-2 months. In rare cases, patients need surgical intervention to suture the nerve (in case of mechanical injuries accompanied by rupture of the nerve) or eliminate its compression, and sometimes the disease becomes chronic and worsens under the influence of negative factors, which include hypothermia, bruises, incorrect posture during sleep, etc.
Clinical picture: symptoms and manifestations
The intensity of symptoms depends on the degree of damage to the ulnar nerve and the individual characteristics of the patient. Peripheral nerve fibers consist of sensory, autonomic and motor neurons.
When each of them is damaged, the following clinical picture is observed:
- With neuritis, changes in tactile perception are observed in the area of the hand and fingers. Sensory neurons of the ulnar nerve do not innervate the skin of the forearm.
Numbness may develop, which is accompanied by a decrease or complete loss of sensitivity in the affected area.In some cases, paresthesia appears. When they occur, the patient feels tingling and frequent goosebumps.
- Impaired motor activity is accompanied by the appearance of paralysis or paresis.
The pathological process can cover the area from the elbow joint to the fingertips. There is muscle weakness in the skeletal muscles innervated by the ulnar nerve. If left untreated, atrophy and loss of tendon reflexes may develop. Due to lack of physical activity, the muscles decrease in size, so the affected forearm appears thinner when compared to the healthy arm. - Autonomic disorders are accompanied by trophic changes. The limb swells, blueness of the skin and depigmentation are observed. Hair falls out on the arm and sweating increases. Nails often break and trophic ulcers appear.
- When the ulnar nerve is pinched in the musculoskeletal canal, tunnel syndrome occurs.
The pathology is accompanied by pain . As the disease progresses, it leads to numbness of half the ring finger and little finger on the palmar side.
On the back of the hand, there is a loss of sensitivity in half of the middle finger and a complete loss of tactile perception in the ring and little fingers.
Numbness of the fingers is accompanied by muscle weakness, muscle wasting and atrophy. The brush resembles a bird's paw .
Possible patient complaints
Patients come with complaints of periodic numbness of the arm in areas innervated by the ulnar nerve. Loss of sensitivity is observed in the IV, V, half of the third finger on the back of the hand, the skin on the palms .