VSD of the mixed type has common features with some autonomic dysfunctions, such as orthostatic hypotension and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. These features include orthostatic intolerance and vasovagal syncope. Vegetative-vascular dystonia also has overlaps with other medical diagnoses, including post-traumatic stress disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, major depressive disorder and somatoform disorder.
VSD of mixed type
Vegetovascular dystonia of the mixed type in the strict sense of this definition is not a disease. It is a collective term that summarizes a number of different symptoms (syndromes) associated with dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. Symptoms include nervousness, sleep disturbances, seizures and cardiovascular problems.
The name “dystonia” comes from the Greek word “tonos” - tension (dis- + tension). Autonomic dystonia literally means “dysregulated tension (dystonus) of the autonomic nervous system” - a violation of the interaction between the sympathetic and parasympathetic departments. This, in turn, leads to physical complaints not related to organic causes.
The autonomic nervous system (autonomic nervous system), part of the peripheral nervous system, supports physiological functions associated with the cardiovascular, respiratory and gastrointestinal systems, but is also closely connected with higher brain systems involved in the emotional and psychological aspects of human life. In the mature brain, it maintains a background level of functioning by communicating with the limbic structures of the brain, which are involved in regulating mood, memories and emotional state.
It includes all areas involved in the control of "autonomic", unconscious and involuntary functions in the context of overall body homeostasis:
- blood pressure;
- heartbeat;
- breath;
- activation of sweat glands;
- extracellular fluid volume composition;
- blood flow;
- metabolic rate;
- digestion;
- kidney function;
- muscle tone of internal organs and so on.
When a person perceives consciously (for example, decides to move), the somatic nervous system is activated. Most of the time, both systems work closely together.
The autonomic nervous system is divided into two functional antagonists:
- Sympathetic department.
- Parasympathetic department.
While the sympathetic system speeds up the heart rate and breathing and primes the entire body for the fight-or-flight response, the parasympathetic system is primarily responsible for the processes of relaxation and regeneration. If the interaction between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves does not work properly, symptoms may be classified as autonomic dystonia.
Patients' complaints are based on whether tension has shifted in favor of the sympathetic or parasympathetic: therefore, people with increased sympathetic activity (sympathetotonia) are prone to nervousness, palpitations, high blood pressure and diarrhea. If, on the other hand, the parasympathetic (vagotonia) is dominant, it may be associated with low blood pressure, cold hands and feet, lethargy and constipation.
Helpful information
However, vegetative-vascular dystonia as a diagnosis is controversial, given that various symptoms can be generalized under this term.
Despite the fact that there is no single classification, doctors divide vegetative-vascular dystonia into types, depending on the disorders of the cardiovascular system: hypertensive, hypotensive, normotensive and mixed type VSD, which includes symptoms characteristic of any of the types.
Folk remedies
When using folk remedies, it is important to choose herbal decoctions that correspond to the type of dystonia. So, for low blood pressure, tonic herbs are used, and for high blood pressure, soothing herbs are used. Herbal therapy is effective at the initial stage of the disease, with long-term treatment. The following decoctions and infusions are easy to prepare at home:
- a mixture of hawthorn, St. John's wort and valerian;
- a mixture of hawthorn, rose hips, motherwort;
- a mixture of St. John's wort, mint, lemon balm.
Valerian has the most powerful calming effect. For low blood pressure and bradycardia, ginseng, eleutherococcus, dandelion, and alfalfa effectively tone the body. To improve the condition of blood vessels, it is useful to drink freshly squeezed juices from carrots, beets, and pumpkins. To quickly relieve headaches due to cerebral dystonia, experts advise washing your face with cold water or soaking your feet in cold water for several minutes. You can perform a light massage of the temporal area.
Causes
In most cases, vegetative-vascular dystonia does not have a clear cause and occurs as a result of the interaction of various factors. If, after all the necessary medical examinations, a purely physical cause for the symptoms concerned can be ruled out, psychosomatic causes must be considered. Often, excessive psychological stress, in addition to other factors (overstimulation, unfavorable diet, environmental stress, toxins, genetic, hormonal factors), plays a significant role. VSD of the mixed type can sometimes cause frightening conditions (tachycardia) and remain a heavy burden in the long term. Therefore, somatoform disorders are just as serious as those that have physical causes.
Often there is an individual predisposition (genetic predisposition) to the development of one or another form of autonomic disorder. There is a known predisposition to the development of migraine-type headaches to other forms of autonomic disorder, in which a certain organ area is particularly affected, such as the gastrointestinal tract, or colon or other organ system. Thus, an individual threshold value can be reached or, in a particular case, exceeded by the interaction of various factors, and then decompensation, and, thus, the occurrence of an individual symptom complex can be explained as a consequence of mixed type VSD.
Main symptoms
VSD represents a theory that explains the occurrence of an individual symptom complex, and on the basis of which the relationship between individual conditions can be understood and explained. Therefore, we can also say that the term mixed type VSD is a medical concept with which certain clinical manifestations can be explained.
Various physical symptoms may occur with VSD:
- general malaise with nausea and vomiting;
- blood pressure surges;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- nervous tremor;
- increase or decrease in heart rate;
- dyspnea;
- increased sweating;
- muscle spasms (calf muscle cramps, toe cramps, muscle tremors, muscle twitching);
- heart problems (irregular heartbeat, heart spasms, heart pain, chest tightness);
- cold hands (caused by spasms of blood vessels);
- nervousness, anxiety, irritability;
- insomnia;
- loss of sexual desire and other symptoms.
VSD symptom complexes of mixed type often occur together and are sometimes considered as independent diseases with an unknown cause. One example is hyperkinetic cardiac syndrome, which is associated with rapid heartbeat and large fluctuations in blood pressure.
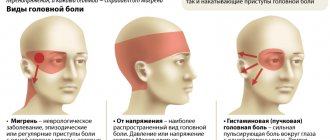
Symptoms of cerebral vascular dystonia
In all cases, patients with cerebral dystonia complain of frequent tinnitus, dizziness, and numbness. The main symptom is headache. Dystonia of cerebral vessels is felt by pain in the temples and crown. The disease is accompanied by nervous disorders: apathy, depression, anxiety, rapid breathing, and confusion. A person’s performance capacity sharply decreases and lethargy appears.
In the morning, there is increased swelling of the face, which goes away by noon. Cerebral dystonia according to symptoms is usually divided into the following groups:
- Cardialgic manifestations. Characterized by stabbing or aching pain in the heart area. They appear both during physical activity and in a state of complete rest.
- Arrhythmic manifestations. Sudden or systemic heart rhythm disturbances. They can be caused by a variety of diseases.
- Bradycardic symptoms. They manifest themselves as a decrease in heart rate to 40–50 beats per minute. In this case, dizziness, chills, and fainting occur.
- Tachycardia. It is characterized by a sharp (over 90 beats per minute) increase in heart rate without any compelling reason.
Diagnostics
Vegetovascular dystonia is not a diagnosis in the sense of a specific disease, although it includes an uncharacteristic condition in which various functions of the autonomic nervous system are disrupted. Typically, the treating physician will ask about the patient's medical history, pre-existing health conditions, medications the patient is taking, relevant life situation, including alcohol or drug use, how long symptoms have been present, and in what situations they occur.
And even on the basis of certain disorders, it is impossible to determine VSD or exclude such a disorder. The attending physician cannot objectify such a diagnosis and remains dependent on the general impression of the patient’s health status. That is, it only creates a clinical picture demonstrating symptoms. Even the frequently mentioned autonomic signs (sweating, trembling of hands, eyelids) may not always be present.
- Measuring your pulse and blood pressure is especially useful if you have circulatory problems. The patient is able to check fluctuations throughout the day using a hand-held sphygmomanometer.
- If there are complaints in the heart area, the doctor listens to heart sounds with a stethoscope.
- A blood test is used to check whether there is inflammation in the body, whether there are nutritional deficiencies, or an excess or deficiency of specific hormones. In this way, possible physical causes (thyroid dysfunction or iron deficiency) are excluded.
- If a physical illness cannot be ruled out and symptoms persist for a long time, special tests (depending on the symptoms) may be carried out. Examples are an electrocardiogram, stool or urine examination, or imaging procedures such as ultrasound and x-rays. However, the doctor will usually try to avoid unnecessary and possibly stressful examinations.
The problems that arise when diagnosing mixed-type VSD also complicate therapy. When selecting the myriad of sedatives, care must be taken to account for the addictive effects.
Treatment
Treatment of VSD of mixed type is carried out mainly by conservative methods. The daily routine is of great importance in complex therapy. Doctors recommend proper rest and restful sleep for at least eight hours. It is important to maintain sleep hygiene - maintain a comfortable temperature in the bedroom, provide ventilation and access to fresh air.
The patient needs to choose the right bedding - an orthopedic mattress and pillow, bed linen made from natural materials that absorb excess moisture well. Deep, long sleep helps normalize blood pressure. Before going to bed, you should limit the amount of time you watch TV and work on the computer. Other recommendations:
- Alternating loads and rest. If, due to professional duties, you have to work at a computer, you need to take frequent breaks, exercises to relax the neck muscles and exercises for the eyes. Rest breaks will prevent the development of cephalgia and the appearance of other signs of VSD.
- Regular walks in the fresh air. Doctors advise spending at least 2 hours in the fresh air every day.
- Dosed physical activity, sports. Recommended sports: cycling, aerobics, fitness, swimming, skating. For exercise at home, exercise equipment is used, including a cardio stepper, treadmill, exercise bike, and rowing machine. Sudden movements and intense physical activity, which is associated with increased cardiac activity, should be avoided.
- Diet. A mixed-type diet for VSD involves consuming foods rich in vitamins, plant fiber, and microelements, including potassium and magnesium. Excess body weight correlates with increased manifestations of pathology. Weight correction is necessary if there is a significant excess of the norm. You should limit the amount of table salt, fatty meat, bakery products made from premium flour, and confectionery.
- Water procedures. Hardening procedures (douches, rubdowns), hydromassage, circular shower, contrast baths, Charcot's shower are used.
- Physiotherapy. Electrosleep sessions and electrophoresis are recommended. The exposure mode is selected taking into account the leading clinical syndrome.
- Massage, reflexology. A targeted effect on biologically active zones stimulates cerebral blood flow and central nervous system activity. For a mixed form of VSD, a combination of superficial massage (rubbing, vibration) performed at a fast pace and a soothing massage (kneading) performed slowly is recommended.
- Psychotherapy. Auto-training and meditation are effective therapeutic techniques that promote relaxation, eliminate muscle and nervous tension, and normalize the activity of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
Effective treatment of mixed-type vegetative-vascular dystonia involves an integrated approach - the inclusion of medicinal and non-medicinal methods. The main goal of therapy is to eliminate clinical symptoms and achieve a state of long-term remission.
Drug therapy
Treatment of mixed type autonomic dysfunction with pharmaceutical drugs is carried out to eliminate pain, sensory disturbances, motor deficits and other neurological manifestations. In case of development of sympathoadrenal crises (panic attack accompanied by an unmotivated progressive feeling of fear and severe autonomic disorders), Carbamazepine is used.
Correction of metabolic disorders is carried out with the drugs Pyridoxine (vitamin B6), Thiamine (vitamin B1), Cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12). Sedative (general calming effect on the central nervous system) and anxiolytic (reducing the severity, suppressing fear, anxiety, restlessness) therapy is carried out with the following drugs: Chlorprothixene, Phenibut, Carbamazepine, Amitriptyline.
Folk remedies
Treatment of mixed-type cerebral vascular dystonia with folk remedies is carried out using decoctions, infusions, and tinctures prepared from medicinal plants. Traditional healers advise using home remedies based on ginseng root, Eleutherococcus, Leuzea, Aralia, and Zamanikha, which are considered natural stimulants of one’s own immune defense. These plants have pronounced tonic properties and have a general strengthening effect on the body.
Diuretics prepared from juniper, bearberry, lingonberry leaves and berries are useful. Particularly useful in the mixed form are home remedies with a calming, sedative effect, including decoctions of mint, lemon balm, valerian and peony root, hop cones, and sage. On forums on the Internet you can find many recipes for preparing medicinal home remedies.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia of mixed form is manifested by a large number of symptoms that reflect disturbances in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. Timely diagnosis and correct therapy will help eliminate disorders and improve well-being.
Treatment methods
In most cases, medications are not necessary, but they can be used to treat symptoms if patients are suffering greatly. These include, for example, painkillers, sleeping pills, and various antidepressants. The attending physician discusses the procedure with the patient and selects the medicine individually for each case. As a rule, VSD is not a permanent problem and can only be temporarily treated with medications.
Medication methods
During treatment, strengthening agents are usually prescribed, which contain vitamins, minerals, trace elements, herbal supplements, and sedatives. Also:
- Antioxidant drugs (succinic acid, eltacin).
- Dietary supplements (elastoin).
- Correctors for cerebrovascular disorders (vinpocetine, vincamine, cinnarizine).
- Anticholinergics (platifilline or combination drugs containing this alkaloid).
- Vasodilators.
- Antihypertensive drugs.
- Homeopathic remedies (Acidum phosphoricum, Acidum picricum, Argentum nitricum, Arsenicum album, Avena sativa, Cocculus, Gelsemium, Kalium phosphoricum).
In addition, there are so-called cardiotonics (cardiac glycosides). These are means to strengthen the heart, especially the heart muscle, containing herbal ingredients (arnica, horsetail, valerian, garlic, lemon balm, mistletoe, hawthorn). Each active ingredient has a specific area of application, but when combined, the components should produce a heart-strengthening effect.
A high intake of lecithin may also help reduce vascular damage, especially in cases of excessive consumption of nicotine, caffeine and alcohol.
Non-drug methods
In the long-term treatment of functional complaints, the priority remains physical methods that have a strengthening, regulating and balancing effect on the nervous system, and hydrotherapy. This:
- walks, sunbathing;
- swimming, if possible in natural waters;
- breathing exercises;
- recreational gymnastics (tai chi, yoga);
- massage;
- autogenic training;
- baths with valerian, lemon balm or thyme, pine baths.
Important information
In addition, it is important to follow a diet, consume more raw vegetables and fruits, grains than meat products.
Doctors often advise waiting and observing the development of symptoms - somatoform disorders may recur after some time. If this is not the case, then psychotherapy may be recommended. Some psychotherapists specialize in somatoform disorders or autonomic dystonia.
Complications of VSD
How mixed-type VSD works depends on various circumstances. Overall the prognosis is good. The condition does not limit life expectancy. In 50–75% of cases, somatoform disorders are mild, and symptoms improve over time. Patients with depression or anxiety disorders have a worse prognosis. This also applies to strong psychosocial stresses that are difficult to resolve. “Severe” mixed VSD means that symptoms become more severe over time and become chronic if not treated early. But this does not mean that they persist only because they could not be cured in the first place. There is always a possibility of VSD regression.
Diagnostic methods
When making a diagnosis, the following parameters are taken into account:
- variety and inconsistency of complaints;
- lability of blood pressure, heart rate;
- the presence of diseases in the parents, in which the psychosomatic development mechanism predominates - neurodermatitis, peptic ulcer, bronchial asthma, hypertension;
- no changes in ECG and EEG, ultrasound, blood and urine tests.
Basic EEG rhythms in VSD
Prevention
Prevention remains the best therapy. This is generally relevant for psychosomatic disorders and means, among other things:
- regular exercise, fitness;
- walks in the open air;
- sauna, contrast shower;
- healthy eating (avoiding toxins such as nicotine, excessive alcohol consumption);
- life coaching for a balanced quality of life in all areas (partnership, family, work, leisure, etc.).
Taking into account the interaction between body, mind and soul, only a holistic approach leads to improvement or even cure of symptoms. In this context, targeted body therapy and psychotherapy can strongly support the course of recovery.