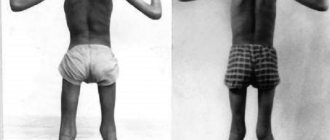
Muscular dystonia is a syndrome in which the patient experiences uncontrolled muscle contraction. As a result, the patient is forced to take an unnatural posture; if the limbs are affected, they are unusually curved. A diagnosis such as muscular dystonia is very often given to children at an early age. This is due to the fact that the pathology in the vast majority of cases manifests itself immediately after birth. Less commonly, young, adult and elderly patients suffer from muscular dystonia.
At CELT you can get advice from a neurologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,200
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
Kinds
The etiology and various manifestations of the disease suggest different types of muscular dystonia. Its course is influenced by the causes, the age at which the first signs appeared, the area of the lesion, and the features of the manifestation.
Development factors
Genetic predisposition causes the occurrence of primary (idiopathic) dystonia. It is already detected in infants. At least in the initial stages of the disease, dystonia is not associated with damage to other organs.
Secondary dystonia occurs as a consequence of other diseases, intoxication, and medication.
Age of onset of symptoms
This criterion allows us to distinguish dystonia of several ages. Infant is detected from birth to two years, children - up to 12 years, teenage - up to 20. Young is diagnosed up to 40 years. The last type is adult dystonia.
Damage area
If pathological muscle contraction is characteristic of only one part of the body, we speak of focal dystonia. The most common subtypes are torticollis and blepharospasm.
Involvement of multiple sites characterizes multifocal dystonia.
If the muscle tone of the entire body or more of it is impaired, they speak of a generalized form of pathology. It is characterized by strange postures that are very difficult for a person to maintain in a normal state. Patients can unnaturally arch their spine and lie like that.
A change in tone on one side of the body indicates hemidystonia.
If muscle disorders affect several neighboring parts of the body, they speak of segmental dystonia. In most cases, this pathology is characteristic of adulthood and is accompanied by head trembling.
Voltage level
The most well-known classification of dystonia, which every mother has encountered after the birth of her baby, is the separation of increased and decreased tone.
In the first case we are talking about hypertonicity. It is characterized by too much simultaneous tension in the flexor and extensor muscles. It is difficult for a child with hypertonicity to put clothes on, and it is difficult for him to play. Many poses cause pain and discomfort. Hence the frequent tearfulness and anxiety.
At the same time, E. Komarovsky says that hypertonicity is normal for a baby up to 3-4 months.
Less attention is usually paid to hypotension in children. It is characterized by muscle weakness. A baby who has dystonia of this type sleeps a lot and does not show anxiety. Everything seems to be fine with him. However, this form of the disease is dangerous. It leads to delayed physical development. Children with hypotonia later begin to hold their head up, sit, walk, and cannot hold objects in their hands.
Some children exhibit symptoms of both forms of dystonia at the same time. In this case, the lower extremities are usually characterized by excessive tension, while the upper extremities are characterized by weakness of muscle tissue.
Both forms also occur in older age as a result of the development of neurological, mental, and infectious diseases.
Development mechanism
Maintaining muscle tone, changing it, and ensuring complex movements are among the functions of the extrapyramidal system. It includes the subcortical nuclei, cerebellum, medulla oblongata, and cortex. The contraction process also involves the nerves that innervate the skeletal muscles, as well as the muscle fibers themselves, the complex structure of which ensures movement.
Muscle tissue consists of elongated cells - myocytes, the sarcoplasmic reticulum, rich in calcium, and myofibrils, which look like elongated filaments.
Muscle contraction occurs when a nerve impulse emanating from the brain reaches it. The nerve cell synthesizes the mediator acetylcholine and provokes the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Calcium interacts with the protein troponin. The latter is contained in myofibrils and causes actin filaments to approach each other. As a result, the sarcoplasmic reticulum decreases and muscles contract.
Due to dysfunction of the extrapyramidal system, the synthesis of acetylcholine and other mediators that ensure communication between neurons is disrupted. Incomplete processing of impulses leads to a simultaneous contraction of antagonist and agonist muscles, although in a normal situation they oppose each other.
This process underlies the development of convulsive phenomena, as well as tone disturbances.
Acuity of manifestation
Sometimes dystonia occurs as an acute reaction to certain psychotropic medications. If symptoms appear in a situation associated with severe mental stress, they speak of egodystonia. This type of pathology is a psychological disorder and is temporary.
Etiology and Pathogenesis
The clinical picture of torsion dystonia was first described in 1907 by M. W. Schwalbe. He observed a family for many years, in two generations there were 5 patients who, in his opinion, suffered from hysterical neurosis, but in reality - torsion dystonia. In 1911, G. Oppenheim established that torsion dystonia is an organic disease of the brain caused by damage to the subcortical nodes, and proved that attributing it to hysteria is erroneous. The question of the nosological affiliation of Etc. remained controversial for a long time. According to some scientists, torsion dystonia is an independent hereditary disease. Other researchers not only did not attach importance to heredity in the etiology of etc., but also believed that there are only torsion-dystonic syndromes in pathologies of the extrapyramidal system of various etiologies - infectious and toxic encephalitis, traumatic brain injury, birth trauma, vascular diseases of the brain and others. It is now generally accepted that T. is an independent nosological form, in the etiology of which the hereditary factor is of primary importance. The type of inheritance is different. In some families, the disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, in others, which is more common, in an autosomal recessive manner. Etc., inherited according to the first type, was traced for 2-3 generations, and in some families for 4-5 generations. With autosomal recessive inheritance, cases of consanguinity between parents have been reported. Sporadic cases of Etc. are often encountered.
Pathogenesis has not been established. No primary metabolic defect was identified. It is assumed that disturbances in the content of catecholamines (see), mainly dopamine, are important in the pathogenesis. The pathophysiological essence of T. is a violation of the subcortical regulation of muscle tone (see). A postmortem examination reveals mild degenerative changes in the cerebral cortex and more pronounced ones in the basal ganglia, red nucleus, Lewis body (nucleus subthalamicus), substantia nigra, and dentate nucleus of the cerebellum.
Causes
Muscular dystonia in children and adults occurs due to various reasons. What is common is a genetic predisposition - it leads to the appearance of primary dystonia, not associated with any other diseases. An example of such a disease is Duchenne dystrophy.
Infants
In newborns and children under two years of age, the development of muscular dystonia is associated with hypoxia, abnormal development, brain pathologies that occur during intrauterine development, and birth injuries. These are various diseases and habits of the expectant mother: hypertension, diabetes, smoking, alcoholism, drug use, toxicosis.
Another group of factors that cause muscular dystonia in infants is associated with disorders of pregnancy and childbirth: placental abruption, polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios, umbilical cord entanglement, long anhydrous period, rapid labor, improper management of delivery.
Children and teenagers
The main reason for the appearance of dystonia in children over the age of two years is diseases of the nervous system, infectious diseases, and the occurrence of neoplasms. Often spasms and tone disturbances occur with encephalitis and meningitis.
Dystonia is one of the characteristics of cerebral palsy. Pathology occurs due to injury and intoxication.
Adults
The range of diseases that cause muscular dystonia in adults is quite wide and includes encephalitis, cerebral hemorrhages, Huntington's disease, oncology, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's, Wilson-Konovalov's diseases. Just as in children, infectious diseases, injuries, and poisoning lead to pathology.
Symptoms
Features of the manifestation of dystonia, manifested in increased or decreased muscle tone, are different. In this regard, it is customary to distinguish signs of hypertonicity and hypotonicity.
Symptoms of hypertension
Noteworthy is the tendency of most babies to keep their limbs slightly bent and spread to the side. Any attempt to straighten them meets resistance. Breasts with increased tone often throw their heads back. Other symptoms include restlessness, crying, sleep disturbances, and trembling of the chin when crying. Such babies often burp when they eat or after eating.
As the child develops, involuntary spasms of the arms and legs become noticeable. It is possible to walk on your toes, leading to improper formation of the foot. With high muscle tone in the body, curvature of the spine develops.
Adolescents and adults experience impaired handwriting, numbness or stiffening of muscles after prolonged exercise, and the development of convulsive phenomena. Muscle pain appears.
Symptoms of hypotension
Newborns with decreased tone sleep most of the time, eat little, are not interested in what is happening around them, and do not want to move. They quickly begin to lag behind in development. Older children cannot hold objects or a pen in their hands.
In adults, the pathology is characterized by general weakness, apathy, and inability to perform any actions.
Symptoms of asymmetric tone
In the presence of both increased and decreased tension, the child attempts to take an unusual position, depending on the type of tone. Lying on his tummy, he will constantly strive to turn to the side with increased muscle tension. An arched bending of the entire body is possible.
When lying on the back, the child turns his head. Some curvature of the pelvis is noticeable.
An additional symptom is a bending of the limb on one side, a relaxed state on the other. In a small child these manifestations are most noticeable.
Other signs
Other signs also indicate muscle dystonia. These are various involuntary movements, shouting sounds, words, changing the timbre of the voice. Speech becomes blurred and incomprehensible. A person is unable to maintain a certain position.
Syndromes
The combination of several symptoms allows us to distinguish the following syndromes:
- Cervical dystonia. The pathology is otherwise called spastic torticollis. Appears due to damage to the muscle fibers responsible for the position of the head. Torticollis can be recognized by the characteristic turn of the head.
- Cranial. Involves the muscles of the neck, head, and face.
- Torsion bar. A genetically determined pathology is associated with the formation of postures that are either difficult or impossible for a healthy person to assume. Pathology leads to disability. Develops mainly in childhood.
- Writer's cramp. Contraction occurs in the muscles of the hand when writing.
- Blepharospasm. Dystonia first manifests itself as uncontrollable bouts of rapid blinking, later leading to the inability to open the eyelids. In especially severe cases, blindness occurs.
Feedback
Call:
+7(495)104-44-16
Leave a request
and our manager will contact you!
Consultation is free if you have a compulsory medical insurance policy and a passport
ArthroMedCenter tries to make treatment at the Clinic not only comfortable, but also affordable, therefore we systematically develop special offers and promotions for our clients.
Muscular-tonic syndrome is a common case of manifestation of spinal osteochondrosis. Pain in the spine is not caused by disc protrusion or herniation. A sharp deterioration in health occurs due to painful spasms in the muscles. It accompanies degenerative spinal diseases.
Treatment
At the initial stage of development of muscular dystonia, drug treatment is not carried out. Physiotherapy, massage, exercise therapy are recommended. As the disease progresses, the use of medications is indicated.
Drug therapy
To improve the conduction of nerve impulses, drugs are prescribed to regulate the action and content of neurotransmitters. Benzotropine blocks acetylcholine, Lorezapam and Diazepam regulate GABA, Levodopa activates the production of dopamine.
Nootropic drugs are prescribed aimed at improving the metabolic process, for example, Cerebrolysin, Nootropil, Glycine.
Brain activity is improved by Semax drops. To compensate for calcium deficiency, calcium gluconate is used.
In some cases, botulinum toxin injections are recommended. The substance blocks the transmission of nerve impulses to the muscle for several months.
Brain stimulation
In severe situations, electrodes are implanted into the brain. They block the transmission of impulses.
Massage
One of the effective methods of normalizing muscle tone and reducing spasms is massage. It is taught in courses twice a year, but some elements can be done at home for children and adults.
Before doing a massage, you should definitely consult a neurologist and orthopedist. He will recommend which elements are shown on which part of the body, specify the duration of the course, and indicate the diagnosis. Based on this information, the massage therapist will create the correct set of exercises.
For hypertonicity, procedures aimed at relaxing muscle tissue are indicated. Use stroking and rubbing with an open palm and fingers. In some cases, acupressure is indicated. Patting and tapping with the edge of the palm is contraindicated.
For hypotension, a more intense massage is performed. The affected area is pinched, rubbed, and squeezed. Such actions will help restore normal muscle growth and development.
Regardless of who performs the massage and where, certain rules must be followed. The procedure begins an hour after eating. The ambient temperature should not exceed 22 °C. In order not to damage the delicate skin, a special cream or oil is used.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is performed to relieve the symptoms of muscular dystonia. Mud and relaxing baths, water procedures, and electrophoresis are prescribed.
To reduce hypertension in infants at home, it is recommended to make paraffin boots. Older children and adults are given acupuncture courses.
Exercise therapy
Patients with dystonia are required to undergo physical therapy. Two to three times a year, classes are conducted with a physiotherapist, the rest of the time - independently at home.
Infants are advised to exercise on a fitball. Patients of any age, in the absence of contraindications, are prescribed swimming.
Prevention
To reduce the likelihood of muscular dystonia in a child, expectant mothers are advised to eat a balanced diet, walk outside, and conduct regular medical examinations.
After birth, the child is examined by all specialists in accordance with the schedule. Any symptoms of pathology should be discussed with a doctor. This also applies to older children and adults.
Muscular dystonia appears as a primary disease caused by genetic disorders, and sometimes develops as a result of central nervous system pathology or infectious diseases. It manifests itself as involuntary contractions, increased, decreased or asymmetrical tone.
Diagnosis of muscular dystonia syndrome
Diagnostic criteria for diagnosing muscular dystonia syndrome are as follows:
- determining the presence of dystonic postures or movements;
- assessment of maternal labor and early development of a child suspected of having dystonia;
- determining the absence of diseases or taking medications that can cause dystonia;
- determination of the absence of paralysis and epilepsy;
- determination of the results of instrumental and laboratory tests (for example, copper metabolism studies, electroencephalography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging).