Features of the disease
Cerebral palsy is a pathology caused by damage to parts of the brain. As a result of the disorder, problems arise with coordination of movements, difficulties with hearing, speech, and vision. The infant exhibits mental retardation and may even experience convulsions.
Cerebral palsy appears in newborns more often than in children after a year of life. A feature of the pathology is that the symptoms of the disease do not progress. The damage to parts of the brain that has occurred will appear less in the future if you pay attention to the condition of the baby in time. If cerebral palsy is detected early in a child, then timely massage therapy and physical therapy will reduce movement disorders.
Effective diagnostic techniques
It is important to identify cerebral palsy in newborns in the maternity hospital in order to begin treatment as early as possible. Then it will be as effective as possible. A thorough examination by a qualified pediatrician will identify warning signs.
It is especially important to monitor children at risk: premature babies, those infected by the mother, those who have suffered a birth injury, or those with jaundice.
If alarming symptoms are detected, hardware diagnostics are prescribed - ultrasound of the brain, electroneurography, electromyography, electroencephalography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
Monitoring the baby becomes the responsibility of a neurologist. Additionally, consultation with an otolaryngologist, ophthalmologist, psychiatrist, or epileptologist may be required.
It is important to differentiate pathology from the individual characteristics of the baby. Some babies up to six months experience slight trembling of the chin and hands, and high tone of the limbs. Normally, such excitability disappears without a trace when the baby begins to crawl and stand on its feet.
The main causes of pathology
The causes of pathology of the nervous system are based on disruptions in the intrauterine development of the fetus. That is why the first signs of cerebral palsy are detected in newborns immediately after birth.
The health of pregnant women plays an important role in the occurrence of paralysis in infants. During pregnancy, women may experience infections. And hypoxia during childbirth is considered the main cause of damage to parts of the fetal brain.
Cases of cerebral palsy occur due to:
- severe infections in an infant;
- exposure to radiation and x-rays on a child’s body;
- poisoning of both mother and baby with drugs, chemicals, and food.
The causes of cerebral palsy in children are associated with chromosomal abnormalities. More than four hundred reasons provoke a terrible disease. If a newborn has decreased or increased muscle tone, then you should immediately seek help from a pediatrician.
Signs of cerebral palsy in a child
Doctors are not able to notice and identify the first signs in every case, so an invaluable diagnostic role is given to the mother, who spends the most time with the baby.
First signs
How does cerebral palsy manifest in an infant (first manifestations):
- there is a clear asymmetry between the buttocks and the torso as a whole;
- the curvature of the spine in the lumbar region is poorly manifested;
- no fold between the buttocks;
- muscle tone in the limbs (tight or flaccid);
- muscle cramps, paralysis;
- poor sleep, anxiety, loss of appetite;
- weakening of the muscles on one side of the body and increased tone in the other half, as a result, shortening of the limbs, curvature of the spinal column;
- movements with only one arm or leg;
- The child cannot turn his head independently.
2 months and older
Symptoms of cerebral palsy in infants from 2 months:
- trembling of the limbs when trying to lift;
- stiffness in the arms and legs when moving;
- it is difficult for the baby to control his head when trying to lift it;
- problems during feeding (weakness of the sucking reflex, difficulty biting, tongue sticking).
6 months and older
Signs of illness from six months:
- it is difficult to roll over on your side on your own;
- the baby does not control the process of raising his head;
- feeding problems continue;
- the child extends one hand, and the other clenches into a fist.
10 months and older
Symptoms from 10 months of age:
- the baby cannot sit down on his own and remain in this position without outside help;
- doesn't try to talk;
- does not respond to his name;
- When moving, he uses one arm and leg, and drags the opposite ones behind him.
12 months and older
Signs of illness from year to year:
- does not crawl independently;
- cannot stand without assistance;
- does not speak simple words;
- does not look for toys that hide in his presence.
The following video is about the symptoms of cerebral palsy, filmed by the TVC program “Doctors”.
Stages of the disease
A disease such as cerebral palsy in newborns appears gradually, developing from two months to three years:
- At an early stage, the child notices a lag in movements from a normal peer. Even at four months, the baby will not reach for toys or turn towards the sound. This is due to decreased muscle tone. Some experience limb cramps.
- Since the brain of a newborn works with deviations from the norm, the development of a child up to three years is chaotic. At 8 months he cannot hold his head up, but he tries to sit up.
- At the late stage, residual, signs of paralysis appear clearly with skeletal deformation, lack of coordination, mental and mental retardation.
Parents themselves may notice deviations in the child’s behavior. To do this, you need to carefully monitor the behavior of the baby from the first months of life.
Why do premature babies have retinopathy (retinal detachment)
Vessels growing from the underdeveloped retina penetrate the eyeball. As a result, the child sees poorly and goes blind.
In premature babies, the muscles are swollen, in which the cell nuclei are displaced from the center to the periphery, so the muscle cells cannot relax completely. Due to incompletely stretched muscles, the child sucks poorly, spits up, suffers from obstructive bronchitis and sudden cessation of breathing (apnea).
The diagnosis of cerebral palsy in premature babies is made at 1 year!
In the first year after the birth of a child, there is a lag in motor development. By the end of the year, the muscle condition does not improve, and you think that the problem is in the brain cells. The experts around you claim that the cells are damaged and will refer to the results of MRI and ultrasound.
Neurologists diagnose premature babies:
- Perinatal encephalopathies (intracranial hemorrhages, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathies), movement disorder syndrome closer to 6 months and cerebral palsy of various forms at 1 year:
G 80.0. Spastic tetraparesis (double hemiplegia)
G 80.1. Spastic diplegia
G 80.2. Hemiplegia, spastic unilateral cerebral palsy
G 80.3. Dyskinetic cerebral palsy
G 80.4. Ataxic form of cerebral palsy
- Respiratory distress syndrome.
- General edema syndrome.
- Hyperbilirubinemia and “kernicterus”.
- Necrotizing enterocolitis.
- Anemia.
- Pneumonia.
Doctor Nikonov
My opinion : MRI and ultrasound do not show pathological changes in the brain with a diagnosis of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, movement disorder syndrome and cerebral palsy. But neurologists need this diagnosis to declare that hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy causes periventricular leukomalacia, which is the cause of seizures. Although neurologists admit that there are no clinical manifestations specific to this pathological condition!
Doctor Nikonov
My opinion : ultrasound can reveal echo density, which proves the state of edema, but not the death of brain neurons! With intraventricular hemorrhages, very premature babies die a few hours after birth.
I believe that the lymphatic system of muscle cells does not develop at the same rate as muscle cells. There are more and more muscle cells, and the lymph is not able to carry away waste products from muscle and fat cells.
Due to the accumulation of own waste in the muscle cell, swelling occurs.
Comment to the photo:
The green color in the first image shows the lymphatic trunk of the lymphatic system, which develops normally and without deviations from the norm. The second image shows the immature lymphatic vessels of the embryo. The picture shows the vessels in the form of a mesh. Please note that these images were taken with an electron microscope.
Doctor Nikonov
My point of view is supported by Professor Kiyotoshi Sekiguchi from Osaka Medical University, Japan, who, at my request, conducted a number of studies. As a result, the professor discovered that the primitive lymphatic system (up to 9 weeks of embryo development) stops growing and does not branch due to the fact that the polydom building protein is not produced by endothelial cells and mesenchymal cells.
Muscle cells grow, but lymphatic vessels do not.
My point of view is also supported by Professor Sergey Savelyev, who is the head of the laboratory of human brain morphology at the Russian Academy of Sciences. Sergei Savelyev argues that it is not the brain cells that are important, but the connections between these cells. If some of the cells die, then another part of them restores the damaged connections over the course of three months and the muscle cells receive the correct commands from the brain. But they cannot perform them due to the presence of edema.
Main symptoms
You can detect the disease by knowing the signs of infantile paralysis. Symptoms of cerebral palsy in children under one year of age are associated with paralysis and muscle weakness, involuntary movements, and lack of coordination.
The child does not have a fold between the buttocks, one side of the body is asymmetrical in relation to the other. In newborn infantile paralysis, the muscles are either relaxed or tense and twitching. And the child’s movements are unnatural and chaotic. In addition, anxiety is felt in the baby’s behavior and loss of appetite.
Paralysis in an older child can be determined more quickly. The disease is diagnosed by spinal curvature and hip dysfunction.
Forms and severity
There are 5 types of cerebral palsy, based on the nature of motor disorders:
We recommend reading: Brain hypoxia in a newborn
- Spastic tetraplegia . The most severe form of the disease is when all 4 limbs are affected. Half of children with this diagnosis suffer from epileptic seizures, hearing and speech disorders, and strabismus. The torso and limbs are subject to deformation. With this form, the child cannot take care of himself and do basic things.
- Spastic diplegia . The so-called Little's disease, in which the legs suffer the most, the spine and joints are deformed. If the hands work well and mental development does not suffer, it is possible to achieve social adaptation at the level of healthy people.
- Hemiplegia . A condition where only one hemisphere of the brain, responsible for movement, is affected. As a result, paresis of the limbs affects only one side of the body.
- Hyperkinetic form . Recognizable by involuntary movements, tics, increased muscle tone, and incorrectly positioned limbs when walking. But intelligence practically does not suffer.
- The ataxic form develops due to damage to the cerebellum. Low muscle tone, poor coordination and poor balance are characteristic signs of this form of cerebral palsy.
There are 3 degrees of severity of the disease:
- Easy. The child moves independently, is able to perform simple tasks, goes to a regular school and subsequently acquires a profession.
- Average. Although socialization of the child is possible, he needs outside help.
- Heavy. The child’s dependence in all respects on loved ones. Cannot take care of himself.
The first symptoms of cerebral palsy are...
Among the initial signs of cerebral palsy in a child under one year old are those that prompt parents to urgently examine the baby. If the functions of parts of the brain are impaired in a newborn, the following is noted:
- lethargy;
- anxiety;
- convulsions;
- inability to turn your head in one direction or another;
- tension or complete relaxation of the upper and lower extremities;
- asymmetry of movements.
Characteristic signs of developing pathology are associated with the condition of the baby’s muscles and his motor activity.
Signs of cerebral palsy in children under 1 year of age
Symptoms of cerebral palsy differ depending on the form of the pathology. Based on the predominance of signs of pathology, experts have identified 5 main forms:
- Athetosis is involuntary muscle activity;
- Spasticity – increased tone with a constant increase in hypertonicity after each condition;
- Increased muscle density (rigidity) – manifested by increased resistance to acts of contraction and relaxation;
- Twitching of legs and arms;
- Partial falls due to imbalance of balance (ataxia).
Most children have a spastic or athetoid type of disorder. The specificity of the described manifestations of pathology corresponds to reality.
Based on the prevalence of symptoms of infantile palsy (cerebral palsy), there are 4 main forms of pathology:
- Quadriplegic – characterized by damage to both arms and legs;
- Diplegic - with the disease, pathologies of two upper or lower extremities are observed;
- Hemiplegic – manifested by pathological disorders on one half of the body;
- Monoplegic – characterized by a decrease in muscle activity on the part of only one limb.
Studies of each individual form have revealed unique mechanisms of occurrence, pathogenetic mechanisms, and brain disorders.
For example, in the diplegic form, brain damage is formed due to disruption of the activity of the nervous system in utero for various reasons, but examinations of patients with cerebral palsy have shown that in most cases the cause of fetal hypoxia is infection.
The child's legs are crossed, elongated, and the tone is increased - these are signs of a diplegic form. Lack of leg mobility makes it impossible for the child to roll over independently. The inability to turn over or assume a sitting position is also characteristic of the diplegic form.
When this form is identified, a lag in physical development is observed. Somewhat above we described the child’s inability to stand on his full foot when held with his hands under his arms. The manifestation is typical for the diplegic form with pathology of the legs. The condition determines an important sign of cerebral palsy - walking on tiptoes when bringing the knees together. Pathology leads to impaired intelligence and slower physical development.
The hemiplegic form of cerebral palsy occurs due to damage predominantly to one hemisphere of the brain due to intrauterine infection and hemorrhage. Restricted mobility of the limbs and increased deep reflexes are acute symptoms of hemiplegia in cerebral palsy in children.
When attempting to move, contractions of the muscle fibers of the affected area can be observed.
The hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy develops in children with damage to the subcortical ganglia. The variety occurs when there is an immune conflict between the blood of the baby and the mother.
Symptoms of the disease are manifested by an abnormality of muscle tone with periods of normalization and increase. In rare cases, hypotonicity is observed, but the condition is not typical for acute hyperkinetic forms.
The nosology is easy to determine in children by the adoption of unusual poses and pretentious forms. Most patients with hyperkinetics retain their intelligence.
Symptoms for different forms of cerebral palsy
Signs of cerebral palsy in a newborn manifest themselves differently and depend on what form of paralysis the baby suffers from:
- With spastic diplegia, or Little's disease, the lower extremities are affected, and less often the upper extremities. Symptoms appear from the first months of life. When bathing or swaddling a child, they notice an increase in muscle tone. Children with the syndrome begin to walk later and move their legs with difficulty, relying only on their toes. They cannot sit up on their own.
- Spastic hemiplegia develops against the background of trauma or encephalitis suffered at an early age. After the cessation of the acute period with convulsions, consciousness returns, but paralysis of one half of the body remains.
- In patients with atonic-astatic form of paralysis, in addition to the lack of movements, mental retardation and instability of the mental state are noted.
- Uncontrolled movements in the fingers and toes, and the production of involuntary sounds are characteristic of the hyperkinetic type of cerebral palsy. Along with hyperkinesis, spastic symptoms are also observed. The child has difficulty grasping objects with his hands. The baby is capricious, crying for no reason.
The prognosis of the disease depends on the degree of brain damage and the timeliness of treatment of the disease.
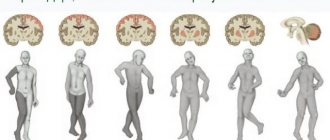
Types of cerebral palsy
Forms of cerebral palsy, depending on the affected areas of the brain
Cerebral palsy has many manifestations, so doctors distinguish between several types of this disease. Each of them is characterized by certain changes in the brain and a disorder of certain organs or systems.
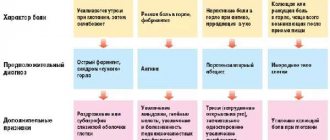
| Syndrome | Brain lesions | Signs |
| Spastic diplegia | Foci of death, presence of neoplasms | Impaired functioning of the limbs, most often the lower ones (the arms retain full or partial functionality). Increased muscle tone is noted in the legs; when crawling, the baby moves his hands, but pulls up his legs, practically without moving them. The baby begins to walk later, crossing his legs with support under his arms. Intellect and speech are preserved in most patients; children can care for themselves |
| Spastic tetraplegia | Multiple foci of death and developmental defects, damage to the white matter of the hemispheres | Impaired swallowing function, hypertonicity of all extremities (on one side it can be more pronounced), difficult motor activity, often epilepsy, mental development defects. Such children remain mentally retarded throughout their lives. |
| Hemiplegia | Usually cerebral hemorrhages | Impaired functioning of the limbs on one side, most often on the right. This may not be noticeable in the first months after birth, but later the symptoms become severe. One arm may be constantly twisted and pressed against the body, and convulsive syndrome is noted. Such children begin to sit up and walk on time or with a slight delay; in most cases, intelligence is not affected |
| Extrapyramidal form | Damage to a specific area of the brain | Characterized by a decrease in muscle tone, the child does not hold his head well, begins to walk late, episodes of hypertonicity and impaired swallowing function are possible. Intellectual development is usually not impaired |
The severity of the disease depends on how severely the child's brain is affected. With mild cerebral palsy, children can move independently, look after themselves and perform simple tasks. They are able to study in a regular school and engage in almost all types of professional activities. Patients with moderate damage cannot do without outside help, but are able to live in society and even work. A severe degree of cerebral palsy means that the child will be completely dependent on others and will not be able to care for himself.
Video - Cerebral palsy. Symptoms, signs and treatments
How to recognize the disease?
In children with cerebral palsy, abnormalities can be detected quickly if the baby actively moves the limbs on only one side of the body. In addition, the child cannot turn his head or hold it independently. Depending on the age of the baby, the presence of paralysis is determined:
- At two months old, the baby's legs cross with scissors and are stiff. Increased muscle tone in the arms and trembling of the limbs are noted. The baby finds it difficult to suck. He lacks characteristic reflexes. Constantly nodding the head or freezing in one position is typical for a child with cerebral palsy.
- At 3 months of life, the disease often manifests itself as excessive lethargy or irritability. Head movements are poorly controlled by the baby. When checking the palm-oral reflex, when the child opens his mouth while pressing the palm, its absence is noted. Also, when a healthy child is placed on his feet, he rests on his entire foot. A sick baby stands on his toes. During this period, muscle hypertonicity is noticed on one side of the body and a lack of tone on the other.
- At 4–5 months, a newborn with cerebral palsy moves one arm and holds the other to the body. The patient's movements are awkward. Even on the face, muscle asymmetry is visible. Often a child suffers from strabismus.
- From 6 and 7 months, the child is unable to roll over on his own. The control of raising the head continues to decline.
- At 8 months, the baby is noted to be behind in development compared to his peers: he does not sit independently and moves with difficulty. At 10 months, deviations from the norm become more obvious.
The older the child gets, the more pronounced the problems in his development become. And here not only motor function suffers, but also mental activity.
More often, the presence of paralysis can be determined by the absence of characteristic reflexes.
At what age can cerebral palsy be diagnosed?
Despite the fact that the disease is present in most patients with cerebral palsy from the moment of birth, it can be very difficult to identify it in the first weeks of life. The fact is that newborns spend almost all their time sleeping, and their movements are limited, so at this stage only severe forms of the disease are detected.
At 3-4 months, babies with normal health lose some of their reflexes (Moro, crawling, etc.), which makes it possible to develop normally and acquire new skills. In children diagnosed with cerebral palsy, these reflexes persist, interfering with their further development, so it is at this stage that the presence of the disease can be suspected.
Video - Moro reflexes and support reflexes
Here are the main such reflexes
Parents can determine the presence of pathology in a child by checking his reflex:
- Moro, when they lift a child up, the baby waves his arms;
- crawling while supporting your heels with your hand;
- imitation of walking while in an upright position.
Not only impaired muscle function is a sign of paralysis. A sick child is characterized by an indifferent attitude towards toys and staying in one position for a long time.
The main methods for diagnosing cerebral palsy in newborns are in the hands of a pediatrician, who will use them to identify the disease.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis begins with examining the child, checking his reflexes and muscle tone. The child's movements will differ from the normal movements of peers.
If a sign of cerebral palsy is present, then consultation with a neuropsychiatrist is required. It is possible to differentiate the diagnosis from similar disorders by using diagnostic methods such as brain tomography and ultrasound examination of a small patient.
An accurate diagnosis of cerebral palsy in newborns is made by specialists who select ways to correct the baby’s development.
To make a diagnosis, the pediatrician must:
- conduct an anamnestic analysis, focusing on the course of the mother’s pregnancy, the peculiarities of the birth of the baby;
- examine the baby to check his basic reflexes;
- write out a referral for tests to determine the causes of the pathology.
Therapy for infantile paralysis will be successful, and the baby will be able to live happily ever after if timely measures are taken to rehabilitate the child.
How to cope with adversity?
For parents, the diagnosis of cerebral palsy in their child is considered a serious death sentence. But a properly selected treatment system will do its job. Together, therapy will give the child a chance to become a full-fledged member of society.
To correct muscle weakness, therapeutic exercises, massage, and acupuncture are selected. Therapy with the help of horses is effective - hippotherapy.
Together with drug treatment and physical methods, complete correction of a child with cerebral palsy is possible. The signs of paralysis will not go away completely, but the patient will feel the taste of life and learn to overcome difficulties physically and emotionally.
And the main role here is played by early recognition of the disease and the first signs of infantile paralysis.