Problems of the disease
Problems of cerebral vascular dystonia are often manifested by a violation of the regulation of heart tone. There is excessive tension during the rest period, and during the period when hard work is needed, the heart tone decreases. The body reacts to such an imbalance and disturbance of tone with multiple dystonic disorders. Patients with vascular dystonia often, and sometimes continuously, have headaches, dizziness, etc.
With the development of cerebral vascular dystonia, impaired vascular tone in the head negatively affects the condition of the entire vascular system of the body. It should be borne in mind that the symptoms of vascular dystonia, which are not related to the brain area, differ significantly from the symptoms of cerebrovascular lesions, although the principles of the approach to the treatment of all such problematic disorders and their causes do not differ.
Forecast
Vascular dystonia practically does not interfere with life, but in 45% of cases it can be complicated by various additional reactions of the autonomic nervous system (serious sleep disorders, panic attacks and sudden attacks).
Timely detected vascular dystonia of the brain can be cured with a 90% probability. Unfortunately, most patients and doctors do not consider the initial stage of dystonia worthy of attention.
Eight out of ten patients seek help when the symptoms of the disease become unbearable or cause serious changes in behavior (uncontrollable aggression, tearfulness, suspiciousness, panic). But even in such cases, the disease does not pose a threat to life and can be successfully corrected. If there is a crisis form of dystonia, the patient is registered with observation and treatment during periods of seasonal exacerbations (spring and autumn).
Medicinal and restorative correction in this case requires patience and perseverance for a long time, but leads to a positive result and a reduction in all manifestations of dystonia in most cases.
Symptoms of cerebral vascular dystonia
Signs of vascular dystonia are usually divided into several complex groups of symptoms; pathological manifestations can:
- feel pain in the heart area - complex cardiological symptoms;
- feel very frequent heartbeats up to 150 per minute - tachycardic symptoms;
- be observed with a decrease in heart rate below 60 beats/min. – bradycardic symptoms;
- accompanied by a feeling of lack of air when breathing - complex respiratory symptoms;
- provoke an increase (hypertension) and a decrease in blood pressure;
- create temperature changes on the body surface - a thermoregulatory package of symptoms;
- negatively affect the performance of the digestive system – complex dyspeptic symptoms;
- increase the patient's nervousness, changing the mood and creating feelings of anxiety - a neurotic set of symptoms.
All of the listed complex groups of symptoms of vascular dystonia can appear in combination with each other, which complicates the treatment process.
When diagnosed by the attending physician, any type of vascular dystonia is indicated as a concomitant disease to some other disease. Pathology is not diagnosed as something independent.
With vascular dystonia, doctors usually assess the patient’s condition as not posing a significant threat to their life. It sometimes does not have a noticeable effect even on a decrease in labor productivity and ability to work. But vascular dystonia can worsen the quality of life very significantly.
In the direction of cerebral vascular dystonia, treatment can be quite effective. There are many cases of complete recovery. It is important to promptly diagnose vascular dystonia and remove the causes that contribute to the development of the disease.
There are also negative statistics, according to which almost 80 percent of patients with cerebral vascular dystonia aged 20-40 years acquire significant, difficult-to-treat functional disorders as a result of the disease. Female cerebral vascular dystonia is diagnosed several times more often than males.
Medicines for the treatment of cerebral vascular dystonia are needed only for a third of patients; the treatment process is carried out under the supervision of a therapist. If, as a result of the development of the disease, problems arise in certain systems of the patient’s body, a specialized doctor, cardiologist, endocrinologist, etc. is involved. It is he who prescribes medications for one or another problematic disorder accompanying vascular dystonia.
List of complaints of patients with vascular dystonia, including the brain
Patients diagnosed with vascular dystonia complain that they:
- Fatigue is felt and general weakness is observed;
- Problematic tolerance to weather changes;
- Feelings of pain in the chest from the heart;
- Exhaustion of the body, both physically and mentally;
- Difficulty breathing and feeling close to suffocation;
- Strong heartbeat, accompanied by sudden freezing;
- Feeling of a heavy head and debilitating pain;
- There is a feeling of heat in the head and the face “burns”;
- For no apparent reason, the face turns very red, and then suddenly becomes pale;
- My head is spinning;
- Noisy in the ears;
- Problematic sensations in the digestive system, accompanied by nausea and problems walking “largely”;
- Frequent urge to urinate, which is very copious;
- The pressure “jumps”: sometimes high, sometimes low;
- Increased sweating is replaced by severe chills;
- The head and fingers are shaking;
- Excessive nervousness, panic, feelings of fear and anxiety;
- Urticaria and other types of allergies, etc.
The symptoms of VSD that appear from this list either appear, then go away, or are replaced by others.
Causes of vascular dystonia
A wide range of factors can be responsible for creating conditions for the manifestation of vascular dystonia.
The functionality of the brain and the entire vegetatively branched system of nerves can be negatively affected by:
- predisposition due to hereditary factors;
- cerebral pathology and other pathological diseases of the central nervous system, both congenital and acquired;
- hormonal disruptions during periods of body restructuring during puberty and other cases;
- injuries, including those received at birth;
- infectious, endocrinological and other chronic diseases;
- alcohol addiction and other habits harmful to health in general and the brain in particular;
- physical inactivity;
- state of depression;
- problems of acclimatization in a new place;
- lack of vitamins caused by an unbalanced diet;
- poisoning of the body, including some low-quality medications or medications that do not correspond to the disease, etc.
From this list of possible causes of vascular dystonia, including the brain, we should especially highlight the stress that 7-15 year old children and adolescents receive at home and at school. It is caused by conflicts of various kinds in school and family, situations with parents’ divorce, alcoholism of one of them, etc.
Reasons for the development of dystonia
There are several main factors leading to the emergence of a pathological symptom complex:
- Intrauterine anomalies of fetal development. Such problems can cause significant disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system, for example, leading to the occurrence of vegetative-vascular dystonia of the brain.
- Injuries during childbirth, as well as infectious diseases in infancy. Bacterial and viral lesions can disrupt the normal processes of formation of vascular structures and the nervous system. Damage to the fetal head during passage through the woman’s genital tract, as well as hypoxic phenomena, are among the causes of vascular dystonia.
- Hormonal changes during puberty. The growth and development of internal organs can outpace the formation of neurohumoral mechanisms regulating homeostasis, which leads to the appearance of symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Chronic diseases affecting the arteries and veins, digestive and respiratory tracts have a negative impact. Many pathologies alter the processes of nervous regulation and also provoke venous congestion in the internal organs, which leads to the formation of characteristic symptoms of the lesion.
- A common cause of signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia in women is pregnancy. This condition is accompanied by rapid and pronounced changes in hormonal levels, and also leads to increased stress on the body.
- A factor that can provoke the problem is stress. Chronic psycho-emotional stress is especially dangerous.
Symptoms that require you to see a doctor
At the onset of the disease, symptoms of vascular dystonia appear in a mild form. There is no decrease in performance observed. If you don't see a doctor, you can make the situation worse. The number of symptoms will increase, which will worsen the patient’s quality of life. Failure to take treatment measures will provoke the development of the disease. In case of cerebral vascular dystonia, timely and early consultation with a doctor is the key to eliminating the problem.
You should seek medical attention if you observe signs of health problems in your body in the form of:
- the appearance of swelling of the eyelids and face in the morning;
- dizziness;
- debilitating headaches;
- shortness of breath;
- constant drowsiness;
- causeless mood changes, etc.
Symptoms of sudden attacks
Sudden crises are characteristic of 45 percent of cases in which the course of cerebral vascular dystonia is influenced by some provoking factors: disruptions of the hormonal system, infections, etc.
Symptoms of crises of vascular dystonia allow us to divide sudden attacks into three groups: sympathoadrenal, vagoinsular and mixed crises.
During sympathoadrenal attacks, a release of adrenaline produced by the adrenal glands into the blood occurs, provoking an exacerbation of the situation. The attack is characterized by increasing pain symptoms in the head, rapid heartbeat, chest pain, increased blood pressure, panic in the patient, tremors in the limbs, etc.
During a vagoinsular attack, pancreatic insulin is released into the blood. A patient with cerebral vascular dystonia has pallor of the skin, a weak pulse with long intervals between beats, he complains of a lack of air for breathing and darkening in the eyes, he has low blood pressure, and the glucose level is below normal at 3.5 mmol/l. There is sweating, a state close to fainting, increased bowel function, etc.
In a mixed crisis, symptoms of two previously described attacks are present. Vegetative vascular crises are characterized by a sudden onset and rapid cessation of the manifestation of these symptoms. After a crisis, a person feels exhausted both physically and mentally. After the first crisis that occurs, you should immediately consult your doctor.
Diagnostics
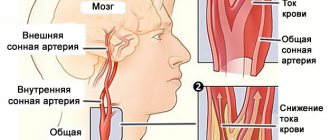
Complaints from a patient with cerebral vascular dystonia do not make it possible to make a correct, accurate and unambiguous diagnosis. The reason is the variety of forms of manifestation of vascular dystonia, including in the form of venous discirculation of the brain.
The doctor prescribes various diagnostic procedures, including the need for an MRI if autonomic dystonia syndrome is suspected.
To correctly diagnose the problem, it is necessary to conduct studies and tests in addition to MRI of the brain:
- urine and blood;
- in the format of various types of functional diagnostics from electrocardiography to transcranial Dopplerography;
- X-rays of the vertebral sections, etc.
The patient should be examined by an endocrinologist, urologist and other specialized specialists. The entire range of measures is aimed at accurately diagnosing cerebral vascular dystonia, which is complicated by the presence of similar symptoms to other diseases.
General characteristics and diagnosis of the disease
Dystonia of the brain implies a discrepancy between the inadequate functioning of blood vessels and the need of cells for certain volumes of oxygen.
Blood circulation is disrupted. Pathology also develops as a result of spasm. Against this background, venous tone decreases. A negative process can be detected at any age. The disease affects both older people and infants. As the disease progresses, the nervous system suffers greatly, some of its areas become almost uncontrollable. Therefore, several types of dystonia are distinguished: hypotonic (the parasympathetic branch predominates), hypertensive (the influence of the sympathetic branch predominates), and normotonic. In the latter case, the activity of both departments is disrupted.
The disease is characterized by dysfunction of the regional-cerebral, neuro-cerebral and normo-hypotonic type. An accurate diagnosis will require a thorough examination of the vascular system of the brain. Pathology must be treated using different methods. In most cases, the prognosis is favorable.
To make a diagnosis of cerebral dystonia, the doctor examines the patient’s medical history and conducts appropriate examinations. Initially, the person is sent for urine and blood tests. They also perform an electrocardiogram, study the condition of the cerebral vessels, and prescribe an MRI. During the diagnostic process, consultation with several specialists may be necessary.
Treatment
How to treat vascular dystonia? A special feature of correcting this problem is, in addition to medication and other measures, the need to change lifestyle.
It is important to establish the correct mode of work, alternating with regular rest. Patients with cerebral vascular dystonia should go to bed early and get up early. It is advisable to stick to the same sleep schedule and duration. You should review your food preferences, remove coffee, tea, alcohol in any form, as well as spicy and fried foods from your diet. Baths with pine needles can be a positive measure to reduce fatigue. Honey with milk at night promotes quality sleep. Physical stress and strong emotional stress should be avoided. A contrast shower is advisable.
Drug therapy for cerebral vascular dystonia suggests using:
- vitamins;
- antioxidants;
- drugs that help improve blood circulation and normalize blood pressure; hypnotic;
- sedatives;
- adrenergic blockers (anaprilin);
- nicotinic acid;
- cinnarizine;
- tranquilizers, etc.
For cerebral vascular dystonia, therapeutic exercises, auto-training and massage are necessary. Physiotherapeutic procedures of acupuncture, electrophoresis, etc. are desirable.
Headache treatment
The program for the prevention and treatment of hypertension in neurocirculatory dystonia includes a variety of activities, including treatment:
- etiological,
- pharmacological: pathogenetic, symptomatic,
- psychotherapeutic.
Good results in the treatment of cephalgia with vegetoneurosis are shown by:
- phytotherapy,
- acupuncture,
- massage,
- general strengthening activities,
- Spa treatment.
Etiological measures
Aimed at eliminating factors that provoke the development of pain syndrome in neurocirculatory dystonia. Elimination of etiological causes helps to reduce the frequency and intensity of headaches, significantly improves the general well-being of the patient, often leads to stable remission and often to complete recovery.
In case of headache of psychogenic origin, it is necessary to eliminate or minimize the negative impact of psycho-emotional stressors:
- optimize family relationships,
- normalize contacts in society,
- eliminate industrial conflicts.
Often the vascular nature of hypertension manifests itself as a result of mental overload.
If the pain syndrome is caused by infectious or toxic factors, it is necessary to pay close attention to the elimination of chronic foci of infection.
If you have tension headaches, you should avoid intense physical activity and resort to “gentle” sports:
- swimming,
- walking,
- cycling,
- gymnastics,
- wushu,
- yoga.
For headaches directly related to hormonal changes, it is recommended to coordinate the treatment regimen with an endocrinologist and gynecologist.
Pharmacological treatment
- Pathogenetic therapy is aimed at normalizing the impaired functions of the limbic system (in particular: the hypothalamus and cingulate gyrus of the brain), failure of which leads to improper functioning of the autonomic nervous system.
- For mild VSD accompanied by cephalalgia, natural sedatives and antispasmodics are used, for example: tincture of valerian (Tinctura Valerianae). A good therapeutic effect for psychogenic hypertension is shown by Tricardin, which contains: valerian rhizomes, motherwort herb and hawthorn fruits.
- For persistent attacks of neurotic headaches and frequent vegetative crises, the prescription of tranquilizers for a course not exceeding 3 weeks is justified. Elenium has a muscle relaxant effect on cerebral vascular spasms.
- For tension headaches and arterial hypertension, the first choice is the anxiolytic diazepam (Diazepamum). The drug not only eliminates productive symptoms of psychogenic origin, but also increases the pain threshold. Mezapamum, which is often used in VSD to prevent attacks of migraine-like headache, has a vegetative-stabilizing effect.
- Vegetative correctors used for headaches associated with NCD are preparations based on belladonna alkaloids. Belloid and Bellataminalum are used for therapeutic purposes.
- For headaches combined with depressive states, they resort to prescribing antidepressants with a strictly differentiated choice of drugs. As a rule, for neurogenic headaches of a chronic nature and in order to prevent migraine-like crises, amitriptyline (Amitriptylinum) is used.
- Nootropic drugs are effective neurometabolic agents that improve blood supply to the brain and reduce the harm of hypoxia. Their properties have found application in the treatment of headaches due to VSD. Prescribe medications with the active ingredient piracetam (Pyracetamum) for a course of at least 1 month.
- Cerebroangiocorrectors are effective for headaches with autonomic symptoms, for example: Cavinton. The action of the drugs is aimed at dilating the blood vessels of the brain, increasing blood flow, improving the supply of oxygen to the brain, which is advisable for cerebral angiodystonic hypertension and concomitant osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
- In case of hypertensive variant of the development of headache with NCD, frequent sympathoadrenal crises, beta-blockers, for example: anaprilin (Anaprilinum), have a positive effect.
- Patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia are sensitive to changes in weather conditions and are poorly adapted to the effects of stressors. Changes in weather conditions or unfavorable situations cause severe and prolonged headaches. To minimize the influence of external factors, adaptogens of plant origin are used, for example: ginseng tincture (Tinctura Ginseng) or Chinese lemongrass tincture (Tinctura schizandrae) for hypotension.
- Symptomatic therapy for hypertension is aimed at eliminating pain. For these purposes, analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and antispasmodics are used, for example Sedalgin, Spasmalgon, Drotaverine.
Psychotherapeutic treatment
Psychotherapeutic measures often show greater effectiveness than complex treatment with pharmacological drugs. The task of the psychotherapist: to carry out explanatory work about the nature of the disease, to emphasize the benign nature of headaches with NCD, and to focus on a favorable prognosis for treatment.
Methods of psychotherapy (in particular: rational-emotive-behavioral) are the most important way to treat headaches with neurocirculatory dystonia.
A major role in preventing attacks of cephalalgia and reducing the intensity of pain is assigned to:
- methods of self-hypnosis,
- auto-training (essentially a light form of hypnosis applied to oneself),
- muscle relaxation (techniques for getting rid of painful spasms by reducing the activity of muscle tissue).
If the headache is persistent, it is possible to conduct sessions of Ericksonian hypnosis. Today, aesthetic therapy has become widespread in the treatment of cephalalgia caused by psychogenic factors - the use of music, arts and crafts, dance schools, and literature.
Phytotherapy
The “green pharmacy” has various herbal remedies in its arsenal. Long-term use in the form of infusions and decoctions of parts of medicinal plants is recommended for the treatment of headaches with VSD:
- valerian,
- peppermint,
- lemon balm,
- motherwort,
- hawthorn,
- oregano,
- elderberries,
- rosemary,
- daisies,
- thyme.
Massage
A course of restorative or gentle massage of the collar area brings significant relief to people suffering from headaches due to VSD. No less useful is acupressure, which you can do yourself at home.
Acupuncture
Various acupuncture techniques allow you to:
- normalize the functioning of the autonomic nervous system,
- prevent vegetative crises,
- relieve pain syndrome,
- have an analgesic effect during prolonged, monotonous headaches,
- stabilize blood pressure,
- achieve a sedative effect,
- relieve muscle tension.
Physiotherapy
To eliminate or alleviate attacks of cephalgia in vegetative-vascular dystonia, use:
- electrosleep,
- galvanization,
- medicinal electrophoresis,
- darsonvalization,
- laser therapy,
- balneotherapy.
General strengthening and preventive measures
A variety of water procedures can alleviate the course of neurocirculatory dystonia and eliminate painful cephalalgia. It is recommended to conduct sessions of a circular or underwater shower, and contrast douches.
Warm pine, valerian, oxygen, and pearl baths show a pronounced sedative effect. For the hypertensive type of VSD, radon or iodine-bromine procedures are prescribed, for the hypotensive type - carbon dioxide or hydrogen sulfide.
Prevention measures for VSD are:
- Maintaining a correct lifestyle;
- Stop smoking and drink alcohol wisely;
- Normalization of sleep;
- Daily stay in the fresh air, familiarization with nature;
- Regular gentle physical activity;
- Adequate nutrition with limited stimulants (strong tea, coffee);
- Stabilization of the emotional sphere through aesthetic therapy.
- Carrying out exercise therapy;
- Sanatorium-resort treatment: climatic influence, mineral springs, sea bathing.