Senile insanity, sclerosis, atherosclerosis, vascular dementia and encephalopathy in the elderly
- Why are mental disorders more common among older people;
- Symptoms of age-related depression;
- Senile dementia, dementia and vascular psychosis;
- Treatment at the Echinacea Clinic;
Treatment of senile depression, sclerosis, atherosclerosis, vascular dementia and encephalopathy in the elderly.
You can trust us with the health of your family and friends. Psychiatry and neurology are one of the main areas of our work. In our clinic you will find doctors with experience in caring for elderly patients: psychiatrist, neurologist, therapist, cardiologist and others. In most cases, the state of mind and brain function can be improved even in a very elderly person. It is clear that in old age several health problems are usually relevant at once, but the amount of medications taken must be adequate and consistent. If a brain disease is combined with other diseases, we practice a patient management scheme in which one responsible attending physician (usually a therapist) combines and adjusts the prescriptions of narrow specialists.
Primary characteristics of the disease
Vascular psychoses include psychoses that develop as a result of atherosclerosis, stroke, hypotension, hypertension, thrombosis or other cerebral vascular diseases.
Vascular psychosis can develop in several forms:
- Acute form . Characterized by a state of “confusion” of consciousness. The psychotic state occurs periodically and lasts several hours. Most often, the attack occurs at night, and during the daytime the patient has a clear consciousness.
- Subacute forms a. A complicated type in which psychosis lasts longer. It may be accompanied by confusion, or, with the patient clearly conscious, it may be characterized by intermediate syndromes. This form is characterized by disorders that are complicated by so-called “small-scale” delusions and verbal hallucinatory experiences.
From the point of view of the origin of mental disorders caused by vascular dysfunction, there are:
- syndromes at the inception stage, in a pseudoneurotic form - such disorders usually appear if vascular disease is at the initial stage of development;
- vascular dementia : neurological and mental disorder associated with a certain stage of development of vascular disease;
- other syndromes caused by external factors (exogenous): delusional disorders, hallucinations and others.
Kinds
There are acute and protracted forms of vascular psychoses that arise against the background of existing non-psychotic mental disorders of vascular origin - pseudoneurasthenic manifestations and phenomena of intellectual decline of varying degrees (vascular dementia). However, first it is necessary to mention the symptoms that can serve as harbingers of vascular psychosis: increasing headaches, increasing tinnitus, numbness in certain areas of the face, impaired coordination of movements, dizziness, difficulty falling asleep, unstable mood with tearfulness and irritability (weakness). Speech becomes slurred and incomprehensible. Anxious fears of hypochondriacal content (fear of death or belief in the presence of a fatal disease) may appear. Patients may become more sloppy, gluttonous, and sometimes sexually disinhibited.
Acute form
The acute form is manifested primarily by phenomena of confusion with disorientation in time, surroundings, lack of recognition of others, often psychomotor agitation, influxes of visual and auditory hallucinations (essentially vascular delirium). Most often it develops in the evening or night hours, during the day the consciousness is clear. It usually lasts several hours, after the acute period amnesia develops - patients do not remember what they did during the exacerbation. This condition is prone to recurrence - repeated many times if the patient does not receive the necessary therapy. Very often, the plot of the experience is as follows: the patient believes that he is on a visit (to a hospital, a hotel), and at night he begins to get ready to go home; if the patient is inattentive on the part of his loved ones, he can actually leave home and get lost. Plots of hallucinations often involve meetings with deceased relatives. Additional factors provoking psychosis may be taking certain medications (cardiovascular, sleeping pills, Corvalol or Valocordin, a number of nootropics), fever, sharp fluctuations in blood pressure in any direction, diabetes mellitus. Some authors consider vascular delirium as one of the harbingers of an imminent stroke.
Protracted vascular psychoses
Protracted psychoses can develop as a transition from an acute state, or independently. The transition to protracted psychosis from an acute state can occur through a series of convulsive attacks, through the development of Korsakov psychosis with severe memory impairment (inability to record what is happening, replacement of memory loss with false memories), confusion, through the development of a pseudoparalytic state with carelessness, foolishness, ridiculous actions and ideas of grandeur or through severe asthenia (neuropsychic exhaustion).
Prolonged vascular psychoses most often occur as various variants of hallucinatory-delusional syndrome, that is, the main content of painful experiences is hallucinations and associated delusional ideas (false statements that cannot be dissuaded). Less often, they occur in the form of depression at a psychotic level (with or without anxiety) - patients feel deep sinfulness, for which there is no forgiveness, or a feeling that they have actually died and their body has already begun to decompose (Cotard's delirium). With various forms of vascular lesions of the brain, patients experience various additional symptoms.
Causes and mechanisms of the disorder
The main reason for the development of this form of psychosis is diseases associated with disruption of the vascular system of the human body.
Among the diseases that most often provoke psychosis of vascular origin are:
- atherosclerosis;
- stroke;
- hypertension;
- thromboangiitis;
- endarteritis.
What leads to mental disorders in the case of these deviations and diseases? What is the sequence of processes that determines the mechanisms of the appearance and progression of the disease? To date, there is no exact answer to this question. There is no clear understanding of why only some vascular diseases and brain injuries lead to the appearance of mental disorders.
We can only talk about the following cause-and-effect relationships:
- Sudden changes in blood pressure can lead to changes in the structures of the brain, which leads to the appearance of acute or subacute psychosis. Its main features are confusion and hallucinations.
- The progress of psychotic deviations of vascular origin is influenced by the individual characteristics of the body , which have developed on the basis of hereditary and acquired properties, as well as general somatic factors.
- An acute form of the disorder may occur due to a decrease in blood pressure at night , which, in turn, provokes a deficiency in the blood supply to the brain. The development of deviations is promoted by atherosclerotic damage to the heart vessels and various types of infectious diseases.
- Mental disorder often occurs during a period of severe disruption of blood circulation in the brain , so vascular psychosis is a common occurrence after a stroke.
Why are mental disorders more common among older people?
Modern medicine has the ability to optimize the functioning of the nervous system of even a very elderly person. There are people over 80 years of age without any signs of dementia or “senile sclerosis.” Old age is not a disease. Dementia (senile dementia or senile insanity) and age-related depression are diseases with their own clearly defined causes and treatment options.
The nervous system of an elderly person has a number of features.
- Insufficient blood supply to the brain. With age, blood vessels, including those of the brain, become less elastic, and “plugs” – atherosclerotic plaques – appear inside the vessels. The brain finds itself in a state of lack of blood flow and nutrition. And brain cells are very “gluttonous” and under conditions of nutritional deficiency they work worse and then die. During this period, a kind of senile egoism and insomnia often appear.
- Slower brain cell renewal . The older we get, the slower the renewal process goes, especially in conditions of reduced blood flow.
- Changes in biochemical processes in the brain . An electrical impulse is transmitted from one nerve cell to another with the participation of special chemicals - neurotransmitters. These include, for example, serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine. In older people, the ability to produce and accumulate these substances decreases. Therefore, the conduction of nerve impulses suffers, and, as a result, the overall productivity of the brain weakens, deviations in behavior, emotional, mental and motor spheres arise.
Our task at the examination stage is to unambiguously determine the dominant cause of brain suffering, then our treatment will be exactly as intended.
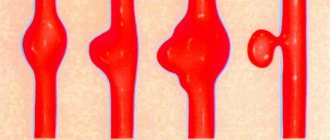
Two cases of vascular dementia (senile dementia) from our practice. The symptoms are similar, but the treatment required is different.
MRI of the brain. The brain appears gray, the cerebrospinal fluid appears black, and the affected areas of the brain appear white.
- LEFT – normal brain.
- IN THE CENTER – the brain is partially replaced by fluid, arrows indicate areas of reduced blood circulation. The reason is the formation of blood clots due to heart rhythm disturbances + the entry of these blood clots into the brain.
- RIGHT - brain mass is seriously reduced with replacement by fluid, white spots are an area of massive death of brain cells. The reason is a narrowing of the carotid arteries by 75% and 80% by cholesterol plaques.
Features of the clinical picture
With this type of disorder, non-psychotic symptoms, intertwined with disorders of an organic nature, are combined with symptoms of a psychopathological type. The latter have mildly expressed neurological features.
Symptoms that make it possible to diagnose vascular psychosis at the initial stage of development:
- sudden onset and then quickly disappearing tinnitus;
- in the morning there may be pain in the back of the head;
- numbness of the lower part of the face (cheeks, chin), voluntary contraction of the facial muscles;
- non-recurrent dizziness, uncoordination of movements when walking;
- sleep disorder: the patient is able to sleep for only 3 hours, and upon waking up, cannot fall asleep again;
- unstable emotional background: constant desire to cry, forgetfulness, increased fatigue, inattention;
- reaction and speech slow down;
- The appearance of hypochondria cannot be ruled out.
Symptoms characteristic of mental disorders arise much later and manifest themselves as delusions, hallucinations, and a schizophrenic picture.
Causes of mental changes
The most common pathologies leading to mental disorders are hypertension, cerebral atherosclerosis, thromboangiitis obliterans, and cerebrovascular form of rheumatism (cerebral rheumovasculitis). It should be noted that arterial hypertension plays a role only in the initial stages of the process. Subsequently, persistent lesions occur as a result of chronic hypoxia (oxygen starvation), which occurs due to narrowing of blood vessels affected by atherosclerosis.
Diagnosis of the disease
At an early stage, when there are symptoms of a neurotic nature, vascular psychosis is diagnosed based on signs of hypertension, arteriosclerotic stigmas, changes in the fundus, and mild neurotic abnormalities.
It is more difficult to diagnose vascular dementia. It is not easy to distinguish from senile dementia. Characteristic features of dementia are random deviations and flickering of the main signs in vascular disorders.
With age-related dementia, symptoms will only increase and no periods of stabilization can be expected. In addition, the onset of vascular psychosis is more acute and may be accompanied by increased confusion.
Treatment options
Treatment is best started with treatment of the underlying vascular disease that caused the psychosis.
Psychotropic medications will definitely be prescribed. Their choice is determined by the type of mental disorder. At the first stage of treatment, tranquilizers are prescribed: Atarax, Phenazepam, Rudotel and others. Antipsychotics are usually prescribed Propazine (the dose of this drug varies 25-75 mg/day), Rispolept in the form of drops.
If the patient has anxiety-depressive syndrome, then atypical antidepressants are prescribed, such as Remeron, Cipramil and others.
Treatment is not limited to the use of specialized products. The patient should take vitamins, general health-improving medications, and medications intended to affect the higher mental functions of the brain (Mexidol, Piracetam).
The patient will have to give up smoking, alcohol, avoid overwork and emotional outbursts.
It is impossible to cure vascular psychosis or dementia. There is no chance for a person to recover completely, but you can try to raise your standard of living to the highest possible level.
Etiology
As mentioned above, the main cause of a disease such as senile aggression is degenerative processes in neurons.
There is an opinion about the influence of infectious processes of the membranes and substance of the brain, a history of traumatic brain injuries and hereditary etiology on the occurrence of the pathological condition.
Background predisposing factors include disruption of sleep patterns in the direction of its reduction, deficiency of protein and vitamins in consumed food, age-related hearing loss and/or vision, limitation in physical activity and walks in the fresh air.
Preventive measures
The prevention of mental disorders associated with dysfunction of the vascular system will be facilitated by:
- timely diagnosed vascular disease;
- establishing a constant and orderly daily routine;
- preventing excessive loads;
- giving up smoking, alcohol and other bad habits;
- proper, balanced, dietary nutrition;
- giving up a sedentary lifestyle;
- physical therapy classes;
- constant monitoring of blood pressure and taking measures to normalize it even with minor deviations from the norm.
The disorder never goes away without a trace. Modern medicine is not able to completely cure it; you can only take drugs that improve the blood supply to the brain, drugs that help strengthen memory, but in any case it will not be possible to completely get rid of all the symptoms. They will appear again at one time or another.
Treatment at the Echinacea Clinic
Treating older adults with age-related depression, dementia, and vascular problems is a process that requires patience and a positive attitude. We will be happy to help you.
- If necessary, we will offer you the help of a neurologist, psychiatrist, psychotherapist, cardiologist, examination of the heart and blood vessels, and the necessary laboratory tests.
- Visits to the clinic are only when absolutely necessary.
- We need cooperation between the doctor, the patient and his relatives, you must be prepared for this.
What do we do. First of all, we will find out what led to the brain damage. The reasons may be in different combinations:
- Atherosclerotic plaques;
- Increased blood clotting with blockage of small and large cerebral vessels;
- Stroke;
- Arrhythmias leading to the formation of microthrombi in the vessels of the brain;
- High blood pressure accompanied by spasm of cerebral vessels;
- Alzheimer's disease and other primary dementias.
In all these cases, the treatment will be different and will correspond to the source of the problem. For example, drugs to prevent blood clots will not affect the growth of atherosclerotic plaques and will not normalize blood pressure.
Our clinic has the necessary diagnostic capabilities to assess the condition of cerebral vessels, heart rhythm disturbances, blood clotting and cholesterol levels in an elderly person. If any types of diagnostics have already been performed before, be sure to show their results to the doctor, this will help avoid unnecessary tests.
Treatment will be based on the results of the research. It may include a number of medications, diet, daily routine and exercise, psychotherapy and, if necessary, even therapeutic hypnosis.