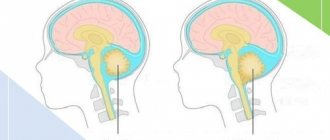
Spina bifida is a pathological condition in which the patient experiences a protrusion of the contents of the spinal canal through a defect in the arches or vertebral bodies.
This is a congenital pathology, a rather rare developmental defect. According to research, the anomaly is detected in approximately 0.1% of newborns (a latent form is observed in 15% of the population), in some of whom the disease becomes a cause of disability. May be combined with other developmental anomalies.
Spina bifida is a congenital malformation
Causes
The reasons for the development of pathology are not fully understood. The main factors contributing to the occurrence of spina bifida include:
- lack of vitamins (especially folic acid) in a woman’s body before and during pregnancy;
- genetic predisposition;
- pregnancy at an early age;
- abuse of alcohol and/or drugs by a woman during pregnancy;
- intoxication of the body;
- infectious diseases in the expectant mother.
In adult patients, existing pathology may manifest itself under the influence of the following provoking factors:
- lack of timely treatment of osteochondrosis;
- spinal injury;
- lifting weights;
- staying in an uncomfortable position for a long time (for example, while working);
- strength sports;
- metabolic disorders (overweight);
- incorrect posture;
- infectious diseases.
Let's sum it up
Spina bifida is an extremely serious disease that can affect both children and adults. It has many causes and symptoms, which creates some obstacles in identifying the source of the problem.
With proper effort, getting rid of spina bifida is quite possible.
In general, a positive prognosis depends on how advanced the hernia is, its location, and the timing of treatment.
A person suffering from spina bifida must completely change his habits and reconsider his lifestyle. If you put in enough effort, it is possible to recover from such a disease.
Kinds
Depending on the location, hernias of the following parts of the spine are distinguished:
- cervical;
- chest;
- lumbosacral (the most common option).
Based on the contents of the hernial sac, pathology is divided into several groups, which are presented in the table.
| Type of pathology | Description |
| Meningocele | The spinal cord is correctly formed and functions normally; only the spinal membrane penetrates into the intervertebral defect |
| Myelomeningocele | There is protrusion of the meninges and substance of the spinal cord, neurological symptoms develop |
| Meningoradiculocele | There is protrusion of the meninges and spinal roots |
| Myelocystocele | The most dangerous form; the hernial sac consists of cerebrospinal fluid accumulated in the expanded central canal of the spinal cord, which is surrounded by the thinned substance of the spinal cord, its membranes and the dorsal roots of the spinal nerves |
Features and classification of intervertebral hernias
Intervertebral hernia is a disease of the musculoskeletal system . Usually hernias are a complication of osteochondrosis. Characterized by protrusion of the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc .
This condition is formed by a dystrophic process in the spine. At a critical moment, the fibrous ring that holds the nucleus breaks. The intervertebral disc becomes deformed and its ability to absorb shock is lost.
There are certain stages of hernia occurrence:
- Disc protrusion. At this stage, the fibrous ring ruptures and part of the nucleus comes out. No special treatment is required yet; you can cope on your own. The pain is still weak, but after exercise it intensifies.
- Partial prolapse . The nucleus pulposus is already protruding strongly. The blood supply to the disc is disrupted and the pain becomes stronger.
- Complete prolapse. The core is almost completely out, but its normal shape is still preserved. The pain increases, motor functions are impaired, and numbness occurs in the area of the shoulder blades.
- Sequestration. The intervertebral disc is displaced and the nucleus falls out completely. The nerve endings are pinched, and a real hernia occurs. The pain syndrome becomes permanent.
The ICD 10 code for intervertebral herniation is assigned in accordance with the site of localization and type of disc damage . A hernia in the cervical region is indicated in a medical document by code M 50. In the thoracic and lumbar region - M 51 .
Spinal hernias are divided into many groups. This gradation helps doctors determine the location of the hernia, the method of treatment and the amount of work to be done. You can also predict possible complications.
Classification of intervertebral hernias
Belonging to a specific segment of the spine
The following types are distinguished:
- In the cervical region - about 4%.
- In the breast - 31%.
- In the lumbar region - almost 65%.
The frequency of formation in a particular section depends on the load experienced by the corresponding section of the spinal column. The degree of mobility also affects.
Primary and secondary
Primary hernias occur when there is excessive stress or injury to the spinal column.
Secondary are the consequences of disc degeneration. Its shell dries out or completely collapses.
According to the size of the protruding part
- Protrusion - protrusion up to 3 mm.
- Prolapse – loss of up to 6 mm.
- Full hernia - from 6 to 15 mm.
Anatomical differences
Free . The contents of the disc pass through the longitudinal ligament, which maintains the vertical position of the spinal column, but the connection is preserved.
Wandering . In this case, the connection between the prolapsed fragment and the intervertebral disc is lost. Such a hernia is dangerous due to inflammation and compression of the spinal cord.
Moving . Occurs due to injury or extreme stress with disc displacement. If the load stops, the disk core returns to its original place. Sometimes fixed in the wrong position.
In the direction of protrusion of the disc nucleus
Anterolateral . Located in the front of the vertebra. They violate the integrity of the longitudinal ligament and cause severe pain.
Posterolateral . Penetrate through the posterior wall of the annulus fibrosus.
By the type of tissue that protrudes beyond the boundaries of the intervertebral space
- Pulpous . The nucleus falls out through cracks in the annulus fibrosus.
- Cartilaginous . The intervertebral cartilage, which has lost its elasticity, begins to be squeezed out.
- Bone . It mainly occurs in older people. They often have bone growths and spondylosis. Osteophytes begin to put pressure on the nerve roots.
By the way, it should be noted that several different hernias are often detected, differing in location and type. Therefore, a thorough diagnosis is needed in order to correctly develop treatment tactics.
Video: “What is an intervertebral hernia?”
Symptoms
The course of the disease depends on the degree of damage to the spinal column and the volume of tissue that forms the hernial sac.
The mildest type of pathology is spina bifida. This reveals a slight deformation of one of the vertebrae, which, as a rule, does not cause much discomfort in a person. This form of pathology is often asymptomatic, but such patients may also show signs of prolapse; in some cases, neurological symptoms occur with this form of the disease. In some patients, clinical signs of pathology may appear in adulthood due to intense physical activity or other reasons.
A more serious defect occurs with spina bifida, in which a protrusion consisting of fluid and meninges is visually noticeable. In the most severe cases, the nerve roots and spinal cord are involved in the pathological process.
The photo shows that spina bifida is visualized as a round protrusion in the spine. On palpation it has a soft consistency. The skin over the formation is usually shiny and thinned, with a reddish or cyanotic tint.
The patient may complain about:
- weakness in the upper and lower extremities;
- violation of all types of sensitivity (temperature, tactile, pain);
- dry skin;
- non-healing ulcerations;
- coldness of the extremities.
May be observed:
- decreased limb reflexes (knee, plantar, grasping);
- atrophy of the muscles of the arms and legs;
- various forms of deformation of the lower extremities (clubfoot is often detected).
Symptoms also depend on the area in which the hernia developed.
| Spine department | Manifestations |
| Cervical | The pathology affects the upper part of the spinal cord, which leads to a decrease in motor activity of the upper and lower extremities. The patient may also experience problems with the heart and lungs. |
| Chest | Disorders of the respiratory system, heart, stomach, liver, spleen. |
| Lumbosacral | Disturbances in the functioning of the organs of the genitourinary system, gastrointestinal tract, and lower extremities. Patients may experience problems with urination and defecation (including urinary and fecal incontinence). |
Treatment of spina bifida
Spina bifida has its own characteristics that must be taken into account when choosing a course of treatment.
First of all, you should pay attention to non-surgical treatment methods.
- Acupuncture (also known as acupuncture).
- Vitamin therapy - taking vitamins A, B, C, E.
- Taking medications aimed at improving the conductivity of nervous tissue (nootropic medications).
- Treatment with vacuum cups.
- Massotherapy.
- Laser therapy and/or magnetic therapy – to improve the condition of soft tissues.
- Physiotherapy.
- Hippotherapy.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a treatment method based on the use of needles in specific parts of the human body. It is an integral part of the Chinese healthcare system, which dates back at least 2,500 years.
The general theory of acupuncture is based on the assumption that there are various currents of Qi energy flow in the body that are responsible for health. Disturbances in this flow are thought to cause disease.
Ancient Chinese medicine still protects health today
Acupuncture restores this flow and relieves various disorders in the body. This is achieved by penetrating the skin with thin, hard metal needles that are manipulated manually or through electrical stimulation.
If you want to learn in more detail how to treat a hernia with acupuncture, and also consider the description, preparation and effectiveness of treatment, you can read an article about this on our portal.
The practice of acupuncture to treat identifiable illnesses was rare in Europe until the twentieth century. Since then, this trend has gained wide popularity in the West and in our country as well.
Video - How to heal the spine with acupuncture
Vitamin therapy
Vitamin therapy is a treatment method based on the intravenous or oral administration of vitamins, minerals and other nutrients to the patient. It is not new - this method has been popular since the 1930s. It is known that vitamins, minerals and other nutrients are essential for health, but it is not always possible to obtain them in full from food. The duration of treatment for this therapy varies greatly and depends on the disease and individual tolerance to vitamins.
Prices for vitamins and minerals
Drug treatment
This treatment method is based on the use of medications to improve health and get rid of the underlying causes of the disease.
With spina bifida, the blood supply to organs (including the brain) is primarily affected. The fact is that this disease causes spasm of the vertebral arteries, which play an important role in blood circulation.
Medicines are the first aid in treating the symptoms of spina bifida
The patient begins to suffer from pain, dizziness, nausea, weakness and other symptoms of a hernia. Therefore, treatment of spina bifida involves taking nootropic medications aimed at improving blood circulation and stimulating metabolism in the brain.
Such drugs include:
- "Fezam"
"Fezan"
- Vinpocetine is a corrective medicine that restores normal brain function. It dilates blood vessels, increases the amount of oxygen entering the blood and protects the nerve structure. In addition, it significantly increases blood supply to the brain;
- "Piracetam" is a drug that equalizes blood flow and accelerates metabolic processes in the brain;
- "Cortexin"
"Cortexin"
Vacuum treatment
Vacuum therapy is an alternative method of treating diseases that uses the process of “suction” created by cups with suction cups located on the human body. This therapy helps to get rid of headaches, arthritis, rheumatism, fibromyalgia, fatigue and problems with the musculoskeletal system. Vacuum therapy promotes self-healing, capillary regeneration, increased blood flow to the problem area, maintaining homeostasis and getting rid of inflammation and toxins.
In this procedure, cups with suction cups are placed on the body and left in place for several minutes. The vacuum they create lifts the skin and tightens the lower soft tissues.
Massotherapy
Therapeutic massage is a technique based on the use of special sets of hand movements that have a beneficial effect on the patient’s health and well-being.
For spina bifida, massage improves blood flow in the affected areas of the body - spine, legs, arms, lower back.
Therapeutic massage helps a sick person get rid of pain
Important! Massage is performed only by a specialist, since there is a danger that most movements can negatively affect a person’s health by damaging a weakened skeleton.
Laser therapy and magnetic therapy
Laser therapy is a treatment method that uses a focused beam of light. Unlike most light sources, the light from a laser is tuned to a specific wavelength. This makes it possible to use powerful beams. Laser light is so intense that it is even used to shape diamonds or cut steel.
Laser therapy
In medicine, lasers help surgeons perform actions with high precision in a small area. Laser therapy produces less pain, swelling, and scarring than traditional surgery. However, laser therapy is an expensive procedure and requires repeated treatment to consolidate the effect.
An alternative to laser therapy is magnetic therapy. This technique is based on the use of magnets in specific parts of the human body for pain or pathologies. The field is created by a biomagnetic pair, that is, the interaction of positive and negative magnets. This field improves the body’s Ph indicators and eliminates the negative consequences of diseases.
Magnetic therapy has no contraindications
Magnetic therapy is also used to relieve pain in joints and bones.
Physiotherapeutic devices
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy is a treatment method that is based on performing various exercises to strengthen muscles and improve the condition of the musculoskeletal system.
At first, exercises should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. Of particular note is hanging on the horizontal bar - doctors highly recommend this method for non-surgical treatment. This exercise relieves pain and restores flexibility to the spine.
For spina bifida, exercises are performed only in a lying position. Movements are slow and gentle. The amplitude or duration of exercises may be reduced if the patient is not feeling well. On average, it is recommended to exercise for half an hour a day.
Listed below are a few exercises that will help improve your health.
- You need to bend your elbows and place them in the chest area. Bend your chest to create something like a half-bridge, and hold in this position for a short time. Then straighten your chest and take your starting position. All this needs to be done relaxed. The optimal number of times is eight.
- Straighten your legs. Extend your arms and place them on the floor along your body. Straining your back muscles, try to lift your pelvis up, depriving it of support in the form of the floor. In this case, the palms and shoulders are pressed tightly to the floor. Then stay in this position for a while. Afterwards, lower your pelvis down. You need to repeat this exercise four times.
Hippotherapy
Hippotherapy is a type of physical therapy that uses horseback riding as a means of developing and improving the functioning of the body at a neurological and physical level. Hippotherapy is based on a theory that states that human development is enhanced when a person copies the pace, rhythm, gait and frequency of the way a horse moves.
Horseback riding is not only pleasant, but also useful
This technique is considered non-standard because it involves direct contact with the animal. However, numerous studies have proven that this technique helps people strengthen their back muscles and improve blood circulation.
Operation
If non-surgical methods do not have an effect, then surgical intervention is required to remove the spina bifida. To do this, do the following:
- the hernial sac and its contents are assessed;
- dead tissue is found and removed;
- The defect in the spinal canal that led to the problem is eliminated.
As a rule, surgery is performed for a hernia in an adult.
Surgery has a positive effect, but also leads to some complications. They are as follows:
- after surgery, the suture may ooze;
- high likelihood of bleeding and infection;
- problems in the proper functioning of nerve endings;
- possible relapse.
Possible complications
- Pyelonephritis, renal failure due to urinary disorders.
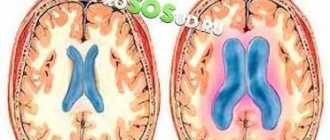
- Increased intracranial pressure due to fluid retention in the brain, which can lead to atrophy of areas of nervous tissue, the development of meningitis, and encephalitis.
- Flexion contractures, paresis, paralysis.
- Infertility, erectile dysfunction in men.
- Pinched nerves, which leads to severe pain, decreased sensitivity, and decreased motor activity.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Decreased cognitive abilities.
- Vision disorders.
- Congestive pneumonia and pulmonary failure as a consequence of prolonged bed rest.
- Diseases of internal organs.
- Disability. In severe cases, the patient needs constant care at home, supportive treatment, and regular medical monitoring.
Diagnostic methods
A herniated disc causes long-term pain in the spine. But in order to confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a lot of research. This will rule out tumors, infections or consequences of injury. You should definitely visit a doctor if the pain persists for more than 2 months.
Only a comprehensive diagnosis will help to distinguish a hernia from other conditions. But first you need to contact a therapist, who will determine the examination strategy and refer you to specialized specialists.
The basis of diagnosis is instrumental research. The most informative of them :
. This is the most accurate method for detecting intervertebral hernia. Tomography allows you to visualize a hernia, detect its location and determine the stage of the process. If such a study is not possible, then contrast myelography is used.
MRI- To determine a hernia in the cervical spine, vascular studies are indicated: REG and ultrasound of the spinal arteries. The examination is carried out with head turns (with functional tests).
- ECG and radiography of the OGK . They are used for hernia in the thoracic region, but after consultation with a cardiologist and pulmonologist.
A hernia is not visible on ordinary radiographs; it can only be suspected by severe pain. During diagnosis, it is imperative to differentiate intervertebral hernia from spondyloarthrosis, myositis and Schmorl's hernia.
Diagnostics
Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to detect fetal pathology even during intrauterine development. This usually occurs during a screening ultrasound examination. In order to clarify the diagnosis, laboratory determination of alpha-fetoprotein levels and a number of other tests may be required.
In a latent form, the defect can be determined during diagnosis for another reason, as well as when determining the causes of back pain.
The examination includes:
- collection of complaints and medical history, objective examination;
- neurological examination – allows you to assess motor activity, muscle tone of the upper and lower extremities;
- transillumination - a method that allows you to determine the nature of the contents of the hernial sac;
- computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging - allow you to identify concomitant lesions of the tissues of the brain and spinal cord, as well as get a detailed picture of the hernia;
- laboratory tests: general and biochemical blood tests, general urine tests, etc.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of spina bifida begins with an initial examination in the form of palpation of the area where its location is possible. The doctor then asks some questions and takes a medical history.
Diagnosis of spina bifida has its own characteristics
After this, he prescribes additional instrumental examination methods to clarify the problem. These include:
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging;
- transillumination;
- contrast myelography.
Let's take a closer look at the last two methods.
Transillumination is a method of instrumental examination, which consists in assessing the situation by illuminating the hernia protruding outward. This is done with the aim of studying its structure in detail and finding the best treatment option.
Contrast myelography allows you to assess how severely damaged the spinal cord is. This is done by intravenous injection of a special contrast agent, which will accumulate at the site of the hernia, which will make it easier to study. As a rule, this method is used in conjunction with radiography.
Contrast myelography helps find the cause of a hernia
If it is difficult to find an appropriate course of treatment, the attending physician may consult with a neurosurgeon (in case the nerves are too damaged) or a geneticist (in case of abnormalities in the development of the body).
Treatment
Typically, treatment of spina bifida involves its surgical removal, since conservative therapy, as a rule, is ineffective and is used only as an auxiliary one.
Surgery
During the operation, the defect in the spine is reconstructed and the unclosed hole is closed. Non-viable structures are removed from the hernial sac, and healthy spinal cord tissue is returned to the spinal canal.
An operation to remove the hernial sac and eliminate a spinal defect can be carried out already in the first weeks of a child’s life. Surgical treatment is postponed if a mild form of pathology is detected (no need for surgery).
Treatment of spina bifida is only surgical
For hydrocephalus, a shunt may be placed to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid into the thoracic lymphatic duct.
After surgery, the patient requires rehabilitation, which allows:
- eliminate pain syndrome faster;
- prevent the development of possible complications (secondary infection, thrombosis, etc.);
- restore normal muscle tone;
- correct posture and gait disorders;
- improve general condition;
- minimize the risk of relapse.
Conservative treatment
In order to prevent the progression of the pathology, as well as to improve the general condition of the patient, he may be prescribed neurometabolic stimulants and vitamin therapy (vitamins A, E, C, group B). Physiotherapeutic techniques (magnetic therapy, laser therapy), therapeutic exercises can be used.
Patients with disorders of the digestive system require a diet. It is recommended to include more fiber-rich foods in your diet to normalize intestinal motility.
What is spina bifida?
Spina bifida is a disease that manifests itself at any age. It is the result of a defect in the spinal canal. The defect causes cerebrospinal fluid to escape and the spinal cord to bulge. This causes disruption to its operation. In addition, this prevents the vertebrae from connecting.
As a rule, this disease appears most often in the lower back.
Spina bifida
Thanks to modern medical technologies, today such a disease is detected even before the child is born. It appears in one out of 30,000 newborns, which, in general, suggests a low frequency of occurrence.
Treatment of spina bifida in children is much easier than in adults, since their body is just developing. However, it should be noted that only a small number of people are able to fully recover after the disappearance of a hernia. For the rest, in one form or another, an “echo” will remain in the form of some defects and problems of a secondary nature.
Prevention
Prevention should be carried out in the prenatal period. To this end, a woman planning a pregnancy, as well as during it, should:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- stop the uncontrolled use of medications;
- limit contact with aggressive chemicals (including household chemicals);
- not be exposed to ionizing radiation;
- reduce the risk of contracting a viral infection (avoid being in crowded places during periods of seasonal increases in the incidence of ARVI).
Symptoms of a hernia of the lumbar spine
The disease begins slowly, in most cases asymptomatic or with minimal symptoms. The starting factor (trigger) can be any sudden movement or lifting of weight, leading to acute pain.
First signs
The initial symptoms of a lumbar disc herniation can be so subtle that not everyone pays attention to them. But if you listen to your body, you will notice:
- a feeling of fatigue in the lower back when sitting or standing for a long time;
- sensory disturbance - numbness of the skin or a crawling sensation in the lumbar region, groin, lower extremities;
- the appearance of transient lower back pain;
- weakness in the legs, gait disturbance.
Obvious symptoms
In some patients, the obvious symptoms of lumbar intervertebral hernia are periodic and moderate, while in others they are pronounced and constant. Symptoms of the disease are associated with compression of the spinal cord or spinal nerve roots. Characteristic symptoms of the disease:
- Local pain syndrome. Pain in the lumbar region can have different duration and character. There are sharp, weak, aching, pressing, burning pains, permanent or transient. They intensify with physical stress, sudden turns of the body, etc.
- Radicular pain associated with pinched spinal nerve roots. When different lumbar discs are affected, the pain will have different localization:
- L1-L2, L2-L3
- hernias are very rare; manifested by pain and loss of sensitivity on the inner and front surface of the thigh; early symptoms of pelvic organ dysfunction may appear; - L3-L4
- pain spreads along the front and inner surface of the thigh, moving to the lower leg and inner ankle; accompanied by increased skin sensitivity and muscle weakness in this area; - L4-L5
- pain spreads from the upper gluteal region to the outer thighs and lower legs, extends to the rear and 1 - 3 toes; accompanied by increased skin sensitivity and muscle weakness in the same areas; - L5-S1
- pain moves from the middle of the buttock along the back and outer surfaces of the thigh and lower leg, radiates to the heel, and then along the outer edge of the foot to the 4th - 5th toes; accompanied by increased skin sensitivity and muscle weakness in the same areas. - Symptoms associated with compression of motor nerves - muscle weakness, fatigue when walking, gait disturbance.
- Symptoms associated with compression of the autonomic (innervating internal organs, walls of blood vessels, sweat glands) nerves - pallor and sweating of certain areas of the skin, the appearance of vascular spots on it.
At different stages of lumbar intervertebral hernia, different symptoms appear
Dangerous symptoms of lumbar hernia
The most dangerous symptoms are the consequences of compression of the spinal cord - paresis and paralysis, dysfunction of the pelvic organs - fecal and urinary incontinence, reproductive dysfunction.
If such symptoms appear, even if they are transient, you should immediately seek medical help.
Symptoms of a hernia of the lumbar spine in men
In addition to the general manifestations of the disease, which are characteristic of men and women, men may experience symptoms of reproductive dysfunction. This is due to impaired blood circulation and innervation in the pelvic organs and is manifested by erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation.
In advanced diseases, spermatogenesis – the synthesis and maturation of sperm – may also be affected. The number of sperm decreases, they become less mobile, often incapable of fertilization - infertility occurs. But with adequate treatment, restoration of reproductive function is possible in most cases.
Symptoms of a hernia of the lumbar spine in women
Poor circulation in the pelvis cannot but affect women's health. Depending on the type of hernia and its size, the following symptoms may appear:
- menstrual irregularities and, as a consequence, infertility;
- frequent inflammatory processes of the genital organs, as a result of which adhesions are formed in them, preventing conception and pregnancy;
- difficulties during pregnancy and childbirth.
But all this can be restored if you consult a doctor in a timely manner and follow all his instructions. A lumbar hernia is not an obstacle to the birth of a child, but requires mandatory pregnancy planning with a preliminary course of treatment and constant monitoring during pregnancy by an obstetrician-gynecologist and a neurologist at the antenatal clinic. Delivery is most often carried out by caesarean section.