The most valuable thing in the life of each of us is children, which is why their health should be monitored from birth, so as not to encounter numerous problems and complications that worsen the lives of children and parents. Pseudocyst of the brain in newborns, according to experts, is the safest complication that can appear during childbirth. Approximately one in 100 cases is diagnosed with this disease.
The appearance of such a formation does not entail serious consequences, but requires close monitoring by doctors. The pathology detected in infants is not reflected in the functioning of the brain. Moreover, it does not affect mental abilities or the appearance of mental problems.
The concept of pseudocyst
Formations of the cystic type are peculiar cavities, characterized by a round shape and having a small size. They are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (exudate or other substances). The bulges are concentrated on one or both sides at the same time. The mechanism of development of this pathology in infants has not been fully studied to this day. It may happen that, in the presence of alarming prognosis, a baby is born absolutely healthy, and a second newborn is born with damage to the nervous system, with completely normal prognosis.
With the rather rapid intrauterine development of the brain, the vacated territory located in the area of the choroid plexuses is filled with a special fluid (cerebrospinal fluid). These are the processes that are observed during the development of a pseudocyst. It is safe for the life of the baby and is most often detected during an ultrasound scan of the fetus in the womb.
A large percentage of cystic formations resolve before birth. If this does not happen, then experts explain this by the presence of a herpes infection in the mother.
Types of cystic formations
The plexus of cerebral vessels takes an active part in the production of cerebrospinal fluid, which subsequently provides nutrition to the brain and is responsible for its functional development. Cystic formations are a consequence of intensive growth of the brain, when a free cavity appears between the plexuses of blood vessels, which is filled with fluid inside. Choroid plexus cysts in the fetus are a fairly common diagnosis, especially during fetal development and in children under one year of age.
Left choroid plexus cyst
Formations occur against the background of viral and infectious diseases suffered by the expectant mother, as well as during severe pregnancy. The cyst is localized in the intracranial space close to the choroid plexuses. This type of formation does not require any therapeutic measures, since they do not pose a threat to the health and life of the child. In most cases, they resolve as the child grows.
Cyst of the right vascular formation
This type of formation is diagnosed in both newborns and infants. In some cases, it can be detected in adulthood, but since cysts do not have pronounced symptoms, a person may not be aware of the presence of pathology. Right-sided cystic formations do not harm the body and do not affect the psychomotor development of the child.
Bilateral pseudocysts
There are no visible changes or disturbances in the structure of the brain. The choroid plexuses of the lateral ventricle are involved in the process. As a rule, as the body grows, the neoplasm goes away without outside help. Bilateral cysts are numerous, they are recorded in adults and children. In some cases, the formation of a bilateral cyst may indicate a disruption in the course of pregnancy, but this does not mean that the baby will be born with a pathology.
Such cysts are called neoplasms of the choroid plexus; they are visualized in the posterior horn of the right lateral ventricle as formations with clear, even edges. Neoplasms do not cause disturbances in the dynamics of the cerebrospinal fluid and an increase in extracellular space.
Reasons for appearance
The causes of a cerebral pseudocyst in a newborn baby can be very different. In most cases, the etiology of the appearance is associated with disorders observed during prenatal development of the fetus.
As a rule, the stimulating factors are:
- hemorrhages in the brain;
- hypoxia;
- disruptions in the functioning of the circulatory system caused by a lack of nutrients for the full development of the baby.
The most dangerous is the subependymal pseudocyst, which appears as a result of hemorrhages. In some cases, pathology occurs due to birth injuries.
Possible symptoms and treatment
A brain cyst resulting from a hematoma, stroke, or aneurysm is one of the options for the outcome, which is generally favorable and is sometimes discovered only posthumously, however, along with a cyst formed as a result of a viral infection, it can sometimes have undesirable consequences, manifested by:
- Signs of hypertension in newborns;
- Feeling of compression of the brain;
- Some visual and/or hearing impairments;
- Minor motor coordination disorders;
- Epileptic seizures, which, of course, can be considered the most serious complication.
Clinical manifestations indicating the presence of a cystic formation occur in cases where the cyst compresses neighboring tissues and interferes with their normal functioning, that is, if it is of significant size or “settled” in unacceptable proximity to important centers of higher nervous activity.
In most cases, a brain cyst, like a choroid plexus cyst, does not require special treatment, however, if immunological studies have proven the presence of herpetic, cytomegalovirus or other infection, then treatment directed at the virus is indicated. In the presence of epileptic seizures, the patient is prescribed anticonvulsants, and, if necessary, surgical intervention is performed to eliminate the source.
If the symptoms are mild, but the patient occasionally complains of vascular manifestations of the cyst (dizziness, compression headaches, etc.), he is prescribed medications such as cinnarizine or Cavinton , which are well tolerated by the patient, improve blood supply to the brain and help normalize well-being.
Diagnostics
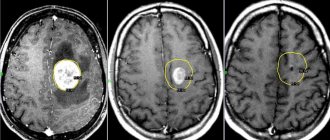
Ultrasound is most often used to confirm the presence of a false mass in the brain area. This method is the most popular, but it does not provide the opportunity to conduct a thorough inspection of the walls, as well as the internal space of the existing cavity. The emphasis is on specific areas where false benign formations most often form.
Particular attention is paid to the cerebral hemispheres. Also, emphasis is placed on the lateral ventricles, the area where the head of the nucleus (caudate) is located and some other areas. Features of the location of the pathology make it possible to distinguish it from a true cyst.
The presence of formations is confirmed by echo signs of a subependymal pseudocyst in the area of the right as well as the left ventricle. The use of ultrasonic waves is effective only in cases where the baby’s age has not reached 1 year. In this case, the fontanel located on the head is not covered by bones.
A newborn is examined for the presence of a pseudocyst if:
- the child was born prematurely;
- the birth was accompanied by serious complications;
- observation of insomnia, excessive tearfulness and anxiety in a newborn;
- the presence of convulsive muscle contractions, dizziness and other neurological signs.
When conducting research, the following methods for identifying the disease can be used:
- Doppler encephalography.
- Neurosonography.
- MRI and computed tomography.
- Cerebral scintigraphy and some other techniques.
If there is a suspicion that the fetus has genetic disorders, a chromosomal analysis of the fluid (amniotic fluid) may be prescribed. This intervention is invasive and is therefore used in very rare cases.
Methods for diagnosing a child
Pathology in the brain tissue of a newborn requires increased attention from doctors and parents. Children with this diagnosis need regular examination.
An ultrasound examination, in which a pseudocyst is diagnosed, does not always allow one to examine the cavity and walls of the formation. A pseudocyst can have any shape and size, but is always localized in one place: in the cerebral hemispheres between the thalamus and the head of the caudate nucleus. If the location is different, then it is a true cyst.
For a comprehensive diagnosis, modern medicine offers several methods:
- Doppler study;
- neurosonography;
- MRI;
- positron emission or computed tomography, etc.
An ultrasound of the brain is informative only in the first year of a child’s life, before the fontanel overgrows (for more details, see the article: when and how does the crown of a child overgrow?). It is prescribed to premature babies, as well as those who have suffered oxygen deprivation and difficult childbirth. Children over one year of age and adults undergo an MRI. These methods differentiate between a cyst and a pseudocyst.
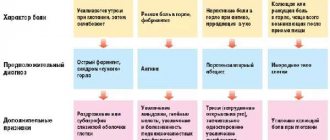
Difference between cyst and pseudoplasm
False formations that appear in the brain area have significant differences from the true ones. They are distinguished by:
- Place of appearance. In most cases, pseudoformation is located in the zone of the subcortical nuclei, or rather between them. The pseudocyst is localized near the lateral ventricles or in the area of the cerebral hemispheres.
- Reason for appearance. The disease can be secondary or acquired. An accurate diagnosis is made through instrumental diagnostics. If a specialist has directed you to undergo an examination, you should not abandon this step, since timely detection of pathology will prevent the occurrence of serious violations.
Choroid plexus cyst in newborns
A choroid plexus cyst in a newborn is by far the most dangerous pathology in children in the first year of life. As a rule, it is detected during intrauterine development of the fetus at a period of 24-30 weeks. During the development of the fetus, education does not pose a threat to its health and life.
A choroid plexus cyst is a benign formation with clear contours, filled with fluid. It occurs among normal pregnancies with a frequency of approximately 3%.
Cystic formations of the choroid plexus tend to self-resolve, suggesting that they are pseudocysts. Bilateral choroid plexus cysts of the brain are very often observed, but by the 28th week of pregnancy they resolve, which is associated with the active development of the fetal nervous system. In cases where the cyst continues to be detected during an ultrasound scan until childbirth, then its significance does not particularly increase.
One of the early signs of the formation of the central nervous system in the embryo is the choroid plexus. They act as structural units in the formation of the right and left hemispheres of the brain. The choroid plexuses do not have nerve endings, but they ensure timely maturation and sufficient blood supply to the brain in the fetus.
A choroid plexus cyst of the brain has the following characteristics:
- minimal harm to health;
- lack of significance for concomitant pathologies;
- not affecting any of the vital systems and functions of the body;
- lack of growth and deformation.
Education does not cause significant harm or danger to either the fetus or the infant; it does not affect the functioning of the brain. However, they can increase the risk of developing other pathologies or cause functional impairment of all body systems.
One of the hypotheses for the formation of cysts is the theory of congenital pathologies provoked by genetic mutations of cells. In this case, the localization of the formation cavity on the left, right or simultaneously on both sides does not matter
It is important to note that the cyst does not provoke the development of anomalies, but, on the contrary, pathologies of intrauterine formation contribute to their formation
The main reason for the development of vascular pathology in the fetus is the presence of the herpes virus in the pregnant woman
Choroid plexus cysts in the fetus are detected at 14-22 weeks of intrauterine development. This type of education is safe for the child, as it does not cause neurological symptoms. In the future, the mental abilities of such children do not differ from the abilities of their peers.
Vascular compactions are diagnosed during special diagnostic methods, so ultrasound and neurosonography can provide a complete description of the cyst. According to accepted WHO recommendations, these studies must be carried out on all children under one year of age to exclude possible neurological disorders.
In infants, cystic formation is practically asymptomatic
You can also read: Malformation of blood vessels of the head
- trauma during childbirth;
- high risk of intrauterine infection;
- oxygen starvation of the fetus;
- severe pregnancy;
- the presence of chronic diseases in the mother;
- intense physical activity during pregnancy;
- deviations in the physical development of the newborn (underweight, insufficient growth);
- severe deformation of the anatomical parts of the skull.
According to statistical data, cystic formations are recorded both in children without deviations in physiological development and in those with developmental delays.
The plexus of cerebral vessels takes an active part in the production of cerebrospinal fluid, which subsequently provides nutrition to the brain and is responsible for its functional development. Cystic formations are a consequence of intensive growth of the brain, when a free cavity appears between the plexuses of blood vessels, which is filled with fluid inside.
Is a pseudocyst dangerous and why?
The existing pseudocyst in the head of a newborn in all cases has a second cause of development. The following reasons may act as a catalyst for the appearance:
- lack of oxygen;
- problematic childbirth;
- presence of injury.
A false cyst in an infant is not dangerous to health. This pathology should cause alarm in cases where the formation rapidly increases in size.
There is no need to perform any specific therapeutic procedures in the treatment of pseudocysts in infants. All that is necessary is to regularly visit a neurologist and carry out restorative therapy designed to combat the emergence of possible complications that often appear against the background of injury.
If after 12 months the formation and the baby have not gone away, doctors diagnose a true cyst. In such situations, you should be observed by a neurologist throughout your life.
What is the difference between a pseudocyst and a cyst?
A cavity formation containing cerebrospinal fluid in the central part, which occurs after the birth of a child, in adults causes clinical symptoms and is capable of progression.
Pseudocysts form in utero or directly during childbirth. The soft bones of the baby's skull, when moving along the birth canal, can cause excess pressure on the brain tissue. Lack of oxygen supply (hypoxia) leads to the formation of cystic cavities as a result of rupture of blood vessels. Gradually, such cavities resolve.
False cystic cavities are formed under the influence of the following etiological factors:
- No genetic predisposition;
- Multichamber cavities of the lateral ventricles arise due to abundant vascular ruptures;
- Pseudoformations are localized between the caudate nucleus and the optic thalamus.
The absence of damage to the tissue of the lateral ventricles and periventricular space is not accompanied by clinical symptoms.
Treatment
The course of pathology observed in a newborn child should be monitored by a pediatric neurologist. The following techniques can be used during therapy.
Medicines
As a rule, doctors prescribe a number of drugs to children, the action of which is aimed at improving blood circulation in the brain, and also prescribe antihypoxants:
- Mexidol;
- Cytoflavin;
- Vitamins belonging to group B;
- Mildralex.
If hyperactivity is observed, the use of drugs such as:
- Glycine;
- Pantocalcin, as well as Pantogam.
To strengthen the musculoskeletal system, you should attend massage sessions, but only if they are recommended by your doctor.
If the false cyst was not subject to resorption during the first year of the child’s existence, and it increases in size, surgery will be required. Removal of the formation is carried out through craniotomy using endoscopy and shunting techniques.
Surgery
Endoscopic surgical procedures are by far the best ways to treat tumors in children. But such operations are not carried out in all cases. If your baby has been diagnosed with a cyst of the septum pellucida developing in the brain area, then this technique is perfect for treatment. The treatment is not accompanied by complications and avoids excessive trauma to the small patient.
The recovery period after surgery to remove a cyst is different for each case, and depends on the general well-being and state of health of the child.
Folk remedies
To improve the well-being of children with large cystic formations in the brain, in addition to the use of medications, folk remedies can also be used. The most effective are the following recipes:
- a decoction made from hawthorn fruits. The liquid is taken internally to strengthen the nervous system. This product helps improve baby's sleep;
- horsetail, cinquefoil, as well as capitol and violet are distinguished by their ability to lower intracranial pressure;
- Hemlock is endowed with excellent absorbent properties;
- herbal infusions for taking soothing baths.
To prepare a decoction that has a calming effect, you will need to take raspberry leaves, yarrow, as well as chamomile, licorice rhizome and calamus. The components are used in equal proportions and mixed. Composition in the amount of 2 tbsp. should be placed in a container, pour boiling water (0.5 l) and leave for 8 hours. After this, the liquid is filtered and added to the baby’s bathtub.
Before using traditional medicine in the fight against pseudocyst, you should consult with your doctor.
Medical supervision
In most cases, if a pseudocyst is detected, no treatment is required. It resolves on its own (usually after 10 months), surgical intervention is excluded. The formations disappear within the first year after birth. In some cases, medications may be prescribed that promote better blood circulation (Actovegin, etc.).
The entire treatment process is monitored in the clinic by a pediatric neurologist. The child’s condition is examined, and the rate at which pseudocysts decrease in size is monitored.
After a year has passed, it is necessary to perform a repeat ultrasound. Research should never be neglected. The results will show how correct the preliminary conclusions about the nature of the pathology were.
The pseudocyst should have disappeared by then. If the structure is preserved, it becomes clear that the diagnosis was incorrect and this formation is a cyst. Constant monitoring by a neurologist and appropriate treatment are required.
Some parents additionally use folk remedies (decoctions, baths, etc.). You should know that many medicinal plants can cause allergies in children. Any treatment of pseudocysts should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor or after consultation with him.
In the overwhelming majority of cases, it turns out that the favorable prognosis was justified. There is usually no danger of enlargement or degeneration. Therefore, treatment is most often not required or the intervention is minimal and painless.
All types of brain pseudocysts in children play almost no role in the growing body. At the same time, the child feels fine. Pseudocysts do not cause any complications and do not affect development. Therefore, there is no need to look for the best doctors and worry.